Identification of nitrate sources of groundwaters in the Zhaotong basin using hydrochemistry, nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and its impact on the environment
-
摘要:
研究目的 由于人类活动的影响,地下水硝酸盐(NO3-)污染越来越严重。
研究方法 利用水化学和硝酸盐氮氧同位素(δ15NNO3与δ18ONO3)研究云南昭通盆地地下水NO3-来源与转化过程,用SIAR模型定量计算泉水和民井中不同NO3-来源的比例。
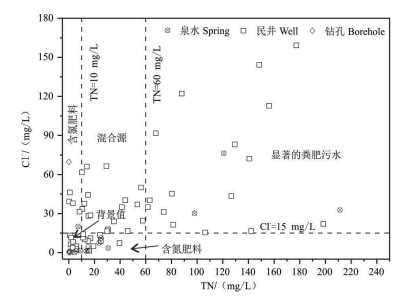
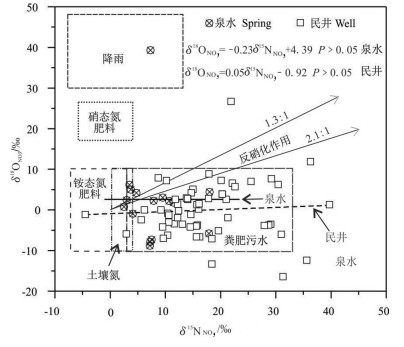
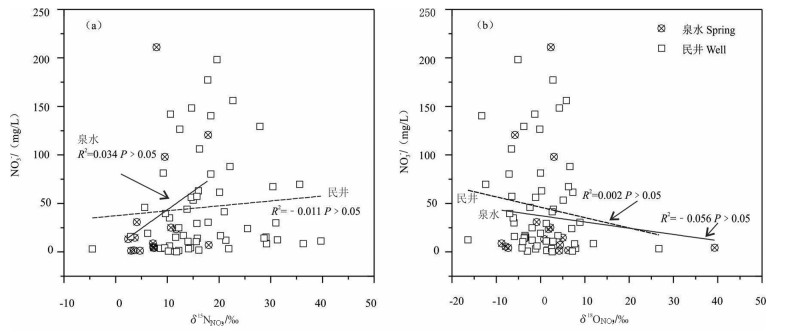
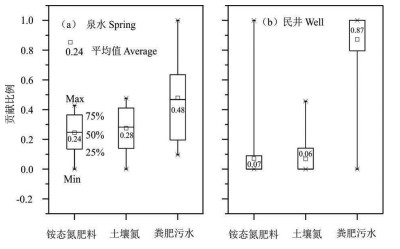
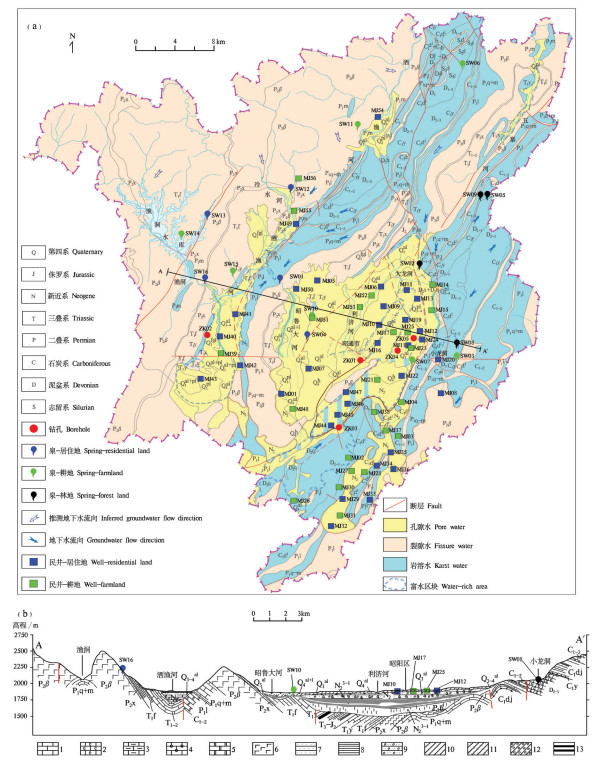
研究结果 结果表明:(1)研究区钻孔水水质良好,但19%的泉水NO3-超过生活饮用水标准限值,13%的民井因NO3-超标而不适宜灌溉;(2)泉水和民井中δ15NNO3值分别介于2.4‰~18‰和-4.5‰~39.7‰,平均值为7.9‰和17.3‰,δ18ONO3值介于-8.8‰~39.3‰和-16.4‰~26.7‰,平均值为2.5‰和0‰,同位素组成和水化学指示硝化作用主导着研究区氮循环;(3)粪肥污水、土壤氮和铵态氮肥料是地下水中NO3-主要来源,其对泉水的NO3-平均贡献率分别为48%、28%和24%,对民井的NO3-平均贡献率分别为87%、6%和7%。
结论 居住区和耕地区地下水中NO3-的粪肥污水源分别高达89%和72%,林地地下水仅为27%,表明受人类活动影响越强烈的地区地下水NO3-污染越严重。
Abstract:This paper is the result of the water resources and environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective Nitrate contamination of groundwater is becoming more and more serious resulting from intensive human activities.
Methods Hydrochemistry and stable nitrogen and oxygen isotopes were used to trace the nitrate sources and transformation groundwaters in the Zhaotong basin, China. As well as, the origin of nitrate in the spring and well waters was quantitatively analyzed by SIAR model.
Results The results showed that: (1) The water quality of boreholes is good, while approximately 19% of the spring samples are not drinkable due to nitrate exceed the drinking water standard, and 13% of the well samples are unsuited to irrigation due to the high nitrate concentrations; (2) The ranges of δ15NNO3 in spring and well waters were 2.4‰-18‰ (mean of 7.9‰) and -4.5‰-39.7‰ (mean of 17.3‰), respectively, and the values of δ18ONO3 ranged from -8.8‰ to 39.3‰ (mean of 2.5‰), and from -16.4‰ to 26.7‰ (mean of 0‰), respectively. Based on the hydrochemical data and stable isotopic compositions, nitrification was the dominant process in the study area; (3) Nitrate in spring and well waters were mainly from manure & sewage, soil nitrogen, and ammonium nitrogen fertilizer. The SIAR model showed that the contributions of manure & sewage, soil nitrogen, and ammonium nitrogen fertilizer to spring were 48%, 28% and 24%, respectively, and to well water were 87%, 6% and 7%, respectively.
Conclusions Manure & sewage end-member accounted for 89% and 72% in the groundwaters from residential and agricultural areas, respectively, while it only accounted for 27% in the groundwater from forestry land, indicating that the more strongly affected by human activities, the more serious nitrate contamination of groundwater.
-

-
表 1 地下水水化学和同位素组成
Table 1. Hydrochemistry and isotopic compositions in groundwaters

-
Boshers D S, Granger J, Tobias C R, Böhlke J K, Smith R L. 2019. Constraining the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate produced by nitrification[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(3): 1206-1216. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b03386
Boumaiza L, Chesnaux R, Drias T, Walter J, Huneau F, Garel E, Knoeller K, Stumpp C. 2020. Identifying groundwater degradation sources in a Mediterranean coastal area experiencing significant multi-origin stresses[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 746: 141203. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141203
Chen F, Jia G, Chen J. 2009. Nitrate sources and watershed denitrification inferred from nitrate dual isotopes in the Beijiang River, south China[J]. Biogeochemistry, 94: 163-174. doi: 10.1007/s10533-009-9316-x
Chen Jianyao, Wang Ya, Zhang Hongbo, Zhao Xinfeng. 2006. Overview the studies of nitrite pollution in groundwater[J]. Progress in Geography, 25(1): 34-44(in Chinese with English abstract).
Clague J C, Stenger R, Clough T J. 2015. Evaluation of the stable isotope signatures of nitrate to detect denitrification in a shallow groundwater system in New Zealand [J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 202: 188-197.
Grimmeisen F, Lehmann M F, Liesch T, Goeppert N, Klinger J, Zopfi J, Goldscheider N. 2017. Isotopic constraints on water source mixing, network leakage and contamination in an urban groundwater system[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 583: 202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.054
Hosono T, Tokunaga T, Kagabu M, Nakata H, Orishikida T, Lin I, Shimada J. 2013. The use of δ15N and δ18O tracers with an understanding of groundwater flow dynamics for evaluating the origins and attenuation mechanisms of nitrate pollution[J]. Water Research, 47(8): 2661-2675. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.020
Hu M, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Dahlgren R A, Chen D. 2019. Coupling stable isotopes and water chemistry to assess the role of hydrological and biogeochemical processes on riverine nitrogen sources[J]. Water Research, 150: 418-430. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.082
Jin Zanfang, Zhang Wenliao, Zheng Qi, Zhu Chenyang, Li Feili. 2018. Contribution of nitrogen sources in water sources by combining nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and SIAR [J]. Environmental Science, 39(5): 2039-2047(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kendall C. 1998. Tracing Nitrogen Sources and Cycling in Catchments[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 517-576.
Li C, Li S L, Yue F J, He S N, Liu C Q. 2020. Nitrate sources and formation of rainwater constrained by nitrate isotopes in Southeast Asia: Example from Singapore[J]. Chemosphere, 241: 125024. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125024
Liang Xing, Sun Liqun, Zhang Xin, Zhang Jie, Fu Pengyu. 2020. Mechanism of inorganic nitrogen transformation and identification of nitrogen sources in water and soil [J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4333-4344(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liao Lei, He Jiangtao, Zeng Ying, Peng Cong, Huang Deliang. 2016. A study of nitrate background level of shollow groundwater in the Liujiang Basin[J]. Geology in China, 43(2): 671-682(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin J, Böhlke J K, Huang S, Gonzalez-Meler M, Sturchio N C. 2019. Seasonality of nitrate sources and isotopic composition in the Upper Illinois River[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 568: 849-861. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.11.043
Liu J, Shen Z, Yan T, Yang Y. 2018. Source identification and impact of landscape pattern on riverine nitrogen pollution in a typical urbanized watershed, Beijing, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 628/629: 1296-1307. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.161
Lu Lu, Dai Erfu, Cheng Qianding, Wu Zhenzhen. 2019. The sources and fate of nitrogen in groundwater under different land use types: Stable isotope combined with a hydrochemical approach [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 74(9): 1878-1889(in Chinese with English abstract).
Nyilitya B, Mureithi S, Bauters M, Bauters M, Boeckx P. 2021. Nitrate source apportionment in the complex Nyando tropical river basin in Kenya[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 594(12): 125926.
Panno S V, Kelly W C, Hwang H H, Greenberg S E, O'Kelly D J. 2006a. Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water [J]. Ground Water, 44: 176-187. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.00127.x
Panno S V, Kelly W R, Martinsek A T, Hackley K C. 2006b. Estimating background and threshold nitrate concentrations using probability graphs [J]. Ground Water, 44, 697-709. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00240.x
Parnell A C, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson A L, Rands S. 2010. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation [J]. PLoS ONE, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009672.
Peterson B J, Wollheim W M, Mulholland P J, Webster J R, Meyer J L, Tank J L, Marti E, Bowden W B, Valett H M, Hershey A E, McDowell W H, Dodds W K, Hamilton S K, Gregory S, Morrall D D. 2001. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams [J]. Science, 292(5514): 86-90. doi: 10.1126/science.1056874
Ren Kun, Pan Xiaodong, Liang Jiapeng, Peng Cong, Zeng Jie. 2021. Sources and fate of nitrate in groundwater in a typical karst basin: Insights from carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen isotopes[J]. Environmental Science, 42(5): 2268-2275(in Chinese with English abstract).
Seiler R L. 2005. Combined use of 15N and 18O of nitrate and 11B to evaluate nitrate contamination in groundwater[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 20(9): 1626-1636. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.04.007
Tian Yongzhu, Han Zhiwei, Zhao Ran, Li Geng, Zeng Xiangying, Huang Jiayan. 2020. Analysis of nitrate sources in different waters of a karst basin [J]. Environmental Science, 41(7): 3157-3164(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Chunying, Li Yuzhong, Li Qiaozhen, Mao Lili, Lin Wei, Qiang Xiaojing, Zheng Qian. 2016. Determination of 15N and 18O isotope abundance in the extractable soil nitrate by the denitrifier method[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(9): 1829-1836.
Xue Dongmei, Baets B D, Cleemput O V, Hennessy C, Berglund M, Boeckx P. 2012. Use of a Bayesian isotope mixing model to estimate proportional contributions of multiple nitrate sources in surface water[J]. Environmental Pollution, 161: 43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.09.033
Xue D, Botte J, Baets B D, Accoe F, Boeckx P. 2009. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface and groundwater[J]. Water Research, 43(5): 1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048
Yin Chao, Yang Haiquan, Chen Jingan, Guo Jianyang, Wang Jingfu, Zhang Zheng, Tang Xunyin. 2020. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and hydrochemical characteristics during wet season in Lake Caohai, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 32(4): 989-998(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2020.0408
Yue F J, Li S L, Liu C Q, Zhao Z Q, Hu J. 2013. Using dual isotopes to evaluate sources and transformation of nitrogen in the Liao river, northeast China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 36: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.06.009
Zhang H, Kang X, Wang X, Zhang J, Chen G. 2020. Quantitative identification of nitrate sources in the surface runoff of three dominant forest types in subtropical China based on Bayesian model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 703: 135074. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135074
Zhang Xu, Hao Hongbing, Liu Kanglin, Mao Wulin, Xiao Yao, Zhang Wen. 2020. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic model of Oiga Graben Geothermal Waters System in Xizang[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1702-1714(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Kelly W R, Panno S V, Liu W T. 2014. Tracing fecal pollution sources in karst groundwater by Bacteroidales genetic biomarkers, bacterial indicators, and environmental variables [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 490: 1082-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.086
Zhang Y, Shi P, Li F, Wei A, Song J, Ma J. 2018. Quantification of nitrate sources and fates in rivers in an irrigated agricultural area using environmental isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model [J]. Chemosphere, 208: 493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.164
Zheng W, Wang S, Tan K, Lei Y. 2019. Nitrate accumulation and leaching potential is controlled by land-use and extreme precipitation in a headwater catchment in the North China Plain [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 707: 136168.
Zhu A, Chen J, Gao L, Shimizu Y, Liang D, Yi M, Cao L. 2019. Combined microbial and isotopic signature approach to identify nitrate sources and transformation processes in groundwater[J]. Chemosphere, 228: 721-734. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.163
陈建耀, 王亚, 张洪波, 赵新峰. 2006. 地下水硝酸盐污染研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展, 25(1): 34-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2006.01.004
金赞芳, 张文辽, 郑奇, 朱晨阳, 李非里. 2018. 氮氧同位素联合稳定同位素模型解析水源地氮源[J]. 环境科学, 39(5): 2039-2047. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201805010.htm
梁杏, 孙立群, 张鑫, 张杰, 付鹏宇. 2020. 无机态氮素转化机制及水土体氮源识别方法[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4333-4344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202009055.htm
廖磊, 何江涛, 曾颖, 彭聪, 黄德亮. 2016. 柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸盐背景值研究[J]. 中国地质, 43(2): 671-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.026 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160226&flag=1
路路, 戴尔阜, 程千钉, 邬真真. 2019. 基于水环境化学及稳定同位素联合示踪的土地利用类型对地下水体氮素归趋影响[J]. 地理学报, 74(9): 1878-1889. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201909014.htm
任坤, 潘晓东, 梁嘉鹏, 彭聪, 曾洁. 2021. 碳氮氧同位素解析典型岩溶流域地下水中硝酸盐来源与归趋[J]. 环境科学, 42(5): 2268-2275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202105020.htm
田永著, 韩志伟, 赵然, 李耕, 曾祥颖黄家琰. 2020. 岩溶流域不同水体硝酸盐的来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 41(7): 3157-3164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202007021.htm
谢先军, 甘义群, 刘运德, 李俊霞, 李小倩, 杜尧. 2019. 环境同位素原理与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
徐春英, 李玉中, 李巧珍, 毛丽丽, 林伟, 强晓晶, 郑欠. 2016. 土壤浸提液中硝酸盐氮氧同位素组成的反硝化细菌法测定[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(9): 1829-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201609026.htm
殷超, 杨海全, 陈敬安, 郭建阳, 王敬富, 张征, 唐续尹. 2020. 基于水化学和氮氧同位素的贵州草海丰水期水体硝酸盐来源辨析[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(4): 989-998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202004008.htm
章旭, 郝红兵, 刘康林, 毛武林, 肖尧, 张文. 2020. 西藏沃卡地堑地下热水水文地球化学特征及其形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1702-1714. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200608&flag=1
-



 下载:
下载: