Geothermal field division and its geological influencing factors in Guanzhong basin
-
摘要:
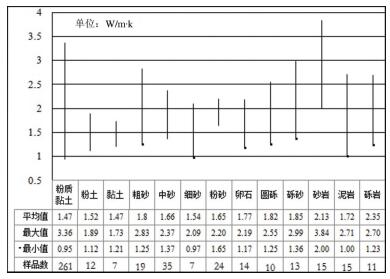
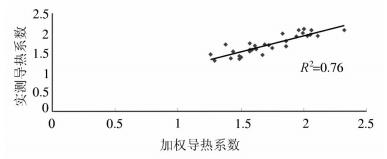
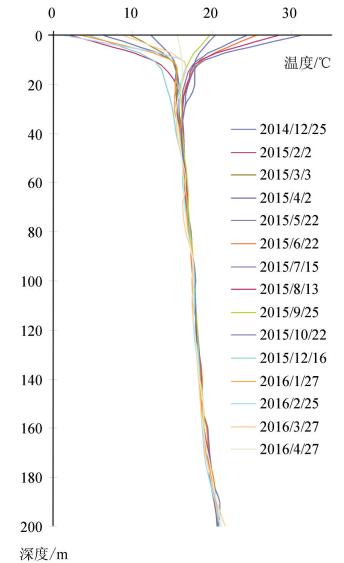
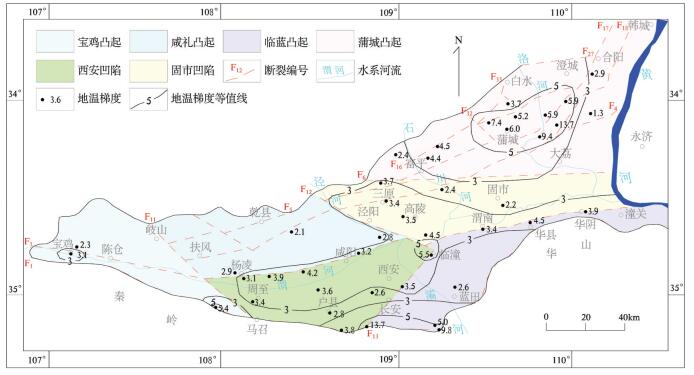
具有无污染、可再生、分布广、储量大以及可就近利用等诸多优势的地热能是一种洁净能源,应用前景广阔。地热能的开发利用与区域地温场划分紧密相关,关于关中盆地整体地温场划分的研究鲜有报道。根据关中盆地的工程地质、水文地质、环境地质条件等因素,总结了岩体类和砂土类的热物性质特征。通过灰色关联分析方法,分析了岩土体热物性参数的影响因素,认为干燥重度对导热系数的影响程度最大,含水率、天然重度、孔隙率三者影响程度相近;干燥重度对比热容影响程度最大,天然重度次之,含水率和孔隙率影响最弱。利用盆地内多个地温常观孔,绘制了地温变化曲线和地温梯度等值线,认为关中盆地常温带位于15~20 m埋深处,地温梯度总体呈中部高、东西低,固市凹陷、西安凹陷、蒲城凸起、断裂及断裂汇合区域地温梯度较大,宝鸡凸起、咸礼凸起以及临蓝凸起地温梯度较小,产生差异的原因包括地质构造、地下水活动、岩土体热物性参数等三方面。利用热物性参数和地温梯度值,计算了盆地内浅层和深层的大地热流值,并分析了两者差异的成因,经对比全国区域地热资料,认为关中盆地是一个复杂的坳陷型中低温地热田,地热资源潜力巨大,居全国上游。该文旨在系统地分析关中盆地地温场特征,为地热能的勘查评价提供基础数据支持,促进关中盆地地热开发利用,为构建环境友好型社会服务。
Abstract:Shallow geothermal energy is a renewable and widely distributed clean energy, it has broad prospects for development and utilization. The exploitation and utilization of geothermal energy are closely related to the division of regional geothermal field; nevertheless, there are few reports about Guanzhong basin at present. Based on regional geological and hydrogeological conditions and the classification of lithology, the authors summarized the thermal properties of rocks and soil. The influence of soil thermal conductivity and the specific heat capacity based on gray relational analysis reveal the main factors controlling the thermal conductivity and specific heat. The drying severity has the greatest impact on the thermal conductivity, whereas water content, natural gravity and porosity exhibit similar influences. The dry severity has the greatest impact on the specific heat capacity, followed by the natural gravity, whereas the water content and porosity play the weakest role. Based on the long-term observation data of downhole temperatures in the Guanzhong basin, the authors presented downhole temperature logs and temperature gradient contours. Normal temperature zone lies in the depths of 15-20 m in Guanzhong basin. The geothermal gradient is high in the middle part and low in the east and west part. The areas with large geothermal gradient include Gushi depression, Xi'an depression, Pucheng bulge and faults. The geothermal gradient of Baoji bulge, Xianyang-Liquan bulge, and Lintong-Lantian bulge is relatively small. The reasons of the differences include geological structure, groundwater activity and thermal and physical parameters of rock and soil. The heat flow in the basin was calculated using thermal physical parameters and geothermal gradient values, and the reasons which produce the heat flow difference between the shallow and the deep were analyzed. Compared with the regional geothermal background, the Guanzhong basin is hotter and its geothermal resources are abundant. The purpose of this paper is to systematically analyze the characteristics of the geothermal field in the Guanzhong basin so as to provide a basis for exploration and evaluation as well as the development of geothermal energy and to serve the construction of a good environment and society.
-
Key words:
- Guanzhong basin /
- geothermal field /
- geology /
- thermal property determination /
- heat flow
-

-
表 1 岩土体导热系数的筛选依据
Table 1. Selection of thermal conductivities of rock and soil
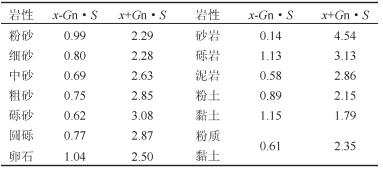
表 2 岩土体比热容的筛选依据
Table 2. Selection of specific heat capacities of rock and soil
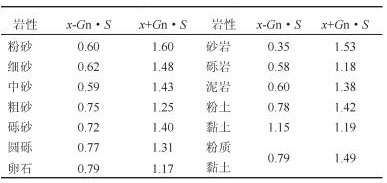
表 3 岩土体导热系数关联度计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of correlation coefficients of thermal conductivity of rock and soil
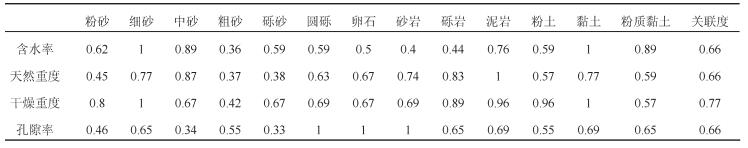
表 4 岩土体比热容关联度计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of the specific heat capacities of rock and soil
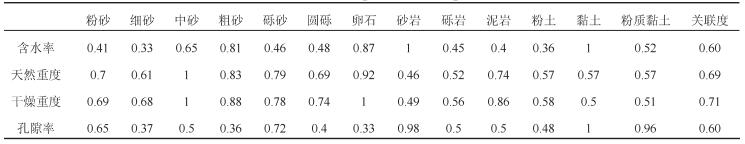
表 5 岩土体导热系数加权值与实测值对比
Table 5. Comparison of the weighted and measured values of thermal conductivity of rock and soil
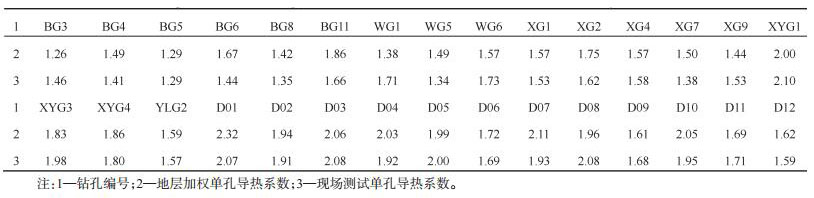
表 6 关中盆地浅层和深层大地热流值计算成果
Table 6. The calculation of the earth heat flow values in the shallow and deep layers of Guanzhong Basin
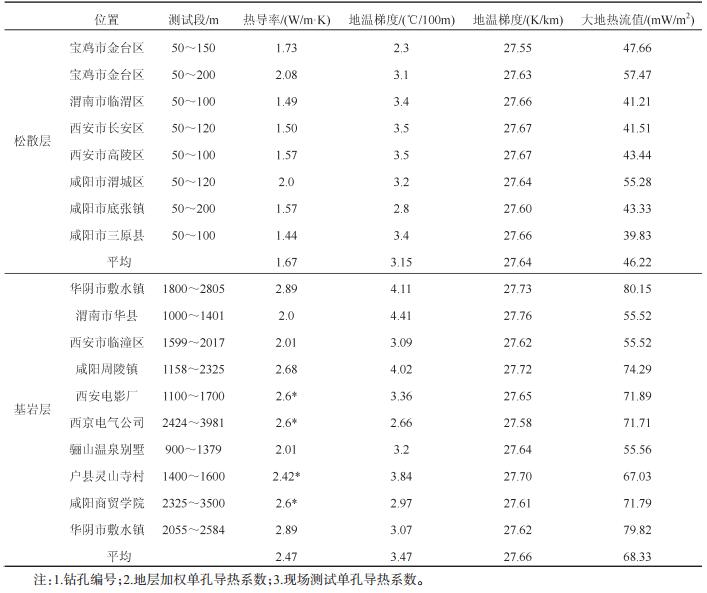
表 7 关中盆地与部分地区大地热流值(mW/m2)对比
Table 7. Contrast of the earth heat flow values in Guanzhong Basin and other areas
-
Chen Xiaodong, Jin Xu, Guan Yanwu, Shi Zhuo, Gao Yi.2006.The influence of daily and annual variation of the surface temperature on near-surface temperature survey[J].Progress in Geophysics, 21(3):1008-1011.
Feng Chaochen, Huang Wenfeng.2015.Evaluation of geothermal resources in fault zone of Heze City, the Western LiaochengLankao Shandong Province[J].Geological Survey of China, 2(8):55-59(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0375674213002033
Hu Shengbiao, He Lijuan, Wang Jiyang.2001.Complation of heat flow data in the China continental area (3rd edition)[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 44(5):611-623(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263620492_Compilation_of_Heat_Flow_Data_in_The_China_Continental_Area_3rd_Edition
Li Shaohua, Qin Xiangxi, Niu Dinghui, Mao Hanchuan.2015. Analysis of influence factors for field heat response test of ground heat conduction coefficient[J].Heating Ventilating&Air Conditioning, 45(12):49-52.
Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli, Wang Guiling.2013.The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J].Geology in China, 40(1):312-321(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286072143_The_assessment_of_geothermal_resources_potential_of_China
Li Gongke, Wang Weixing, Li Hong, Yang Fengtian, Wang Linhai, Fang Wanling.2014.Temperature distribution and controlling factors of the Tangquan geothermal field in Hebei Province[J].Geology in China, 41(6):2099-2109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287067321_Temperature_distribution_and_controlling_factors_of_the_Tangquan_geothermal_field_in_Hebei_Province
Liu Peng, Yan Changhong, Xu Yang, Zou Mingyang, Zhou Yinkang.2016.Laboratory research on influence factors of thermal conductivity for Xiashu Loess in the area of Nanjing[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 36(5):847-852. http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXK201605024.htm
Luan Yingbo, Zheng Guisen, Wei Wanshun.2013.The experimental study of the factors affecting the rate of thermal conductivity of silty clay in Beijing plain[J].Geology in China, 40(3):981-988(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289011959_The_experimental_study_of_the_factors_affecting_the_rate_of_thermal_conductivity_of_silty_clay_in_Beijing_plain
Wang Guiling, Lin Wenjing, Zhang Wei.2012.Evaluation on utilization potential of shallow geothermal energy in major cities of China[J].Building Science.28(10):1-3, 8. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JZKX201210002.htm
Wei Wanshun, Zheng Guisen, Luan Yingbo.2010.Characteristics and influencing factors of the shallow geothermal field in Beijing plain area[J].Geology in China, 37(6):1733-1739(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jun, Huang Shangyao, Huang Geshan.1990.Basic Characteristics of Geothemal Distribufion in China[M].Beijing:Seismological Press.80-100(in Chinese).
Xu Ming, Zhao Ping, Zhu Chuanqing.2010.Borehole temperature logging and terrestrial heat flow distribution in Jianghan Basin[J].Chinese Journal of Geology, 45(1):317-323. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288358250_Borehole_temperature_logging_and_terrestrial_heat_flow_distribution_in_Jianghan_basin
Zhou Yang, Li Feng, Yan Wenzhong, Mu Genxu, Liu Jianqiang.2016.Research on shallow geothermal energy resources occurrence rule of major cities in Guanzhong basin[J].Geological Survey of China, 3(4):12-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://pangea.stanford.edu/ERE/db/WGC/papers/WGC/2015/08010.pdf
Zhou Yang, Deng Niandong, Wang Feng, Mu Genxu, Liu Jianqiang.2017.Fractal theory of suitability zoning structure of shallow geothermal energy[J].Geological Survey of China, 4(1):18-23(in Chinese with English abstract).
陈晓冬, 金旭, 管彦武, 石卓, 高艺.2006.长春地区地表温度日变、年变对地温测量的影响[J].地球物理学进展, 21(3):1008-1011. http://www.docin.com/p-517585498.html
冯超臣, 黄文峰.2015.山东省菏泽市聊城-兰考断裂带西部地区地热资源评价[J].中国地质调查, 2(8):55-59. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/dixs201301016
胡圣标, 何丽娟, 汪集旸.2011.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第三版)[J].地球物理学报, 44(5):611-623. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2001.05.005
栾英波, 郑桂森, 卫万顺.2013.北京平原区粉质黏土热导率影响因素实验研究[J].中国地质, 40(3):981-988. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130328&flag=1
李攻科, 王卫星, 李宏, 杨峰田, 王林海, 房万嶺.2014.河北汤泉地热田地温场分布及其控制因素研究[J].中国地质, 41(6):2099-2109. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140623&flag=1
李少华, 秦祥熙, 牛定辉, 毛汉川.2015.现场热响应试验测定导热系数的影响因素分析[J].暖通空调, 45(12):49-52. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90570X/201512/666922925.html
蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 王贵玲.2013.中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J].中国地质, 40(1):312-321. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130121&flag=1
刘鹏, 阎长虹, 徐杨, 邹明阳, 周殷康.2016.南京地区下蜀土导热系数影响因素室内试验研究[J].防灾减灾工程学报, 36(5):847-852. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk201605024&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
王贵玲, 蔺文静, 张薇.2012.我国主要城市浅层地温能利用潜力评价[J].建筑科学, 28(10):1-3, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8528.2012.10.001
王均, 黄尚瑶, 黄歌山.1990.中国地温分布的基本特征[M].北京:地震出版社:80-100.
卫万顺, 郑桂森, 栾英波.2010.北京平原区浅层地温场特征及其影响因素研究[J].中国地质, 37(6):1733-1739. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100619&flag=1
徐明, 赵平, 朱传庆.2010.江汉盆地钻井地温测量和大地热流分布[J].地质科学, 45(1):317-323. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/f70936e1aef8941ea76e0522.html
赵振, 于漂罗, 陈惠娟, 罗银飞, 赵东阳, 边疆.2015.青海省西宁地热田成因分析及资源评价[J].中国地质, 42(3):803-810. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150329&flag=1
周阳, 李锋, 闫文中, 穆根胥, 刘建强.2016.关中盆地主要城市浅层地热能资源量赋存规律研究[J].中国地质调查, 3(4):12-18. http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgdzdc/2016-4.aspx
周阳, 邓念东, 王凤, 穆根胥, 刘建强.2017.浅层地热能适宜性分区结构的分形原理[J].中国地质调查, 4(1):18-23. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdzdc201701003
-



 下载:
下载: