Palynological assemblages of typical black soil profile in the eastern Songliao Plain and their age and its implication for paleoclimatic
-
摘要:
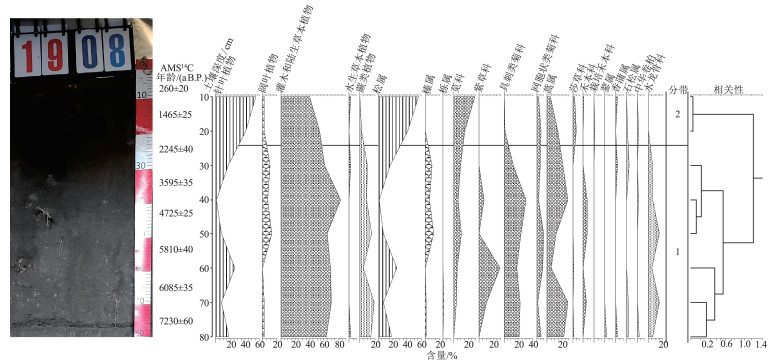
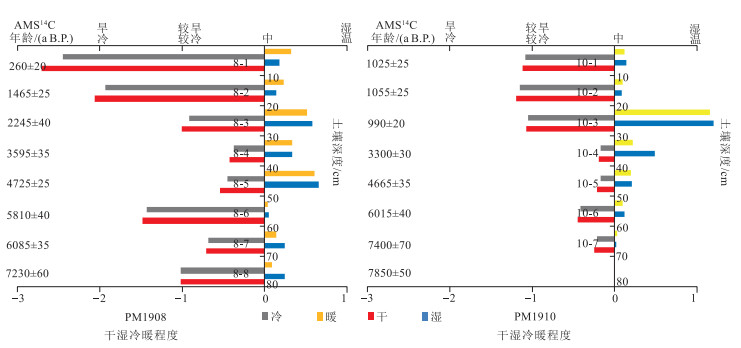
自然黑土区是环境演化和气候变化的重要地质记录。研究黑土区形成的时代及古气候环境演变, 清楚黑土的形成机制, 对黑土资源的可持续利用、保护东北大粮仓具有重要的意义。在松嫩平原东部海伦地区典型黑土剖面中采集15件孢粉样品进行孢粉学研究, 并对相同层位土壤样品中总有机碳进行了AMS14C测年。系统的分析、鉴定和研究表明, 典型黑土剖面自下而上可划分为2个孢粉组合, 下部孢粉组合以Echinate Asteraceae-Artemisia-Boraginaceae-Pinus为代表, 上部孢粉组合以Pinus-Amaranthaceae-Artemisia为代表。通过AMS14C测年认为, 松嫩平原东部海伦地区典型黑土为中全新世及晚全新世早期的产物。综合元素地球化学、古植物、孢粉分析表明, 松嫩平原东部典型黑土主要形成于中全新世7400 a B.P.以来的大暖期, 形成于松嫩平原温暖半湿润的气候环境, 植被为以草本灌木为主的草原植被。
Abstract:Natural black soil area is an important geological record of environmental evolution and climate change.Studying the formation of the black soil area and the evolution of the paleoclimatic environment, and knowing how the black soil came from, is of great significance for the sustainable use of black soil resources and protecting the large granary in the Northeast.Fifteen sporopollen samples were collected from a typical black soil profile in the Helen area of the eastern Songnen Plain for pollen research, and total organic carbon in soil samples from the same stratum was AMS14C dated.2 sporo-pollen assemblages which represented by Echinate Asteraceae-Artemisia-Boraginaceae-Pinus of lower part and Pinus-Amaranthaceae-Artemisia of upper part were identified from the typical black soil profile after systematical analysis, identification and research.AMS14C dating indicates that the typical black soil in the Helen area of the eastern Songnen Plain is a product of the Middle Holocene and the early Late Holocene.Comprehensive element geochemistry, paleontology, and spore pollen analysis indicate that the typical black soil was mainly formed during the warm period since 7400 a B.P. in the Holocene.Which Formed in the warm and semi-humid climate of the Songnen Plain, the vegetation is mainly grassland vegetation with herbaceous shrubs.
-

-
表 1 白春村典型黑土土壤剖面描述
Table 1. Description of typical black soil profile in Baichun Village
距表层深度/cm 发生层 详细描述 0~30 A层 润,黑色,中壤,有团粒结构,较松,多根孔,含大量草根和木本根系 30~80 AB层 润,黑色,中壤,有团粒结构,较紧实,较多木本根系 80~150 B1层 润,黑色-棕黄色,重壤,有小团块结构,紧实,少量木本根系 150~200 B2层 潮,棕黄色,重壤,块状,结实,偶见木本根系 表 2 新立村典型黑土土壤剖面描述
Table 2. Description of typical black soil profile in Xinghai Village
距表层深度/cm 发生层 详细描述 0~20 AP层 润,黑色,中壤,有团粒结构,较松,多根孔,含大量草根和木本根系 20~40 A层 润,棕黑色,中壤,有团粒结构,含大量木本根系 40~70 B1层 润,棕黑色,中-重壤,有团粒结构,较紧实,含较多木本根系 70~120 B2层 润,棕黄色,重壤,有小团块结构,紧实,少量木本根系 120~180 B3层 潮,棕黄色,重壤,块状,结实,偶见木本根系 表 3 PM1908和PM1910典型黑土剖面有机碳、Δ14C及14C表观年龄结果
Table 3. Apparent age of organic carbon, Δ14C and 14C in typical black soil profile of PM1908 and PM1910
样品编号 深度/cm C/% Δ14C/‰ N/% 14C
年龄
/(a B.P.)σ-14C
年龄
/a样品编号 深度/cm C/% Δ14C/‰ N/% 14C
年龄
/(a B.P.)σ-14C
年龄
/aPM1908-1 0~10 2.44 -39.6 0.18 260 20 PM1910-1 0~10 1.89 -127.3 0.15 1025 25 PM1908-2 10~20 1.28 -173.7 0.10 1465 25 PM1910-2 10~20 1.79 -130.6 0.15 1055 25 PM1908-3 20~30 1.09 -250.0 0.10 2245 40 PM1910-3 20~30 1.70 -123.4 0.14 990 20 PM1908-4 30~40 0.95 -365.9 0.08 3595 35 PM1910-4 30~40 1.22 -342.4 0.10 3300 30 PM1908-5-2 40~50 0.87 -449.3 0.07 4725 25 PM1910-5 40~50 1.05 -445.1 0.08 4665 35 PM1908-6 50~60 0.84 -518.9 0.07 5810 40 PM1910-6 50~60 0.89 -530.9 0.07 6015 40 PM1908-7 60~70 0.88 -535.0 0.07 6085 35 PM1910-7 60~70 0.68 -605.5 0.06 7400 70 PM1908-8-1 70~80 0.57 -597.0 0.06 7230 60 PM1910-8-1 70~80 0.53 -626.8 0.05 7850 50 表 4 白春村典型黑土土壤剖面PM1908和PM1910元素分析结果
Table 4. Major and trace elements contents of typical black soil PM1908 and PM1910 profile in Baichun Village
样号 深度/cm 主量元素含量/% 微量元素含量/10-6 Sr/Cu Mg/Ca Al2O3/MgO FeO/MnO FeO MnO MgO CaO Al2O3 Sr Cu PM1908-1 0-10 2.01 0.105 1.20 1.35 14.02 187 21.7 8.62 0.75 11.64 19.16 PM1908-2 10-20 2.24 0.094 1.34 1.37 14.41 184 23.1 7.99 0.82 10.72 23.87 PM1908-3 20-40 2.27 0.089 1.37 1.27 14.63 176 23.8 7.38 0.91 10.69 25.58 PM1908-4 40-60 2.31 0.082 1.44 1.22 14.57 177 21.7 8.16 0.99 10.13 28.22 PM1908-5 60-80 2.32 0.075 1.48 1.21 14.82 177 23.0 7.69 1.03 10.03 31.04 PM1908-6 80-100 2.38 0.074 1.53 1.25 14.92 180 24.7 7.30 1.03 9.72 32.31 PM1908-7 100-120 2.45 0.094 1.58 1.30 15.05 189 26.4 7.15 1.02 9.52 25.96 PM1908-8 120-140 2.33 0.098 1.43 1.24 15.07 175 27.5 6.38 0.97 10.53 23.81 PM1908-9 140-160 2.31 0.118 1.43 1.29 14.82 184 26.4 6.98 0.93 10.38 19.67 PM1908-10 160-180 2.23 0.094 1.37 1.27 14.59 182 27.5 6.63 0.91 10.63 23.63 PM1910-1 0-10 2.09 0.109 1.24 1.47 13.67 193 21.7 8.91 0.71 11.03 19.11 PM1910-2 10-20 2.18 0.109 1.28 1.37 13.81 191 22.2 8.62 0.78 10.81 20.05 PM1910-3 20-40 2.12 0.089 1.26 1.21 14.18 175 22.0 7.95 0.87 11.25 23.97 PM1910-4 40-60 2.30 0.074 1.40 1.18 14.61 179 21.8 8.20 1.00 10.41 30.95 PM1910-5 60-80 2.36 0.082 1.45 1.18 14.91 180 24.3 7.41 1.03 10.28 28.88 PM1910-6 80-100 2.41 0.093 1.49 1.20 14.99 181 25.1 7.23 1.04 10.09 26.04 PM1910-7 100-120 2.37 0.100 1.48 1.22 14.84 186 24.9 7.46 1.02 10.00 23.67 PM1910-8 120-140 2.39 0.126 1.45 1.24 14.67 189 26.0 7.25 0.98 10.10 18.98 PM1910-9 140-160 2.42 0.106 1.43 1.20 14.94 179 25.9 6.91 1.01 10.42 22.82 PM1910-10 160-180 2.40 0.107 1.40 1.17 15.07 174 25.5 6.82 1.01 10.77 22.53 -
[1] 沈承德, 刘东生, 彭少麟, 等. 鼎湖山自然保护区森林土壤14C测定及14C示踪初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(16): 1775-1780. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290029
[2] 邢长平, 沈承德, 孙彦敏, 等. 鼎湖山亚热带森林土壤有机质14C年龄初步研究[J]. 地球化学, 1998, 27(5): 493-499. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1998.05.011
[3] 宁有丰, 刘卫国, 安芷生. 甘肃西峰黄土-古土壤剖面的碳酸盐与有机碳的碳同位素差值(△δ13C)的变化及其古环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(15): 1828-1832. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/kxtb200615015
[4] 沈承德, 易惟熙, 孙彦敏, 等. 鼎湖山森林土壤14C表观年龄及δ13C分布特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(4): 335-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200004003.htm
[5] Powlson D S, Gregory P J, Whalley W R, et al. Soil management in relation to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem services[J]. Food Policy, 2011, 36: S72-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2010.11.025
[6] Jiang Y F, Guo X, Sun K, et al. Spatial variabil-ity of farmland soil C/N ratio of Jiangxi Province[J]. Environ. Sci., 2017, 38: 3840-3850.
[7] 史文娇, 汪景宽, 魏丹, 等. 黑龙江省南部黑土区微量元素空间变异及影响因子——以双城市为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(2): 342-347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.02.021
[8] 贾树海, 张佳楠, 张玉玲, 等. 东北黑土区旱田改稻田后土壤有机碳、全氮的变化特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(7): 1252-1262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNYK201707008.htm
[9] 韩晓增, 李娜. 中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
[10] Song Y H, Dai H M, Yang F C, et al. A Preliminary Study on Soil Degradation and Nutrient Imbalance of Typical Black Soil in Northeast China[C]//Proceedings of The 6th Academic Conference of Geology Resource Management and Sustainable Development, 2018, 12: 328-335.
[11] Song Y H, Dai H M, Yang F C, et al. Temporal and Spatial Change of Soil Organic Matter and pH in Cultivated Land of the Songliao Plain in Northeast China during the Past 35 Years[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(supp. 1): 142-143.
[12] 崔明, 张旭东, 蔡强国, 等. 东北典型黑土区气候、地貌演化与黑土发育关系[J]. 地理研究, 2008, 27(3): 527-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ200803008.htm
[13] 孙立新, 张云, 张天福, 等. 鄂尔多斯北部侏罗纪延安组、直罗组孢粉化石及其古气候意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(1): 32-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201701004.htm
[14] 郑月娟, 张健, 张海华, 等. 大兴安岭中段晚二叠世林西组介形虫化石及环境意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(6): 1776-1786. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202006013.htm
[15] 陈铁梅. 14C测年与用于研究四万年来的全球变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, (2): 181-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199002008.htm
[16] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 东北松辽平原典型黑土-古土壤剖面AMS14C年龄首次报道[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(6): 1926-1927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006027.htm
[17] 杨胜天. 道库恰耶夫与土壤地理学的研究方法[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1992, 1: 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NATR199201002.htm
[18] 高瑞琪, 赵传本, 乔秀云, 等. 松辽盆地白垩纪石油地层孢粉学[J]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 20-100.
[19] 崔巧玉, 赵艳. 大兴安岭阿尔山天池湖泊沉积物记录的全新世气候突变[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(6): 1346-1356.
[20] Lermanm A. Lakes: chemistry, geology, physics[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978: 79-83.
[21] 初本君, 高振操, 等. 黑龙江省第四纪地质与环境[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989.
[22] 唐克丽, 贺秀斌. 黄土高原全新世黄土-古土壤演替及气候演变的再研讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(2): 129-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200402001.htm
[23] 张玉兰, 杨永兴. 中全新世以来黑龙江同江地区的孢粉组合与植被、气候演化[J]. 地理科学, 2002, 22(4): 426-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200204007.htm
[24] 王秀玲, 介冬梅, 李瑛. 下辽河平原全新世孢粉组合与古气候演化研究[J]. 河南科学, 2010, 28(7): 794-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201007012.htm
[25] 赵超, 李小强, 周新郢, 等. 北大兴安岭地区全新世植被演替及气候响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2016, 46(6): 870-880. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201606011.htm
[26] 裘善文, 孙广友, 夏玉梅, 等. 中国东北平原第四纪自然环境形成与演化[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨地图出版社, 1990: 60-67.
[27] 赵福岳. 松辽平原第四纪地质历史演化规律研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2010, (86)增刊: 152-158.
[28] 宋运红, 张哲寰, 杨凤超, 等. 黑龙江海伦地区垦殖前后典型黑土剖面主要养分元素垂直分布特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 26(6): 543-549. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202006006.htm
[29] 韩晓萌, 戴慧敏, 梁帅, 等. 黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 556-563. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202006008.htm
-




 下载:
下载: