The main types of magmatism gold deposits and their mineralization in Gansu Province
-
摘要:
甘肃作为黄金资源大省之一,金矿类型多样,成矿作用复杂,其中岩浆作用成矿是金矿床的主要成矿机制之一,构造−岩浆−成矿的找矿研究思路更适用于岩浆作用金矿床。甘肃岩浆岩省可划分为10个构造岩浆岩带,分布范围广、规模大的主要有北山构造岩浆岩带、秦岭−大别构造岩浆岩带、塔里木构造岩浆岩带、祁连山构造岩浆岩带、阿尔金构造岩浆岩带、北秦岭构造岩浆岩带等,这些区域也是金矿床分布较集中区域,主要岩浆作用金矿床类型有岩浆型矿床、接触交代型矿床、斑岩型矿床、岩浆热液型矿床和火山岩型矿床五大类。结合甘肃省构造岩浆岩带划分及其主要特征和金矿床分布,重点分析研究了北山构造岩浆岩带和秦岭−大别构造岩浆岩带的岩浆作用金矿床与岩浆岩的时空分布特征、主要类型金矿床的成矿物质来源和物理化学条件,总结了控矿因素,提出有利于金矿找矿的主要岩浆岩类型、空间范围和技术方法。
Abstract:As one of the provinces with large gold resources, Gansu Province has various types of gold ore mineralization and complex metallage, among which magmatic metallogenic is one of the main metallogenic mechanisms of gold deposits, and the prospecting research idea of tectonic−magmatism-metallogenic is more suitable for magmatic gold deposits. The magmatic rock province of Gansu Province can be divided into 10 tectonic magmatic rock belts, which are mainly Beishan tectonic magmatic belt, Qinling−Dabie tectonic magmatic belt, Tarim tectonic magmatic belt, Qilian Mountain tectonic magmatic belt, Altyn tectonic magmatic belt, North Qinling tectonic magmatic belt, etc., these areas are also relatively concentrated areas of gold deposits, and the main types of magmatic gold deposits are magmatic deposits, contact metasomatic deposits, porphyry deposits, magmatic hydrothermal deposits and volcanic rock deposits. Combined with the division of tectonic magmatic rock belts and their main characteristics and the distribution of gold deposits in Gansu Province, this paper focuses on the analysis and study of the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of magmatic gold deposits and magmatic rocks, the mineral-forming sources and physicochemical conditions of the main types of gold deposits in the Beishan tectonic magmatic belt and the Qinling−Dabie tectonic magmatic belt, summarizes the ore control factors, and proposes the main magmatic rock types, spatial ranges and technical methods that are conducive to gold prospecting.
-

-
图 1 甘肃省岩浆岩与金矿分布简图(据李通国等,2021修改)
Figure 1.
图 3 拾金坡金矿区地质平面(a)与剖面略图(b)(据安国堡,2006)
Figure 3.
图 4 西秦岭主要金矿床及花岗岩分布图(据Wang et al.,2019修改)
Figure 4.
图 6 西秦岭地区中酸性岩浆侵位期次图(数据据Sun et al., 2002; 金维浚等,2005; Qin et al., 2009; 张帆等,2009; Zhu et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2012; Zeng et al., 2012; Han et al., 2014; 闫海卿等,2014)
Figure 6.
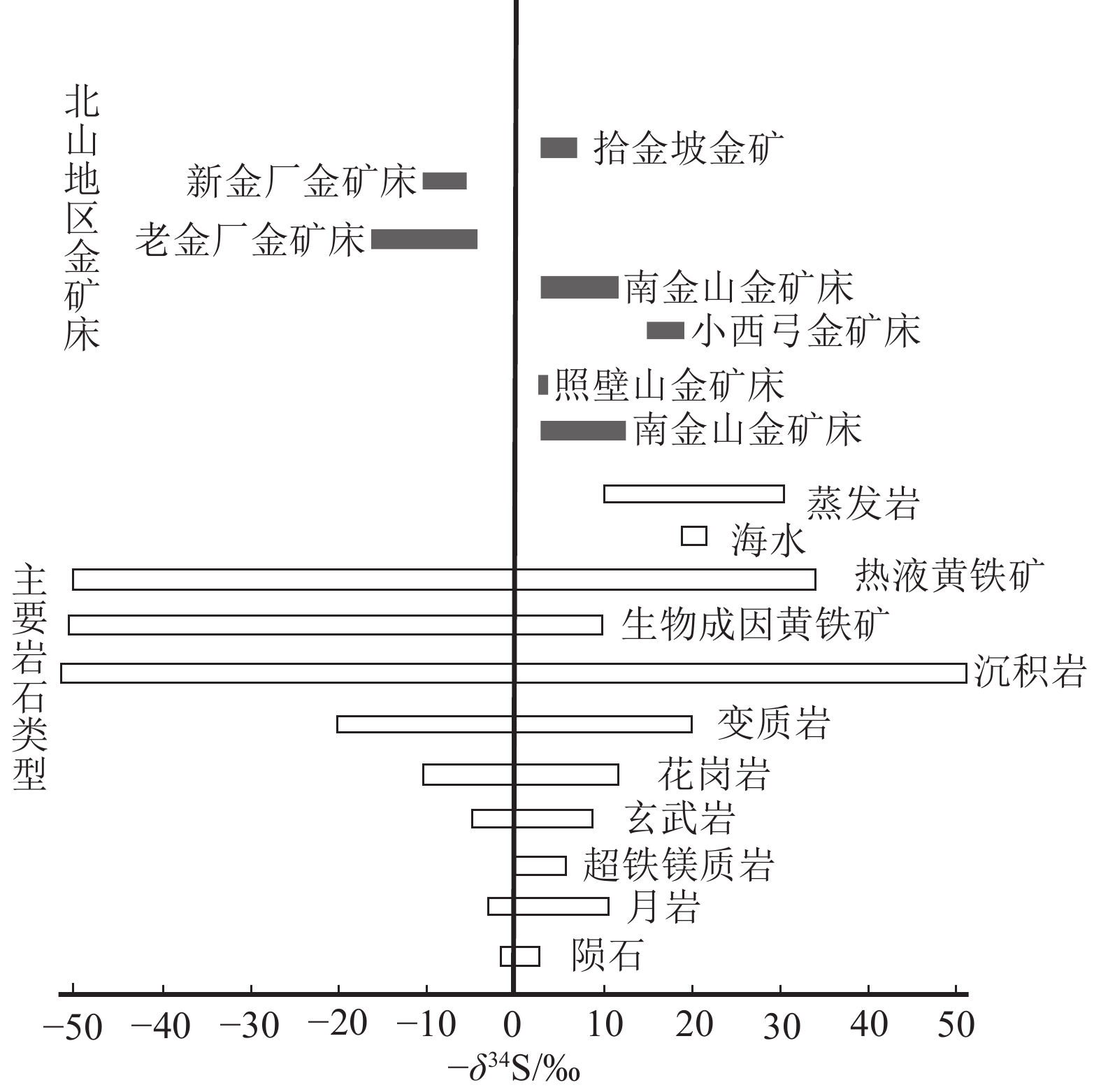
图 8 北山地区金矿硫同位素分布图(数据据聂凤军等,2002a, b;安国堡,2006;刘伟等,2006;胡朋,2007;王玉玺等,2012)
Figure 8.
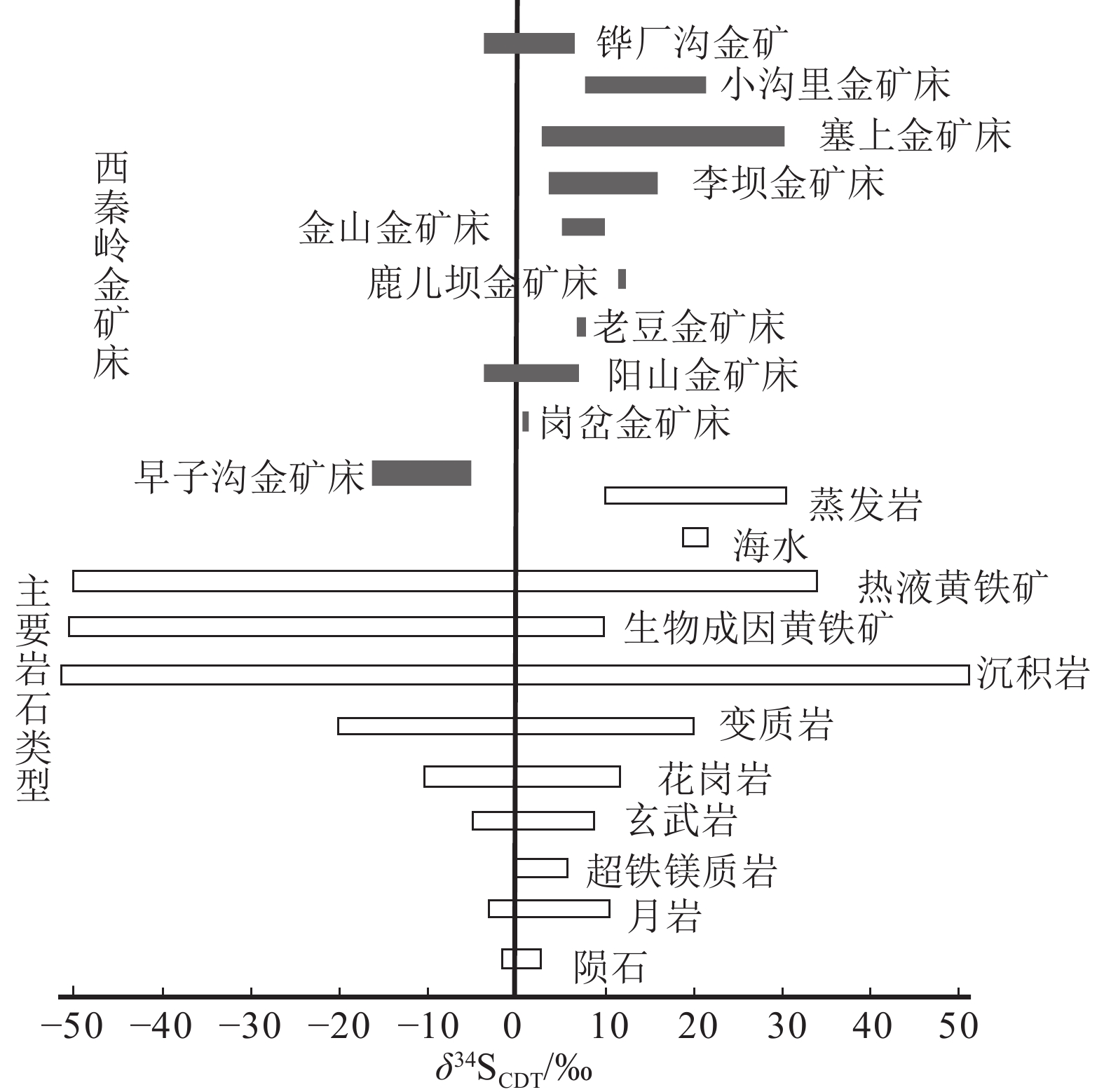
图 9 西秦岭地区金矿硫同位素分布(数据据冯建忠等,2003;张帆等,2009 ;Yang et al.,2012;Zeng et al.,2012)
Figure 9.
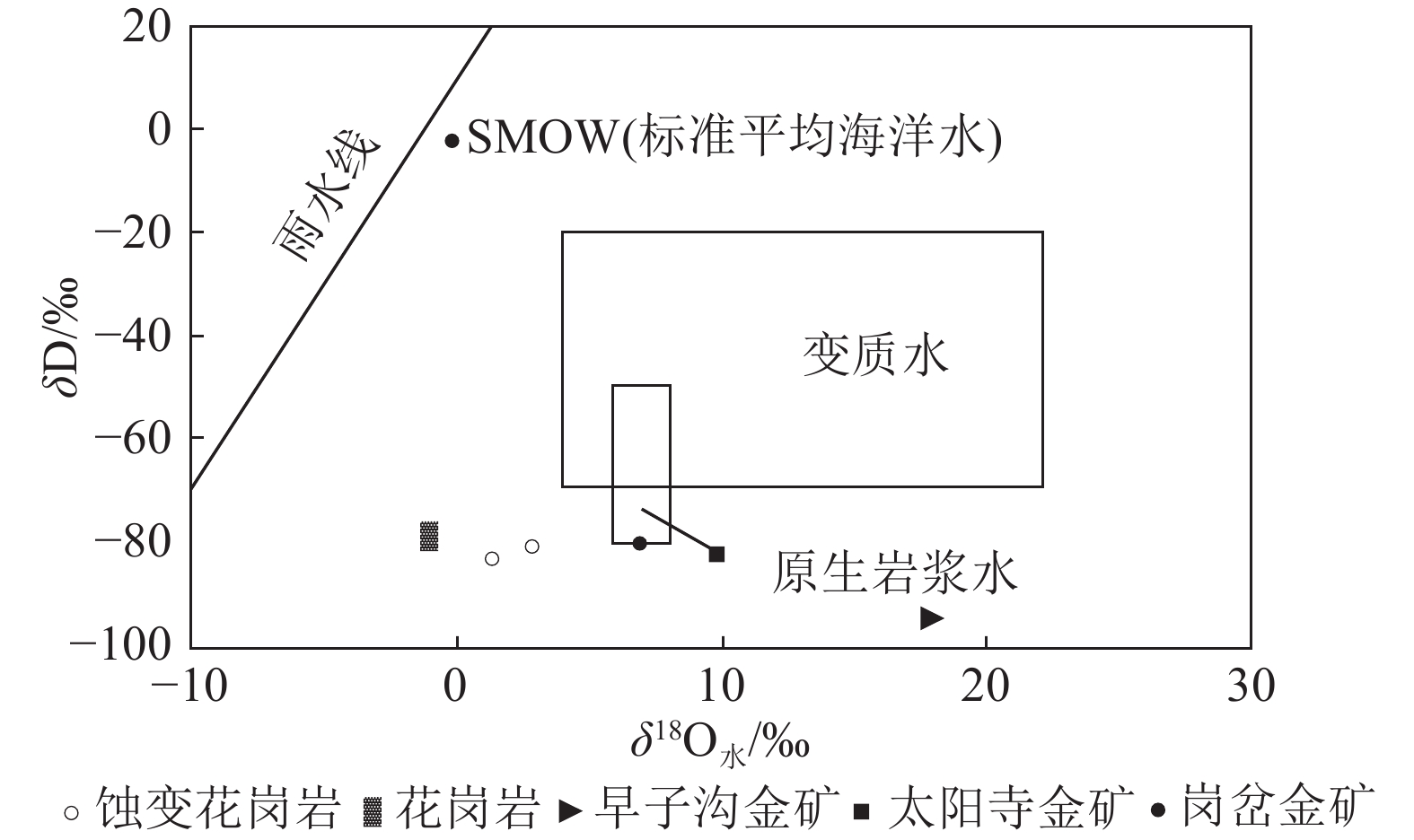
图 10 西秦岭地区金矿氢氧同位素分布(数据据Qin et al., 2009;Yang et al., 2012;张翔等,2017)
Figure 10.
图 11 北山南带岩浆热液型金矿区域成矿模式图(据王玉玺等,2019修改)
Figure 11.
表 1 北山成矿带金矿床成矿年龄与成矿有关岩体年龄对比
Table 1. Comparison table of metallogenic age of gold deposits and age of related rock bodies in Beishan metallogenic belt
位置 矿床名称 成矿时代/Ma 测试方法/测试对象 与成矿有关岩体年龄/Ma 来源文献 北山北带 马庄山 298±28 Rb−Sr/石英流体包裹体 303~301 李华芹等,1999 南金山 242.8 Ar−Ar/绢云母 244.15 江思宏等,2006 流沙山 260±10 Re−Os/辉钼矿 262~261 聂凤军等,2003 北山中带 金窝子 230±5.7 Rb−Sr/石英流体包裹体 375~354.1 胡霭琴等,1982,1986;陈富文等,1999 照壁山 296±5 Ar−Ar/绢云母 296 聂凤军等,2002b 北山南带 小西弓 284~267 K−Ar/绢云母 306~289 聂凤军等,2002a 拾金坡 403 U−Pb/锆石 409.3 安国堡,2006;胡朋,2007 新金厂、老金厂 270 据地质特征推断 270 胡朋,2007 -
[1] Duuring P, Cassidy K F, Hagemann S G. 2007. Granitoid-associated orogenic, intrusion-related, and porphyry style metal deposits in the Archean Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 32: 157−186. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.11.001
[2] Faure Q. 1986. Principles of isotope geology (second edition) [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons Press.
[3] Han J S, Yao J M, Chen Y J. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Dashui adakitic granitoids in the western Qinling Orogen, central China: implications for Triassic tectonic setting[J]. Geological Journal, 49(4/5): 383−401.
[4] Li N, Chen Y J, Fletcher I R, et al. 2011. Triassic mineralization with Cretaceous overprint in the Dahu Au−Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling gold province: Constraints from SHRIMP monazite U−Th−Pb geochronology[J]. Gondwana Research, 20: 543−552. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.013
[5] Mao J W, Wang Y T, Li H M, et al. 2008. The relationship of mantle−derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D−O−C−S isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 33: 361−381. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.01.003
[6] Mao S, Chen Y J, Zhou Z, et al. 2014. Zircon geochronology and Hf isotope geochemistry of the granitoids in the Yangshan gold field, western Qinling, China: implications for Petrogenesis, ore genesis and tectonic stting[J]. Geological Journal, 49(4/5): 359−382.
[7] Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 1999. Timing of collision of the North and South China blocks: Controversy and reconciliation[J]. Geology, 27: 1−96.
[8] Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 323: 183−196. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2
[9] Pirajno F, Bagas L. 2008. A review of Australia's Proterozoic mineral systems and genetic models[J]. Precambrian Research, 166(1/4): 54−80.
[10] Qin J F, Lai S C, Rodney G, et al. 2009. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogen (central China)[J]. Lithos, 112: 259−276. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.03.007
[11] Qiu Y M, Groves D I, McNaughton N J, et al. 2002. Nature, age, and tectonic setting of granitoid−hosted, orogenic gold deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China craton, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 37: 283−305. doi: 10.1007/s00126-001-0238-3
[12] Stacey J S, Kramers J D. 1975. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two−stage model[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 26: 207−221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6
[13] Sun W D, Li S G, Chen Y D, et al. 2002. Timing of synorogenic granotoids in the south Qinling, central China: Constraints on the evolution of the Qinling−Dabie Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Geology, 110: 457−468. doi: 10.1086/340632
[14] Wang Y X, Wang X W, Luo J M, et al. 2019. The quantitative classification of granites and their metallogenetic relations in West Qinling, Gansu Province, China[J]. Big Earth Data, 3(1): 56−66. doi: 10.1080/20964471.2019.1583054
[15] Yang T, Zhu L M, Zhang G W, et al. 2012. Geological and geochemical constraints on genesis of the Liziyuan gold−dominated polymetal deposit, western Qinling orogen, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 54(16): 1944−1966. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2012.704673
[16] Zeng Q T, McCuaig T C, Hart J R C, et al. 2012. Structural and geochronological studies on the Liba goldfield of the West Qinling Orogen, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 47(7): 799−819. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0398-8
[17] Zhang Y, Karrech A, Schaubs P M, et al. 2012. Modelling of deformation around magmatic intrusions with application to gold−related structures in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia[J]. Tectonophysics, 526: 133−146.
[18] Zhu L M, Zhang G W, Ding Z J, et al. 2011. Zircon U−Pb ages and geochemistry of the Wenquan Mo−bearing granitioids in Western Qinling, China: Constraints on the geodynamic setting for the newly discovered Wenquan Mo deposit[J]. Ore Geology Review, 39: 46−62. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.10.001
[19] 安国堡. 2006. 甘肃北山拾金坡金矿床地质特征及成因分析[J]. 矿床地质, 25(4): 483−490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.04.013
[20] 陈富文, 李华芹, 蔡红, 等. 1999. 新疆东部金窝子金矿成因讨论-同位素地质年代学证据[J]. 地质论评, 45(3): 247−254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1999.03.004
[21] 陈祖伊, 张学权, 张昭明, 等. 1993. 北山区域地质发展史和金矿区域成矿模式[J]. 铀矿地质, 9(2): 65−75.
[22] 崔惠文, 陈祖伊. 1996. 甘肃北山地区金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−20.
[23] 冯建忠, 汪东波, 王学明, 等. 2003. 甘肃礼县李坝大型金矿床成矿地质特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 3: 257−263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.03.006
[24] 郭俊华, 齐金忠, 孙彬, 等. 2002. 甘肃阳山特大型金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 黄金地质, 8(2): 15−19.
[25] 胡霭琴, 张积斌. 1982. 据天山东段K−Ar年龄测定结果对天山地槽热历史的探讨[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 4(4): 345−353.
[26] 胡霭琴, 张积斌, 刘菊英, 等. 1986. 天山东段中天山隆起带前寒武系变质时代及演化——据U−Pb年代学研究[J]. 地球化学, (l): 23−35.
[27] 胡朋. 2007. 北山南带构造岩浆演化与金的成矿作用[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文.
[28] 江思宏, 聂凤军. 2006. 北山地区花岗岩类的40Ar/39Ar 同位素年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 22(11): 2719−2732.
[29] 金维浚, 张旗, 何登发, 等. 2005. 西秦岭埃达克岩的SHRIMP定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 21(3): 959−966. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.03.033
[30] 李华芹, 陈富文, 蔡红, 等. 1999. 新疆东部马庄山金矿成矿作用同位素年代学研究[J]. 地质科学, 34(2): 251−256.
[31] 李金祥, 邓军, 吴文根, 等. 2004. 山东招远金矿集中区矿床及围岩中硫和铅同位素的研究[J]. 现代地质, 18(2): 187−192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2004.02.007
[32] 李通国, 黄增宝, 甄红旭, 等. 2021. 中国矿产地质志甘肃卷金矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 602−620.
[33] 刘长江. 2016. 甘肃省肃北县金场沟金矿地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 甘肃科技, 31(20): 44−48.
[34] 刘伟, 潘小菲. 2006. 新疆-甘肃北山金矿南带的成矿流体和成矿机制. 岩石学报, 22(1): 171−188.
[35] 聂凤军, 江思宏, 赵省民, 等. 2000. 北山地区金矿床类型和生成演化[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 30(增刊): 21−26.
[36] 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等. 2002a. 北山地区金属矿床成矿规律及找矿方向[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[37] 聂凤军, 江思宏, 赵省民, 等. 2002b. 北山地区照壁山金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地质科学, 37(2): 207−218.
[38] 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等. 2003. 北山中南带海西-印支期岩浆活动与金的成矿作用[J]. 地球学报, 24(5): 415−422. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.05.004
[39] 潘小菲. 2006. 甘肃-新疆北山地区典型金矿床成矿流体及其成矿机制探讨[D]. 中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文.
[40] 邵世才, 汪东波. 2001. 南秦岭三个典型金矿床的Ar−Ar年代及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 75: 106−110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.01.012
[41] 汤中立. 1996. 中国岩浆硫化物矿床的主要成矿机制[J]. 地质学报, 70(3): 237−243.
[42] 汤中立, 巴恩斯. 1998. 岩浆硫化物矿床成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−150.
[43] 王琦. 2006. 甘肃北山拾金坡金矿床矿物学特征[J]. 甘肃科技, 22(6): 85−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2006.06.034
[44] 王玉玺, 曹海龙, 刘杰. 2012. 甘肃北山地区拾金坡式岩浆热液型金矿成矿模式建立[J]. 甘肃地质, 21(1): 12−18.
[45] 王玉玺, 张渊, 张丹青, 等. 2019. 北山拾金坡−金场沟金成矿带岩浆热液型金矿区域成矿模式的建立[J]. 甘肃地质, 28(1/2): 16−23.
[46] 闫海卿, 贺宝林, 刘巧峰, 等. 2014. 西秦岭大水金矿岩浆岩年代学、地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 36(1): 98−110.
[47] 殷先明, 杜玉良, 殷勇. 2005. 甘肃花岗岩类成矿作用研究与找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 38(4): 26−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.04.005
[48] 殷勇, 殷先明. 2009. 西秦岭北缘与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的斑岩型铜-钼-金成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 25(5): 1239−1252.
[49] 殷勇. 2011. 西秦岭地区脉岩与金矿化的关系[J]. 甘肃地质, 20(1): 28−51.
[50] 袁见齐, 朱上庆, 翟裕生. 1985. 矿床学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[51] 曾长华, 吴大江, 夏文彬, 等. 2002. 北山成矿带金矿成矿规律与远景[J]. 新疆地质, 20(3): 219−223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.03.009
[52] 张帆, 刘树文, 李秋根, 等. 2009. 秦岭西坝花岗岩LA−ICP−MS 锆石U−Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 45(5): 833−840.
[53] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 2001. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1−855.
[54] 张旗, 殷先明, 殷勇, 等. 2009, 西秦岭与埃达克和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的金铜成矿及找矿问题[J]. 岩石学报, 25(12): 3103−3122.
[55] 张旗, 金维浚, 李承东, 等. 2015. 利用镜质体反射率方法寻找隐伏岩体——岩浆热场应用的一个实例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(6): 1094−1107.
[56] 张翔, 戴霜, 刘建宏, 等. 2017. 甘肃西秦岭金矿成矿与找矿研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[57] 张翔, 戴霜, 黄万堂, 等. 2019. 甘肃省玛曲县大水金矿原生金矿石的发现及意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 55(2): 484−495. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2019.02.004
[58] 张新虎, 刘建宏, 梁明宏, 等. 2013. 甘肃省区域成矿与找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 214−371.
[59] 郑永飞, 陈江峰. 2000. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[60] 朱赖民, 丁振举, 姚书振, 等. 2009. 西秦岭甘肃温泉钼矿床成矿地质事件及其成矿构造背景[J]. 科学通报, 54(16): 2337−2347.
-




 下载:
下载: