First discovery of the siliceous sponge spicules from the Middle Triassic Luoping Biota, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
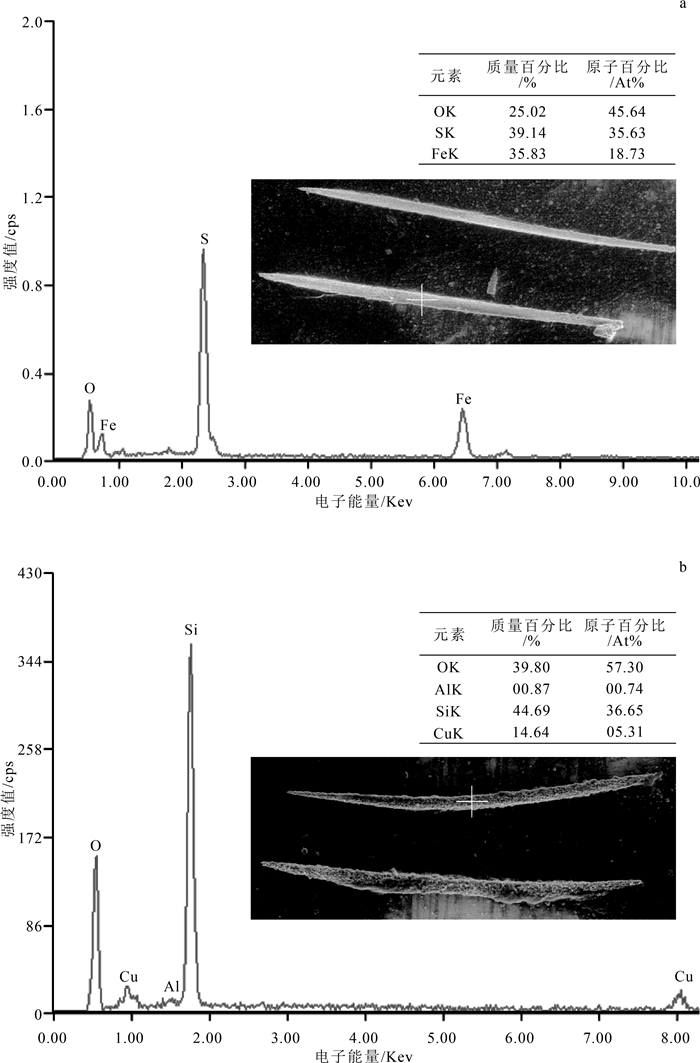
在云南罗平生物群中新发现的硅质海绵骨针化石, 包括单轴骨针和四轴骨针两大类, 其中四轴骨针包含后三叉骨针、前三叉骨针和棘状骨针3种类型。海绵骨针形态保存完整, 并发育微细的轴管构造。扫描电镜能谱(EDS)分析表明, 骨针的构成成分为Si和O元素。骨针的形态类型和组成元素表明, 它们属于普通海绵纲。海绵骨针在罗平生物群化石库中的发现, 显示海绵动物也曾是该生物群中的一员, 丰富了此生物群门类的多样性。
Abstract:Two types of siliceous sponge spicules have been discovered from Luoping Biota from Yunnan Province, southwest China, including the monaxons and tetractines which contains anatriaene, protriaene and calthrops three forms.The spicules are well-preserved with the micro-structure of axial canal.The spicules are composed of the elements of silicon and oxygen by testing with Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS).The element compositions and the types of the spicules indicate that they belong to the Demospongea.These fossil spicules are the first reported in Luoping Biota, they indicate that the sponges used to live together with other fossils in Luoping Biota, and increasing the diversity of this biota.
-
Key words:
- Middle Triassic /
- sponge spicules /
- Luoping Biota /
- Yunnan Province
-

-
[1] Yin Z, Zhu M, Davidson E H, et al. Sponge grade body fossil with cellular resolution dating 60 Myr before the Cambrian[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(12): 1453-1460.
[2] Li C W, Chen J Y, Hua T E. Precambrian Sponges with Cellular Structures[J]. Science, 1998, 279(5352): 879-882. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5352.879
[3] Butler P E. Morphologic classification of sponge spicules, with descriptions of siliceous spicules from the Lower Ordovician Bellefonte dolomite in Central Pennsylvania[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 1961, 35(1): 191-200.
[4] 张维. 海绵的分类, 演化及其地质意义[J]. 古生物学报, 1991, 30(6): 772-785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX199106015.htm
[5] 刘桂春. 华南二叠纪末硅质海绵骨针分类、演化及灭绝原因[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)硕士学位论文, 2009.
[6] 陈方, 董熙平. 湖南西部中寒武世形态变异海绵骨针化石[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 44(6): 883-889. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2008.06.009
[7] Zhang X, Pratt B R. New and extraordinary Early Cambrian sponge spicule assemblage from China[J]. Geology, 1994, 22(1): 43-46. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0043:NAEECS>2.3.CO;2
[8] 刘桂春, 冯庆来, 顾松竹. 华南二叠纪末深水硅质海绵骨针灭绝模式和灭绝过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2008, 38(12): 1533-1542. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2008.12.007
[9] Chen A, Müller W E G, Hou X, et al. New articulated protospongiid sponges from the early Cambrian Chengjiang biota[J]. Palaeoworld, 2015, 24(1/2): 46-54.
[10] Yang X L, Zhao Y L, Babcock L E, et al. Siliceous spicules in a vauxiid sponge (Demospongia) from the Kaili Biota(Cambrian Stage 5), Guizhou, South China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42945. doi: 10.1038/srep42945
[11] Li L, Janussen D, Zhan R, et al. Oldest known fossil of Rossellids (Hexactinellida, Porifera) from the Ordovician–Silurian transition of Anhui, South China[J]. Paläontologische Zeitschrift, 2019, 93(4): 559-566. doi: 10.1007/s12542-019-00452-3
[12] 吴熙纯. 四川盆地西部晚三叠世卡尼期地层及海绵化石一新科[J]. 古生物学报, 1989, 28(6): 766-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX198906008.htm
[13] 吴熙纯. 川西北晚三叠世的灯海绵动物群[J]. 古生物学报, 1990, 29(3): 349-363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX199003010.htm
[14] Stiller F. Sponge from the lower Upper Anisian (Middle Triassic) of Bangtoupo near Qingyan, SW-China[J]. Münstersche Forschungen zur Geologie und Paläontologie, 1998, 85: 251-271.
[15] 张启跃, 周长勇, 吕涛, 等. 云南罗平中三叠世安尼期生物群的发现及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(4): 523-526. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.04.011
[16] 张启跃, 周长勇, 吕涛, 等. 云南中三叠世罗平生物群地层时代的厘定: 来自牙形石的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2009, 39(3): 300-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200903006.htm
[17] 黄金元, 张克信, 张启跃, 等. 云南罗平中三叠世大凹子剖面牙形石生物地层及其沉积环境研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2009, 26(3): 211-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT200903002.htm
[18] 李国祥, 赵鑫. 吉林大阳岔寒武系—奥陶系界线剖面冶里组海绿石化海绵骨针化石[J]. 古生物学报, 2009, 48(1): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200901002.htm
[19] Stiller F. Echinoid Spines from the Anisian (Middle Triassic) of Qingyan, South-western China[J]. Palaeontology, 2001, 44(3): 529-551.
[20] Li L, Feng H, Janussen D, et al. Unusual Deep Water sponge assemblage in South China-Witness of the end-Ordovician mass extinction[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 16060.
[21] 白建科, 张启跃, 黄金元, 等. 云南罗平上石坎剖面中三叠世层序地层及沉积相分析[J]. 地层学杂志, 2011, 35(3): 278-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201103006.htm
[22] Ma Z, Hu S, Liu X, et al. The link between exceptional fossil preservation and palaeo-redox conditions in the Middle Triassic Luoping Biota from South China[J]. Geological Journal, 2021, 56(12): 6231-6244.
[23] 谢韬, 胡世学, 周长勇, 等. 含罗平生物群层位锶同位素组成与演化[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(3): 642-650.
[24] 黄金元, 胡世学, 张启跃, 等. 云南中三叠世罗平生物群中海参骨片化石的发现[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(1): 139-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201301026.htm
[25] 邓占球, 孔磊. 贵州青岩中三叠统化石海绵[J]. 古生物学报, 2005, 44(2): 283-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200502008.htm
[26] 杨荣军, 刘树根, 吴熙纯, 等. 川西上三叠统海绵生物礁的分布及其控制因素[J]. 地球学报, 2009, 30(2): 227-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200902013.htm
-




 下载:
下载: