Characteristics and affecting factors of land subsidence identification based on PSInSAR measures in Shandong Peninsula Blue-Yellow Overlapping Economic Zone
-
摘要:
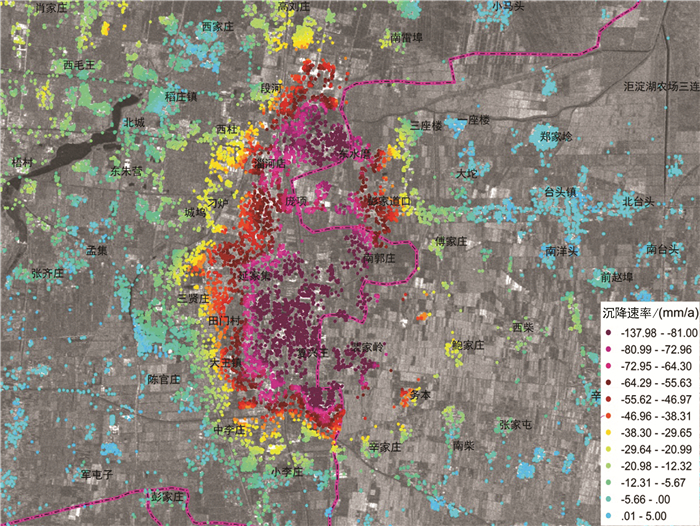
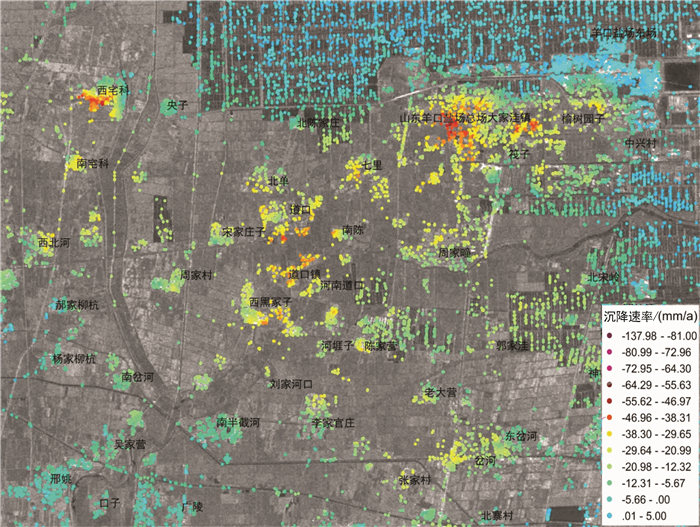
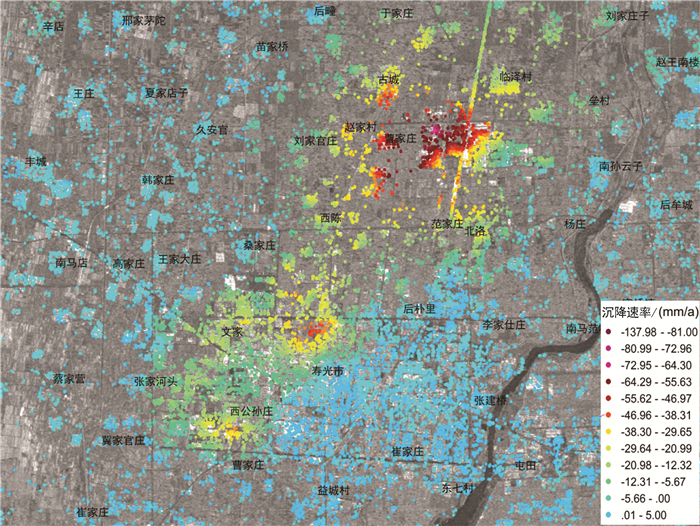
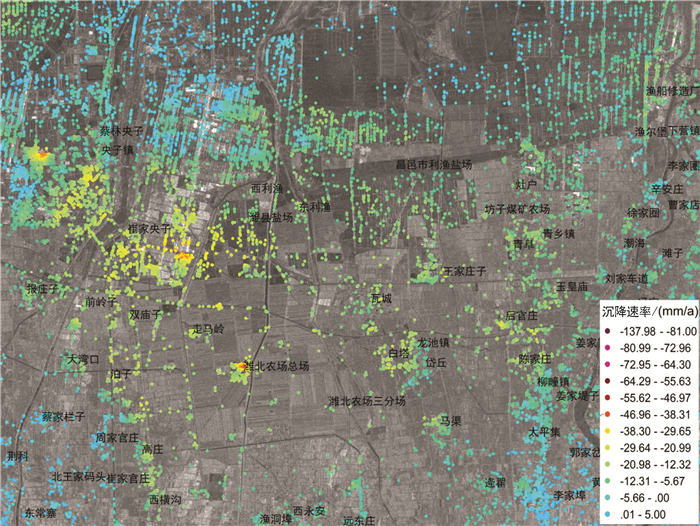
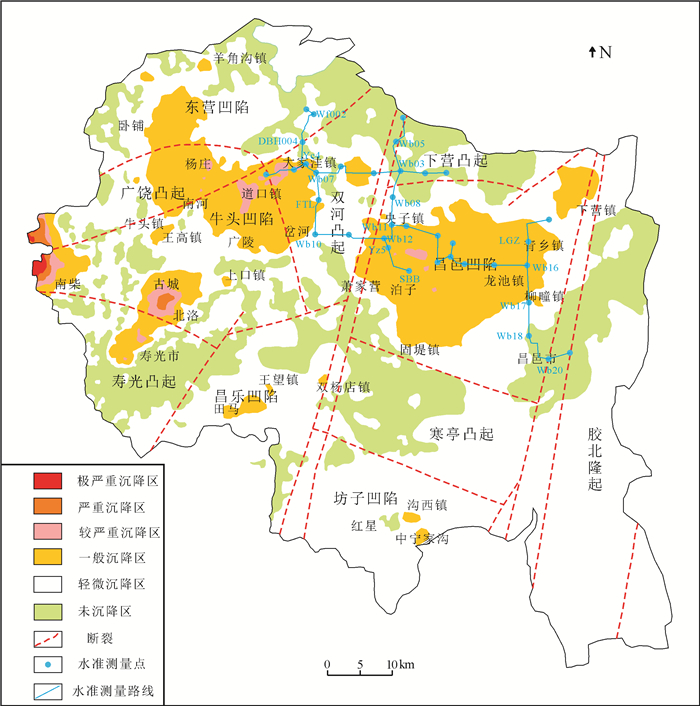
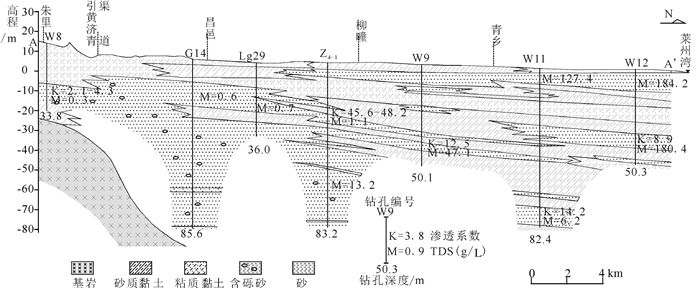
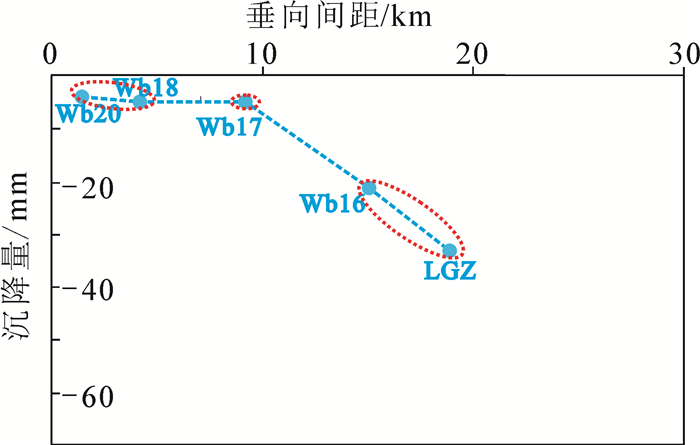
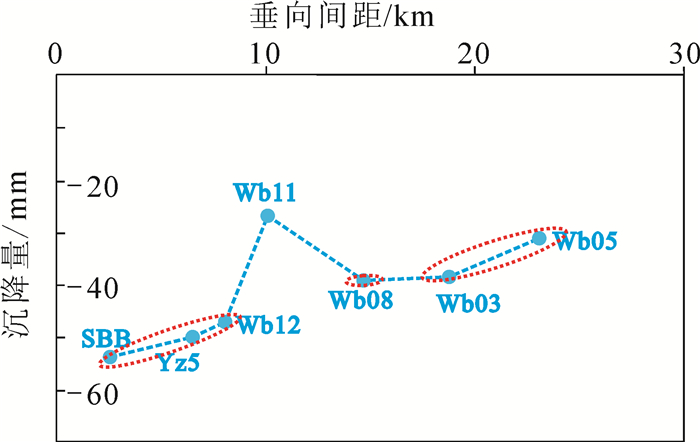
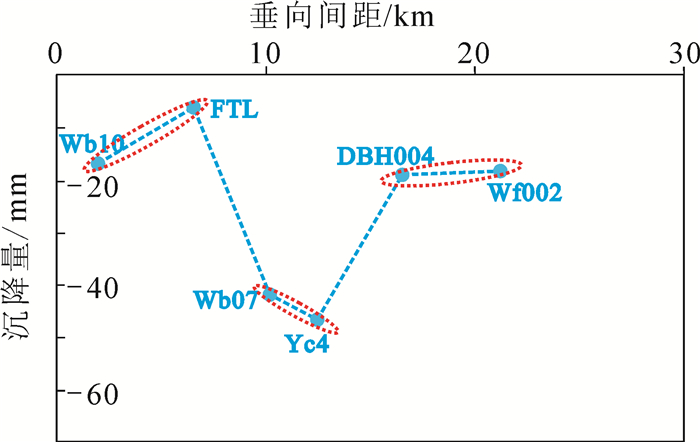
研究区位于山东半岛蓝色经济区和黄河三角洲高效生态经济区的交迭地带,区位优势明显。地面沉降灾害的发生对该区规划建设和港口防潮堤高程构成了威胁,因此,全面了解该区地面沉降的发育特征,尤其是掌握地面沉降的主要影响因素极其重要。前人在不同时段内应用GPS和水准测量方法对该区局部地段地面沉降开展了相应研究,但未对全区地面沉降状况进行分析评价,尚不能有效支撑区域规划建设及地面沉降防控管理。文章在前人研究基础上,基于PSInSAR遥感技术分析了该区地面沉降速率及其变化状况,并与水准测量成果进行了对比。认为多年来该区地面沉降现象明显,超过75%的区域发生了不同程度的地面沉降,在寿光-广饶交界处、寿光-滨海开发区北部、寿光城区西北部和昌邑-滨海开发区北部等存在多个显著片区,且多年变化总体呈现加重趋势;区内存在16个沉降中心,最大沉降速率达到29~168 mm/a,沉降速率超过40 mm/a的占比达到62%以上,主要分布于研究区西部和西北部;该区地面沉降受区域构造、地层结构、地下水开采和地面荷载等因素影响,其中地下水开采是区域地面沉降发生的主致因素,地面荷载加强了局部地段的不均匀沉降程度,区域构造和地层结构为地面沉降发育和加剧提供了地质背景条件。
Abstract:The study area is located along the overlapping zone of the Shandong Peninsula Blue Economic Zone and the Yellow River Delta Highly Efficient Ecological Economic Zone, showing important location advantages. The occurrence of land subsidence disasters has posed threats to the planning and construction of the city and the tide dike height of the port. Therefore, it is utmost important to fully recognize the characteristics of land subsidence and, in particular, to identify the main factors affecting land subsidence. Previous researches have been mainly focused on partial area using GPS and leveling survey methods without covering the whole area, which cannot support the regional city planning efficiently. Based on previous researches, the authors used PSInSAR measuring to analyze the land subsidence rate and its variation in the whole region in comparison with the leveling survey results. The results show that land subsidence has been evidently covering 75 percent of the area in recent years where there have appeared several flat districts at the junctions of Shouguang-Guangrao, northern location of Shouguang-Binhai Development Zone, northwestern Shouguang downtown, and northern location of Changyi-Binhai Development Zone, and there is an increasing trend for the harm degree of land subsidence. There are 16 settlement centers whose maximum settlement rate has reached 29-168 mm/a, and the rates of 62 percent of centers exceed 40mm/a, which are distributed in the west and northwest of the study area. Fault structure, stratigraphic structure, groundwater exploitation and ground load are the influencing factors of land subsidence, among which groundwater exploitation is the main factor of regional land subsidence, and the ground load enhances the uneven settlement of local sections, while the fault structure and stratigraphic structure provide geological background conditions for the development of land subsidence.
-
Key words:
- land subsidence /
- PSInSAR /
- leveling survey /
- evaluation /
- affecting factors /
- Shandong Peninsula
-

-
表 1 区域地面沉降速率分级标准
Table 1. Classification of regional land subsidence rate
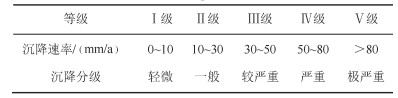
表 2 沉降中心地面沉降速率分级标准
Table 2. Rate classification of land subsidence center

表 3 2012-2014年地面沉降面积统计
Table 3. Area statistics of multi-year land subsidence

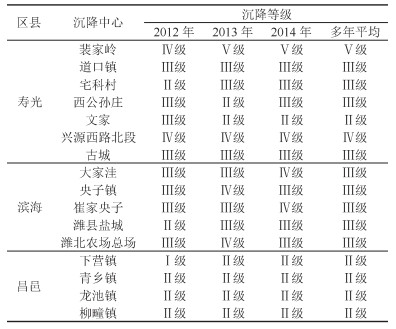
表 4 2012—2014年地面沉降评价分区
Table 4. Land subsidence evaluation divisions in different years
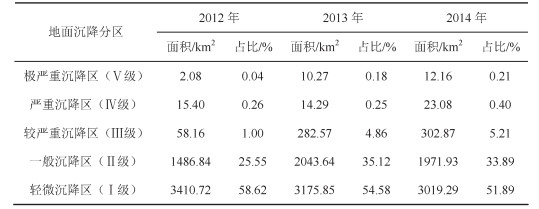
表 5 沉降中心地面沉降评价
Table 5. Evaluation of land subsidence center
-
Bawden G W, Thatcher W, Stein R S, Hudnut K W, Peltzer G. 2001. Tectonic contraction across Los Angeles after removal of groundwater pumping effects[J]. Nature, 412(6849):812-815. doi: 10.1038/35090558
China Geological Survey. 2016. Geological Environment Carrying Capacity Evaluation and Early Monitoring Warning Indicator System and Technical Method[S]. (in Chinese).
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F. 2000. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 38(5):2202-2212. doi: 10.1109/36.868878
Fang Hao, He Qingcheng, Xu Bin, Wang Meihua, Li Xia. 2016. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 43(4):159-164(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz201604026
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. 2006. Spicificaitons for the First and Second Order Leveling (GB/T 12897-2006)[S].(in Chinese).
Galloway D L, Hudnut K W, Ingebritsen S E, Phillips S P, Peltzer G, Rogez F, Rosen P A. 1998. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California[J].Water Resources Research, 34(10):2573-2585. doi: 10.1029/98WR01285
Ge Daqing, Wang Yan, Guo Xiaofang, Liu Shengwei, Fan Jinghui. 2007. Surface deformation monitoring with multi-baseline DInSAR based on coherent point target[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 11(4):574-580 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00024-007-0192-9
Guo Haipeng, Bai Jinbin, Zhang Youquan, Wang Liya, Shi Jusong, Li Wenpeng, Zhang Zuochen, Wang Yunlong, Zhu Juyan, Wang Haigang. 2017. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China, 44(6):1115-1127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706008
Liu Hongwei. 2017. Investigation and Evaluation of Geological Environment in Laizhou Bay[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey (in Chinese).
Li Hongchun, Li Xiaolong, Zhang Yagang. 2015. On the main environmental engineering geological problems and countermeasures in the coastal area of northern Weifang[J]. Value Engineering, 34(23):97-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzgc201523036
Liu Hongwei, Ma Zhen, Chen Sheming, Guo Xu, Su Yongjun, Du Dong, Hu Yunzhuang. 2015. Saltwater intrusion measurement in Laizhou Bay southern area based on hydro-chemical and geophysical methods[J]. Geoscience, 29(2):337-343 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDDZ201502018.htm
Lei Kunchao, Luo Yong, Chen Beibei, Guo Gaoxuan, Zhou Yi. 2016. Distribution characteristics and influence factors of land subsidence in Beijing area[J]. Geology in China, 43(6):2216-2225 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201606029
Li Man, Ge Daqing, Zhang Ling, Liu Bin, Guo Xiaofang, Wang Yan. 2016. Characteristics and influencing factors of land subsidence in Caofeidian newly-developed area based on PSInSAR technique[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 28(4):119-126 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gtzyyg201604021
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. 2015. Specificaiton of Risk Assessment for Geological Hazard(DZ/T 0286-2015)[S]. (in Chinese).
Pacheco-martínez J, Hernandez-marín M, Burbey T J, GonzálezCervantes N, Ortíz-Lozano, JÁZermeño-De-Leon, M E, Solís-Pinto A. 2013. Land subsidence and ground failure associated to groundwater exploitation in the Aguascalientes Valley, México[J]. Engineering Geology, 164:172-186. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.06.015
Tomas R, Herrera G, Delgado J, Mallorquí J J, Mulas J. 2010. A ground subsidence study based on DInSAR data:Calibration of soil parameters and subsidence prediction in Murcia City(Spain)[J]. Engineering Geology, 111:19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.11.004
Tomas R, Romero R, Mulas J. 2014. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena:A review of practical issues through cases in Spain[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 71(1):163-181. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2422-z
Xiao Guoqiang. 2010. Environmental Geological Survey And Vulnerability Assessment of Key Areas in Bohai Region[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey (in Chinese).
Xu Junxiang, Shi Baoyu, Chen Xiuming. 2002. Study on major ecological environment problems and its survey method[J]. Shandong Geology, 18(4):95-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI2002Z1033.htm
Zhang Jinzhi, Huang Haijun, Liu Yanxia, Liu Yong, Ma Lijie. 2013. Monitoring and analysis of ground subsidence in the Modern Yellow River Delta Area based on PSInSAR technique[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(7):831-836 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201307009.htm
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2006.国家一、二等水准测量规范(GB/T 12897-2006)[S].
中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2015.地质灾害危险性评估规范(DZ/T 0286-2015)[S].
中国地质调查局. 2016.地质环境承载能力评价与监测预警指标体系和技术方法[S].
房浩, 何庆成, 徐斌, 汪美华, 李霞. 2016.沧州地区地面沉降灾害风险评价研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 43(4):159-164. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz201604026
葛大庆, 王艳, 郭小方, 刘圣伟, 范景辉.2007.基于相干点目标的多基线D-InSAR技术与地表形变监测[J].遥感学报, 11(4):574-580. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygxb200704020
郭海朋, 白晋斌, 张有全, 王丽亚, 石菊松, 李文鹏, 张作辰, 王云龙, 朱菊艳, 王海刚. 2017.华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J].中国地质, 44(6):1115-1127. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170607&journal_id=geochina
刘宏伟. 2017.莱州湾地质环境调查评价[R].天津: 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心.
李洪春, 李小龙, 张亚刚. 2015.浅析潍坊北部沿海区域主要环境工程地质问题及对策[J].价值工程, 34(23):97-99. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzgc201523036
刘宏伟, 马震, 陈社明, 郭旭, 苏永军, 杜东, 胡云壮. 2015.基于水化学与地球物理法的莱州湾南岸海(咸)水入侵勘查[J].现代地质, 29(2):337-343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.017
雷坤超, 罗勇, 陈蓓蓓, 郭高轩, 周毅. 2016.北京平原区地面沉降分布特征及影响因素[J].中国地质, 43(6):2216-2225. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160629&journal_id=geochina
李曼, 葛大庆, 张玲, 刘斌, 郭小芳, 王艳. 2016.基于PSInSAR技术的曹妃甸新区地面沉降发育特征及其影响因素分析[J].国土资源遥感, 28(4):119-126. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201604021
肖国强. 2010.环渤海地区重点地段环境地质调查及脆弱性评价[R].天津: 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心.
徐军祥, 石宝玉, 程秀明. 2002.山东省主要生态环境地质问题与调查方法探讨[J].山东地质, 18(4):95-99. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sddz200203033
张金芝, 黄海军, 刘艳霞, 刘勇, 马立杰. 2013.基于PSInSAR技术的现代黄河三角洲地面沉降监测与分析[J].地理科学, 33(7):831-836. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201307009.htm
-




 下载:
下载: