Crustal structure and formation mechanism of the fold-and-thrust belt in and around Wuling mountains region
-
摘要:
武陵山褶皱−冲断构造带位于扬子块体东缘,是华南地区最典型的由陆内挤压作用形成的重要线性构造带,了解其地壳结构与变形机制对于进一步深化认识该地区的构造演化过程至关重要。本文在综合多种地球物理成像、构造地质分析和数值、物理模拟研究的基础上,系统分析了该区的地壳深部结构、变形过程及浅表构造响应。结果表明:武陵山地区强重力梯度带的形成主要受控于地壳与岩石圈尺度的结构和物性差异;新元古代扬子和华夏块体的拼合过程造成了目前的地壳结构,形成莫霍界面的起伏、错断、叠置等变形特征;低速滑脱层和先存的区域断裂一起造成了上、下地壳的变形解耦,并在该区的构造演化中发挥了关键控制作用;晚中生代古太平洋板块俯冲产生的远场应力可能是造成该区褶皱−冲断变形的主要动力。本研究可为华南地区陆内变形机制研究提供新的启示,并有助于为其他地区开展类似研究提供借鉴。
Abstract:The Wuling fold−and−thrust belt, located along the eastern margin of the Yangtze block, is a significant linear tectonic belt shaped by the intra−continental compressional forces in South China. Understanding its formation mechanisms is crucial for advancing broader tectonic evolution of the region. This study examines the deep crustal architecture, deformation processes, and surface tectonics within the Wuling fold−and−thrust belt by integrating high−resolution geophysical imaging, detailed tectonic analysis, and recent numerical and analog modeling. The key findings are as follows: ① The pronounced gravity gradient belt across the Wuling Mountains is primarily controlled by structural and compositional variations at the crustal and lithospheric levels; ② The Neoproterozoic collision and subsequent amalgamation of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks shaped the crustal structure, leading to the Moho undulation, break−off, imbrication, and other related features; ③ A low−velocity décollement layer, in combination with pre−existing regional faults, facilitated crustal decoupling and played a critical role in the structural evolution of the belt; ④ Far−field stresses from Paleo−Pacific plate subduction during the Late Mesozoic were the primary drivers of the observed fold−and−thrust deformation. These findings may offer new insights into knowledge on the intra−continental deformation mechanisms in South China and also contribute to refining tectonic models in other similar regions.
-

-
图 1 武陵山褶皱-冲断带及邻区地质构造简图(红色虚线范围为研究区武陵山褶皱−冲断带;褶皱信息据张岳桥等,2012;地质图数据据Steinshouer et al., 1999)
Figure 1.
图 3 A-A′构造廊带辖区重力异常与地形和构造特征(廊带位置见图2–b;据Yan et al., 2003; 胡召齐等, 2009; 吴航等,2019修改)
Figure 3.
图 4 穿过武陵山褶皱−冲断带的深反射地震偏移叠加剖面(a)及对本地震剖面的构造解译(b)(据Li et al., 2018修改,测线位置见图2)
Figure 4.
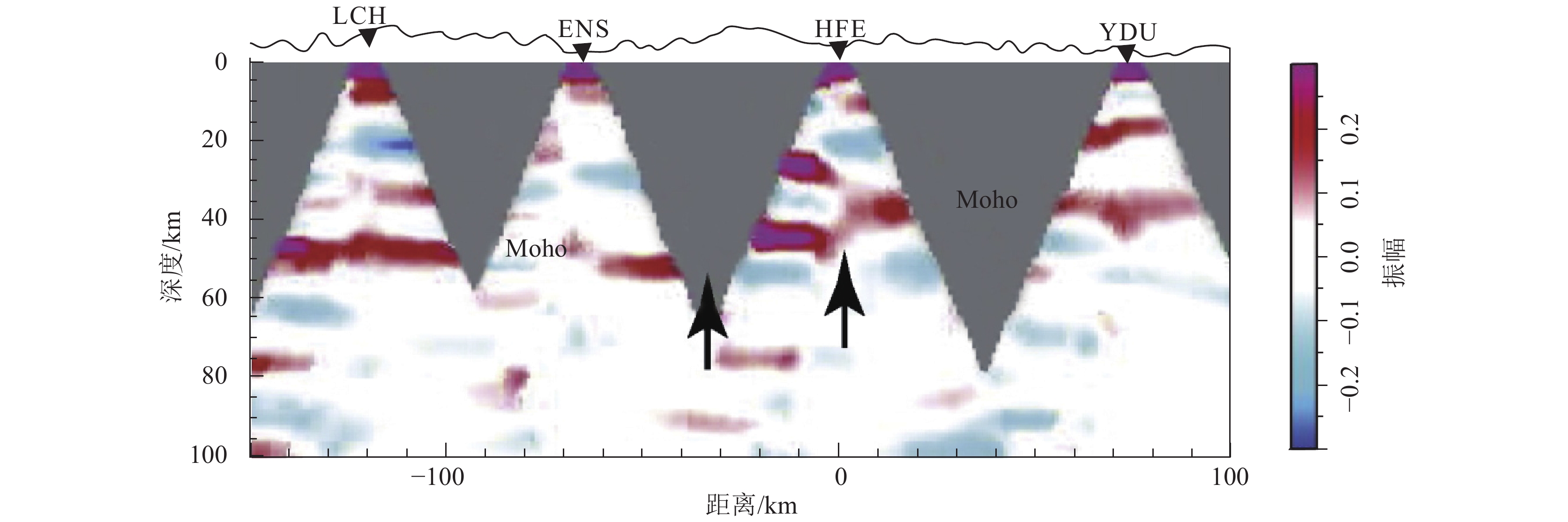
图 6 跨武陵山褶皱-冲断带剖面的接收函数共转换点叠加成像(据Huang et al., 2014修改;剖面位置见图2-b,LCH、ENS、HFE、YDU为地震台站名称)
Figure 6.
图 7 跨武陵山褶皱−冲断带的S波速度结构剖面(速度模型数据据Zhang et al., 2024;剖面中黑色和红色线条为根据深反射地震偏移叠加剖面解译的深部地层与构造起伏形态,据Li et al., 2018修改;断裂名称缩写同图1)
Figure 7.
图 8 武陵山褶皱−冲断带形成过程的物理模拟(a)和离散元数值模拟(b)(据Feng et al., 2023修改;图中不同颜色表示模拟中设计的不同层位信息,图a中红色线条表示断裂;断裂名称缩写同图1)
Figure 8.
-
[1] Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, et al. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad−band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 169: 1239−1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
[2] Cawood P A, Wang Y J, Xu Y J, et al. 2013. Locating South China in Rodinia and Gondwana: A fragment of greater India lithosphere?[J]. Geology, 41(8): 903−906. doi: 10.1130/G34395.1
[3] Charvet J, Shu L S, Shi Y S, et al. 1996. The building of south China: collision of Yangzi and Cathaysia blocks, problems and tentative answers[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 13: 223−235. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(96)00029-3
[4] Chu Y, Lin W, Faure M, et al. 2012. Phanerozoic tectonothermal events of the Xuefengshan Belt, central South China: Implications from U−Pb age and Lu−Hf determinations of granites[J]. Lithos, 150: 243−255. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.005
[5] Coblentz D F, Richardson R M. 1995. Statistical trends in the intraplate stress field[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(10): 20245−20255.
[6] Cui S Q. 1999. On global Meso Cenozoic intracontinental orogenesis and orogenic belts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 4: 283−293(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Deng Y F, Xu Y G, Chen Y. 2021. Formation mechanism of the north–south gravity lineament in eastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 818: 229074. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.229074
[8] Dewey J F, Bird J M. 1970. Mountain belts and the new global tectonics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(14): 2625−2647. doi: 10.1029/JB075i014p02625
[9] Deng Y F, Li S L, Fan W M, et al. 2011. Crustal structure beneath South China revealed by deep seismic soundings and its dynamics implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(10): 2560−2574(in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Ding D G, Liu G X, Lü J X, et al. 2007. Progressive deformation of Middle Paleozoic marine basins in the Yangtze plate, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(9): 1178−1188(in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Dong, S W, Zhang Y Q, Gao R, et al. 2015. A possible buried Paleoproterozoic collisional orogen beneath central South China: Evidence from seismic−reflection profiling[J]. Precambrian Research, 264: 1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.04.003
[12] Echavarria L, Hernández R, Allmendinger R, et al. 2003. Subandean thrust and fold belt of northwestern Argentina: Geometry and timing of the Andean evolution[J]. AAPG Bull., 87: 965−985. doi: 10.1306/01200300196
[13] Feng C M, Liu J, Song L J. 2008. Formation mechanism of the tectonic deformation belt and the prognosis of favorable oil and gas exploration areas in the Middle and Upper Yangtze valley[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(2): 199−204(in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Feng Q Q, Qiu N S, Wu H, et al. 2023. Thermo−kinematic constraints on restoration of the eastern Sichuan fold−and−thrust belt, South China[J]. Tectonics, 42(9): e2022TC007630. doi: 10.1029/2022TC007630
[15] Feng X Y, Meng X G, Shao Z G, et al. 2003. A preliminary discussion on features and dynamics of sequence deformation in South China and neighboring areas[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 24(2): 115−120(in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Gao R, Chen C, Wang H Y, et al. 2016. Sinoprobe deep reflection profile reveals a Neo−Proterozoic subduction zone beneath Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 454: 86−91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.08.030
[17] Guan S W, Stockmeyer J M, Shaw J H, et al. 2016. Structural inversion, imbricate wedging, and out−of−sequence thrusting in the southern Junggar foldand−thrust belt, northern Tian Shan, China[J]. AAPG Bull., 100: 1443−1468. doi: 10.1306/04041615023
[18] Harrison J C. 1995. Tectonics and kinematics of a foreland folded belt influenced by salt, arctic Canada, salt tectonics: A global perspective[J]. AAPG Memoir, (65): 379−412.
[19] Hillis R R, Sandiford M, Reynolds S D, et al. 2008. Present−day stresses, seismicity and Neogene−to−Recent tectonics of Australia's 'passive' margins: intraplate deformation controlled by plate boundary forces[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 306(1): 71−90. doi: 10.1144/SP306.3
[20] He W G, Zhou J X, Yuan K. 2018. Deformation evolution of Eastern Sichuan−Xuefeng fold−thrust belt in South China: Insights from analogue modelling[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 109: 74−85. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2018.01.002
[21] He W G, Zhou J X. 2018. Analogue modeling of feature and formation mechanism of horsetail−shaped fold belt in Southeast Sichuan Basin, South China[J]. Earth Science, 43(6): 2133−2148(in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] He W G. 2020. Influence of mechanical stratigraphy on the deformation evolution of fold−thrust belts: Insights from the analogue modeling of eastern Sichuan−Western Hunan and Hubei, South China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 31(4): 795−807. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1281-2
[23] Hu R Z, Bi X W, Zhou M F, et al. 2008. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary[J]. Economic Geology, 103: 583−598. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.103.3.583
[24] Hu S Q, Zhu G, Liu G S, et al. 2009. The folding time of the eastern Sichuan Jura−type fold belt: Evidence from Unconformity[J]. Geological Review, 55(1): 32−42(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Hsü K J, Sun S, Li J L, et al. 1988. Mesozoic over thrust tectonics in south China[J]. Geology, 16: 418−421.
[26] Huang R, Zhu L P, Xu Y X. 2014. Crustal structure of Hubei Province of China from teleseismic receiver functions: Evidence for lower crustal delamination[J]. Tectonophysics, 636: 286−292. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.09.001
[27] Huang G M, Zhang Z, Zhang H, et al. 2020. Development of contrasting folding styles in the western Yangtze block, South China: Insights from numerical modeling[J]. Tectonophysics, 792: 228579. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2020.228579
[28] Jiang C X, Yang Y J, Zheng Y. 2016. Crustal structure in the junction of Qinling orogen, Yangtze Craton and Tibetan Plateau: implications for the formation of the Dabashan orocline and the growth of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 205(3): 1670−1681. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw096
[29] Johnston S T. 2008. The Cordilleran ribbon continent of North America[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 36(1): 495−530.
[30] Langston C A. 1979. Structure under Mount Rainier, Washington, inferred from teleseismic body waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 84(B9): 4749−4762. doi: 10.1029/JB084iB09p04749
[31] Li J, Zhao G, Johnston S T, et al. 2017. Permo−Triassic structural evolution of the Shiwandashan and Youjiang structural belts, South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 100: 24−44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.05.004
[32] Li J H, Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, et al. 2014. Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China: apreliminary synthesis[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 134: 98−136. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.008
[33] Li J H, Dong S W, Cawood P A, et al. 2018. An Andean−type retro−arc foreland system beneath northwest South China revealed by SINOPROBE profiling[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 490: 170−179. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.03.008
[34] Liu S Z. 1995. My Opinion of structural pattern of thin−skinned structure in East Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, (4): 264−267(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Li S Z, Li X Y, Zhao S J, et al. 2016. Global Early Paleozoic orogens(Ⅲ): Intracontinental orogen in South China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 46(4): 1005−1025(in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Li S Z, Suo Y H, Li X Y, et al. 2018. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono−magmatic response in the East Asian ocean−continent connection zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(16): 1550−1593(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/N972017-01113
[37] Li W, Chen Y, Yuan X, et al. 2022. Intracontinental deformation of the Tianshan Orogen in response to India−Asia collision[J]. Nature Communication, 13: 3738. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30795-6
[38] Li Y K, Gao W J, Han J, et al. 2019. Geophysical evidence for thrusting of crustal materials from orogenic belts over both sides of the Yangtze Block and its geological significance[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 49(4): 687−705(in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Li Y K, Gao J W, Han J, et al. 2019. Geophysical evidence for thrusting of crustal materials from orogenic belts over both sides of the Yangtze Block and its geological significance[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 62: 812−831. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9290-0
[40] Li Z X, Li X H. 2007. Formation of the 1300−km−wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat−slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 35(2): 179−182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[41] Liu C Q, Zhou J X, Lang J. 2013. Study on restrictive factor of fold−thrust belt formation with multiple decollements: Taking Eastern Sichuan−Xuefeng tectonic belt as an example[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(2): 45−55(in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Lü Q T, Meng G X, Zhang K, et al. 2021. The lithospheric architecture of the Lower Yangtze metallogenic belt, East China: Insights into an extensive Fe–Cu mineral system[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 132: 103989. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.103989
[43] Luo F, Yan J Y, Fu G M, et al. 2019. Crust thickness and its apocalyptic of mineralization in South China: Constraint from satellite gravity data[J]. Geology in China, 46(4): 759−774(in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Luo S, Huang R, Zhu L P, et al. 2020. The formation of the Dabashan orocline, central China: Insights from high−resolution 3D crustal shear−wave velocity structure[J]. Tectonophysics, 774: 228244. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.228244
[45] Mei L F, Liu S Q, Tang J G, et al. 2010. Mesozoic intra−continental progressive deformation in Western Hunan−Hubei−Eastern Sichuan Provinces of China: Evidence from apatite fission track and balanced cross−section[J]. Earth Science, 35(2): 161−174(in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Peng M L, Yi J, Yao R, et al. 2011. Physical simulation experiments on the multilayer nappe−detachment structure system in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(2): 198−206(in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Philippe Y. 1994. Transfer zone in the Southern Jura thrust belt (Eastern France): Geometry, development, and comparison with analogue modeling experiments, hydrocarbon and petroleum geology of France[M]. Springer: 327–346.
[48] Poblet J, Lisle R J. 2011. Kinematic evolution and structural styles of fold−and−thrust belts[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 349(1): 1−24. doi: 10.1144/SP349.1
[49] Raimondo T, Hand M, Collins W J. 2014. Compressional intracontinental orogens: Ancient and modern perspectives[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 130: 128−153. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.009
[50] Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Stehly L, et al. 2005. High−resolution surface−wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science, 307: 1615. doi: 10.1126/science.1108339
[51] Shen W S, Michael H, Ritzwoller, et al. 2016. A seismic reference model for the crust and uppermost mantle beneath China from surface wave dispersion[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 206(2): 954−979. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw175
[52] Sherkati S, Letouzey J, Frizon de Lamotte D. 2006. Central Zagros fold−thrust belt (Iran): New insights from seismic data, field observation, and sandbox modeling[J]. Tectonics, 25: TC4007.
[53] Shu L S, Wang B, Cawood P A, et al. 2015. Early Paleozoic and early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia Block, South China[J]. Tectonics, 34(8): 1600-1621.
[54] Shu L S, Deng X L, Ma X X. 2019. Tectonic affinity between central Tianshan basement and Tarim Block craton[J]. Earth Science, 44(5): 1584−1601(in Chinese with English abstract).
[55] Song P H, Teng J W, Zhang X M, et al. 2018. Flyover crustal structures beneath the Qinling orogenic belt and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(8): 6703−6718. doi: 10.1029/2017JB015401
[56] Steinshouer D W, Qiang J, McCabe P J, et al. 1999. Maps showing geology, oil and gas fields, and geologic provinces of the Asia Pacific region[R]. U. S. Geological Survey Open−File Report 97−470−F, https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr97470F.
[57] Teng J W, Zhang Z J, Zhang X K, et al. 2013. Investigation of the Moho discontinuity beneath the Chinese mainland using deep seismic sounding profiles[J]. Tectonophysics, 609: 202−216. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.11.024
[58] Wang E, Meng K, Su Z, et al. 2014. Block rotation: Tectonic response of the Sichuan basin to the southeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau along the Xianshuihe−Xiaojiang fault[J]. Tectonics, 33(5): 686−718. doi: 10.1002/2013TC003337
[59] Wang S Y, Hearn T M, Xu Z H, et al. 2001. Pn wave velocity structure at the uppermost mantle of China[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 6: 449−454+529(in Chinese with English abstract).
[60] Wang X W, Wo Y J, Zhou Y, et al. 2010. The kinematics of the fold−thrust zones in the western Yangtze Area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 200−212(in Chinese with English abstract).
[61] Wang Y J, Zhang Y H, Fan W M, et al. 2005. Structural signatures 40Ar/39Ar and geochronology of the Indosinian Xuefengshan tectonic belt, South China Block[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 27(6): 985−998. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2005.04.004
[62] Wang Z X, Li C L, Li H J, et al. 2019. Tectonic architecture and evolution of the eastern Sichuan−Wulingshan area , South China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 827−839(in Chinese with English abstract).
[63] Wang Z X, Zhang J, Li T, et al. 2010. Structural analysis of the multi−layer detachment folding in Eastern Sichuan province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 84(3): 497−514. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00269.x
[64] Wei Z G, Chen L, Li Z W, et al. 2016. Regional variation in Moho depth and Poisson’s ratio beneath eastern China and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 115: 308−320. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.10.010
[65] Wu H, Qiu N S, Chang J, et al. 2019. Physical simulation on development of multilayer detachment fold belt in eastern Sichuan[J]. Earth Science, 44(3): 784−797(in Chinese with English abstract).
[66] Yan D P, Qiu L, Chen F, et al. 2018. Structural style and kinematics of the Mesozoic Xuefengshan intraplate orogenic belt, South China Block[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(1): 1−13(in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Yan D P, Wang X W, Liu Y Y. 2000. Analysis of fold style and it's formation mechanism in the areaof boundary among Sichuan, Hubei and Hunan[J]. Geoscience, 14(1): 37−43(in Chinese with English abstract).
[68] Yan D P, Zhou M F, Song H L, et al. 2003. Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi−layer over−thrust system within the Yangtze Block (South China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 361: 239−254. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00646-7
[69] Yan D P, Zhang B, Zhou M F, et al. 2009. Constraints on the depth, geometry and kinematics of blind detachment faults provided by fault−propagation folds: An example from the Mesozoic fold belt of South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 31: 150−162. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.11.005
[70] Zhang B L, Zhu G, Hu S Q, et al. 2009. Numerical modeling and formation mechanism of the eastern Sichuan Jura−type folds[J]. Geological Review, 55(5): 701−711(in Chinese with English abstract).
[71] Zhang G W, Guo A L, Wang Y J, et al. 2013. Tectonics of South China continent and its implications[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 43(10): 1553−1582(in Chinese with English abstract).
[72] Zhang H J, Lü Q T, Wang X L, et al. 2023. Seismically imaged lithospheric delamination and its controls on the Mesozoic magmatic province in South China[J]. Nature Communications, 14: 2718. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37855-5
[73] Zhang W W, Zhang Y Q, Huang Y P, et al. 2022. Research progress and prospect of seismic ambient noise tomography[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 37(1): 125−141(in Chinese with English abstract).
[74] Zhang W W, Zhang Y Q, Lü Q T, et al. 2024. New seismic imaging of the crustal structure beneath the eastern Sichuan and Wuling Mountains, South China: Insights into the formation of fold−and−thrust belts[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 95(1): 421−434. doi: 10.1785/0220230105
[75] Zhang X Q, Shan Y H, Nie G J, et al. 2013. Numerical modeling of the Mesozoic East Sichuan fold belt: Influence of detachment depth on the fold pattern in the platform cover[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(4): 622−632(in Chinese with English abstract).
[76] Zhang X Q, Shan Y H, Ni Y J, et al. 2015. Numerical modeling of the mesozoic east sichuan fold belt: A two−stage tectonic model[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(6): 1022−1032(in Chinese with English abstract).
[77] Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Li J H, et al. 2012. The new progress in the study of Mesozoic tectonics of South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 33(3): 257−279(in Chinese with English abstract).
[78] Zhang Y Q, Shi D N, Lü Q T, et al. 2021a. The crustal thickness and composition in the eastern South China Block constrained by receiver functions: Implications for the geological setting and metallogenesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 130: 103988. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.103988
[79] Zhang Y Q, Shi D N, Lü Q T, et al. 2021b. A fine crustal structure and geodynamics revealed by receiver functions along the Guangchang−Putian line in the Cathaysia Block, South China[J]. Tectonophysics, 815: 229007. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.229007
[80] Zhang Y Q, Yan J Y, Li C L, et al. 2021. Preliminary study on the deep structure and intra−continental deformation in the eastern Sichuan and Wuling mountains region[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 36(6): 2423−2432(in Chinese with English abstract).
[81] Zhang Y Y, Chen L, Ai Y S, et al. 2018. Lithospheric structure of the South China Block from S−receiver function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(1): 138−149(in Chinese with English abstract).
[82] Zhou L Q, Xie J Y, Shen W S, et al. 2012. The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath South China from ambient noise and earthquake tomography[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 189(3): 1565−1583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05423.x
[83] Zhou X M, Sun T, Shen W Z, et al. 2006. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 29(1): 26−33. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i1/004
[84] Zhu L P. 2000. Crustal structure across the San Andreas Fault, southern California from teleseismic converted waves[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 179(1): 183−190. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00101-1
[85] Zhu L P, Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B2): 2969−2980. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900322
[86] 陈学波, 赵静娴, 李金森, 等. 1995. 长江三峡及邻区地壳上地幔结构特征及其在区域构造中的意义[C]//中国地球物理学会. 1995年中国地球物理学会第十一届学术年会论文集.
[87] 崔盛芹. 1999. 论全球性中—新生代陆内造山作用与造山带[J]. 地学前缘, 4: 283−293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.011
[88] 崔作舟, 陈纪平, 吴苓. 1996. 阿尔泰−台湾岩石圈地学断面综合研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[89] 邓阳凡, 李守林, 范蔚茗, 等. 2011. 深地震测深揭示的华南地区地壳结构及其动力学意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(10): 2560−2574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.10.013
[90] 丁道桂, 刘光祥, 吕俊祥, 等. 2007. 扬子板块海相中古生界盆地的递进变形改造[J]. 地质通报, 26(9): 1178−1188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.09.019
[91] 冯常茂, 刘进, 宋立军. 2008. 中上扬子地区构造变形带成因机制及有利油气勘探区域预测[J]. 地球学报, 29(2): 199−204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.02.010
[92] 冯向阳, 孟宪刚, 邵兆刚, 等. 2003. 华南及邻区有序变形及其动力学初探[J]. 地球学报, 24(2): 115−120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.02.004
[93] 何文刚, 周建勋. 2018. 川东南马尾状褶皱带特征与形成机制的物理模拟[J]. 地球科学, 43(6): 2133−2148.
[94] 胡召齐, 朱光, 刘国生, 等. 2009. 川东“侏罗山式”褶皱带形成时代: 不整合面的证据[J]. 地质论评, 55(1): 32−42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.01.004
[95] 李英康, 高建伟, 韩健, 等. 2019. 扬子块体两侧造山带地壳推覆的地球物理证据及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(4): 687−705.
[96] 李三忠, 李玺瑶, 赵淑娟, 等. 2016. 全球早古生代造山带(Ⅲ): 华南陆内造山[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(4): 1005−1025.
[97] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等. 2018. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造−岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报, 63(16): 1550−1593.
[98] 刘尚忠. 1995. 川东薄皮构造模式之我见[J]. 四川地质学报, (4): 264−267.
[99] 刘重庆, 周建勋, 郎建. 2013. 多层滑脱条件下褶皱—冲断带形成制约因素研究: 以川东—雪峰构造带为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 35(2): 45−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.02.005
[100] 罗凡, 严加永, 付光明, 等. 2019. 华南地区地壳厚度变化及对成矿类型的制约: 来自卫星重力数据的约束[J]. 中国地质, 46(4): 759−774. doi: 10.12029/gc20190407
[101] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等. 2010. 湘鄂西−川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形: 来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J]. 地球科学−中国地质大学学报, 35(2): 161−174.
[102] 彭美丽, 易金, 姚蓉, 等. 2011. 华南多层推滑构造系的物理模拟实验[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(2): 198−206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.02.004
[103] 舒良树, 邓兴梁, 马绪宣. 2019. 中天山基底与塔里木克拉通的构造亲缘性[J]. 地球科学, 44(5): 1584−1601.
[104] 汪素云, Hearn T M , 许忠淮, 等. 2001. 中国大陆上地幔顶部Pn速度结构[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 6: 449−454, 529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2001.06.002
[105] 汪新伟, 沃玉进, 周雁, 等. 2010. 上扬子地区褶皱−冲断带的运动学特征[J]. 地学前缘, 17(3): 200−212.
[106] 王宗秀, 李春麟, 李会军, 等. 2019. 川东—武陵地区构造格局及其演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 827−839.
[107] 吴航, 邱楠生, 常健, 等. 2019. 川东多套滑脱层褶皱构造带形成物理模拟[J]. 地球科学, 44(3): 784−797.
[108] 颜丹平, 汪新文, 刘友元. 2000. 川鄂湘边区褶皱构造样式及其成因机制分析[J]. 现代地质, 14(1): 37−43.
[109] 颜丹平, 邱亮, 陈峰, 等. 2018. 华南地块雪峰山中生代板内造山带构造样式及其形成机制[J]. 地学前缘, 25(1): 1−13.
[110] 张必龙, 朱光, 胡召齐, 等. 2009. 川东“侏罗山式”褶皱的数值模拟及成因探讨[J]. 地质论评, 55(5): 701−711.
[111] 张国伟,郭安林,王岳军,等. 2013. 中国华南大陆构造与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 43(10): 1553−1582.
[112] 张小琼, 单业华, 聂冠军, 等. 2013. 中生代川东褶皱带的数值模拟: 滑脱带深度对地台盖层褶皱型式的影响[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(4): 622−632.
[113] 张小琼, 单业华, 倪永进, 等. 2015. 中生代川东褶皱带的数值模拟: 两阶段的构造演化模型[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(6): 1022−1032.
[114] 张文文, 张永谦, 黄跃鹏, 等. 2022. 地震背景噪声成像技术研究进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 37(1): 125−141. doi: 10.6038/pg2022FF0241
[115] 张永谦, 严加永, 李春麟, 等. 2021. 川东—武陵山地区的深部结构与陆内变形机制初探[J]. 地球物理学进展, 36(6): 2423−2432. doi: 10.6038/pg2021FF0087
[116] 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 2012. 华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J]. 地球学报, 33(3): 257−279. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.03.01
[117] 张耀阳, 陈凌, 艾印双, 等. 2018. 利用S波接收函数研究华南块体的岩石圈结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(1): 138−149. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0226
-




 下载:
下载: