Lithologic classification method based on multi-source remote sensing and aero geophysical data
-
摘要:
遥感影像可以获取地表岩性的光谱、色调、纹理等信息,但其所提取的信息局限于地表,对深层地质问题解释并无明显优势;航空物探数据则对地下深部异常体信息的提取更具优势。单一某类数据难以满足基础地质、资源勘查等方面复杂应用的需求。因此,提出一种遥感与航空物探信息联合分析方法,以新疆某地为研究区,结合遥感与航空物探多源数据特征,基于随机森林方法对研究区岩性进行分类。结果表明,与使用单一某类数据相比,遥感与航空物探信息联合分析方法能提高岩性分类精度。该方法对于推动遥感与航空物探技术在地质填图中的精细化应用,具有一定实用价值与指导意义。
Abstract:Remote sensing images can acquire the spectrum, tone, texture and other information of the surface rocks, but the extracted information is limited to the surface and has no obvious advantage in the interpretation of deep geological information.Aero geophysical data has more advantages in extracting information of underground abnormal bodies. A single type of data cannot meet the needs of complex applications in basic geology and resource exploration.Therefore, a combined method of remote sensing and aero geophysical analysis was proposed. A certain area in Xinjiang was taken as the study area to classify the lithology through the analysis of multi-source remote sensing images and aero geophysical data based on the random forest method.The results show that the proposed method can improve the accuracy of lithologic classification in the study area compared with a single type of data.The proposed method has certain practical value and guiding significance in promoting the fine application of remote sensing and aero geophysical exploration technology in geological mapping.
-
Key words:
- remote sensing /
- geophysics /
- joint /
- multi-source features /
- lithologic classification /
- geological survey engineering
-

-
表 1 遥感与物探信息特征提取
Table 1. Feature extraction from remote sensing and geophysical data
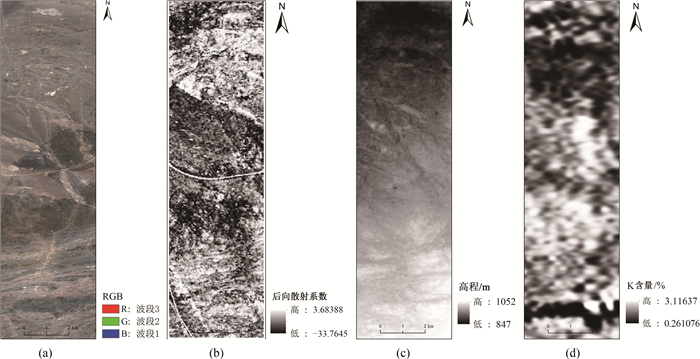
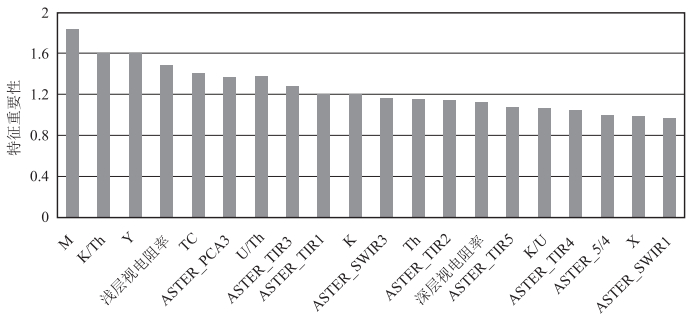
特征类型 特征参数 数据源 遥感信息特征 光谱特征 VNIR1-3, SWIR1-6, TIR1-5 ASTER 波段比值 2/1, 4/3, 5/3, 5/4, 5/6, 5/3+1/2, 9/8, (4+6)/5, (5+7)/6, (7+9)/8 主成分分析 PC1-PC9 纹理特征 均值,方差,同质性,反差,差异性,熵,二阶矩,相关性 GF-2 地形特征 TPI, TRI, Roughness DEM 空间坐标信息 X, Y 后向散射系数 VV, VH Sentinel-1 物探信息特征 化极磁场 化极磁场值M 1:2.5万航空放射性测量 伽玛能谱 U, Th, K与总道计数率(TC) 1:2.5万频率域航电测量 比值特征 K/U, K/Th, U/Th 电阻率 视电阻率值 1:2.5万航空磁测 表 2 岩性分类特征组合
Table 2. Different feature combination for lithology classification
组号 特征组合 特征个数/个 A 遥感信息特征 48 B 物探信息特征 10 C 遥感信息和航空物探信息联合特征 58 表 3 岩性分类样本选取
Table 3. Sample selection for lithology classification
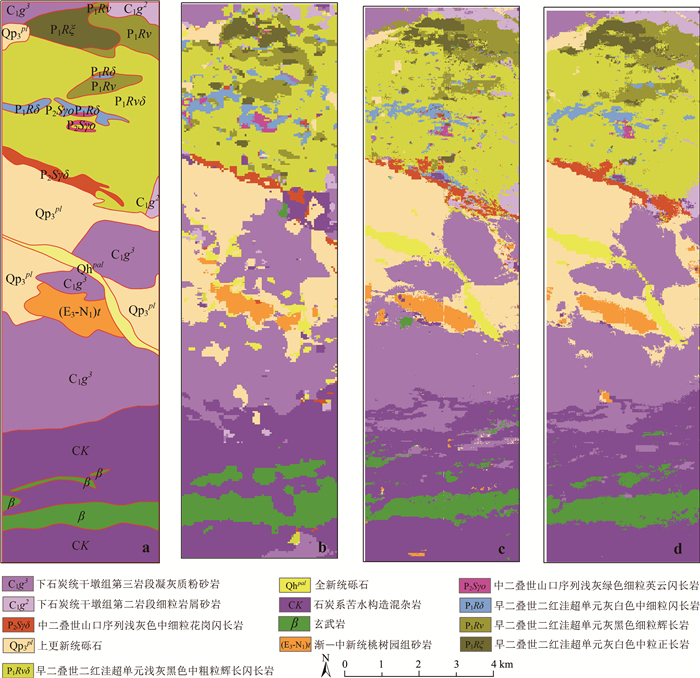
类别 训练样本/个 验证样本/个 下石炭统干墩组第二岩段细粒岩屑砂岩(C1g2) 162 107 石炭系下石炭统干墩组第三岩段凝灰质粉砂岩(C1g3) 1275 512 早二叠世二红洼超单元灰白色中粒正长岩(P1Rξ) 213 135 早二叠世二红洼超单元灰黑色细粒辉长岩(P1Rν) 324 207 早二叠世二红洼超单元灰白色中细粒闪长岩(P1Rδ) 171 117 早二叠世二红洼超单元浅灰黑色中粗粒辉长闪长岩(P1Rvδ) 912 549 中二叠世山口序列浅灰绿色细粒英云闪长岩(P2Sγo) 46 34 中二叠世山口序列浅灰色中细粒花岗闪长岩(P2Sγδ) 152 145 上更新统砾石(QP3pl) 1130 567 全新统砾石(Qhpal) 161 232 渐—中新统桃树园组砂岩(E3-N1)t 244 214 石炭系苦水构造混杂岩(CK) 1540 498 玄武岩(β) 597 301 总数 6927 3618 表 4 不同特征组合岩性分类的精度对比
Table 4. Accuracy comparison of lithology classification of different feature combinations
组号 特征组合 RF 总体精度/% Kappa/% A 遥感信息特征 70.95 67.06 B 物探信息特征 65.48 60.81 C 遥感和航空物探信息联合特征 80.29 77.74 -
[1] Abrams M J, Ashley R P, Rowan L C, et al. Mapping of hydrothermal alteration in the Cuprite mining district, Nevada, using aircraft scanner images for the spectral region 0.46 to 2.36μm[J]. Geology, 1977, 5(12): 713-718. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1977)5<713:MOHAIT>2.0.CO;2
[2] Rowan L C, Goetz A F H, Ashley R P. Discrimination of hydrothermally altered and unaltered rocks in visible and near infrared multispectral images[J]. Geophysics, 1977, 42(3): 522-535. doi: 10.1190/1.1440723
[3] Crosta A, Moore J M M. Enhancement of Landsat Thematic Mapper imagery for residual soil mapping in SW Minais Gerais State, Brazil: a prospecting case history in Greenstone belt terrain[C]//Proceedings of the 7th ERIM Thematic Conference: Remote sensing for exploration geology, 1989: 1173-1187.
[4] Ruiz-armenta J R, Prol-ledesma R M. Techniques for enhancing the spectral response of hydrothermal alteration minerals in Thematic Mapper images of Central Mexico[J]. Int. J. Remote Sens., 1998, 19(10): 1981-2000. doi: 10.1080/014311698215108
[5] Guha A, Ghosh B, Vinod K, et al. Implementation of reflection spectroscopy based new ASTER indices and principal components to delineate chromitite and associated ultramafic-mafic complex in parts of Dharwar Craton, India[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56: 1453-1468. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.043
[6] Masoumi F, Eslamkish T, Abkar A A, et al. Integration of spectral, thermal, and textural features of ASTER data using Random Forests classification for lithological mapping[J]. J. Afr. Earth Sci., 2017, 129: 445-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.01.028
[7] Kassouk Z, Thouret J-C, Gupta A, et al. Object-oriented classification of a high-spatial resolution SPOT5 image for mapping geology and landforms of active volcanoes: Semeru case study, Indonesia[J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 221: 18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.04.022
[8] Kruger J, Westermann R. Linear algebra operators for GPU implementation of numerical algorithms[J]. ACM Transaction on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 908-916. doi: 10.1145/882262.882363
[9] Enton B. Mineral mapping in the Kap Simpson complex, central East Greenland, using HyMap and ASTER remote sensing data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2011, 47(1): 60-73. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2010.08.021
[10] 方迎尧, 王卫平, 肖刚毅, 等. 频率域航空电磁法岩性地质单元填图技术[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(3): 308-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201003010.htm
[11] 丁志强, 程志平, 李飞, 等. 频率域航空电磁法视电阻率转换在岩性构造填图中的应用[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2013, 33(1): 45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2013.01.008
[12] Youssef M, Elkhodary S T. Utilization of airborne gamma ray spectrometric data for geological mapping, radioactive mineral exploration and environmental monitoring of southeastern Aswan city, South Eastern Desert, Egypt[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2013, 195: 1689-1700. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt375
[13] Zhang H, Jia P, Zhang X, et al. The application of airborne geophysics data for rapid regional geological mapping in Northwestern Angola[J]. Sains Malaysiana, 2017, 46(11): 2109-2118. doi: 10.17576/jsm-2017-4611-11
[14] Maacha L, Jaffal M, Jarni A, et al. A contribution of airborne magnetic, gamma ray spectrometric data in understanding the structure of the Central Jebilet Hercynian massif and implications for mining[J]. J. Afr. Earth Sci., 2017, 134: 389-403. . doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.07.012
[15] Akinlalu A A, Adelusi A O, Olayanju G M, et al. Aeromagnetic mapping of basement structures and mineralisation characterisation of Ilesa Schist Belt, Southwestern Nigeria[J]. J. Afr. Earth Sci., 2018, 138: 383-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.11.033
[16] Mohammad G A, Atef A M I, Ahmed A E, et al. Analysis and interpretation of aeromagnetic data for Wadi Zeidum area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt[J]. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 2018, 27: 285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpe.2017.04.002
[17] Ranjbar H, Masoumi F, Carranza E J M. Evaluation of geophysics and space borne multispectral data for alteration mapping in the Sar Cheshmeh mining area, Iran[J]. Int. J. Remote Sens., 2011, 32(12): 3309-3327. doi: 10.1080/01431161003745665
[18] Hewson R, Robson D, Mauger A, et al. Using the Geoscience Australia-CSIRO ASTER maps and airborne geophysics to explore Australian geoscience[J]. Journal of Spatial Science, 2015, 60(2): 207-231. doi: 10.1080/14498596.2015.979891
[19] 王东明, 田世攀, 张昱, 等. 森林-沼泽浅覆盖区地质填图方法试验——以黑龙江1: 5万望峰公社幅为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(5): 782-797. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210513&flag=1
[20] 王涛, 计文化, 胡健民, 等. 专题地质填图及有关问题讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(5): 633-641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160501&flag=1
[21] 胡健民, 陈虹, 邱士东, 等. 覆盖区区域地质调查(1: 50000)思路、原则与方法[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(12): 4291-4312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202012002.htm
[22] 廖桂香, 李振辉. 航空物探方法(航电、航磁、航放)解决的地质问题实例四则[J]. 贵州地质, 2013, 30(3): 213-218 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2013.03.008
[23] 祁程, 田宇, 沈正新, 等. 小兴安岭成矿带航放场特征[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(增4): 53-54 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2017S1029.htm
[24] 张文斌. 高精度航空物探综合测量在地质填图中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, 28(4): 283-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2004.04.001
[25] 史静静, 杨琳, 曾灿英, 等. 土壤制图中多目标属性的环境因子及其尺度选择——以黑龙江鹤山农场为例[J]. 地理研究, 2018, 37(3): 635-646. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201803015.htm
[26] 王恒, 姜亚楠, 张欣, 等. 基于梯度提升算法的岩性识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(3): 940-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202103026.htm
[27] 黄文, 王正林. 数据挖掘: R语言实践[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014: 220-222.
[28] 徐珉久. R语言与数据分析实战[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017.
-




 下载:
下载: