Geochemical characteristics of ultramafic rocks in Sumdo area, Tibet and its enlightenment for the evolution of the Sumdo Paleo-Tethys Ocean
-
摘要:
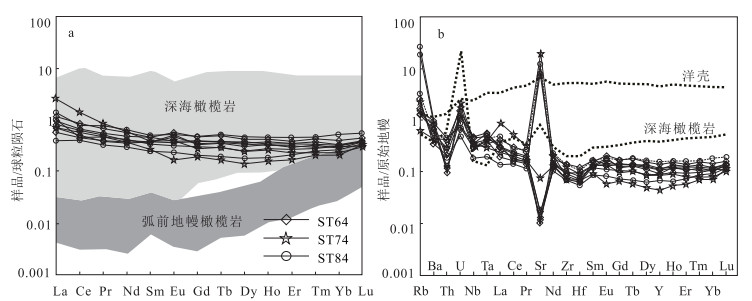
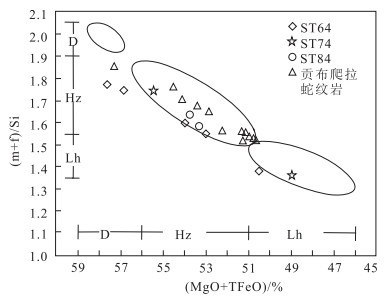
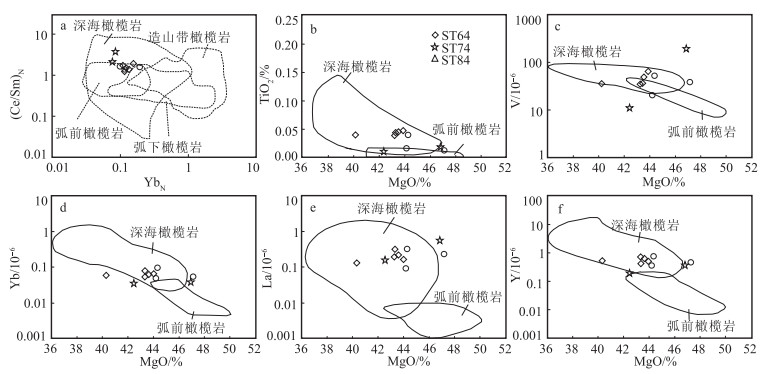
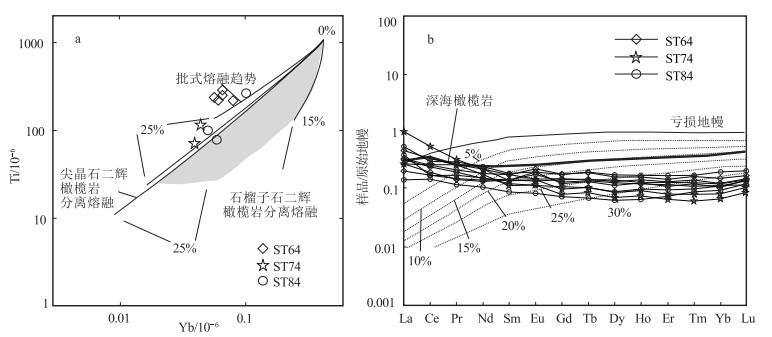
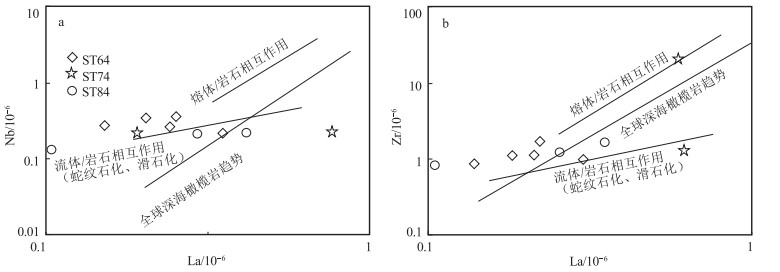
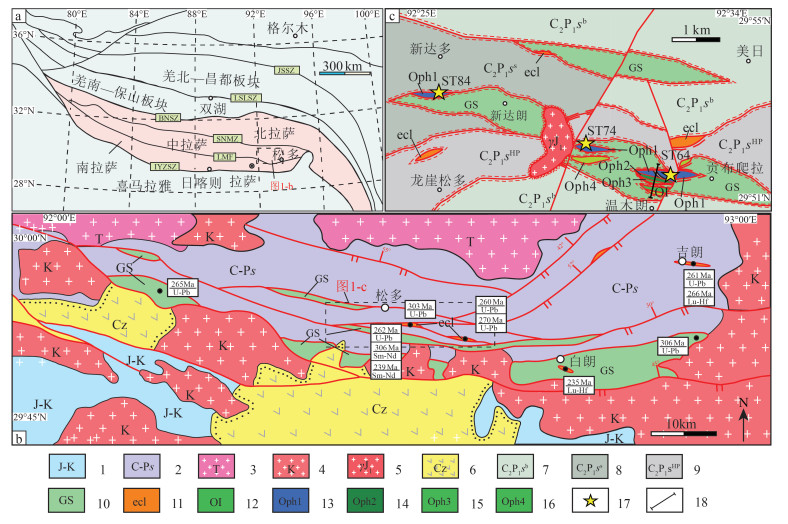
唐加-松多古特提斯缝合带的提出改变了地学界对青藏高原古特提斯演化格局的认识。为进一步约束唐加-松多古特提斯缝合带中蛇绿岩的岩石成因及类型, 以松多地区的超基性岩为研究对象, 对其进行了岩石学和全岩地球化学研究。结果显示, 松多地区超基性岩与原始地幔相比具有较高的MgO和TFe2O3含量, 以及较低的Al2O3和TiO2含量。样品稀土元素总含量介于4.04×10-6~9.31×10-6之间, 大部分低于原始地幔值。稀土元素配分曲线呈较宽缓的"U"型, 轻稀土元素较富集。微量元素分布形式与全球深海橄榄岩的微量元素分布形式基本一致, 具有明显的Th、Nb负异常, 大部分样品具有轻微的Zr、Hf负异常。定量模拟估算表明, 研究区超基性岩主要为尖晶石二辉橄榄岩地幔批式熔融后的难熔残留体, 熔融程度大于25%, 并具一定程度石榴子石相熔融的特征, 未受到后期岩石-熔体反应的改造, 其原岩应为亏损的深海橄榄岩。结合区域研究成果, 松多地区超基性岩可能形成于大洋中脊(MOR)环境, 为典型的大洋中脊玄武岩(MORB)型蛇绿岩端元之一。
Abstract:The proposal of Tangjia-Sumdo Paleo-Tethys suture zone has changed the understanding of Paleo-Tethys evolution pattern in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau.The petrological and geochemistry of ultramafic rocks in Sumdo area are studied to manifest the genesis and type of the ophiolite in the Tangjia-Sumdo Paleo-Tethys suture zone.The results show the ultramafic rocks have higher MgO and TFe2O3 but lower Al2O3and TiO2 contents compared with those of the primitive mantle.The total rare-earth element(REE)contents of the samples are 4.04×10-6~9.31×10-6, which are lower than those of the primitive mantle.The chondrite-normalized REE patterns display a U-type, and they are enrichment in LREE.The primitive mantle-normalized spider diagrams show an abyssal peridotites affinity, there are obvious negative anomalies of Th and Nb.Most of the samples show slight negative Zr and Hf anomalies.Through quantitative modeling, we conclude that the ultramafic rocks are refractory residual formed by more than 25% batch melting of spinel lherzolite mantle, and the inheritance of some garnet signatures was observed in the samples to a certain extent.They are not modified by later rock-melt reaction, the protolith of the ultramafic rocks may be depleted abyssal peridotite.Combining with regional geology, we suggest that the ultramafic rocks in Sumdo area may have been formed in the mid ocean ridge(MOR)setting and are one of the typical end members of mid ocean ridge basalt(MORB)type ophiolites.
-
Key words:
- Qinghai-Tibet Plateau /
- Sumdo /
- ophiolite /
- ultramafic rocks /
- geochemistry /
- Paleo-Tethys Ocean
-

-
表 1 松多超基性岩全岩地球化学分析结果
Table 1. Whole rock composition of the ultramafic rocks in Sumdo
样品编号 ST64H1 ST64H2 ST64H3 ST64H4 ST64H5 ST74H1 ST74H2 ST84H1 ST84H2 ST84H3 SiO2 40.36 44.26 37.65 41.34 38.30 43.28 39.15 40.90 37.59 41.14 TiO2 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 Al2O3 0.52 0.53 0.65 0.71 0.61 0.67 0.87 0.81 0.72 0.66 TFeO 9.41 9.19 12.98 8.78 11.69 5.63 7.73 8.75 9.19 8.33 MnO 0.17 0.12 0.18 0.15 0.14 0.06 0.23 0.12 0.14 0.10 MgO 39.08 36.52 39.50 39.21 39.83 36.69 42.48 40.91 42.89 39.82 CaO 0.08 0.00 0.01 0.21 0.06 0.09 0.08 0.72 0.35 0.10 Na2O 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.02 K2O 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.01 P2O5 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 烧失量 9.33 8.36 8.13 8.55 8.38 12.67 8.59 6.75 8.09 8.80 总计 99.01 99.03 99.14 99.00 99.08 99.12 99.19 99.04 99.05 99.01 Li 0.20 1.00 0.44 0.71 1.13 0.30 0.40 0.82 0.65 3.61 Sc 10.99 10.12 10.02 10.61 11.63 7.94 4.56 9.88 8.65 8.97 V 49.04 35.26 36.18 35.38 65.34 10.54 206.8 52.98 38.42 19.68 Cr 4708 3950 3940 4396 5628 1997 13052 3162 2878 3914 Co 130.9 124.6 142.3 127.6 139.5 87.9 123.3 137.1 124.5 123.0 Ni 1196 1173 1132 1209 1298 2112 2022 2574 2408 2424 Cu 3.24 4.58 4.30 3.28 4.08 4.49 2.94 0.84 1.84 5.66 Zn 65.68 47.90 64.56 57.12 52.02 45.36 113.6 47.90 49.22 62.52 Ga 2.05 2.07 1.93 2.21 3.19 0.73 2.27 1.14 0.98 1.05 Rb 1.68 0.86 1.11 0.88 0.99 0.42 1.40 2.25 19.58 14.08 Sr 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.4 1.7 428.6 363.2 238.2 354.8 Y 0.57 0.53 0.44 0.68 0.54 0.22 0.42 0.76 0.43 0.33 Zr 1.68 0.86 1.11 0.98 1.10 0.84 1.28 1.64 1.22 0.82 Nb 0.36 0.28 0.27 0.22 0.35 0.23 0.23 0.22 0.22 0.14 Cs 0.13 0.39 0.19 0.21 0.17 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.08 0.13 Ba 2.61 5.02 4.18 6.15 7.08 3.23 3.02 4.48 6.71 6.89 La 0.22 0.14 0.22 0.31 0.18 0.17 0.63 0.36 0.26 0.10 Ce 0.46 0.31 0.43 0.58 0.35 0.38 0.93 0.52 0.31 0.27 Pr 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.09 0.08 0.05 0.03 Nd 0.25 0.20 0.21 0.30 0.19 0.19 0.30 0.33 0.21 0.15 Sm 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.06 0.04 Eu 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 Gd 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.11 0.09 0.04 0.06 0.11 0.07 0.05 Tb 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 Dy 0.11 0.10 0.09 0.12 0.10 0.04 0.07 0.13 0.07 0.05 Ho 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 Er 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.07 0.07 0.03 0.04 0.08 0.05 0.04 Tm 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Yb 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.10 0.06 0.05 Lu 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 Hf 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 Ta 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Pb 0.61 0.29 0.38 0.32 0.36 0.37 0.44 0.94 0.41 0.38 Th 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.02 U 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.01 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
[1] Liu Y M, Li S Z, Santosh M, et al. The generation and reworking of continental crust during early Paleozoic in Gondwanan affinity terranes from the Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2019, 190: 486-497. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.01.019
[2] Xu Z Q, Dilek Y, Cao H, et al. Paleo-Tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the East Cimmerides and West Cathaysides[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105(1): 320-337.
[3] 李才. 龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与羌塘古特提斯洋演化记录[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(1): 13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.01.003
[4] Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Li Z L, et al. Discovery of an Eclogite Belt in the Lhasa Block, Tibet: A New Border for Paleo-Tethys?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(1): 76-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.04.001
[5] Cheng H, Zhang C, Jeffrey D V, et al. Zircon U-Pb and garnet Lu-Hf geochronology of eclogites from the Lhasa Block, Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2012, 155: 341-359. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.09.011
[6] Cheng H, Liu Y M, Jeffrey D V, et al. Combined U-Pb, Lu-Hf, Sm-Nd and Ar-Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(2015): 1482-1499.
[7] Li Z L, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. Geochemistry and Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic composition of eclogite in the Lhasa terrane, Tibet, and its geological significance[J]. Lithos, 2009, 109: 240-247. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.01.004
[8] 申婷婷, 张聪, 田作林, 等. 拉萨地块吉朗榴辉岩的岩石学研究及其对古特提斯洋壳俯冲折返过程的限定[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(6): 51-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201806004.htm
[9] Weller O M, St-Onge M R, Rayner N, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology and phase equilibria modelling of a mafic eclogite from the Sumdo complex of south-east Tibet: insights into prograde zircon growth and the assembly of the tibetan plateau[J]. Lithos, 2016, 262: 729-741. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.06.005
[10] Zeng L S, Liu J, Gao L E, et al. Early Mesozoic high-pressure metamorphism within the Lhasa block, Tibet and implications for regional tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(2): 140-151.
[11] Zhang C, Bader T, van Roermund H, et al. The metamorphic evolution and tectonic significance of the Sumdo HP-UHP metamorphic terrane, central-south Lhasa Block, Tibet[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 2019, 474: 209-229. doi: 10.1144/SP474.4
[12] 黄杰, 田作林, 张聪, 等. 拉萨地块松多榴辉岩的变质演化过程: NCKMnFMASHTO体系中的相平衡关系[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(5): 1559-1571. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.05.024
[13] Li Y, Zhang C, Liu X, et al. Metamorphism and Oceanic Crust Exhumation-Constrained by theJilang Eclogite and Meta-Quartzite from the Sumdo (U) HP Metamorphic Belt[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2019, 30(3): 510-524. doi: 10.1007/s12583-019-0894-9
[14] Wang B, Xie C M, Fan J J, et al. Genesis and tectonic setting of Middle Permian OIB-type mafic rocks in the Sumdo area, southern Lhasa terrane[J]. Lithos, 2019, 324/325: 429-438. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.11.015
[15] Wang B, Xie C M, Dong Y S, et al. Middle Permian adakitic granite dikes in the Sumdo region, central Lhasa terrane, central Tibet: Implications for the subduction of the Sumdo Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 205(2021): 104610.
[16] Shi R D. Research Progress, Existing Problems and Consideration of Ophiolite[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 51(6): 681-693.
[17] 陈松永. 西藏拉萨地块中古特提斯缝合带的厘定[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2010.
[18] Chen S Y, Yang J S, Li Y, et al. Ultramafic blocks in the Sumdo Region, Lhasa Block, Eastern Tibet Plateau: an ophiolite unit[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009, 20: 332-347. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0028-x
[19] Wang B, Xie C M, Dong Y S, et al. Middle-late Permian mantle plume/hotspot-ridge interaction in the Sumdo Paleo-Tethys Ocean region, Tibet: Evidence from mafic rocks[J]. Lithos, 2021, 390/391(2021): 106128.
[20] Niu Y, O'Hara M J. Origin of ocean island basalts: A new perspective from petrology, geochemistry, and mineral physics considerations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B4): 2209.
[21] Niu Y. Bulk-rock Major and Trace Element Compositions of Abyssal Peridotites: Implications for Mantle Melting, Melt Extraction and Post-melting Processes Beneath Mid-Ocean Ridges[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45(12): 2423-2458. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egh068
[22] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2011, 301: 241-255. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
[23] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 耿全如, 等. 中国境内可能存在一条新的高压/超高压(?)变质带——青藏高原拉萨地体中发现榴辉岩带[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(12): 1787-1792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.001
[24] 王斌. 西藏松多地区蛇绿岩的识别及构造意义[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2019.
[25] 解超明, 宋宇航, 王明, 等. 冈底斯中部松多岩组形成时代及物源: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2019, (7): 2224-2233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201907003.htm
[26] 于红. 陕西商南松树沟橄榄岩矿物地球化学特征及成因机理示踪[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2011.
[27] Coleman R G. Ophiolite-ancient Oceanic Lithosphere[M]. Berlin. Heidelberg, New York, Spring-Verlag. 1977.
[28] Bodinier J L, Godard M. Orogenic, Ophiolitic, and Abyssal Peridotites[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2014, 2: 103-167.
[29] Whattam S A, Stern R J. The subduction initiation rule: a key for linking ophiolites, intra-oceanic forearcs, and subduction initiation[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2011, 162(5): 1031-1045.
[30] Boynton, William V. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2: 63-114.
[31] Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253.
[32] 陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990.
[33] 王希斌, 郝梓国. 中国造山带蛇绿岩的时空分布及构造类型[J]. 中国区域地质, 1994, 13(3): 193-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD403.000.htm
[34] Parkinson I J, Pearce J A. Peridotites from the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Forearc (ODP Leg 125): Evidence for Mantle Melting and Melt-Mantle Interaction in a Supra-Subduction Zone Setting[J]. Jour. Petrol., 1998, 39(9): 1577-1618. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.9.1577
[35] Dick H J B, Bullen T. Chromian spinel as a petrogenetic indicator in abyssal and alpine-type peridotites and spatially associated lavas[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1984, 86(1): 54-76. doi: 10.1007/BF00373711
[36] Uysal I, Kaliwoda M, Karsli O, et al. Compositional variations as a result of partial melting and melt-peridotite interaction in an upper mantle section from the ortaca area, southwestern turkey[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2007, 45(6): 1471-1493. doi: 10.3749/canmin.45.6.1471
[37] Mysen B O, Kushiro I. Compositional variations of coexisting phases with degree of melting of peridotite in the upper mantle[J]. American Mineralogist, 1977, 62(9/10): 843-865.
[38] Jaques A L, Green D H. Anhydrous melting of peridotite at 0-15kb pressure and the genesis of tholeiitic basalts[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1980, 73(3): 287-310. doi: 10.1007/BF00381447
[39] Himmelberg G R, Loney R A. Petrology of the Vulcan Peak Alpine-type peridotite, southwestern Oregon[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1973, 84(5): 1585-1600. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1973)84<1585:POTVPA>2.0.CO;2
[40] Kelemen P B, Dick H J, Quick J E. Formation of harzburgite by pervasive melt/rock reaction in the upper mantle[J]. Nature, 1992, 358(6388): 635-641. doi: 10.1038/358635a0
[41] Crawford A J, Beccaluva L, Serri G. Tectono-magmatic evolution of the West Philippine-Mariana region and the origin of boninites[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1981, 54(2): 346-356. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(81)90016-9
[42] 徐德明, 黄圭成, 雷义均. 西藏西南部拉昂错地幔橄榄岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2008, 27(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200801002.htm
[43] Dupuis C, Hébert R, Dubois C V, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of mafic rocks from mélange and flysch units adjacent to the Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone, southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 214(3/4): 287-308.
[44] 刘函, 王保弟, 陈莉, 等. 日喀则夏鲁N-MORB型辉长岩与辉绿岩: 雅鲁藏布江特提斯洋早白垩世初始俯冲记录[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(11): 1836-1851. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.11.004 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211104&flag=1
[45] Bedarde E, Hebert R, Guilmette C, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of the Saga and Sangsang ophiolitic massifs, Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone, Southern Tibet: Evidence for an arc-back-arc origin[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(1/2): 48-67.
[46] 徐向珍, 杨经绥, 郭国林, 等. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段普兰蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩的岩石学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3179-3196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111003.htm
[47] 徐梦婧, 金振民. 西藏罗布莎地幔橄榄岩变形显微构造特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(12): 1795-1803. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101207&flag=1
[48] 连东洋, 杨经绥, 熊发挥, 等. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩带西段达机翁地幔橄榄岩组成特征及其形成环境分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(8): 2164-2184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201408004.htm
[49] 张利, 杨经绥, 刘飞, 等. 南公珠错地幔橄榄岩: 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段一个典型的大洋地幔橄榄岩[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(12): 95-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201612007.htm
-



 下载:
下载: