Discovery and significant implication of the strike-slip faults in Kaijiang-Liangping Trough of the Sichuan Basin
-
摘要:
研究目的 沉积盆地走滑断层的识别对其控藏作用研究与勘探部署具有重要意义,但走滑断层规模小、地震分辨率低是制约走滑断控油气藏勘探开发的重点难题,为此在四川盆地开江-梁平海槽东部地区新采集三维地震资料的基础上开展了走滑断层的识别。
研究方法 通过提高走滑断层分辨率的导航金字塔处理,进行走滑断层判识标志分析与地震解释,并结合钻井资料分析走滑断层的成藏作用。
研究结果 导航金字塔处理提高了深层微小(垂向断距<30 m)走滑断层的识别精度,提出了高陡直立、花状构造、倾向反转、断距和断层性质突变5个走滑断层剖面识别标志,以及雁列/斜列断层、地质体水平错动、拉分微地堑、马尾构造、类型与高差横向变化和地震属性线性突变6个走滑断层平面识别标志,发现了与北西走向台缘带一致的大型走滑断层带。走滑断层不仅可以沟通烃源岩、有利多层系油气运聚成藏,而且有利于深层碳酸盐岩的天然气富集与高产。
结论 研究提出了深层微小走滑断层的判识标志,形成了走滑断层的识别方法,发现开江-梁平海槽发育大规模走滑断层系统,并对天然气成藏与分布具有重要控制作用,为开拓四川盆地走滑断控气藏新领域提供了新思路。
Abstract:Objective The identification of strike−slip faults in sedimentary basins is of great significance to the study of the strike−slip fault−controlled reservoir and its exploitation deployment. However, the small−scale and low seismic resolution of strike−slip fault is the key issues restricting the exploration and development of strike−slip fault−controlled oil−gas reservoirs. Therefore, the identification of strike−slip faults is carried out on the basis of new 3D seismic data in the eastern Kaijiang−Liangping Trough of the Sichuan Basin.
Methods Steerable Pyramid reprocessing of the new 3D seismic data is used to enhance the seismic resolution on the strike−slip faults, the identification marks of the strike−slip faults are analyzed and the strike−slip faults are interpreted by seismic methods, and the fault effects on the gas accumulation and enrichment are discussed by the well data.
Results The Steerable Pyramid reprocessing has enhanced the seismic identified resolution of deep small (vertical fault displacement <30 m) strike−slip faults. Five marks in seismic section and six marks in plane attribute are proposed to form a method for seismic identification of small strike−slip faults. These include five section marks of vertical fault, flower structure, fault dip reversal, abrupt change of fault displacement and property, and six plane markers of echelon/oblique faults, horizontal offset of geological body, pull−apart micrograben, horsetail structure, horizontal variation of fault type and throw, and linear mutation of seismic attribute. A large strike−slip fault system is found that is consistent with the NW−trending platform margin. The strike−slip fault can not only connect source rocks and facilitate migration and accumulation, but also favor the gas enrichment and high production from the deep carbonate rocks.
Conclusions This paper proposes the identification markers of deep small strike−slip faults, and put forward the identification method of strike−slip fault. A large strike−slip fault system is found along the Kaijiang−Liangping Trough, and has significant effects on gas accumulation and distribution. This discovery provides a new exploration and development domain of strike−slip fault−controlled gas reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin.
-
Key words:
- strike-slip fault /
- identification /
- carbonate /
- gas reservoir /
- fault effect /
- Sichuan Basin
-

-
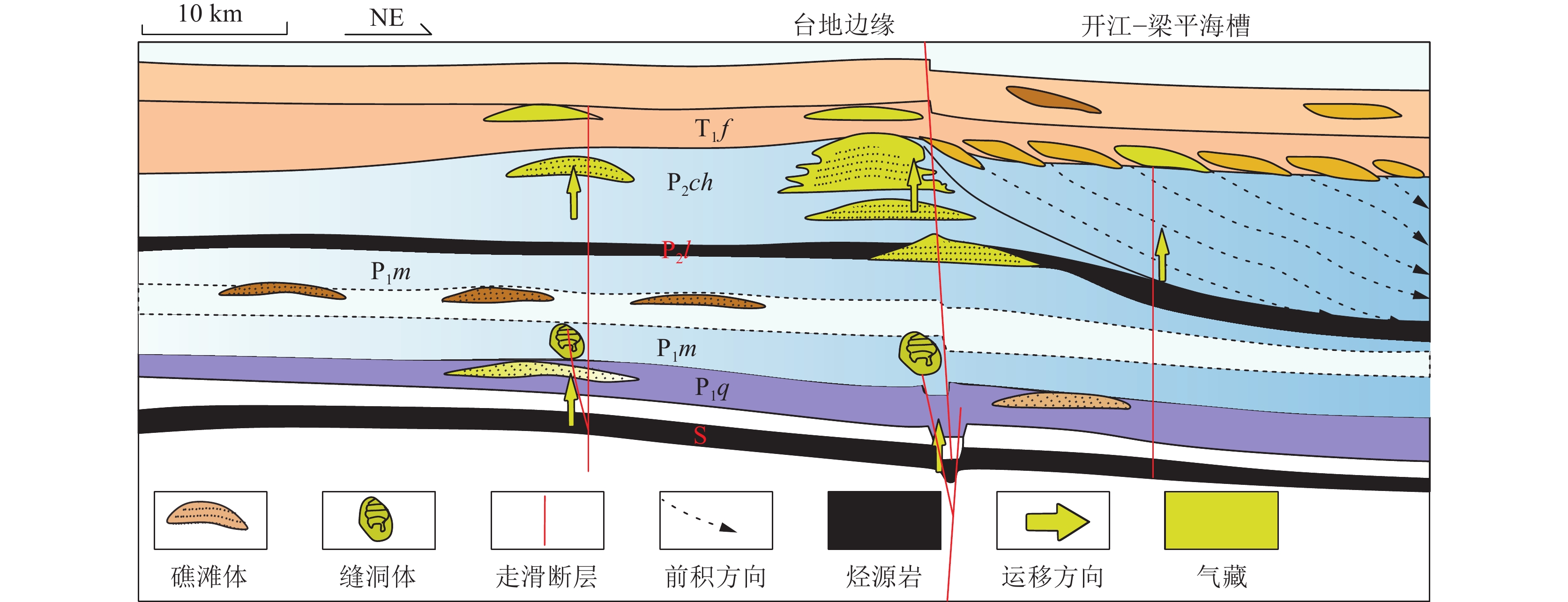
图 1 四川盆地(a)与开江-梁平海槽(b)构造位置及其构造分区简图(c)(据杨雨等,2021;Tang et al., 2022等修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 开江-梁平海槽东南地区典型地震剖面示逆冲构造带(剖面位置见图8)
Figure 2.
图 4 地震剖面与走滑断层的典型标志(剖面位置见图8)
Figure 4.
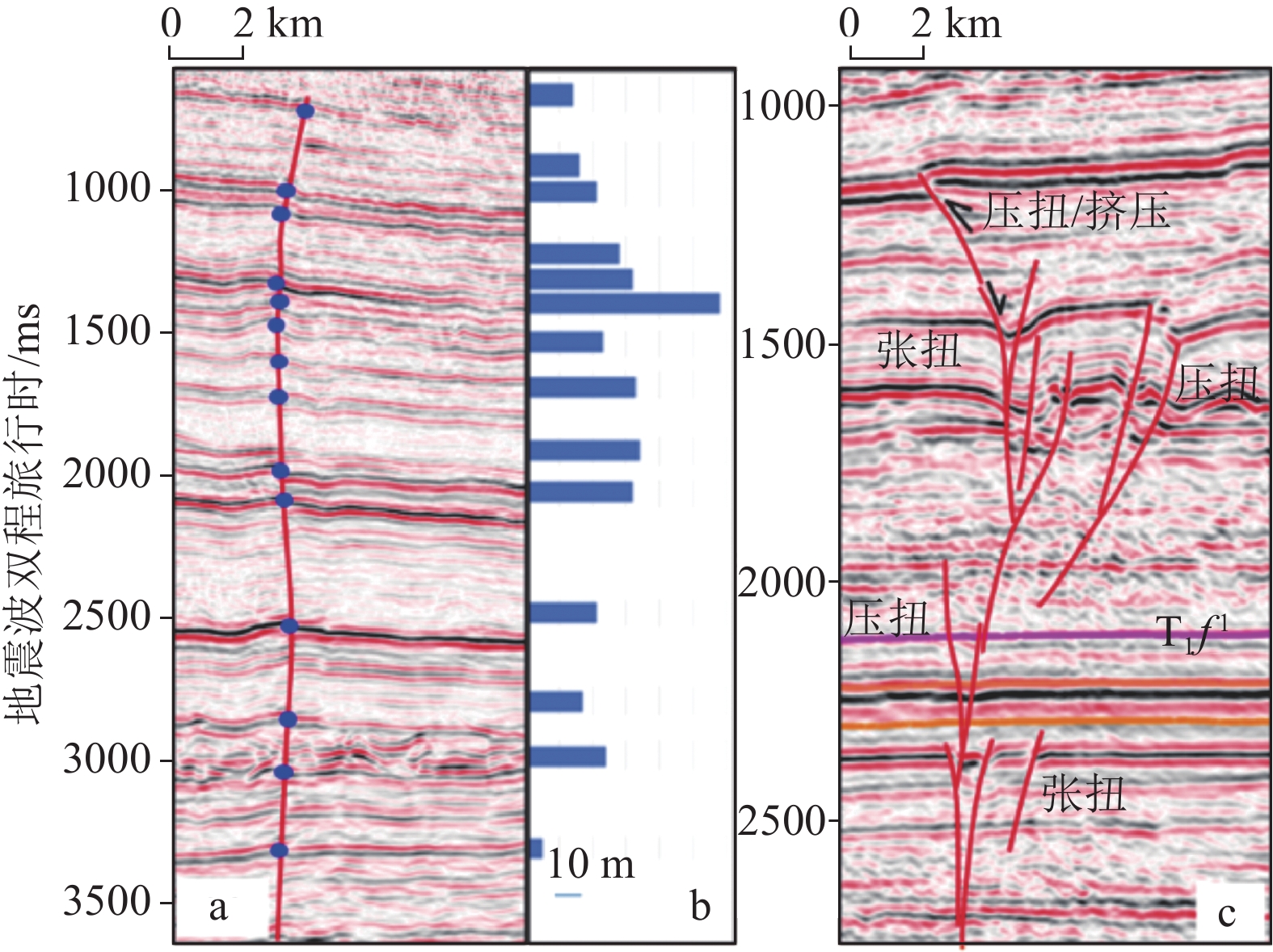
图 5 地震剖面(a)及其垂向断距图(b)和上下断层性质与位置变化(c)(图b为图a中对应各点的构造高差;剖面位置见图8)
Figure 5.
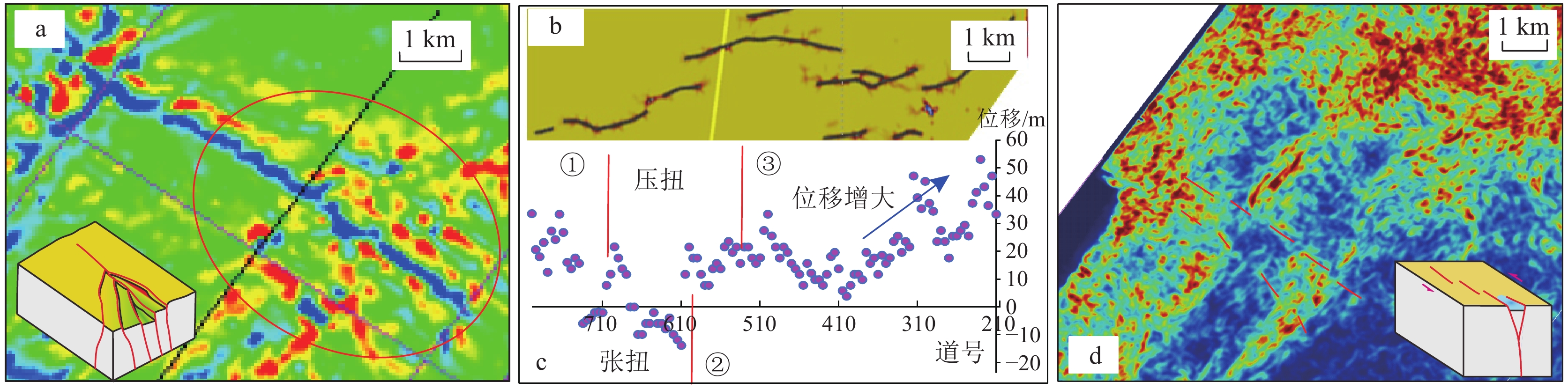
图 6 三叠系增强相干平面属性示雁列断层(a)、长兴组台缘礁滩沿走滑断层发生变化(b)及最大正向曲率示斜列断层组合形成左行左阶步的拉分微地堑(c)(图中立体图示所在构造模式;红色虚线示走滑断层;红色圆圈示微地堑位置;位置见图8)
Figure 6.
图 7 曲率平面图示马尾构造(a)、增强相干属性平面图示斜列断层(b)及沿走向的构造高差示水平方向断层性质与位移突变(c)、导航振幅属性平面图示走滑断层造成的线性突变带(d)(位置见图8)
Figure 7.
图 9 开江-梁平海槽走滑断层解释地震剖面(a,位置见图8)与分层相干属性解释走滑断层平面分布图(b)
Figure 9.
-
[1] Aydin A, Schultz R A. 1990. Effect of mechanical interaction on the development of strike−slip faults with echelon patterns[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 12(1): 123−129. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(90)90053-2
[2] Chen L X, Jiang Z X, Sun C, et al. 2023. An overview of the differential carbonate reservoir characteristic and exploitation challenge in the Tarim Basin (NW China)[J]. Energies, 16: 5586. doi: 10.3390/en16155586
[3] Chen S P, Tian Z J, Xu S D, et al. 2024. Two structural types of shear fracture belts related to wrenches[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 43(1): 13−19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Dou F P, Li J H, Peng M. 2024. Tectonic deformation mechanism of the fault zone in the northwest margin of Junggar Basin: Based on physical experimental simulation[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 43(4): 527−535 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Feng L J, Jiang Y Q, Liu F, et al. 2021. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of oolitic shoal reservoir in Feixianguan Formation in the southern part of Kaijiang−Liangping trough, eastern Sichan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 42(10): 1287−1298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fossen H. 2010. Structural Geology[M]. Cambridge University Press.
[7] Harding T P. 1985. Seismic characteristics and identification of negative flower structures positive flower structures and positive structural inversion[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 69(4): 1016−1058.
[8] Harding T P. 1990. Identification of wrench fault using subsurface structural data: criteria and pitfalls[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 74(10): 1090−1609.
[9] He D F, Li D S, Zhang G W, et al. 2011. Formation and evolution of multi−cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 46(3): 589−606 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Jia C Z, Ma D B, Yuan J Y, et al. 2021. Structural characteristics, formation & evolution and genetic mechanisms of strike–slip faults in the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(8): 81−91(in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Jiao F Z, Yang Y, Ran Q, et al. 2021. Distribution and gas exploration of the strike–slip faults in the central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(8): 59−68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Li H K, Li Z Q, Long W, et al. 2019. Vertical configuration of Sichuan Basin and its superimposed characteristics of the prototype basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 46(3): 257−267 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Liang D X, Hu S Y, Gu Z D, et al. 2015. Formation and evolution process of Kaijiang paleohigh in the Sichuan Basin and its controlling effects on gas pool formation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, (9): 35−41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Liu S G, Yang Y, Deng B, et al. 2021. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China[J]. Earth−science Review, 213: 103470. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103470
[15] Ma D B, Wang Z C, Duan S F, et al. 2018. Strike-slip faults and their significance for hydrocarbon accumulation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(5): 795-805.
[16] Ma X H, Yang Y, Wen Long, et al. 2019. Distribution and exploration direction of medium−and large−sized marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(1): 1−13 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)30001-1
[17] Ma Y S, Cai X Y, Yun L, et al. 2022. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra−deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 49(1): 1−17 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(22)60001-6
[18] Sylvester A G. 1988. Strike−slip faults[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 11(100): 1666−1703.
[19] Tang Q S, Tang S H, Luo B, et al. 2022. Seismic description of deep strike−slip fault damage zone by Steerable Pyramid Method in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Energies, 15(21): 8131. doi: 10.3390/en15218131
[20] Tang Q S, Liu J W, Wu G H, et al. 2024. Seismic description and application of deep carbonate strike−slip fault−controlled “sweet spots” reservoirs in the Anyue Gas Field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 35(11): 2053−2063 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Wang Q H, Yang H J, Wang R J, et al. 2021. Discovery and exploration technology of fault−controlled large oil and gas fields of ultra−deep formation in strike slip fault zone in Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(4): 58−71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wang X Z, Li B, Wen L, et al. 2021. Characteristics of “Guangyuan−Wangcang” trough during late Middle Permian and its petroleum geological significance in northern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(3): 562−574 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Wen L, Zhang Q, Yang Y, et al. 2012. Factors controlling reef−bank reservoirs in the Changxing−Feixianguan formation in the Sichuan Basin and their play fairways[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 32(1): 39−44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Wu G H, Pang X Q, Li Q M, et al. 2016. The structural characteristics of carbonate recks and their effects on hydrocarbon exploration in Craton Basin: A case study of the Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 131−150 (in Chinese).
[25] Wu G H, Zou Y, Xu W, et al. 2023. The strike−slip faults distribution and implications on the Sinian gas exploration in the northern slope of the central paleo−uplift in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 43(77): 26−34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Xia Y P, Liu W H, Xu L G, et al. 2007. Identification of strike−slip fault and its petroleum geology significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 12(1): 17−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Xiong C, Cai Z X, Ma B S, et al. 2024. Controls of strike−slip faults on condensate gas accumulation and enrichment in the Ordovician carbonate reservoirs of the central Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 263: 106019. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2024.106019
[28] Yang H J, Wu G H, Han J F, et al. 2022. The strike−slip fault analysis in the Tarim Basin[M]. Petroleum Industry Press: 38−54 (in Chinese).
[29] Yang Y, Zhong Y, Li L J. 2021. Distribution and gensis of Permian−Triassic reef−shoal combination around Kaijiang−Liangping trough in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 48(6): 683−690 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Zhang J Y, Zhou J G, HAO Y, et al. 2011. A Sedimentary model of Changxing and Feixianguan reservoirs around Kaijiang−Liangping Trough in Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Original Petroleum Geology, 16(3): 45−54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Zou C N, Du J H, Xu C C, et al. 2014. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian−Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(3): 278−293 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Zou Y, Wu G H, Song Y T, et al. 2024. Pitfalls in seismic identification of strike−slip faults in intracraton basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 63(4): 869−880 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 陈书平, 田作基, 徐世东, 等. 2024. 两种结构类型的走滑相关剪断裂带[J]. 地质通报, 43(1): 13−19. doi: 10.12097/gbc.2023.04.005
[34] 豆方鹏, 李江海, 彭谋. 2024. 准噶尔盆地西北缘断裂带构造变形机制——基于物理实验模拟研究[J]. 地质通报, 43(4): 527−535.
[35] 冯林杰, 蒋裕强, 刘菲, 等. 2021. 川东地区开江−梁平海槽南段飞仙关组鲕滩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油学报, 42(10): 1287−1298. doi: 10.7623/syxb202110003
[36] 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等. 2011. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 46(3): 589−606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001
[37] 贾承造, 马德波, 袁敬一, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造特征、形成演化与成因机制[J]. 天然气工业, 41(8): 81−91. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.08.008
[38] 焦方正, 杨雨, 冉崎, 等. 2021. 四川盆地中部地区走滑断层的分布与天然气勘探[J]. 天然气工业, 41(8): 59−68.
[39] 李洪奎, 李忠权, 龙伟, 等. 2019. 四川盆地纵向结构及原型盆地叠合特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 46(3): 257−267.
[40] 梁东星, 胡素云, 谷志东, 等. 2015. 四川盆地开江古隆起形成演化及其对天然气成藏的控制作用[J]. 天然气工业, (9): 35−41.
[41] 马德波, 汪泽成, 段书府, 等. 2018. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪地区走滑断层构造特征与天然气成藏意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 45(5): 795-805.
[42] 马新华, 杨雨, 文龙, 等. 2019. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 46(1): 1−13.
[43] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 49(1): 1−17.
[44] 唐青松, 刘嘉伟, 邬光辉, 等. 2024. 四川盆地安岳气田深层走滑断控“甜点”储层地震刻画与成效[J]. 天然气地球科学, 35(11): 2053−2063.
[45] 王清华, 杨海军, 汪如军, 等. 2021. 塔里木盆地超深层走滑断裂断控大油气田的勘探发现与技术创新[J]. 中国石油勘探, 26(4): 58−71.
[46] 王兴志, 李博, 文龙, 等. 2021. 四川盆地北部中二叠世晚期 “广元−旺苍” 海槽特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 48(3): 562−574.
[47] 文龙, 张奇, 杨雨, 等. 2012. 四川盆地长兴组−飞仙关组礁、滩分布的控制因素及有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业, 32(1): 39−44.
[48] 邬光辉, 庞雄奇, 李启明, 等. 2016. 克拉通碳酸盐岩构造与油气——以塔里木盆地为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 131−150.
[49] 邬光辉, 邹禺, 徐 伟, 等. 2023. 四川盆地川中古隆起北斜坡震旦系走滑断裂分布及其勘探意义[J]. 天然气工业, 43(77): 26−34.
[50] 夏义平, 刘万辉, 徐礼贵, 等. 2007. 走滑断层的识别标志及其石油地质意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 12(1): 17−23.
[51] 杨海军, 邬光辉, 韩剑发, 等. 2022. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造解析[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 38−54.
[52] 杨雨, 钟原, 李林娟. 2021. 开江-梁平海槽周缘二叠系—三叠系礁滩组合分布与成因[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 48(6): 683−690.
[53] 张建勇, 周进高, 郝毅, 等. 2011. 四川盆地环开江−梁平海槽长兴组−飞仙关组沉积模式[J]. 海相油气地质, 16(3): 45−54.
[54] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 2014. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 41(3): 278−293.
[55] 邹禺, 邬光辉, 宋玉婷, 等. 2024. 克拉通内盆地走滑断层地震判识的若干陷阱[J]. 石油物探, 63(4): 869−880.
-




 下载:
下载: