Discovery of Late Devonian monzogranite from the Eastern Tianshan, and its constrains on the tectonic evolution of the Aqishan-Yamansu belt
-
摘要:
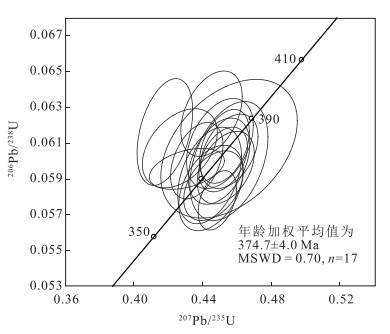
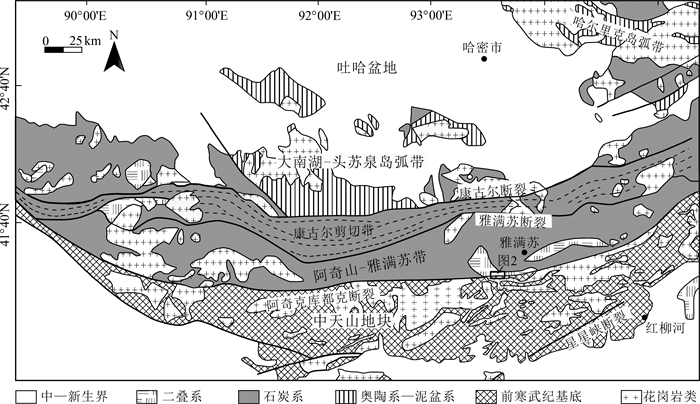
阿奇山—雅满苏带位于东天山南部, 属于中亚造山带的重要组成部分, 其内发育大量岩浆岩, 形成时代主要为石炭纪—二叠纪。目前为止, 尚未有早期岩石的报道。对位于该区南缘的二长花岗岩进行了LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测年研究。结果显示, 二长花岗岩中锆石呈自形—半自形, 具有明显的振荡环带, Th/U值均大于0.4, 显示岩浆锆石特征。这些锆石的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为374.7±4.0 Ma (MSWD=0.7, n=17), 代表岩浆结晶年龄。表明研究区存在晚泥盆世岩浆事件, 阿奇山—雅满苏带的形成至少开始于晚泥盆世。二长花岗岩的形成时代和中天山晚泥盆世岛弧环境岩浆岩形成时代一致, 表明其可能是古大洋板片向南俯冲的产物。
Abstract:The Aqishan-Yamansu belt, located at south of the Eastern Tianshan belt, is a pivotal part of the Central Asian orogenic belt.The most important feature of the Aqishan-Yamansu belt is the occurrence of voluminous igneous rocks, which mainly formed during Carboniferous and Permain with no pre-Carboniferous age has been reported.We present zircon LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb chronology of monzogranite, discovered on the southern margin of the Aqishan-Yamansu belt.The zircons from the monzogranite are mostly euhedral to subhedral, with oscillatory zoning and Th/U ratios more than 0.4, suggesting magmatic origin.Therefore, the obtained weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 374.7±4.0 Ma (MSWD=0.7, n=17) can be used to represent the magma crystallization age.This result suggests that a magmatic event occurred during Late Devonian and formation of the Aqishan-Yamansu belt possibly began in Late Devonian at latest.Combined with the Late Devonian magmatism formed in arc environment in Central Tianshan, we concluded that the monzogranite may have been produced by the southward subduction of ancient oceanic plate beneath the Central Tianshan during Late Devonian.
-
Key words:
- Aqishan-Yamansu belt /
- monzogranite /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- Late Devonian /
- tectonic evolution
-

-
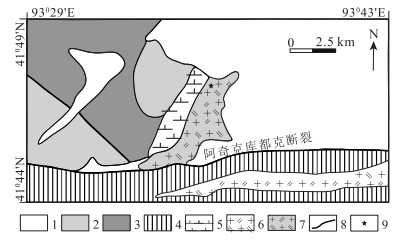
图 2 雅南二长花岗岩侵入体地质图(据参考文献①修改)
Figure 2.
表 1 雅南二长花岗岩锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测年结果
Table 1. Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of Ya'nan monzogranite
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/ 206Pb 1σ 206Pb/ 238U 1σ 207Pb/ 235U 1σ 1 34 306 475 0.64 0.055 26 0.001 08 0.455 65 0.011 04 0.060 55 0.001 37 433 41 379 8 381 8 2 109 1593 1170 1.36 0.055 51 0.001 03 0.455 44 0.015 00 0.060 01 0.002 19 432 44 376 13 381 10 3 35 439 494 0.89 0.054 67 0.000 68 0.452 83 0.009 56 0.060 82 0.001 36 398 28 381 8 379 7 4 36 349 571 0.61 0.053 89 0.001 66 0.455 50 0.026 21 0.060 69 0.002 55 365 69 380 16 381 18 5 35 408 502 0.81 0.054 79 0.000 72 0.452 09 0.009 31 0.060 09 0.001 19 467 30 376 7 379 7 6 31 330 465 0.71 0.051 22 0.000 89 0.418 15 0.010 69 0.061 62 0.001 96 250 40 385 12 355 8 7 30 301 435 0.69 0.051 94 0.000 81 0.445 31 0.011 81 0.062 65 0.001 57 283 36 392 10 374 8 8 28 260 426 0.61 0.053 99 0.000 79 0.450 18 0.012 82 0.060 98 0.001 66 372 33 382 10 377 9 9 67 787 940 0.84 0.054 63 0.000 67 0.449 71 0.011 84 0.060 00 0.001 59 398 27 376 10 377 8 10 29 306 438 0.70 0.055 74 0.000 72 0.444 97 0.012 35 0.058 50 0.001 57 443 29 366 10 374 9 11 54 550 814 0.68 0.055 19 0.000 65 0.453 58 0.010 96 0.059 64 0.001 33 420 27 373 8 380 8 12 95 883 1452 0.61 0.055 65 0.001 10 0.444 23 0.012 25 0.059 20 0.001 77 439 44 371 11 373 9 13 88 730 1353 0.54 0.053 13 0.000 53 0.436 74 0.010 07 0.060 02 0.001 41 345 25 376 9 368 7 14 58 644 825 0.78 0.055 86 0.001 22 0.446 45 0.011 44 0.058 63 0.001 28 456 49 367 8 375 8 15 25 245 337 0.73 0.052 02 0.001 84 0.426 84 0.014 40 0.060 72 0.001 46 287 79 380 9 361 10 16 89 971 1314 0.74 0.057 04 0.000 73 0.448 73 0.007 39 0.057 81 0.001 09 494 29 362 7 376 5 17 23 219 327 0.67 0.052 38 0.001 49 0.430 94 0.014 41 0.059 57 0.000 75 302 65 373 5 364 10 表 2 阿奇山—雅满苏带岩浆侵入体侵位年龄
Table 2. Age data for magmatic intrusions in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt
岩体名称 岩性 测年方法 年龄/Ma 资料来源 岩体名称 岩性 测年方法 年龄/Ma 资料来源 西凤山 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 349±3 [10] 多头山 二长花岗岩
英安玢岩锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb
锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb318±3
197±4[17]
[17]石英滩 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 342±11 [10] 红云滩 花岗闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 329±9 [34] 赤龙峰 黑云闪长岩
花岗闪长岩
正长岩锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb
锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb
锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb317±1
306±2
253±1[38]
[38]
[38]长条山 石英闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 337±3 [10] 百灵山 花岗闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 318±4 [10] 花岗闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 318±2 [35] 红山梁 花岗斑岩
花岗闪长岩
二长花岗岩锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb
锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb
锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb343±2
250±4
236±2[6]
[6]
[6]二长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 314±2 [35] 花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 307±2 [35] 闪长岩包体 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 329±2 [5] 维权 花岗岩 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 297±3 [39] 闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 323±3 [5] 陇东 二长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 276±3 [10] 二长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 313±2 [5] 土墩 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 246±3 [10] 花岗闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 308±2 [5] 雅满苏 花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 227~230 [18] 阿奇山 花岗闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 336±3 [36] 雅满苏北 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 230±1 [1] 钠长斑岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 333±3 [36] 花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 223±1 [40] 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 292±3 [36] 黑峰山 闪长岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 274±2 [16] 二长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 281±2 [36] 花岗岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 274±3 [16] 鄯善采石场 正长花岗岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 272±3 [22] 突出山 花岗岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 317±2 [16] 二长花岗岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 251±4 [22] 闪长岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 326±2 [16] 钾长花岗岩 单颗粒锆石U-Pb 230±2 [37] 沙泉子 闪长岩 锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb 276±1 [16] 多头山 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 272±6 [10] 闪长岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 299±5 [23] 花岗斑岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 316±8 [17] 白石泉 钾长花岗岩 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 303±18 [10] -
[1] 雷如雄, 吴昌志, 张遵忠, 等. 东天山雅满苏北岩体的年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2653-2664. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201308003.htm
[2] 王京彬, 王玉往, 何志军. 东天山大地构造演化的成矿示踪[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(3): 461-469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.002
[3] 邓小华, 王京彬, 王玉往, 等. 东天山卡拉塔格红石铜矿地质特征及矿床成因初步探讨[J]. 矿产勘查, 2014, 5(2): 159-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2014.02.007
[4] Zhang Z Z, Gu L X, Wu C Z, et al. Early Indosinian Weiya gabbro in Eastern Tianshan, China: Elemental and Sr-Nd-O isotopic geochemistry, and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(3): 424-432. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2007.tb00965.x
[5] Zhao L D, Chen H Y, Hollings P, et al. Late Paleozoic magmatism and metallogenesis in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt, Eastern Tianshan: Constraints from the Bailingshan intrusive complex[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 65: 68-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.08.004
[6] Zhao L D, Chen H Y, Hollings P, et al. Tectonic transition in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt, Eastern Tianshan: Constraints from the geochronology and geochemistry of Carboniferous and Triassic igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 2019, 344/345: 247-264. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.06.023
[7] Long X P, Wu B, Sun M, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Carboniferous dykes in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt, Eastern Tianshan: Evidence for a post-collisional slab breakoff[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(1): 347-362. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.06.003
[8] Zhang X R, Zhao G C, Eizenhöfer P R, et al. Late Ordovician adakitic rocks in the Central Tianshan block, NW China: Partial melting of lower continental arc crust during back-arc basin opening[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2016, 128(9/10): 1367-1382.
[9] Zhang X R, Zhao G C, Sun M, et al. Tectonic evolution from subduction to arc-continent collision of the Junggar ocean: Constraints from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from the North Tianshan belt, NW China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2016, 128(3/4): 644-660.
[10] 周涛发, 袁峰, 张达玉, 等. 新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区花岗岩类年代学、构造背景及其成矿作用研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(2): 478-502. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201002014.htm
[11] 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 等. 关于东天山花岗岩与陆壳垂向增生的若干认识[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1103-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605005.htm
[12] Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4): 370-395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
[13] Wang Y H, Xue C J, Liu J J, et al. Early Carboniferous adakitic rocks in the area of the Tuwu deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Slab melting and implications for porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 103(4): 332-349.
[14] Han Y G, Zhao G C. Final amalgamation of the Tianshan and Junggar orogenic collage in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints on the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 129-152. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.012
[15] Zhao L D, Chen H Y, Zhang L, et al. Geology and ore genesis of the late Paleozoic Heijianshan Fe oxide-Cu (-Au) deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 91: 110-132. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.10.014
[16] Liu F, Chai F M, Li Q, et al. Constraints on the timing of Fe-(Cu) metallogenesis in the Eastern Aqishan-Yamansu-Shaquanzi metallogenic belt, Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 113(103089): 1-23.
[17] 张维峰, 陈华勇, 江宏君, 等. 新疆东天山多头山铁-铜矿区花岗岩类的年代学、地球化学、岩石成因及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(6): 1171-1191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201706014.htm
[18] 赵宏刚, 苏锐, 梁积伟, 等. 东天山觉罗塔格雅满苏花岗岩岩石学、地球化学特征及其板内构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(9): 1780-1802. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.09.003
[19] Han C M, Xiao W J, Zhao G C, et al. Late Paleozoic metallogenesis and evolution of the East Tianshan Orogenic Belt (NW China, Central Asia Orogenic Belt)[J]. Geology of Ore Deposits, 2014, 56(6): 493-512. doi: 10.1134/S1075701514060075
[20] 王雯, 夏芳, 柴凤梅, 等. 东天山石炭纪雅满苏组火山岩特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(5): 768-790. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.05.003
[21] 苏春乾, 姜常义, 夏明哲, 等. 北天山东段阿奇山组火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(4): 901-915. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200904014.htm
[22] 王晓丹, 蔡宏明, 吴兆宁, 等. 觉罗塔格造山带阿奇山花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb定年、Lu-Hf同位素及构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(5): 977-988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201905013.htm
[23] Jiang H J, Han J S, Chen H Y, et al. Intra-continental back-arc basin inversion and Late Carboniferous magmatism in Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Constraints from the Shaquanzi magmatic suite[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2017, 8(6): 1447-1467. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2017.01.008
[24] 侯可军, 李延河. 单颗粒锆石8~10μm小斑束LA-MC-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb年龄的测定[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, (S1): 447-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1228.htm
[25] 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200904009.htm
[26] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf Isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
[27] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 1(15): 1535-1546.
[28] Ludwig K R. Isoplot/Ex, version3: A geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, California, 2003.
[29] Rubatto D, Gebauer D. Use of cathodoluminescence for U-Pb zircon dating by ion microprobe: Some examples from the western Alps[C]//Pagel M, Barbin V, Blanc P, et al. Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences. Berlin: Springer, 2000: 373-400.
[30] Wu Y B, Zheng Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15): 1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
[31] 罗婷, 廖群安, 陈继平, 等. 东天山雅满苏组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(6): 1338-1352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201206030.htm
[32] Yin J Y, Chen W, Xiao W J, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic significance of the latest Devonian-early Carboniferous Ⅰ-type granites in the Central Tianshan, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 47: 188-199.
[33] Su B, Qin K, Zhou M, et al. Petrological, geochemical and geochronological constraints on the origin of the Xiadong Ural-Alaskan type complex in NW China and tectonic implication for the evolution of southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 2014, 200: 226-240.
[34] 吴昌志, 张遵忠, Zaw K, 等. 东天山觉罗塔格红云滩花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, (5): 1121-1134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605006.htm
[35] Zhang W F, Chen H Y, Han J S, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of igneous rocks in the Bailingshan area: Implications for the tectonic setting of late Paleozoic magmatism and iron skarn mineralization in the eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 38: 40-59.
[36] Du L, Long X P, Yuan C, et al. Mantle contribution and tectonic transition in the Aqishan-Yamansu Belt, Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Insights from geochronology and geochemistry of Early Carboniferous to Early Permian felsic intrusions[J]. Lithos, 2018(304-307): 230-244.
[37] 李文明, 任秉琛, 杨兴科, 等. 东天山中酸性侵入岩浆作用及其地球动力学意义[J]. 西北地质, 2002, 35(4): 41-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200204004.htm
[38] Zhao L D, Chen H Y, Li Z, et al. The Late Paleozoic magmatic evolution of the Aqishan-Yamansu belt, Eastern Tianshan: Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of igneous rocks[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 153: 170-192.
[39] 王龙生, 李华芹, 刘德权, 等. 新疆哈密维权银(铜)矿床地质特征和成矿时代[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(3): 280-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200503006.htm
[40] Zhang X R, Zhao G C, Sun M, et al. Triassic magmatic reactivation in Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Evidence from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes of granites[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145: 446-459.
① 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第一区域地质调查大队,雅满苏镇幅(K46C003003幅)1:25万区域地质调查报告.2013.
-



 下载:
下载: