Resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
为研究江顶崖古滑坡复活变形特征与稳定性,通过历史资料调研、现场踏勘与监测、卫星遥感和室内土工试验等方法,分析了主滑坡体、滑坡后壁及侧壁的变形特征与稳定性。结果表明:滑体前缘高陡边坡因降雨及河流冲刷导致坡脚失稳;中后部土体受地下水、连续强降雨影响,抗剪强度降低,下滑力增大,逐步向前推移;最终由于前缘土体的滑动,导致抗滑力减小,随之引发整体滑动,为缓慢滑动的牵引式滑坡。滑体后壁、两侧侧壁高陡,变形迹象明显,在强降雨或地震工况下易失稳滑动。江顶崖滑坡具有长期蠕滑变形、多次复活滑动等特点,是甘肃省近年来规模、范围最大的滑坡之一,在地震或暴雨作用下,滑坡有再次复活的可能,建议加强对滑坡区的变形监测,同时,对区域内不稳定斜坡进行加固治理,防止出现重大灾害。
Abstract:In order to study the resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide, the deformation characteristics and stability of the main body, rear wall and side wall of the landslide are analyzed by means of historical data investigation, field survey, monitoring, satellite remote sensing and indoor geotechnical test. The results show that the slope toe is unstable due to rainfall and river scouring; Under the influence of groundwater and continuous heavy rainfall, the shear strength of the middle and rear soil decreases, the sliding force increases and moves forward gradually; Finally, due to the sliding of the front soil, the anti sliding force decreases, resulting in overall sliding, which is a slow sliding traction landslide. The rear wall and side walls on both sides of the landslide are high and steep, with obvious signs of deformation, and are prone to instability and sliding under heavy rainfall or earthquake conditions. Jiangdingya landslide has the characteristics of long-term creep deformation and multiple resurrection sliding. It is one of the largest landslides in Gansu Province in recent years. Under the action of earthquake or rainstorm, the landslide may resurrect again. It is suggested to strengthen the deformation monitoring of the landslide area, and strengthen the treatment of unstable slopes in the area to prevent major disasters.
-
Key words:
- ancient landslide /
- creep /
- resurrection /
- deformation characteristics /
- stability analysis
-

-
表 1 不同滑坡区域的位移距离
Table 1. Displacement distance of different landslide areas
滑坡位置 最大值/m 最小值/m 滑体后部 89.57 80.96 滑体中部 93.25 87.31 滑体前部 90.47 71.48 滑体舌部 34.56 18.49 表 2 滑坡监测点位移数据
Table 2. Landslide monitoring point displacement data
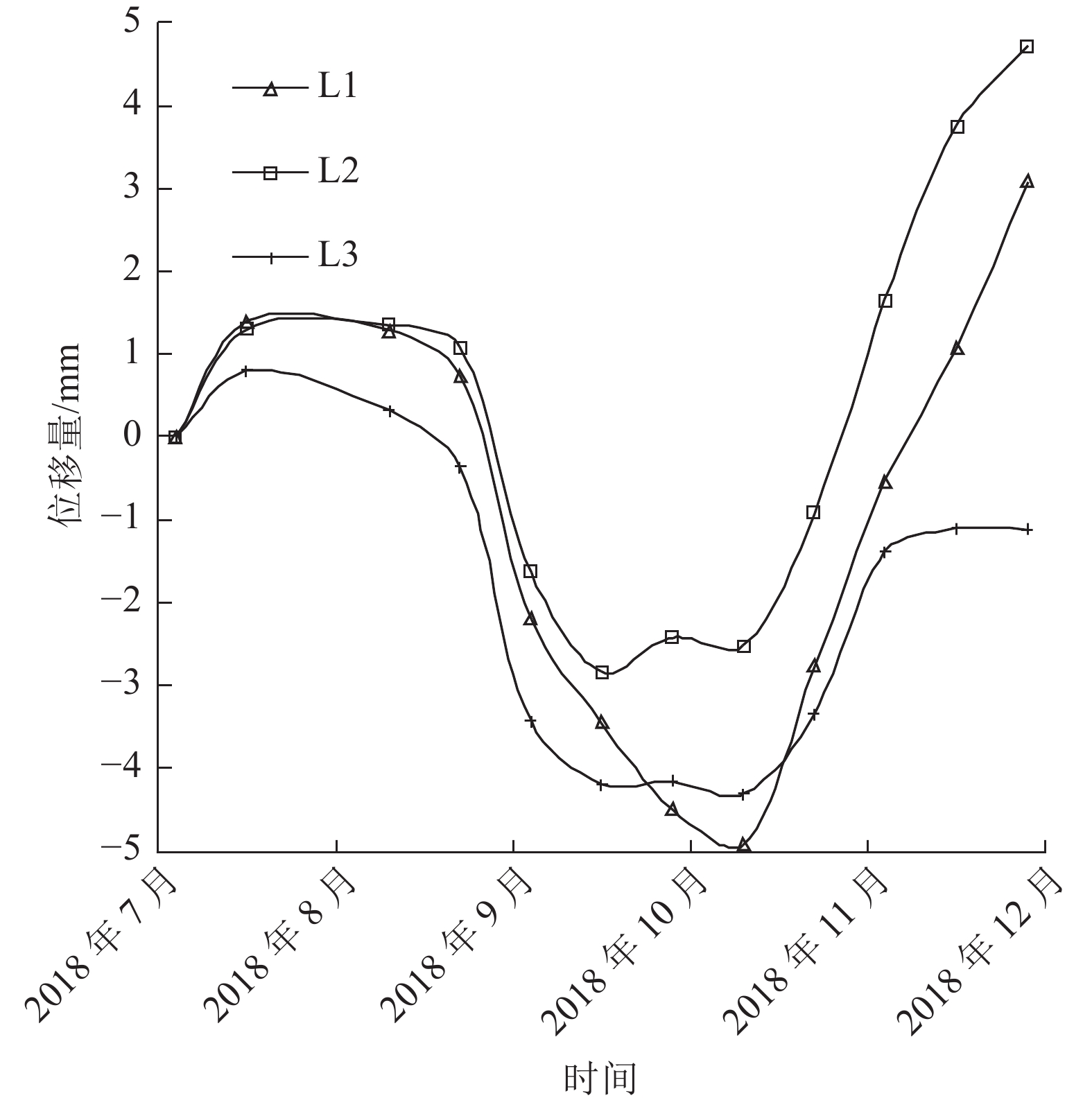
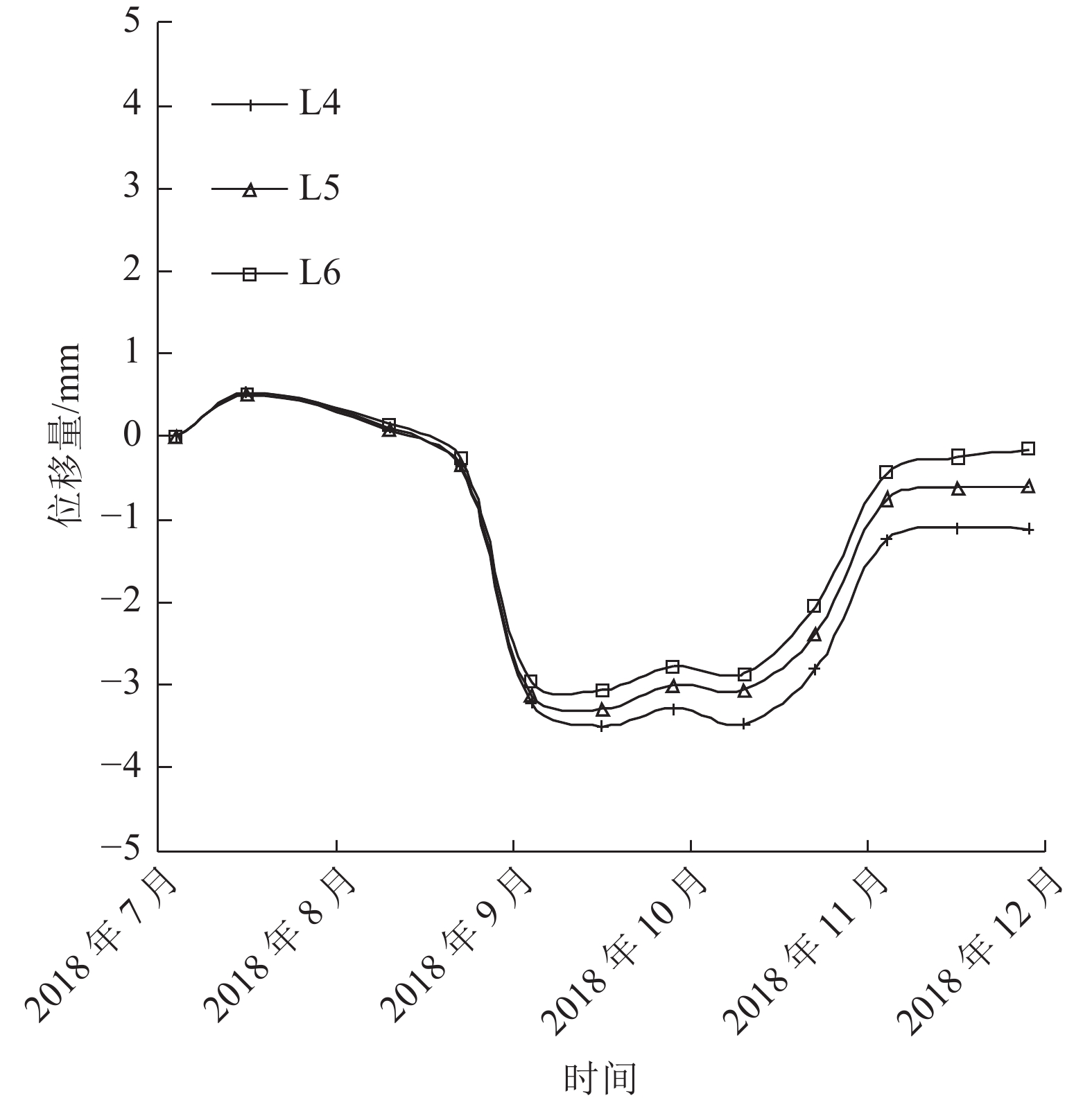
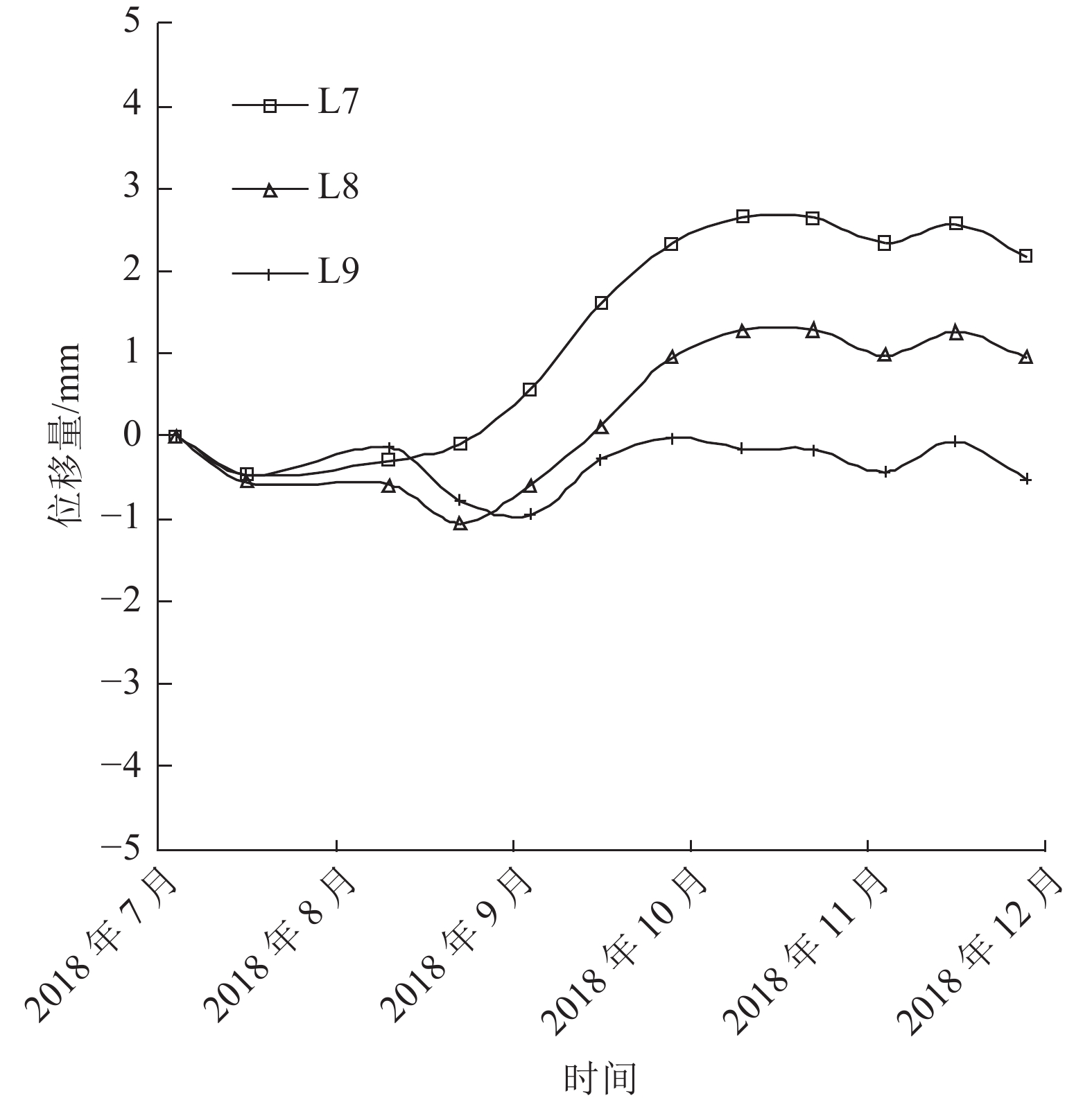
监测点 总变化趋势/mm 最大日变化趋势/(mm·d−1) L1 3.08 4.36 L2 4.72 5.82 L3 1.12 3.07 L4 1.12 2.86 L5 0.61 2.80 L6 0.17 2.71 L7 2.18 1.03 L8 0.95 1.84 L9 0.52 0.67 表 3 稳定性计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of stability
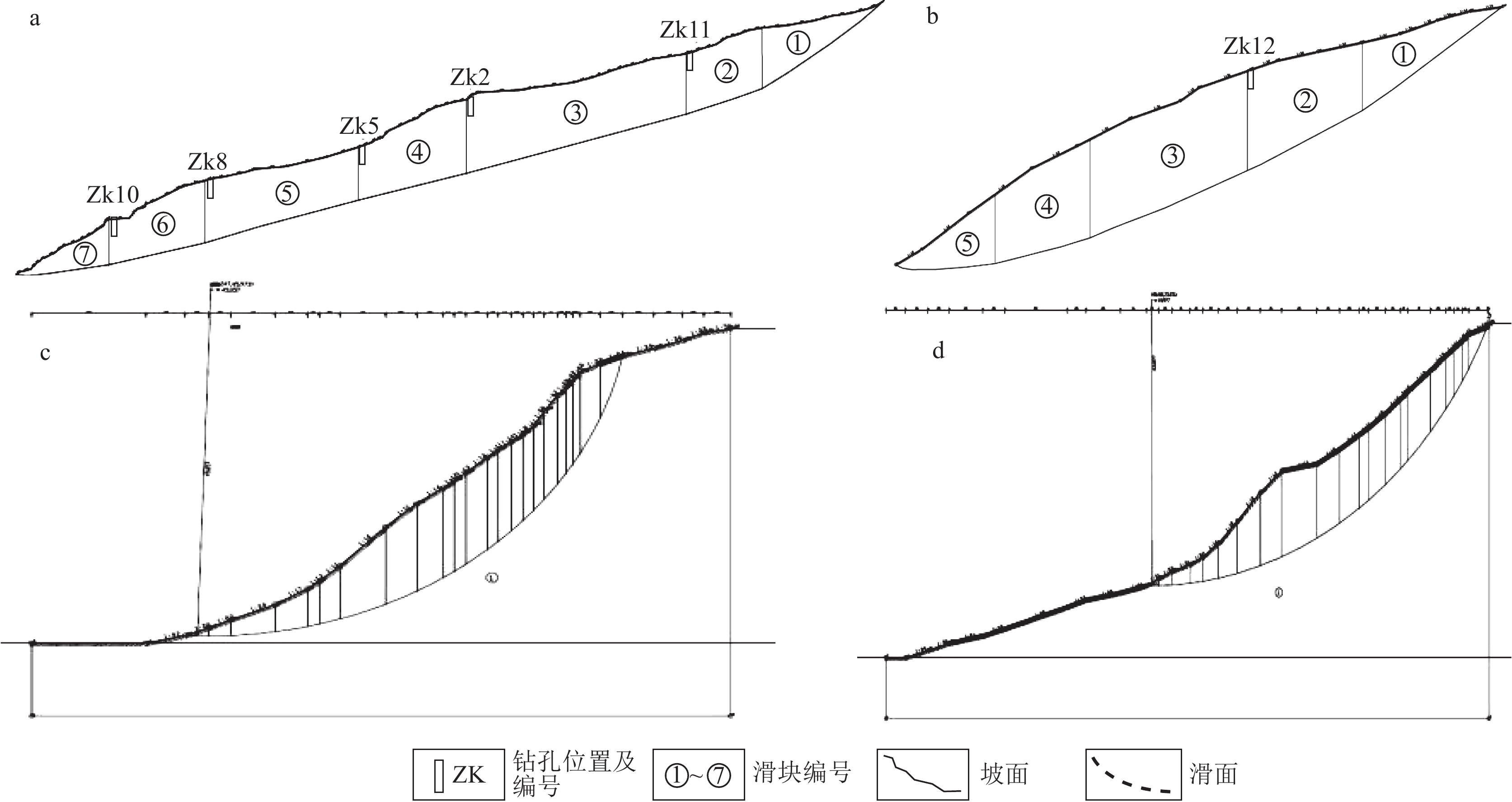
名称 剪出口位置 各工况下稳定性系数FS和稳定状态 自重工况 暴雨工况 地震工况 H1滑坡体 坡脚 1.195(稳定) 1.191(稳定) 1.041(欠稳定) H1滑坡后壁 坡脚 1.087(基本稳定) 0.961(不稳定) 0.973(不稳定) H1滑坡右侧壁 坡脚 1.039(欠稳定) 0.872(不稳定) 0.930(不稳定) H1滑坡左侧壁 坡脚 1.138(基本稳定) 0.986(不稳定) 1.008(欠稳定) 表 4 滑带土综合取值
Table 4. Comprehensive value of sliding-zone soil
状态 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/ ° 重度/(kN·m−3) 试验平均值 工程类比值 反演值 采用值 试验平均值 工程类比值 反演值 采用值 天然 6.4 7 ~ 8.4 6.1 6 16.4 14.8 ~ 15.4 14.9 15 20.5 饱和 / 5.3 ~ 6.7 6.1 6 / 12.1 ~ 13.3 14.9 15 22 -
[1] Guo C B, Zhang Y S, Li X, et al. 2020. Reactivation of giant Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province, China[J]. Landslides, 17: 179−190.
[2] Zhang Z L. 2020. Mechanism of the 2019 Yahuokou landslide reactivation in Gansu, China and its causes[J]. Landslides, 17(1): 1429−1440.
[3] 陈洪天. 1991. 甘肃舟曲县南峪大滑坡简介[J]. 西北水电, (4): 63−63.
[4] 戴可人, 卓冠晨, 许强, 等. 2019. 雷达干涉测量对甘肃南峪乡滑坡灾前二维形变追溯[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(12): 1778−1786,1796.
[5] 黄润秋. 2007. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 26(3): 433−454.
[6] 黄晓, 杨为民, 张春山, 等. 2013. 甘肃南部坪定-化马断裂带锁儿头滑坡成因机制[J]. 地质通报, 32(12): 1936−1942.
[7] 焦斌贝, 王国亚. 2013. 地震荷载对滑坡稳定性的影响评估——以甘肃舟曲南桥滑坡为例[J]. 冰川冻土, 35(3): 692−700.
[8] 蒋树, 文宝萍, 黎志恒, 等. 2016. 甘肃舟曲锁儿头滑坡活动特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 43(2): 69−74,92.
[9] 李文彦, 张媛, 韩鑫, 等. 2013. 舟曲锁儿头滑坡裂缝变形特征研究[J]. 人民长江, 44(3): 33−35+43.
[10] 李媛茜, 张毅, 苏晓军, 等. 2021. 白龙江流域潜在滑坡InSAR识别与发育特征研究[J]. 遥感学报, 25(2): 677−690.
[11] 黎志恒, 文宝萍, 贾贵义, 等. 2015. 甘肃省白龙江流域滑坡分布规律及其主控因素[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 51(6): 768−776.
[12] 穆鹏. 2011. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因及稳定性分析[J]. 中国水利, (4): 50−52.
[13] 司海宝, 杨为民, 谢胜华, 等. 2017. 考虑时间效应的泄流坡滑坡变形特征[J]. 工程地质学报, 25(2): 463−471.
[14] 宿星, 吴玮江, 叶伟林, 等. 2014. 甘肃舟曲县龙江新村滑坡特征及稳定性[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 50(1): 7−14+20.
[15] 王景荣, 祁龙. 1994. 甘肃省舟曲县南峪滑坡分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 14(1): 57−60.
[16] 徐则民, 刘文连, 黄润秋. 2011. 金沙江寨子村巨型古滑坡的工程地质特征及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 30(S2): 3539−3550.
[17] 杨为民, 黄晓, 张永双, 等. 2013. 甘肃南部坪定-化马断裂带滑坡变形特征及其防治[J]. 地质通报, 32(12): 1925−1935.
[18] 杨校辉, 朱鹏, 袁中夏, 等. 2023. 甘肃舟曲牙豁口多级滑坡变形特征及复活机理[J]. 现代地质, 37(4): 1004−1012.
[19] 张卫雄, 翟向华, 丁保艳, 等. 2020. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因分析与综合治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 31(5): 7−14.
[20] 窦晓东, 贾强, 刘心彪, 等. 2018. 舟曲县南峪乡江顶崖滑坡灾害应急治理工程勘查报告[R]. 甘肃省地质环境监测院.
-




 下载:
下载: