Application of P-S method in the shallow fine structure detection in North China Plain
-
摘要:
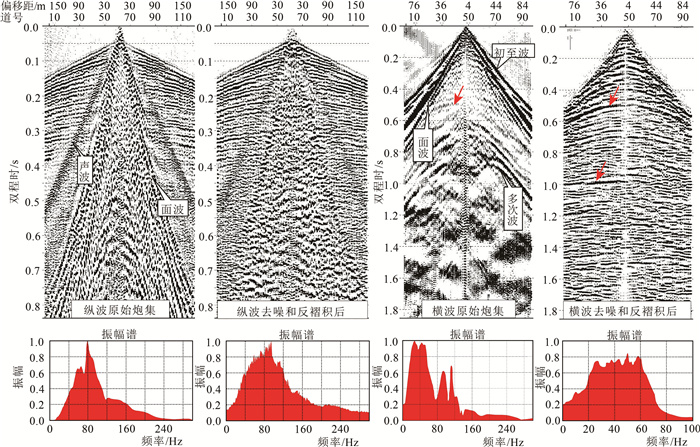
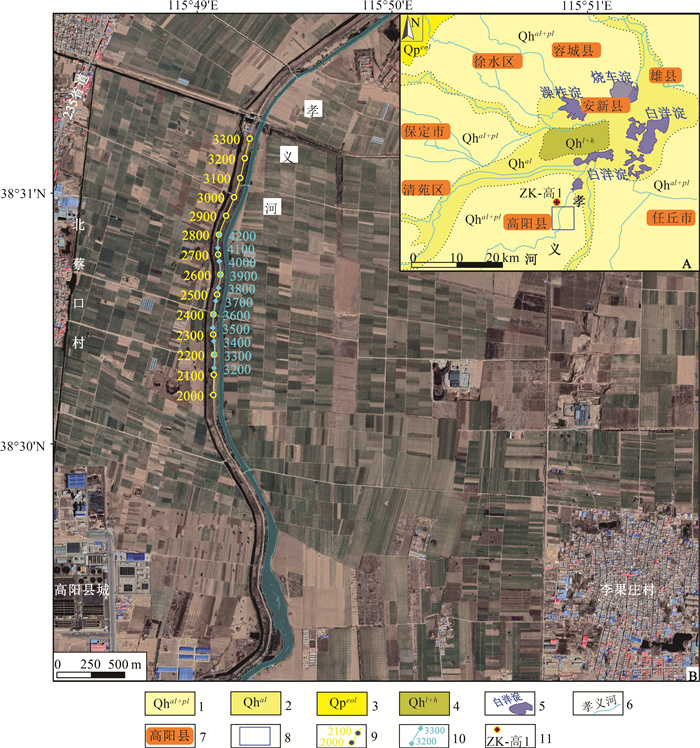
鉴于城建规划等对城市地下空间探测精度要求越来越高的的形势需求,在华北平原雄安新区附近开展了针对浅层的纵横波勘探试验研究。从方法技术层面详细阐述了野外数据采集的相关参数、数据处理流程和关键技术及其试验效果。研究获得了试验区浅层精细地质结构和速度分布特征,纵横波在深度域具有较好的对比性。纵波法在试验区最大有效探测深度达700 m,最浅探测深度为24 m,整体分辨率可达4 m,横波法最大探测深度约220 m,最浅探测深度为9 m,整体分辨率则高达1 m左右。横波弥补了浅表层纵波盲区和分辨率不足的问题,提高了浅表结构划分和断层上断点定位的精度,而纵波则弥补了横波探测深度小的缺陷。
Abstract:In view of the situation that urban planning requires more and more precision of urban underground space detection, a pilot study of shallow P-S wave exploration was carried out near the Xiong'an New Area in North China Plain.The parameters of field data acquisition, data processing flow, key techniques and test results are described in detail from the aspect of method and technology.The study has resulted in fine geological structure and velocity distribution of the shallow layer in the test area, and P -wave and S-wave section have good contrast in the depth domain.In the study area, the detective depth of P-wave method is about 700 m, and the lowest detective depth is 24 m, the overall resolution is 4 m; the S- wave detective depth is about 220 m, the shallowest detective depth is 9 m, and the overall resolution is about 1 m.The S-wave makes up for the deficiency of the blind area and insufficient resolution of P-wave in the shallow layer, which improves the accuracy of the shallow structure division and fault location.The P-wave makes up for the defect of shallow detecting depth of S-wave.
-

-
[1] 赵镨, 姜杰, 王秀荣. 城市地下空间探测关键技术及发展趋势[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2017, 29(9): 61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.09.12
[2] 葛伟亚, 王睿, 张庆, 等. 城市地下空间资源综合利用评价工作构想[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 1601-1608. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211001&flag=1
[3] 刘婷, 王寒梅, 史玉金, 等. 特大型城市地下空间资源承载能力评价方法探索——以上海市为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10): 1609-1616. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211002&flag=1
[4] 徐明才, 高景华, 刘建勋, 等. 城市地震勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
[5] 李华强, 刘桂梅, 王建新, 等. 高分辨率二维地震勘探在城市活动断层探测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2013, 24(2): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201302015.htm
[6] 谢樊, 王海燕, 侯贺晟, 等. 中亚造山带东段浅表构造速度结构: 深地震反射剖面初至波层析成像的揭露[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(2): 584-596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202102024.htm
[7] 徐明才, 高景华, 刘建勋, 等. 应用于城市活动断层调查的地震方法技术[J]. 中国地震, 2005, 21(1): 17-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.01.002
[8] 李燕, 刘保金, 酆少英, 等. 利用地震折射和反射波资料研究银川盆地浅部结构和隐伏断裂[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(8): 3096-3109. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85401-1017112542.htm
[9] 周月玲, 彭远黔, 陈建强, 等. 河西务断裂活动性的综合探测研究[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2018, 13(3): 610-618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY201803013.htm
[10] 盯美青, 胡泽安, 李建宁, 等. 城市地下断裂构造可控震源地震勘探试验研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2017, 39(4): 565-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2017.04.18
[11] 吴双红, 白艳娟, 夏媛媛, 等. 活动断层地质勘探中的浅层反射波方法与层析成像[J]. 能源与环保, 2018, 40(4): 73-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT201804016.htm
[12] 王亚辉, 张茂省, 师云超, 等. 基于综合物探的城市地下空间探测与建模[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 83-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201902013.htm
[13] 商世杰, 丰成君, 谭成轩, 等. 雄安新区附近主要隐伏断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(6): 836-846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201906007.htm
[14] 马岩, 李洪强, 张杰, 等. 雄安新区城市地下空间探测技术研究[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(4): 535-542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202004010.htm
[15] 安好收, 罗传根. 浅层纵横波联合勘探在活动断层探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(3): 543-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201903013.htm
[16] 王小江, 张保卫, 柴铭涛, 等. 纵横波联合勘探在浅层地震中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(6): 824-835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201006030.htm
[17] 陈相府, 安西峰. 地震横波勘探及其在浅层岩土分层中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(5): 1655-1659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.05.049
[18] 顾勤平, 徐汉刚, 赵启光, 等. 纵横波联合勘探应用于栟茶河断裂活动性的调查与研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 2017, 39(4): 774-780. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.04.0774
[19] 易先进. 河北白洋淀地区晚更新世以来环境演变研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2015.
[20] 陈颙, 黄庭芳, 刘恩儒. 岩石物理学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009.
[21] 吕国军, 李红梅, 康江, 等. 河北省地质钻孔资料分析[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 2017, 38(2): 125-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGJ201702022.htm
-



 下载:
下载: