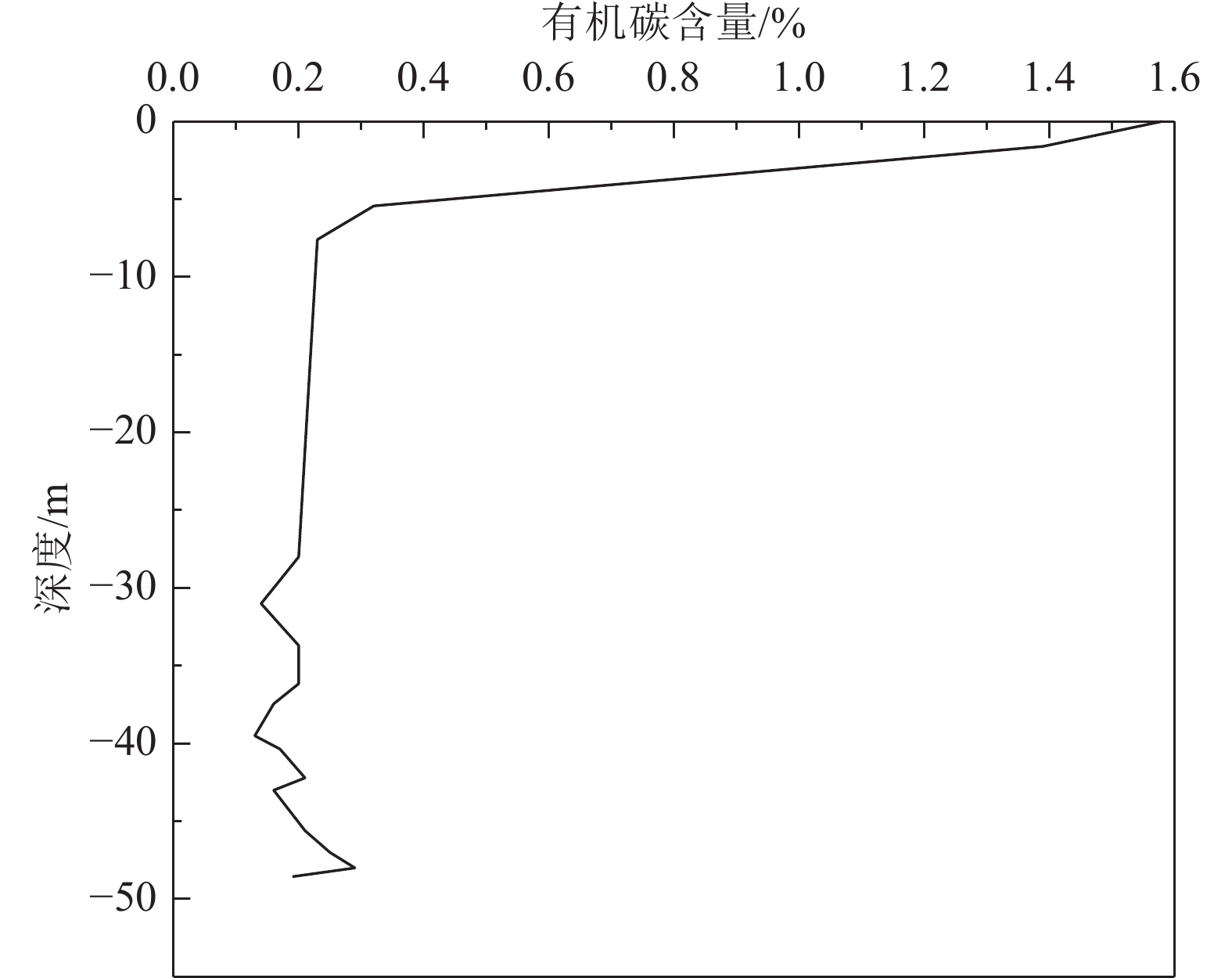
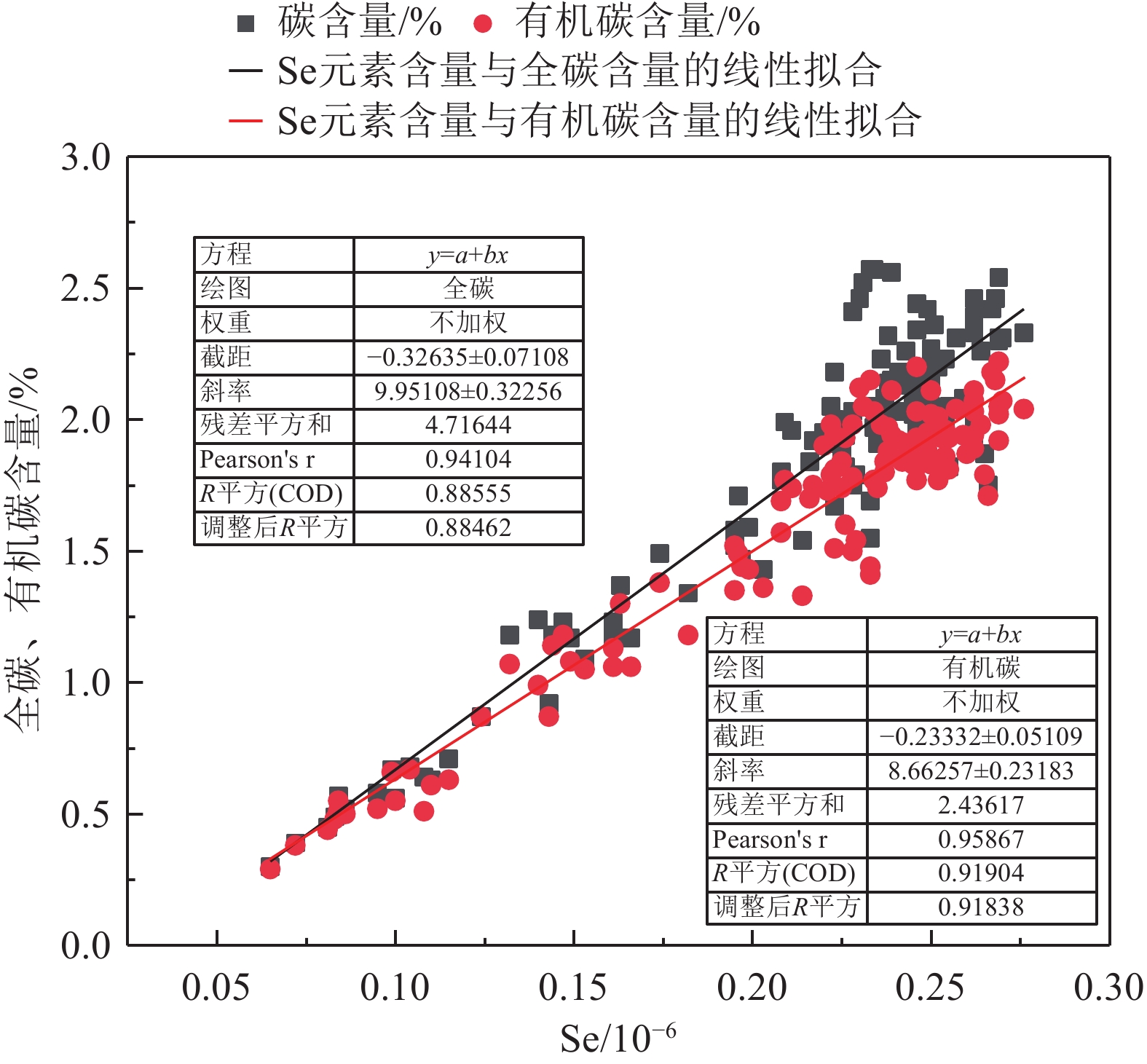
The spatial changes of carbon storage and carbon fixation potential in five counties of Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
黑龙江省齐齐哈尔地区的拜泉、依安、富裕、克山和克东五县市是中国著名的黑土之乡,也是中国最重要的粮食产区。近年来,该区域有关有机碳和全碳密度及储量的研究较少。依托松嫩平原齐齐哈尔地区黑土地地表基质调查的土壤有机碳及全碳测试结果对研究区平原地区地表20 cm以浅的有机碳和全碳储量、密度、空间分布及固碳潜力进行研究,并使用主成分分析法对影响有机碳储量变化的因素进行分析。通过研究得出,黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市五县全碳储量为82.17 Mt,有机碳储量为67.93 Mt,属较高水平。地统计分析结果指示,地区内有机碳储量具有一定空间自相关性,其主控因素主要为嫩江的水蚀作用,其次为土壤类型和土地利用类型的变化。研究区表现出了较强的碳汇效应,表层土壤有机碳的固碳潜力为20.10 Mt,属于较高水平。研究结果表明,稳定良好的土壤环境有利于碳的富集和汇聚,N、S、Se、P等元素的富集对固碳具有极高价值,K2O、Na2O等无机盐的增加和土壤沙化等生态脆弱现象对碳储和碳汇影响较大。
Abstract:The five counties and cities of Baiquan, Yi'an, Fuyu, Keshan, and Kedong in Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province, are famous as the hometown of black soil and also the most important grain producing areas in China. In recent years, there has been relatively little research on the density and storage of organic carbon (Corg) and total carbon (TC) in this region. This article relies on the soil organic carbon and soil total carbon test results obtained from the investigation of the black soil ground substrate in the Qiqihar area of the Songnen Plain to study the Corg and TC reserves, carbon density, spatial distribution, and carbon sequestration potential in the plain areas in the study area of Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province, with a depth of less than 20 cm, and then use principal component analysis to analyze the factors affecting changes in organic carbon storage. It is found that the TC reserves in five counties of Qiqihar City, Heilongjiang Province is 82.17 Mt, and the Corg reserves is 67.93 Mt, which are at a relatively high level. The results of geostatistical analysis indicate that the Corg reserves in the region have a certain spatial autocorrelation, and the main controlling factor is the water erosion of the Nenjiang River, followed by changes in soil type and land use type. It exhibits a strong carbon sink effect, with a carbon sequestration potential of 20.10 Mt for surface soil Corg, which is at a relatively high level. As a result, it has been found that a stable and good soil environment is conducive to the enrichment and aggregation of carbon. The enrichment of elements such as N, S, Se, and P has extremely high value for carbon sequestration. The increase of inorganic salts such as K2O and Na2O and ecological fragile phenomena such as soil desertification have a significant impact on carbon storage and carbon sink phenomena.
-
Key words:
- organic carbon /
- carbon sequestration potential /
- carbon density /
- spatial distribution /
- carbon storage /
- Qiqihar
-

-
表 1 研究区Corg和TC密度
Table 1. List of organic carbon and total carbon density in the study area
参数指标 Corg密度/(kg·m−2) TC密度/(kg·m−2) 平均值 4.111 4.973 含量范围 1.956~6.438 3.038~7.250 方差 0.5882 0.555 标准差 0.764 1.000 变异系数 0.186 0.149 表 2 各县TC和Corg储量分布情况
Table 2. Distribution of total carbon and organic carbon storage in each county
县域 土壤TC
储量/MtTC占总和
百分比/%土壤Corg
储量/MtCorg占总和
百分比/%依安县 17.177 20.90 13.897 20.457 富裕县 20.793 25.30 14.04 20.67 拜泉县 17.166 20.89 15.124 22.26 克山县 15.838 19.27 14.590 21.48 克东县 11.199 13.63 10.281 15.13 总和 82.17 100.00 67.93 100.00 表 3 不同土壤类型中TC和Corg储量分布情况
Table 3. Distribution of total carbon and organic carbon storage in different soil types
土壤发生分类 面积/km2 面积占比/% 土壤TC储量/Mt TC密度/(kg·m−2) 土壤Corg储量/Mt Corg密度/(kg·m−2) 草甸土 6163.053 37.34% 29.822 4.839 24.754 4.016 暗棕壤 438.737 2.66% 2.113 4.816 1.917 4.370 黑土 5283.696 32.01% 26.836 5.079 24.474 4.632 黑钙土 3311.863 20.06% 16.878 5.096 12.111 3.657 风沙土 25.512 0.15% 0.099 3.871 0.071 2.785 其它 1232.006 7.46% 5.177 4.202 3.706 3.008 新积土 89.514 0.54% 0.400 4.473 0.357 3.983 沼泽土 163.359 0.99% 0.847 5.185 0.543 3.323 表 4 不同土地利用类型中TC和Corg储量分布情况
Table 4. Distribution of total carbon and organic carbon storage in different land use types
土地利用类型 面积/km2 面积占比/% 土壤TC储量/Mt TC密度/(kg·m−2) 土壤Corg储量/Mt Corg密度/(kg·m−2) 草地 1710.940 10.33% 7.757 4.534 6.265 3.661 未利用地 39.758 0.24% 0.238 5.982 0.169 4.248 耕地 13209.100 79.75% 66.277 5.018 55.192 4.178 林地 333.237 2.01% 1.531 4.593 1.346 4.039 建筑用地 813.624 4.91% 4.006 4.923 3.365 4.136 湿地 365.743 2.21% 1.979 5.412 1.297 3.547 表 5 土壤因子分析相关结果
Table 5. Results of soil factor analysis
因子 总计 方差贡献率 方差累计贡献率 因子1 6.228 41.520 41.520 因子2 3.633 24.221 65.741 因子3 2.337 15.581 81.322 表 6 因子分析载荷系数
Table 6. Factor analysis load factor table
指标 F1 F2 F3 Corg/N 0.965 −0.041 0.073 Corg 0.959 −0.009 0.123 TC 0.854 0.444 0.038 P 0.818 −0.107 0.132 N 0.732 0.598 0.066 Se 0.618 −0.281 0.381 CaO −0.057 0.968 −0.051 IC 0.1 0.923 −0.134 pH −0.095 0.791 −0.035 SiO2 −0.175 −0.651 −0.609 Al2O3 0.132 −0.255 0.923 Fe2O3 0.164 −0.19 0.892 MgO 0.096 0.458 0.805 K2O −0.258 −0.165 −0.126 Na2O −0.275 0.02 −0.287 表 7 研究区不同土地利用类型土壤固碳潜力
Table 7. Soil carbon sequestration potentials in the plain area of study area
土壤类型 固碳潜力/Mt 草甸土 8.469 暗棕壤 0.323 黑土 5.276 黑钙土 6.594 风沙土 0.0308 新积土 0.080 沼泽土 0.120 其他 1.246 总和 20.997 -
[1] Cao K J, Su H L. 2022. Research on the problems and countermeasures of black soil protection in Qiqihar City[J]. Heilongjiang Grain, (11): 37−39(in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Cheng K, Pan G X, Tian Y G, et al. 2009. Changes in topsoil organic carbon of China's cropland evidenced from the national soil monitoring network[J]. Journal of Agro−Environment Science, 28(12): 2476−2481 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] China Geological Survey. 2014. DZ/T 0258—2014. Specification of multi-purpose regional geochemical survey (1∶250000)[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press (in Chinese).
[4] Dai J R, Hou J H, Yang E X, et al. 2013. Study on soil organic carbon storage and spatiotemporal changes in Shandong Province[C]//Youth Working Committee of the Geological Society of China. Proceedings of the First National Youth Geological Congress(in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Dawson J J C, Smith P. 2007. Carbon losses from soil and its con−sequences for land−usemanagement[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 382(2): 165−190.
[6] Fan Y Q, Zhou G M, Shi Y J, et al. 2012. Relationship of slope aspect and position on biomass and carbon storage in a Phyllostachys edulis stand[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 29(3): 4−10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Guo S P. 2011. Analysis on carbon stock and potential carbon sequestration in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Forest Engineering, 27(3): 9−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Jiang L Q, Zang S Y, Zhang L J, et al. 2017. Temporal and spatial variations of organic carbon and evaluation of carbon sequestration potential in the agricultural topsoil of the Songnen Plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(21): 7068−7081 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Jin F, Yang H, Zhao Q G. 2000. Research progress on soil organic carbon storage and influencing factors[J]. Soils, (1): 12−18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Liu G D, Li Y, Zhang L, et al. 2014. The estimation of soil carbon sequestration potential in southern Songnen plain[J]. Geology in China, 41(2): 658−664 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Liu G Q, Zhang M K. 2020. Effects of land−use patterns and parent material types on accumulation and stability of soil organic carbon in Jinqu Basin[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 32(10): 29−34(in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Ostle N, Ineson P, Benham D, et al. 2000. Carbon assimilation and turnover in grassland vegetation using an in situ 13CO2 pulse labeling system[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrometry, 14(15): 1345−1350. doi: 10.1002/1097-0231(20000815)14:15<1345::AID-RCM22>3.0.CO;2-B
[13] Pan G X, Cao J H, Zhou Y C, et al. 2000. Soil carbon and its significance in carbon cycling of earth surface system[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 20(4): 325−335(in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Pan G X, Li L Q, Zhang X H, et al. 2003. Soil organic carbon storage of China and the sequestration dynamics in agricultural lands[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, (4): 609−618(in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Pan G X, Tao Y X, Teng Y Z, et al. 1998. Influence of pedochemical field on epikarstification in subtropical humid region: Field monitoring and laboratory experiment[J]. Acta Carsologica, 27(11): 175−186.
[16] Pan G X. 1999. Study on Carbon Reservoir in Soils of China[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, (5): 330−332(in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Qin Z L, Yang X M, Song Z L, et al. 2020. Effects of parent materials and land uses on soil organic carbon fractions[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 51(3): 621−629(in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Ren C Y, Zhang C H, Wang Z M, et al. 2013. Organic carbon storage and sequestration potential in cropland surface soils of Songnen plain maize belt[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 28(4): 598−607(in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Sun Y X, Li J F, Hu W H, et al. 2023. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in chernozem soil under straw returning[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, (12): 1−14(in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Swaran H, Berg E V D, Reich P, et al. 1993. Organic carbon in soils of the world[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 57(1): 192−194. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700010034x
[21] Tai J C. 2012. Vartiation of soil organic carbon and the fractions with land use and soil origin of croplands[D]. Ph. D. Dissertation, Nanjing Agricultural University(in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wang C Y, Li Y C, Yu C G, et al. 2021. Compositions and variation rule of soil carbon pool in the coastal area of western Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 30(2): 173−185(in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Wang S L, Hu T R, Zhao Y S, et al. 2004. The causes, types, distribution, and control technologies of desertification land in the Nenjiang sandy land of Qiqihar City[J]. Forestry Science & Technology, (5): 15−17(in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Xi X H, Yang Z F, Liao Q L, et al. 2010. Study on soil carbon storage in typical regions of China[J]. Quaternary Research, 30(3): 573−583(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Xi X H, Yang Z F, Xia X Q, et al. 2009. Calculation techniques for soil carbon storage of China based on multi−purpose geochemical survey[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(1): 194−205(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Xia B W, Pang L, Chang L, et al. 2023. Effects of different mulching methods on soil nitrogen content and distribution of potato in semi−arid rain−fed areas[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 58(1): 55−62(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Xing S H, Wu J J, Lin J L. 1989. Studies on the genesis and classification of paddy soils Ⅱ. The eluviation and accumulation of organic matter and its relation to the eluviation and illuviation of iron and manganese in percogenic and periodically waterlogged paddy soils[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, (2): 212−217(in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Xue L, Xue Y, Lie G W, et al. 2012. Soil organic carbon storage on different slope positions in Cunninghamia Lanceolata stands[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(6): 49−52(in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Zhang C H, Wang Z M, Ren C Y, et al. 2010. Spatial and temporal patterns of soil organic carbon in maize belt farmland in Songnen Plain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 26(S1): 300−307 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Zhang M, Chen G G, Gao C, et al. 2014. Geochemical characteristics of macro elements in soils in the region covered by multi−purpose geochemical survey in eastern China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 44(3): 995−1002(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Zhang X Z, Zhao X L, Li H L, et al. 2011. Research on organic carbon storage and sequestration mechanism of soils in the Hebei Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(6): 41−55(in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Zheng J B. 2007. Effect of land use types on the fixation of soil organic carbon[D]. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University(in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 曹克晶, 苏海龙. 2022. 齐齐哈尔市黑土地保护存在问题及对策研究[J]. 黑龙江粮食, (11): 37−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6019.2022.11.014
[34] 程琨, 潘根兴, 田有国, 等. 2009. 中国农田表土有机碳含量变化特征——基于国家耕地土壤监测数据[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(12): 2476−2481. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.12.006
[35] 代杰瑞, 侯建华, 杨恩秀, 等. 2013. 山东省土壤有机碳储量及时空变化研究[C]//中国地质学会青年工作委员会. 第一届全国青年地质大会论文集.
[36] 范叶青, 周国模, 施拥军, 等. 2012. 坡向坡位对毛竹林生物量与碳储量的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 29(3): 4−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2012.03.001
[37] 郭树平. 2011. 黑龙江省碳储量及碳汇潜力分析[J]. 森林工程, 27(3): 9−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2011.03.003
[38] 姜蓝齐, 臧淑英, 张丽娟, 等. 2017. 松嫩平原农田土壤有机碳变化及固碳潜力估算[J]. 生态学报, 37(21): 7068−7081.
[39] 金峰, 杨浩, 赵其国. 2000. 土壤有机碳储量及影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, (1): 12−18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2000.01.003
[40] 刘国栋, 李瑛, 张立, 等. 2014. 松嫩平原耕层土壤固碳潜力估算[J]. 中国地质, 41(2): 658−664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.026
[41] 刘国群, 章明奎. 2020. 利用方式与成土母质对金衢盆地土壤有机碳积累及其稳定性影响的研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 32(10): 29−34.
[42] 潘根兴. 1999. 中国土壤有机碳和无机碳库量研究[J]. 科技通报, (5): 330−332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.1999.05.002
[43] 潘根兴, 曹建华, 周运超, 等. 2000. 土壤碳及其在地球表层系统碳循环中的意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 20(4): 325−335. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.04.003
[44] 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 张旭辉, 等. 2003. 中国土壤有机碳库量与农业土壤碳固定动态的若干问题[J]. 地球科学进展, (4): 609−618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.04.019
[45] 覃智莲, 杨孝民, 宋照亮, 等. 2020. 成土母质和土地利用方式对土壤有机碳化学组成的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 51(3): 621−629.
[46] 任春颖, 张春华, 王宗明, 等. 2013. 松嫩平原玉米带农田表层土壤有机碳储量和固碳潜力研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 28(4): 598−607. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2013.04.006
[47] 孙轶萱, 李建峰, 胡文河, 等. 2023. 秸秆还田方式下黑钙土土壤碳氮磷钾化学计量特征研究[J]. 玉米科学, (12): 1−14.
[48] 邰继承. 2012. 不同土地利用和起源农田土壤有机碳及其组分含量变化[D]. 南京农业大学博士学位论文.
[49] 王诚煜, 李玉超, 于成广, 等. 2021. 辽宁西部沿海地区土壤碳库构成及变化规律研究[J]. 地质与资源, 30(2): 173−185.
[50] 王树力, 胡天然, 赵雨森, 等. 2004. 齐齐哈尔市嫩江沙地沙化土地的成因、类型、分布及治理技术[J]. 林业科技, (5): 15−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9499.2004.05.005
[51] 奚小环, 杨忠芳, 夏学齐, 等. 2009. 基于多目标区域地球化学调查的中国土壤碳储量计算方法研究[J]. 地学前缘, 16(1): 194−205. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.01.022
[52] 奚小环, 杨忠芳, 廖启林, 等. 2010. 中国典型地区土壤碳储量研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 30(3): 573−583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.03.16
[53] 夏博文, 逄蕾, 常磊, 等. 2023. 半干旱雨养区不同覆盖方式对马铃薯土壤氮含量及分布的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 58(1): 55−62.
[54] 邢世和, 吴金奖, 林景亮. 1989. 水稻土发生分类的研究Ⅱ两种水型水稻土中有机质淋溶累积的特点及其与铁锰淋淀的关系[J]. 福建农学院学报, (2): 212−217.
[55] 薛立, 薛晔, 列淦文, 等. 2012. 不同坡位杉木林土壤碳储量研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 32(6): 49−52.
[56] 张春华, 王宗明, 任春颖, 等. 2010. 松嫩平原玉米带农田土壤有机碳时空格局[J]. 农业工程学报, 26(S1): 300−307.
[57] 张明, 陈国光, 高超, 等. 2014. 华东多目标区域地球化学调查区土壤常量元素地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(3): 995−1002.
[58] 张秀芝, 赵相雷, 李宏亮, 等. 2011. 河北平原土壤有机碳储量及固碳机制研究[J]. 地学前缘, 18(6): 41−55.
[59] 郑杰炳. 2007. 土地利用方式对土壤有机碳固定影响研究[D]. 西南大学硕士学位论文.
[60] 中国地质调查局. 2014. DZ/T 0258—2014, 多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250 000)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
-




 下载:
下载: