Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of the Kujinggou Graphite Deposit in Weining Beishan, Ningxia
-
摘要:
库井沟石墨矿床位于宁夏卫宁北山–内蒙古阿拉善左旗南部地区,矿体赋存于下石炭统臭牛沟组区域变质岩中,原岩为滨浅海相陆源碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩沉积建造。矿体产状与地层产状近于一致,呈平行层状分布于变质石英砂岩中,走向近东西。矿石主要为含石墨碳质板岩,固定碳含量平均为5.53%。石墨主要呈不规则鳞片状单晶或呈块状聚晶集合体产出,多数大于1 μm。石墨矿石整体表现为低Si、低碱、高烧矢量的特点,大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、Sr富集石墨矿石∑REE为101×10−6~137×10−6,平均为117×10−6,围岩的∑REE为42×10−6。石墨矿石和围岩的稀土元素分异程度较高,轻稀土元素明显富集,并都具有δEu和δCe负异常。石墨矿石的C同位素值变化很小,集中在−24.3‰~−24.0‰,表明库井沟矿床中碳质来源主要为有机物,并掺杂部分无机碳。库井沟石墨矿床属于区域变质型,滨浅海相–泻湖相沉积建造是其形成的物质基础,石墨的形成与区域变质变形作用密切相关。
Abstract:The Kujinggou graphite deposit is located in the southern area of Weining Beishan, Ningxia and Alashan Zuoqi, Inner Mongolia. The ore body is hosted in the regional metamorphic rocks of the Lower Carboniferous Chouniugou Formation, and the original rocks are sedimentary construction of shallow marine terrestrial clastic and carbonate rocks. The ore body is distributed in parallel layers in the metamorphic quartz sandstone, which is basically consistent with the stratigraphic production, with a near east-west orientation. The ore is mainly graphite-bearing carbonaceous slate with an average fixed carbon content of 5.53%. Graphite is mainly produced as irregularly scaled single crystals or as massive polycrystalline assemblages, mostly larger than 1 μm. Graphite ore is characterized by low Si, low alkali and high LOI as a whole, and trace element analysis shows enrichment of Rb, Ba and Sr. The ∑REE of graphite ore ranges from 101×10−6 to 137×10−6, with an average of 117×10−6, and the ∑REE of the host rocks is 42×10−6. The REE distribution patterns of both graphite ore and host rocks are high on the left and low on the right, and the ∑REE in graphite ore is higher than that in host rocks, which shows a high degree of REE differentiation in ore and host rocks in general, and a significant enrichment of LREE. The negative anomalies of Eu and Ce are obvious. The carbon isotope values of the graphite ore vary very little and are concentrated between −24.3‰ and −24.0‰, indicating that the carbonaceous source is mainly organic with some inorganic carbon involved. The genesis type of this deposit is regional metamorphic, and the shallow marine and lagoonal sedimentary environment makes the material basis for the graphite formation in Kujinggou, graphite formation is closely related to regional metamorphic deformation
-
Key words:
- graphite deposit /
- carbon isotope /
- ore genesis /
- Kujinggou /
- Weining Beishan
-

-
图 2 库井沟石墨矿床矿区地质略图(据张春林等,2017)
Figure 2.
图 3 库井沟石墨矿床A-A′纵剖面图(据张春林等,2017)
Figure 3.
图 7 石墨矿石La/Yb-∑REE图解(底图据Allegre et al., 1978)
Figure 7.
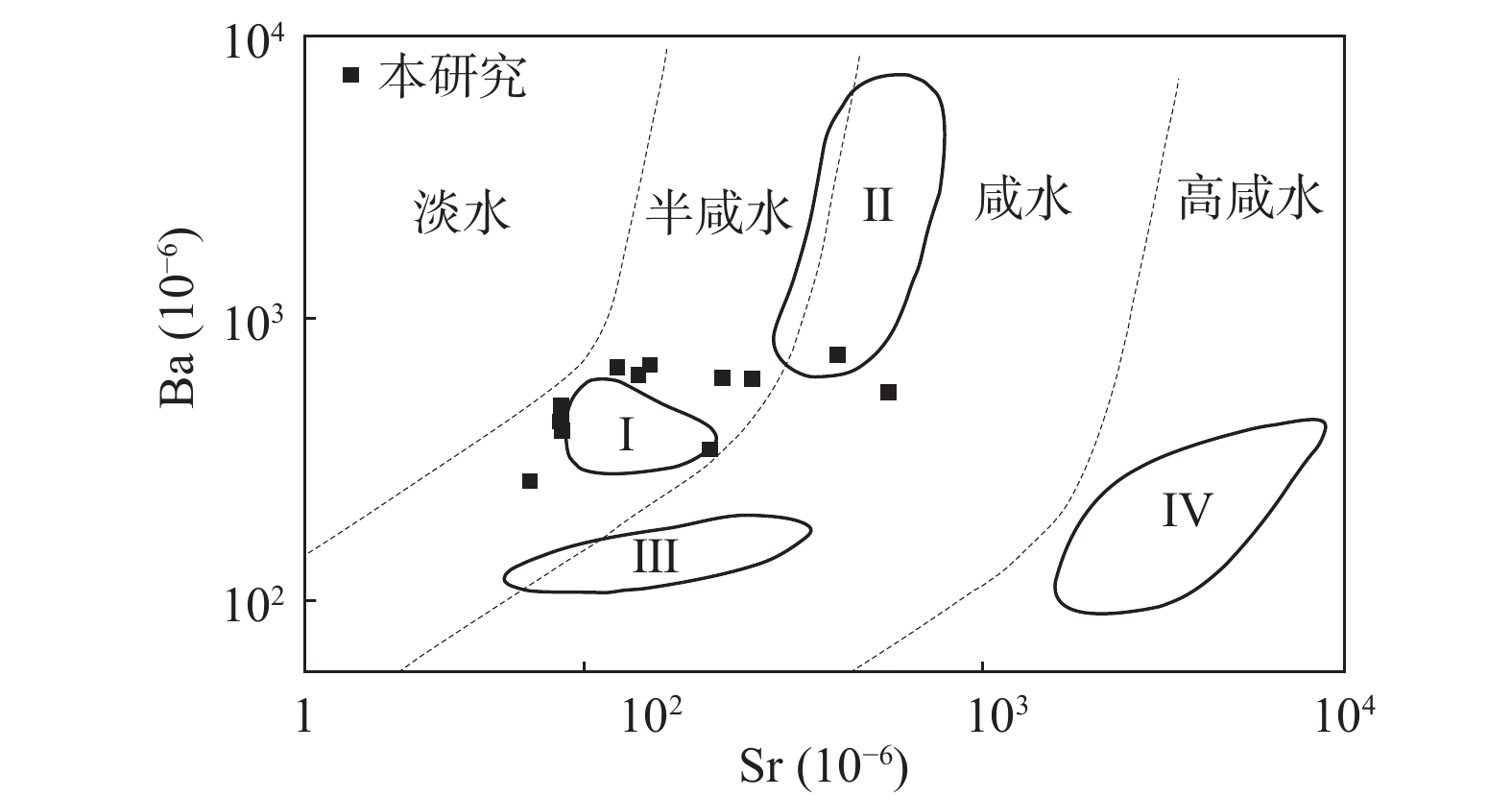
图 8 石墨矿石Ba-Sr图解(底图据王仁民等,1986)
Figure 8.
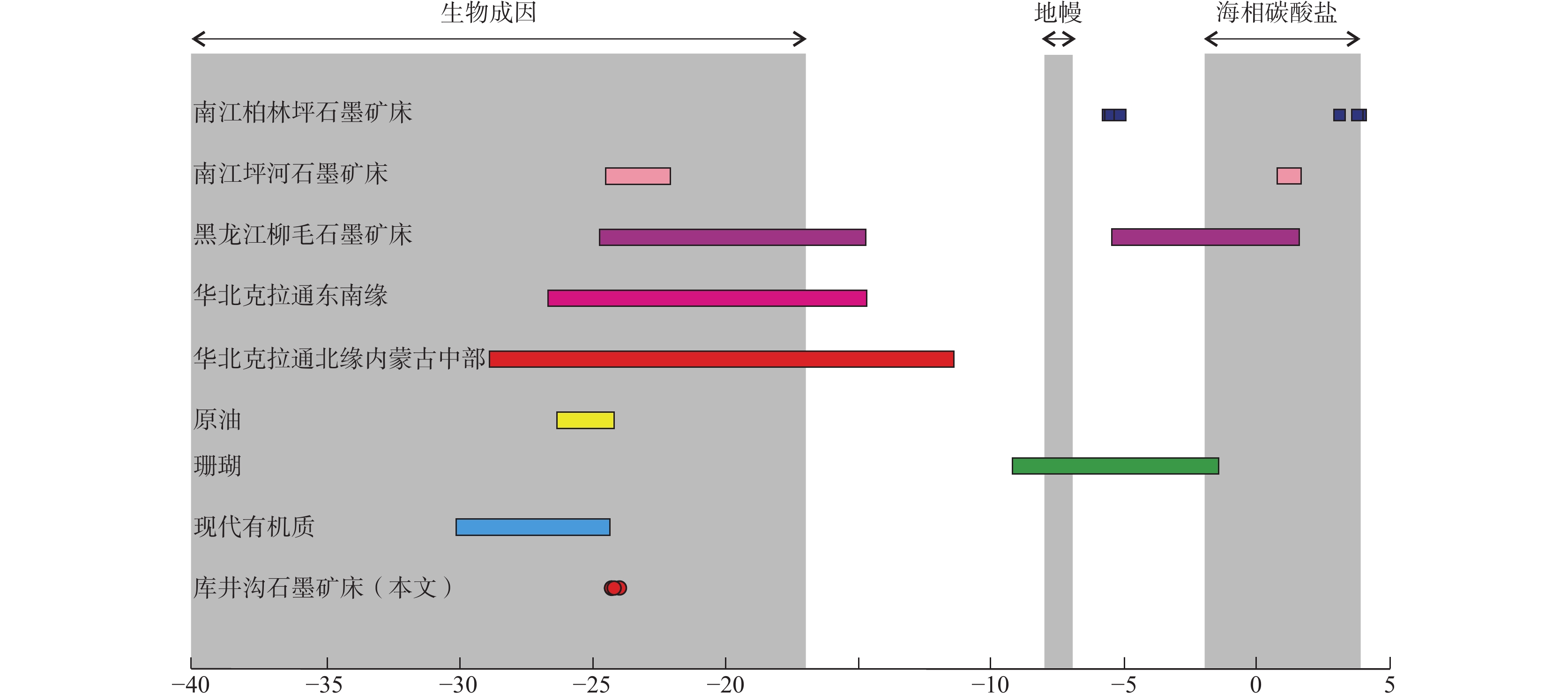
图 9 库井沟与不同地区石墨矿床及含碳物质的C同位素值特征对比(数据引自刘敬党等,2017)
Figure 9.
表 1 库井沟矿区晶质石墨矿矿体特征一览表
Table 1. Characteristics of orebodies in the Kujinggou graphite deposit
矿体
编号矿石
类型赋矿标
高(m)埋藏深
度(m)规模(m) 厚度 厚度变化
系数(%)矿体
形态产状(°) C固 品位(%) 品位变化
系数(%)长度 斜深 最小-
最大平均倾向 倾角 最小-
最大平均Ⅰ 晶质
(鳞片)
状石墨1255 ~1340 44 2103 110~721 2.19~53.0119.73 68.23 似层状 0 0~14 3.04~8.974.87 52.88 Ⅱ 1201 ~1325 102 2200 136~ 1080 2.00~123.2037.78 62.05 似层状 0 0~20 3.03~7.524.34 48.49 Ⅲ 1180 ~1248 159 400 150~322 2.00~50.4825.23 66.21 透镜状 0 2~14 4.11~7.525.50 61.35 Ⅳ 1270 ~1320 56 400 100~358 43.92~85.1757.84 24.49 透镜状 0 4~10 3.86~5.244.54 50.31 表 2 库井沟石墨矿床矿石主量元素测试结果(%)
Table 2. Major element compositions of ore in Kujinggou graphite deposit (%)
样品号 位置(m) SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 TFe2O3 K2O Na2O P2O5 TiO2 V2O5 固定碳 ZK704-DH1 33.60 55.09 0.43 1.52 19.63 6.83 3.49 0.86 0.256 0.43 0.018 2.57 ZK806-DH2 27.90 53.42 0.44 1.83 20.05 7.08 2.84 1.09 0.214 0.39 0.018 2.27 ZK808-DH1 136.40 51.25 0.61 1.83 17.85 7.62 2.89 3.26 0.298 0.39 0.019 2.39 ZK2302-DH2 63.50 53.07 0.42 1.59 18.61 7.01 2.91 2.75 0.335 0.45 0.017 2.41 ZK1506-DH1 162.90 55.73 0.39 1.48 20.60 7.50 3.04 1.50 0.197 0.35 0.021 2.25 ZK1508-DH1 109.77 55.17 0.36 1.63 20.15 5.76 3.28 0.89 0.177 0.49 0.020 2.56 ZK008-DH1 114.00 55.82 0.65 1.82 19.55 6.73 2.99 0.99 0.210 0.40 0.017 2.48 ZK1504-DH1 127.40 54.28 0.33 1.54 20.20 6.77 2.86 1.14 0.270 0.33 0.017 2.58 ZK706-DH1 68.50 55.61 0.29 1.30 20.55 5.04 3.68 0.93 0.213 0.52 0.017 2.51 ZK2001-DH1 106.77 54.34 0.39 1.80 20.19 7.07 3.03 1.09 0.242 0.36 0.019 2.57 ZK2306-DH1 86.20 54.00 0.81 1.64 17.61 7.52 2.60 2.74 0.240 0.41 0.017 2.22 ZK1104-DH1 70.60 70.98 1.99 1.32 10.76 3.99 1.87 0.48 0.072 0.44 0.013 0.51 ZK1105-DH1 83.10 55.94 1.38 2.30 19.97 6.99 2.81 1.25 0.178 0.72 0.030 1.82 XL XT DH-1 36.00 50.43 1.60 1.27 14.40 2.29 2.74 0.88 0.31 0.58 0.19 10.72 XL XT DH-2 55.70 63.33 0.33 0.33 10.66 1.74 1.74 0.32 0.37 0.42 0.12 10.65 XL XT DH-3 49.10 53.42 0.88 0.57 8.56 7.37 1.63 1.59 0.25 0.40 0.08 11.52 XL XT DH-4 38.00 44.22 0.17 0.49 19.82 4.97 3.36 1.09 0.13 0.73 0.049 4.81 XL XT DH-5 53.10 45.71 0.24 0.51 9.18 12.71 2.69 0.84 0.08 0.29 0.11 12.06 表 3 库井沟石墨矿床含矿岩石微量元素分析结果(10−6)
Table 3. Trace elements compositions of graphite ore of the Kujinggou graphite deposit (10−6)
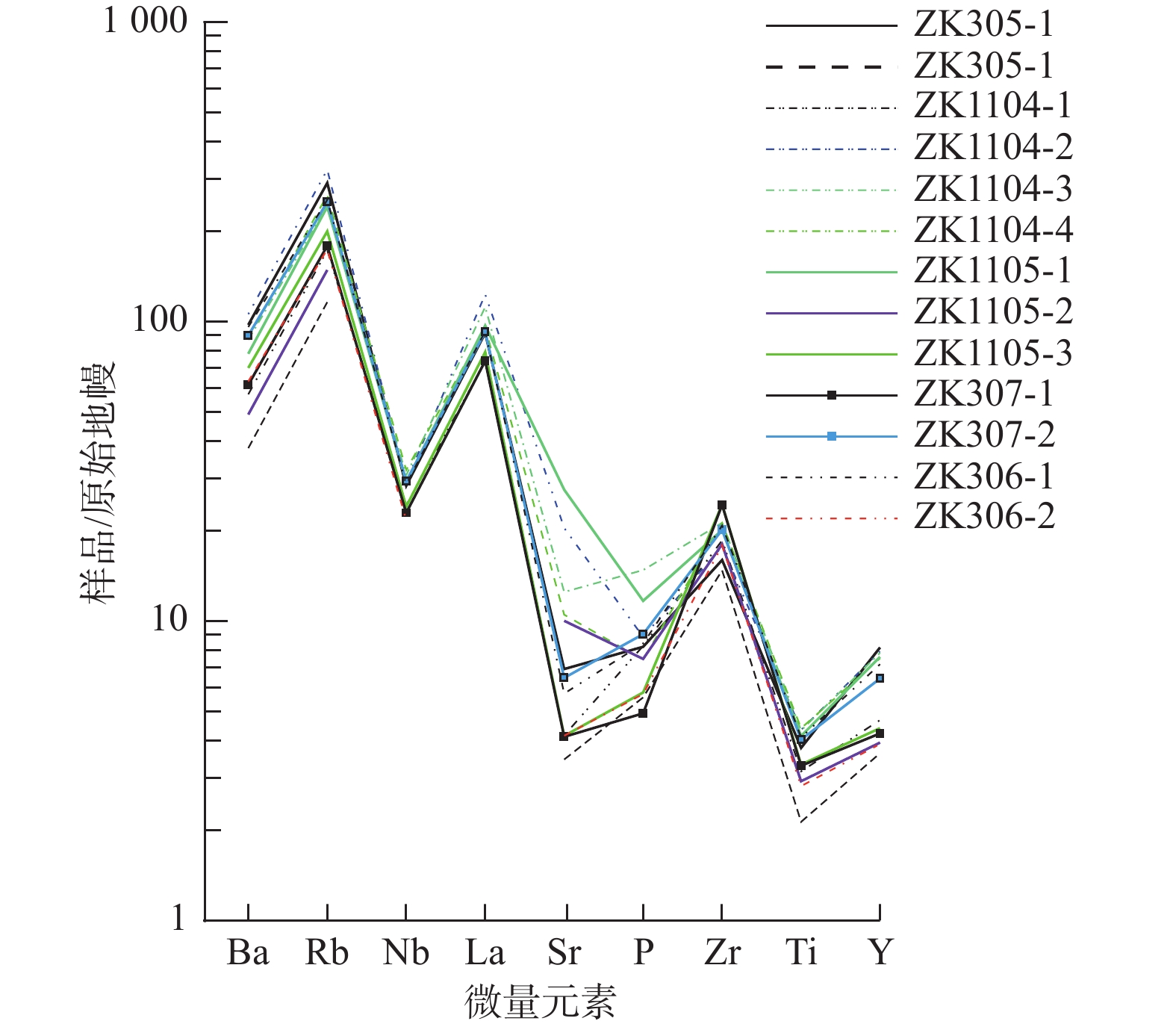
元素 ZK305-1 ZK305-2 ZK1104-1 ZK1104-2 ZK1104-3 ZK1104-4 ZK1105-1 ZK1105-2 ZK1105-3 ZK307-1 ZK307-2 ZK306-1 ZK306-2 Rb 184.5 73.8 110.0 204.3 154.8 168.1 153.7 94.5 127.2 113.8 159.5 162.0 110.8 Sr 146.1 72.9 87.7 432.3 264.2 221.9 580.1 206.4 87.4 86.8 136.5 121.0 87.5 Ba 682.1 264.4 399.9 740.7 608.2 615.6 546 342.4 489.7 430.1 628.4 671.3 441.6 Nb 20.2 / 17.4 20.8 21.9 22.8 20.8 / 17.2 16.4 20.9 20.4 15.6 Zr 179.3 165.6 208.5 198.8 238.6 238 225.8 202.5 274.6 274.1 226.4 233.6 200.5 V 72.2 21.3 32.3 88.0 77.4 86.1 95.7 44.9 32.6 31.5 76.0 86.0 36.0 Cr 81.9 33.7 59.5 84.0 82.7 92.9 98.3 50.9 51.9 50.8 82.3 81.7 45.2 Co 18.3 9.7 14.9 8.7 12.2 11.4 17 16.7 11.1 12 21.1 17.7 13.9 Ni 40.8 18.2 22.6 10.5 34.9 17 42.3 25.9 17.9 19.6 40.7 39.5 21.8 Y 37.2 16.5 21.3 36.1 35.7 34.2 34.6 17.9 20 19.2 29.3 32.7 17.7 La 63 / 50.4 84.8 76.9 65.6 66.7 / 54.4 50.8 63.6 63.9 / P 780.3 528.9 786 841.9 1407.6 706.1 1111.3 711 549.3 467.8 860 800.7 542.8 Ti 4910 2780 4100 5640 5620 5710 5380 3800 4320 4280 5230 5320 3660 Rb/Sr 1.26 1.01 1.25 0.47 0.59 0.76 0.26 0.46 1.46 1.31 1.17 1.34 1.27 Sr/Ba 0.21 0.28 0.22 0.58 0.43 0.36 1.06 0.60 0.18 0.20 0.22 0.18 0.20 Ni/Co 2.23 1.88 1.52 1.21 2.86 1.49 2.49 1.55 1.61 1.63 1.93 2.23 1.57 V/Cr 1.13 1.58 1.84 0.95 1.07 1.08 1.03 1.13 1.59 1.61 1.08 0.95 1.26 表 4 库井沟石墨矿床含矿岩石系稀土元素分析结果(10−6)
Table 4. Rare earth elements compositions of graphite ore of the Kujinggou graphite deposit (10−6)
样品号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Cd Eu Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y XL XT DH-1 30.5 32.5 9.69 30.2 6.07 5.50 1.56 1.07 3.63 1.00 2.39 0.47 2.47 0.54 18.2 XL XT DH-2 32.2 13.1 8.94 27.3 264.2 5.62 1.39 1.00 2.70 0.59 1.34 0.26 1.26 0.28 10.5 XL XT DH-3 31.5 31.8 10.6 35.1 21.9 6.41 1.64 1.23 4.45 1.21 2.82 0.55 2.52 0.55 24.2 XL XT DH-4 11.1 10.2 3.08 9.27 238.6 1.38 0.39 0.30 1.36 0.43 1.11 0.24 1.17 0.26 8.15 XL XT DH-5 15.3 16.7 8.68 26.2 1.07 3.68 1.05 0.77 2.90 0.79 1.81 0.35 1.57 0.34 15.3 表 5 库井沟石墨矿床矿石碳同位素组成测试结果
Table 5. Carbon isotope compositions of graphite ores in the Kujinggou deposit
序号 样品岩性 δ13C(‰) 1 含石墨碳质板岩 −24.0 2 含石墨碳质板岩 −24.3 3 含石墨碳质板岩 −24.3 4 含石墨碳质板岩 −24.3 5 含石墨碳质板岩 −24.2 -
[1] 艾宁, 任战利, 李文厚, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区矿床类型及成矿时代[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(05): 941-948
Ai Ning, REN Zhanli, LI Wenhou, et al. Metallogenic epoch and ore-forming types of ore deposits in Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(05): 941-948.
[2] 陈衍景, 刘丛强, 陈华勇, 等. 中国北方石墨矿床及赋矿孔达岩系碳同位素特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(2): 233-244
CHEN Yanjing, LIU Congqiang, CHEN Huayong, et al. Carbon isotope geochemistry of graphite deposits and ore-bearing khondalite series in North China: implications for several geoscientific problems [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2000, 16(2): 233-244.
[3] 陈正国, 颜玲亚, 高树学. 战略性非金属矿产资源形势分析[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2021, 2: 1–8, 23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2021.02.001
CHEN Zhengguo, YAN Yalin, GAO Shuxue. Analysis on the situation of strategic non-metallic mineral resources [J]. China Non-metallic Minerals Industry, 2021, 2: 1–8, 23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2021.02.001
[4] 程仕俊, 亢威, 周勇, 等, . 四川南江柏林坪石墨矿床成因: 岩石及 C-O 同位素地球化学约束[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2021, 41(4): 1-10
CHENG Shijun, KANG Wei, ZHOU Yong, et al. Genesis of the Bolingping graphite deposit in Nanjiangm Sichuan: constraints of lithological and C-O isotopic geochemistry [J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2021, 41(4): 1-10.
[5] 段威,唐文春,黄健华,等 .四川旺苍大河坝晶质石墨矿地质特征及成因[J].矿产与地质,2020,34(06):15-27.
DUAN Wei, TANG Wenchun, HUANG Jianhua, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Dahaba crystalline graphite deposit in Wangcang, Sichuan [J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2020, 34(6): 15-27.
[6] 郭佩, 刘池洋, 韩鹏, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘下—中侏罗统碎屑锆石 U-Pb 年代学及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(5): 892–907
GUO Pei, LIU Chiyang, HAN Peng, et al. Geochemistry of detrital zircon form the lower-middle Jurassic strata in the southwestern Ordos basin, China, and its geological significance [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(5): 892–907.
[7] 海连富, 刘安璐, 陶瑞, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子金矿床流体来源及矿床成因: 来自流体包裹体和C-H-O同位素证据[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(12): 4274-4290
HAI Lianfu, LIU Anlu, TAO Rui, et al. Source of fluid and genesis of Jinchangzi gold deposit in Weiningbeishan Ningxia: Evidence from fluid inclusions and C-H-O isotopes [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(12): 4274-4290.
[8] 霍福臣, 潘行适, 尤国林, 等. 宁夏地质概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989
HUO Fuchen, PAN Xingshi, YOU Guolin, et al. Introduction to geology of Ningxia [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1989.
[9] 李红霞, 白生明, 黄玮, 等, . 浅析宁夏卫宁北山地区石炭纪地层沉积特征及演化规律[J]. 宁夏工程技术, 2016, 15(3): 217-222
LI Hongxia, BAI Shengming, HUANG Wei, et al. A brief analysis on sedimentary features and evolvement rules of Carboniferous strata in Weining North Mountain area of Ningxia [J]. Ningxia Engineering Technology, 2016, 15(3): 217-222.
[10] 梁利东, 黄瑞. 可控源音频大地电磁测深在卫宁北山石墨调查中的应用 [J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2020, 2: 49-53.
[11] 刘敬党, 肖荣阁, 张艳飞, 等. 华北显晶质石墨矿床[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.
[12] 刘勇, 李延栋, 王彦斌, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子闪长玢岩岩脉地质特征及SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(6): 1575-1583
LIU Yong, LI Tingdong, WANG Yanbin, et al. Geological characteristics and zircon SHRIMP U-Pb data of Jinchangzi dioritic porphyrite dykes in Zhongwei city, Ningxia [J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(6): 1575-1583.
[13] 彭素霞, 陈向阳, 陈隽璐, 等. 新疆东准噶尔地区石墨矿成矿特征及成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(4): 194-201
PENG Suxia, CHEN Xiangyang, CHEN Junlu, et al. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Graphite Ore Belt in East Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(4): 194-201.
[14] 王登红. 关键矿产的研究意义、矿种厘定、资源属性、找矿进展、存在问题及主攻方向[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1189-1209
WANG Denghong. Study on critical mineral resources: significance of research, determination of types, attributes of resources, progress of prospecting, problems of utilization, and direction of exploitation [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1189-1209.
[15] 王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等. 变质岩原岩图解判别法 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1986, 4-7+163-165.
[16] 颜玲亚, 高树学, 陈正国, 等. 中国石墨矿成矿特征及成矿区带划分[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(3): 421-440
YAN Lingya, GAO Shuxue, CHEN Zhengguo, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and metallogenic zoning of graphite deposits in China [J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(3): 421-440.
[17] 杨季华, 罗重光, 杜胜江, 等. 高黏土含量沉积岩古环境指标适用性讨论. 矿物学报, 2020, 40(6): 723-733
YANG Jihua, LUO Chongguang, DU Shengjiang, et al. Discussion on the applicability of paleoenvironment index for sedimentary rocks with high clay eontet. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2020, 40(6): 723-733.
[18] 张春林,白帅龙,袁建江,等.内蒙古自治区阿拉善左旗库井沟矿区晶质石墨矿勘探报告[R].北京:中国煤炭地质总局勘查研究总院.2017.
ZHANG Chunling,BAI Shuailong,YUAN Jianjiang,et al. Exploration Report on Crystalline Graphite Ore in Kujinggou Mining Area, Alxa Left Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[R].Beijing:General Prospecting Institute of China National Administration of Coal Geology.2017.
[19] 张艳飞, 安政臻, 梁帅, 等. 石墨矿床分布特征、成因类型及勘查进展[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(1): 135-150
ZHANG Yanfei, An Zhengzhen, LIANG Shuai, et al. Distribution characteristics, genetic types and prospecting progress of graphite deposits. Geology in China [J], 2022, 49(1): 135-150.
[20] 张艳飞, 梁帅, 赵青, 等. 石墨矿床类型及显晶质石墨矿床成矿模式(Ⅰ): 成矿地质背景[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2020a, 42(1): 1-11, 18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2020.01.001
ZHANG Yanfei, LIANG Shuai, ZHAO Qing, et al. Types of graphite deposits and metallogenic patterns of phanerocrystalline graphite deposits (Ⅰ): metallogenic geological background [J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2020a, 42(1): 1-11, 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2020.01.001
[21] 张艳飞, 梁帅, 赵青, 等. 石墨矿床类型及显晶质石墨矿床成矿模式(Ⅱ): 矿石矿物及矿化特征[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2020b, 42(2): 97-105, 124
ZHANG Yanfei, LIANG Shuai, ZHAO Qing, et al. Types of graphite deposits and metallogenic patterns of phanerocrystalline graphite deposits (Ⅱ): ore minerals and mineralizing charateristics [J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2020b, 42(2): 97-105, 124.
[22] 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院. 中国区域地质志•宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018
Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Institute of Geological Survey. The regional geology of China, Ningxia [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018.
[23] 仲佳鑫, 李欢, 李鹏, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子金矿床地质特征与控矿因素分析[J]. 西北地质, 2012, 45(3): 81-92
ZHONG Jiaxin, LI Huan, LI Peng, et al. Geological Characteristics, Ore-Controlling Factors and Mineralization Law of Gold Ore in the North Mountain of Weining Area, Ningxia[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2012, 45(3): 81-92.
[24] 朱建江, 刘福来, 刘福兴, 等. 胶—辽—吉造山带辽河群石墨矿碳同位素特征及成因分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(2): 599-618 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.02.17
ZHU Jianjiang, LIU Fulai, LIU Fuxing, et al. Carbon isotope and genesis study of graphite deposits in the Liaohe group of the Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(2): 599-618. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.02.17
[25] Allegre C J, Minster J F. Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 38(1): 1-25. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1
[26] Du Y, Song H, Tong J, et al. Changes in productivity associated with algal-microbial shifts during the Early Triassic recovery of marine ecosystems [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2021, 133(1-2), 362-378. doi: 10.1130/B35510.1
[27] Hahn-Weinheimer P, Hirner, A. Isotopic evidence for the origin of graphite [J]. Geochemical Journal, 1981, 15(1): 9-15. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.15.9
[28] Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry [M]. 6th Edition. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2009, 53-107.
[29] Luque F G, Pasteris J D, Wopenka B, et al. Mineral fluid-deposited graphite: Mineralogical characteristics and mechanisms of formation [J]. American Journal of Science, 1998, 298(6): 471-498. doi: 10.2475/ajs.298.6.471
[30] Rudnick, R.L., Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust[A]. The crust[M]. Treatise on geochemistry, 2003, 3: 1−64
[31] Schidlowski M. Application of stable carbon isotopes to early biochemical evolution on Earth [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1987, 15: 47-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.15.050187.000403
[32] Schidlowski M. Carbon isotopes as biogeochemical recorders of life over 3.8 Ga of Earth history: evolution of a concept [J]. Precambrian Research, 2001, 106, 117-134. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00128-5
[33] Sharp Z. Principles of stable isotope geochemistry [M]. New Jersey:Pearson Education, 2007,1-344 .
[34] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes [J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1), 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[35] Taylor S R , Mclennan S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4), 57-72.
[36] Weis P L, Friedman I, Gleason J P, et al. The origin of epigenetic graphite: Evidence from isotopes [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(12): 2325-2332. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90086-7
[37] Zhu J J, Zhang L F, Tao R B, et al. The formation of graphite-rich eclogite vein in S. W. Tianshan (China) and its implication for deep carbon cycling in subduction zone [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 533: 119430. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119430
-




 下载:
下载: