Review on Eco-hydrological Processes of Groundwater-dependent Vegetation in NW China: Progress and Outlook
-
摘要:
植被与地下水之间的关系是人与自然和谐共生的关键科学问题。西北旱区广泛分布地下水依赖型植被,部分地区人类活动造成的水位下降已超过其生态水位阈值,导致生态功能受损,甚至植被大面积枯死,严重威胁区域经济社会可持续发展。笔者基于国内外在区域地下水依赖型植被的识别、生态韧性评价、植被-地下水协同演化以及地下水生态水位确定等4个方面的最新研究进展,总结了当前研究存在的主要问题和亟待解决的难题,并指出未来研究应当关注的重点方向。综合分析表明,西北地区流域尺度地下水依赖型植被的识别研究相对较少,而对识别结果进行地面验证的稳定同位素方法还需改进;生态韧性研究多注重地表生态与环境指标,而忽略了地下水、根系布等地下指标,缺少基于抵抗力、恢复力和适应力的生态韧性综合评价,以定性评价为主的研究不能满足生态保护修复的需要;植被−地下水协同演化研究受限于不能精准探测根系变化,根系动态探测技术及刻画根系-水源协同变化的模型有待进一步发展;生态水位主要是基于现状条件确定的静态水位,对受降水和地下水侧向补给影响下的水位变化空间差异以及植物自身适应性考虑不足,还需研究外界条件改变下的动态生态水位。通过梳理西北地区地下水依赖型植被生态水文过程研究进展,指出当前研究的薄弱研究环节和面临的问题,为进一步开展西北旱区生态水文理论研究与实践提供了依据。
-
关键词:
- 地下水依赖型植被 /
- 西北地区 /
- 生态韧性 /
- 生态水位 /
- 植被与地下水相互作用
Abstract:The relationship between groundwater and vegetation is crucial to achieve a harmonious balance between human and the natural environment. Groundwater-dependent vegetation (GDV) is extensively distributed in the arid and semi-arid regions of Northwest China. In certain areas, the decline in water table levels due to human activities has fallen below ecological water level thresholds, leading to the degradation of ecological functions and, in some cases, widespread vegetation die-off. Therefore, the sustainable development of the region's economy and society is under significant threat. A comprehensive review was conducted concerning GDV mapping, ecological resilience assessment, groundwater-vegetation co-evolution, and ecological water table. Through this review, the main challenges and urgent issues that need to be addressed in current research have been summarized, and future research directions were outlined. The review revealed limited research on GDV mapping at the watershed scale in Northwest China, highlighting the need for further refinement on the stable isotope method for ground validation of mapping results. Current studies on resilience focus on surface ecology and ecological indicators overlook underground indicators, such as groundwater and root distribution, and lack a comprehensive evaluation based on resistance, recovery, and adaptability. Qualitative assessments of ecological resilience prevail in current research, falling short of meeting the requirements for effective ecological conservation and restoration. Challenges in researching the co-evolution of vegetation and groundwater arise from the difficulty in accurately detecting changes in root systems. Further studies are warranted to develop root detection methods and three-dimensional models for simulating the co-evolution of roots and water sources. Concerning ecological water tables, the focus remains on static water levels determined by current conditions, with insufficient consideration of spatial variations in precipitation and lateral groundwater flow as well as plant self-adaptation. Additional research is essential to establish dynamic ecological water levels under varying external conditions. This review aims to summarize the progress and future prospects of research on eco-hydrological processes of GDV, addressing the weak research areas. By doing so, it aims to provide a robust scientific foundation for further theoretical research and practical applications on eco-hydrology in NW China.
-

-
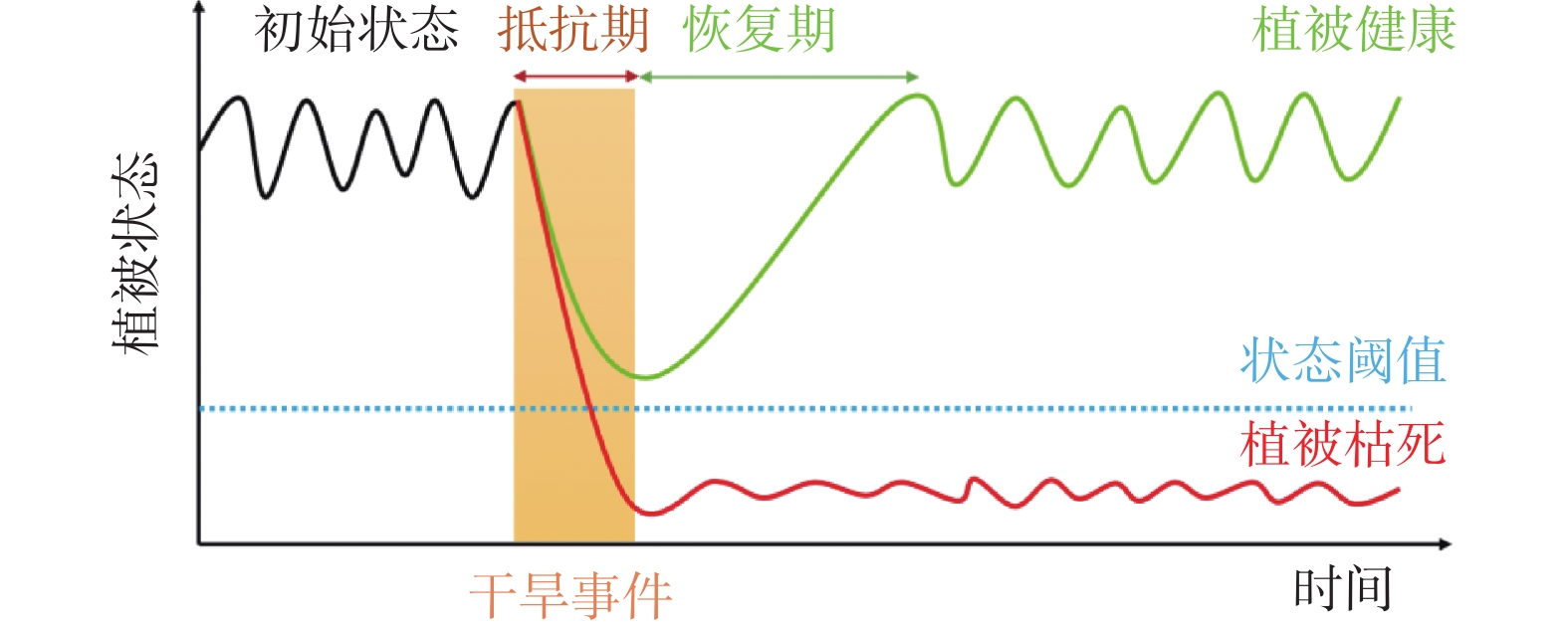
图 1 植被对干旱胁迫响应的韧性特征示意图(据王田野等,2023)
Figure 1.
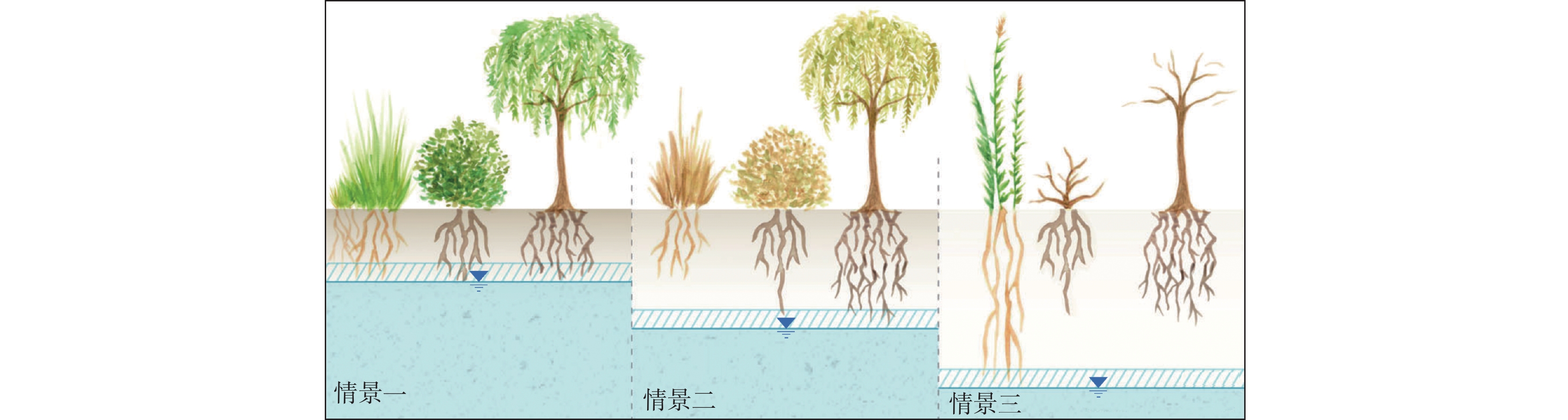
图 2 植物根系与不同地下水位埋深关系示意图(Rohde et al., 2017)
Figure 2.
图 3 典型地下水依赖型植被的适生与极限水位(据张阳阳等, 2020)
Figure 3.
表 1 地下水生态水位确定方法一览表
Table 1. Methods for determining groundwater ecological water level
方法 关键指标 计算方法或模型 野外调查与统计法 植被特征参数(覆盖度、多样性)、
地下水埋深非线性二次曲线模型(如高斯模型、对数正态模型等) 生态水文模型法 植被指数、地下水埋深、土壤含水量 通过饱和非饱和模拟建立地下水位与植被耗水量的关系 毛细上升高度、根系长度 毛细上升高度与根系长度之和 遥感统计分析法 地下水埋深、植被指数(NDVI或是EVI) 分析植被指数与地下水埋深的统计关系 同位素分析法 植物水、土壤水和地下水氢氧同位素 直接比较法或是模型计算(线性端元混合模型、
贝叶斯混合模型) -
[1] 柴建禄 . 采煤对浅层地下水环境的影响及矿井水生态利用分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022 ,50 (7 ):138 −144 .CHAI Jianlu . Influence of coal mining on shallow groundwater environment response to coal mining and mine water ecological utilization analysis[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022 ,50 (7 ):138 −144 .[2] 陈小丽, 陈亚宁, 陈亚鹏 . 黑河下游荒漠河岸林植物水分利用关系研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2014 ,22 (8 ):972 −979 .CHEN Xiaoli, CHEN Yaning, CHEN Yapeng . Relationship among water use of different plants in Heihe River riparian forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2014 ,22 (8 ):972 −979 .[3] 陈亚宁, 李忠勤, 徐建华, 等 . 中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2023 ,38 (3 ):385 −393 .CHEN Yaning, LI Zhongqin, XU Jianhua, et al . Changes and protection suggestions in water resources and ecological environment in arid region of Northwest China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2023 ,38 (3 ):385 −393 .[4] 党学亚, 卢娜, 顾小凡, 等 . 柴达木盆地生态植被的地下水阈值[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019 ,46 (3 ):1 −8 .DANG Xueya, LU Na, GU Xiaofan, et al . Groundwater threshold of ecological vegetation in Qaidam Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (3 ):1 −8 .[5] 党学亚, 张俊, 常亮, 等 . 西北地区水文地质调查与水资源安全[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (3 ):81 −95 .DANG Xueya, ZHANG Jun, CHANG Liang, et al . Hydrogeological Survey and Water Resources Security in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (3 ):81 −95 .[6] 董佳秋, 张俊, 顾小凡, 等. 半干旱区流域尺度植被依赖地下水程度评价: 以鄂尔多斯高原海流兔河流域为例[J/OL]. 中国地质, 2022, 1−19. DONG Jiaqiu, ZHANG Jun, GU Xiaofan, et al. Groundwater dependent ecosystems assessment at catchment scale in semi-arid regions: a case study in the Hailiutu catchment of the Ordos Plateau[J/OL]. Geology in China, 2022, 1−19. [7] 董建红, 张志斌, 刘奔腾, 等 . “三生” 空间视角下西北地区生态环境质量分异机制的地理探测[J]. 干旱区地理,2023 ,46 (4 ):515 −526 .DONG Jianhong, ZHANG Zhibin, LIU Benteng, et al . Geographical exploration of the spatial differentiation mechanism of ecoenvironmental quality in northwest China from the perspective of “production-living-ecological” space[J]. Arid Land Geography,2023 ,46 (4 ):515 −526 .[8] 冯博, 聂振龙, 王金哲, 等 . 石羊河流域绿洲长时间系列遥感动态监测[J]. 地理空间信息,2020 ,18 (12 ):10 −13 .FENG Bo, NIE Zhenlong, WANG Jinzhe, et al . Long-time Series Remote Sensing Dynamic Monitoring of the Oasis in Shiyang River Basin[J]. Geospatial Information,2020 ,18 (12 ):10 −13 .[9] 冯起, 白光祖, 李宗省, 等 . 加快构建西北地区生态保护新格局[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2022 ,37 (10 ):1457 −1470 .FENG Qi, BAI Guangzu, LI Zongxing, et al . Accelerate Construction of New Pattern of Ecological Protection in Northwest China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2022 ,37 (10 ):1457 −1470 .[10] 冯玉新 . 历史地理视域下的西北农牧交错带刍议[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2019 ,33 (12 ):83 −89 .FENG Yuxin . Northwestern farming-pastoral zones in the perspective of historical geography[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2019 ,33 (12 ):83 −89 .[11] 傅朝, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 等 . 西北干旱区一次极端暴雨局地性增强的对流环境特征[J]. 干旱气象,2022 ,40 (6 ):909 −921 .FU Zhao, LIU Weicheng, SONG Xingyu, et al . Local enhanced convective environment characteristics of an extreme rainstorm event in arid region of Northwest China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2022 ,40 (6 ):909 −921 .[12] 郭娜 . 关于煤化工行业高耗水问题剖析及优化措施探讨[J]. 中国化工贸易,2019 ,11 (22 ):75 −75 .[13] 贺军奇, 赵同强, 陈云飞, 等 . 毛乌素沙区地下水对植被盖度空间格局影响分析[J]. 水土保持学报,2023 ,37 (2 ):90 −99 .HE Junqi, ZHAO Tongqiang, CHEN Yunfei, et al . Effect of Subsurface Water on Spatial Pattern of Vegetation Coverage in Mu Us Sandy Area[J]. Journal of Soiland Water Conservation,2023 ,37 (2 ):90 −99 .[14] 侯金鑫, 曹万云, 王德, 等 . 地下水埋深对土壤水盐、植被影响研究进展[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版),2019 ,35 (2 ):150 −156 .HOU Jinxin, CAO Wanyun, WANG De, et al . Research progress on the influence of groundwater depth of soil water, salinity and vegetation[J]. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition),2019 ,35 (2 ):150 −156 .[15] 黄海潮, 雷鸣, 孔祥斌, 等. 中国耕地空间格局变化及其生态系统服务价值响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(1): 339-348. HUANG Haichao, LEI Ming, KONG Xiangbin, et al. Spatial Pattern Change of Cultivated Land and Response of Ecosystem Service Value in China[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(1): 339-348. [16] 计文化, 王永和, 杨博, 等 . 西北地区地质、资源、环境与社会经济概貌[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (3 ):15 −27 .JI Wenhua, WANG Yonghe, YANG Bo, et al . Overview of Geology, Resources, Environment and Social Economy in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (3 ):15 −27 .[17] 贾利民, 郭中小, 龙胤慧, 等 . 干旱区地下水生态水位研究进展[J]. 生态科学,2015 ,34 (2 ):187 −193 .JIA Limin, GUO Zhongxiao, LONG Yinghui, et al . Research advances in ecological groundwater level in arid areas[J]. Ecological Science,2015 ,34 (2 ):187 −193 .[18] 焦继宗, 杨露, 杜婷 . 基于GIS的西北农牧交错带土地利用/覆被时空变化分析[J]. 甘肃科技,2019 ,35 (7 ):139 −143 .[19] 金晓媚, 张强, 杨春杰 . 海流兔河流域植被分布与地形地貌及地下水位关系研究[J]. 地学前缘,2013 ,20 (3 ):227 −233 .JIN Xiaomei, ZHANG Qiang, YANG Chunjie . Research on vegetation distribution and its relationship with topography and groundwater depth in the Hailiutu River Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2013 ,20 (3 ):227 −233 .[20] 拉本, 胡娟, 张旭萍 . 干旱胁迫对植物生理的影响以及分子机制的响应研究进展[J]. 青海草业,2022 ,31 (4 ):31 −35 .[21] 李福杰, 韩风, 马斌, 等 . 塔里木河下游近20年植被演化特征对生态输水的响应[J]. 草业科学,2022 ,39 (12 ):2578 −2588 .[22] 李福林, 陈华伟, 王开然, 等. 地下水支撑生态系统研究综述. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(5): 750-758. LI Fulin, CHEN Huawei, WANG Kairan et al. Comprehensive review of groundwater-dependent ecosystems[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(5): 750-758. [23] 李红梅, 巴贺贾依娜尔·铁木尔别克, 常顺利, 等 . MixSIAR和IsoSource模型对比分析天山北坡不同灌木的夏季水分来源[J]. 干旱区研究,2023 ,40 (3 ):445 −455 .LI Hongmei, Bahejiayinaer TIEMUERBIEKE, CHANG Shunli, et al . Comparative analysis of summer water sources of different shrubs on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains by MixSIAR and IsoSource models[J]. Arid Zone Research,2023 ,40 (3 ):445 −455 .[24] 李荣磊, 黄来明, 裴艳武, 等 . 毛乌素沙地圪丑沟小流域沙柳水分利用来源研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2021 ,35 (2 ):122 −130 .LI Ronglei, HUANG Laiming, PEI Yanwu, et al . Water Use Source of Salix psammophila in Gechougou Small Watershed of Mu Us Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021 ,35 (2 ):122 −130 .[25] 李若怡, 王旭升, 尹立河, 等 . 基于生态约束模拟评价浩勒报吉水源地的地下水可开采量[J]. 工程勘察,2021 ,49 (3 ):36 −42 .LI Ruoyi, WANG Xusheng, Yin Lihe, et al . Simulation and assessment on allowable groundwater exploitation in the Haolebaoji well field based on ecological constraint[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2021 ,49 (3 ):36 −42 .[26] 李文明, 李健强, 徐永, 等 . 西北生态地质调查研究进展与展望[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (3 ):108 −119 .LI Wenming, LI Jianqiang, XU Yong, et al . Progress and Prospects of Ecological Geological Survey in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (3 ):108 −119 .[27] 李霞, 刘传鑫, 徐彬, 等 . 植物拒盐机制的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报,2023 ,39 (27 ):86 −94 .LI Xia, LIU Chuanxin, XU Bin, et al . Plant Salt-exclusion Mechanism: A Review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2023 ,39 (27 ):86 −94 .[28] 李瑛. 鄂尔多斯湖盆高原地下水与植被生态关系研究——以苏贝淖流域流域为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009: 3-61. [29] 刘鹄, 赵文智, 李中恺 . 地下水依赖型生态系统生态水文研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2018 ,33 (7 ):741 −750 .LIU Hu, ZHAO Wenzhi, LI Zhongkai . Ecohydrology of Groundwater Dependent Ecosystems: A Review[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018 ,33 (7 ):741 −750 .[30] 刘强, 梁丽乔 . 依赖地下水生态系统的生态水文研究评述[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2020 ,56 (5 ):693 −699 .LIU Qiang, LIANG Liqiao . Eco-hydrology groundwater-dependent of ecosystem[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science),2020 ,56 (5 ):693 −699 .[31] 刘瑞芳 . 2017年乌审旗气候特征及其对农牧业的影响[J]. 现代农业科技,2018 (14 ):212 −213 .[32] 刘树宝, 陈亚宁, 陈亚鹏, 等 . 黑河下游荒漠河岸林不同林龄胡杨对脉冲式降雨的响应[J]. 干旱区研究,2016a ,33 (1 ):172 −178 .LIU Shubao, CHEN Yaning, CHEN Yapeng, et al . Response of Populus euphratica at Different Ages to Rainfall Pulses in the Desert Riparian Forest of the Lower Reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Arid Zone Research,2016a ,33 (1 ):172 −178 .[33] 刘树宝, 陈亚宁, 陈亚鹏, 等 . 基于稳定同位素技术的黑河下游不同林龄胡杨的吸水深度研究[J]. 生态学报,2016b ,36 (3 ):729 −739 .LIU Shubao, CHEN Yaning, CHEN Yapeng, et al . Study on the depth of water uptake by Populus euphratica trees of different ages in the lower reaches of the Heihe River, based on the stable isotope techniques[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016b ,36 (3 ):729 −739 .[34] 刘子赫, 贾国栋, 刘自强, 等 . 北京山区侧柏用水来源随水分条件变化的多时间尺度[J]. 林业科学,2022 ,58 (3 ):40 −47 .LIU Zihe, JIA Guodong, LIU Ziqiang, et al . Water Source Change of Platycladus orientalis under Different Water Regimes in Beijing Mountainous Area: a Multi-timescale Study[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2022 ,58 (3 ):40 −47 .[35] 马雄德, 黄金廷, 李吉祥, 等 . 面向生态的矿区地下水位阈限研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2019 ,44 (3 ):675 −680 .MA Xiongde, HUANG Jinting, LI Jixiang, et al . Groundwater level threshold under the constrain of ecology security in mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019 ,44 (3 ):675 −680 .[36] 马玉蕾, 王德, 刘俊民, 等 . 地下水与植被关系的研究进展[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2013 ,24 (5 ):36 −40 .MA Yulei, WANG De, LIU Junmin, et al . Research progress on relation between groundwater and vegetation[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2013 ,24 (5 ):36 −40 .[37] 孙自永, 王俊友, 葛孟琰, 等 . 基于水稳定同位素的地下水型陆地植被识别: 研究进展, 面临挑战及未来研究展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2020 ,39 (1 ):11 −20 .SUN Ziyong, WANG Junyou, GE Mengyan, et al . Isotopic approaches to identify groundwater dependent terrestrial vegetation: Progress, challenges, and prospects for future research[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020 ,39 (1 ):11 −20 .[38] 万彦博, 师庆东, 戴岳, 等 . 沙漠腹地天然绿洲不同林龄胡杨水分利用来源[J]. 应用生态学报,2022 ,33 (2 ):353 −359 .WAN Yanbo, SHI Qingdong, DAI Yue, et al . Water sources of Populus euphratica with different tree ages in the oasis of desert hinterland[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2022 ,33 (2 ):353 −359 .[39] 王根绪, 夏军, 李小雁, 等 . 陆地植被生态水文过程前沿进展: 从植物叶片到流域[J]. 科学通报,2021 ,66 (Z2 ):3667 −3683 .WANG Genxu, XIA Jun, LI Xiaoyan, et al . Critical advances in understanding ecohydrological processes of terrestrial vegetation: From leaf to watershed scale[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2021 ,66 (Z2 ):3667 −3683 .[40] 王红宝, 郑伶杰, 丁丁, 等 . 7种柽柳属植物对NaCl胁迫的生长生理响应与耐盐性差异[J]. 山东农业科学,2022 ,54 (11 ):31 −38 .WANG Hongbao, ZHENG Lingjie, DING Ding, et al . Growth and Physiological Response to NaCl Stress and Salt Tolerance Differences of Seven Tamarix Linn. Species[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2022 ,54 (11 ):31 −38 .[41] 王金华 . 煤化工行业高水耗问题分析与改进措施[J]. 化工管理,2020 (34 ):102 −103 .WANG Jinhua . Analysis and Improvement Measures of High Water Consumption in Coal Chemical Industry[J]. Chemical Enterprise Management,2020 (34 ):102 −103 .[42] 王金哲, 张光辉, 王茜, 等 . 西北干旱区地下水生态功能评价指标体系构建与应用[J]. 地质学报,2021 ,95 (5 ):1573 −1581 .WANG Jinzhe, ZHANG Guanghui, WANG Qian, et al . Construction and application of evaluation index system of groundwater ecological function in northwest arid area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021 ,95 (5 ):1573 −1581 .[43] 王田野, 王平, 吴泽宁, 等 . 干旱胁迫下植被生态韧性研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2023 ,38 (8 ):790 −801 .WANG Tianye, WANG Ping, WU Zening, et al . Progress in the study of ecological resilience of vegetation under drought stress[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2023 ,38 (8 ):790 −801 .[44] 王文科, 宫程程, 张在勇, 等 . 旱区地下水文与生态效应研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018 ,33 (7 ):702 −718 .WANG Wenke, GONG Chengcheng, ZHANG Zaiyong, et al . Research Status and Prospect of the Subsurface Hydrology and Ecological Effect in Arid Regions[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018 ,33 (7 ):702 −718 .[45] 王旭升, 尹立河, 方坤, 等 . 鄂尔多斯浩勒报吉水源地开采地下水的环境影响分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019 ,46 (2 ):5 −12 .WANG Xusheng, YIN Lihe, FANG Kun, et al . Inspection and assessment of the environmental impacts of groundwater exploitation at the Haolebaoji wellfield in Inner Mongolia[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (2 ):5 −12 .[46] 王颖, 崔文洁, 吴新越, 等 . 新疆喀什噶尔河岸植被对地下水埋深的退化响应[J]. 环境生态学,2022 ,4 (4 ):65 −71 .WANG Ying, CUI Wenjie, WU Xinyue, et al . Degradation response of riverbank vegetation in Kashgar, Xinjiang to groundwater burial depth[J]. Environmental Ecology,2022 ,4 (4 ):65 −71 .[47] 王振, 李均力, 张久丹, 等 . 输水漫溢对塔里木河中游胡杨林恢复的影响[J]. 干旱区地理,2023 ,46 (1 ):94 −102 .WANG Zhen, LI Junli, ZHANG Jiudan, et al . Influences of ecological water conveyance on Populus euphratica forest restoration in the middle reaches of Tarim River[J]. Arid Land Geography,2023 ,46 (1 ):94 −102 .[48] 魏光辉, 周海鹰, 徐继红 . 塔里木河流域生态廊道治理与修复对策[J]. 中国水利,2023 (6 ):19 −23 .WEI Guanghui, ZHOU Haiying, XU Jihong . Management and measures for restoration of ecological corridor in the Tarim River Basin[J]. China Water Resources,2023 (6 ):19 −23 .[49] 武文豪, 杨琰瑛, 马田田, 等 . 农牧交错区农业资源利用与优化模式——以榆林市为例[J]. 农业资源与环境学报,2023 ,40 (5 ):1231 −1244 .WU Wenhao, YANG Yanying, MA Tiantian, et al . Utilization characteristics and optimization modes of agricultural resources in agro-pastoral ecotones of China: a case study of Yulin City[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment,2023 ,40 (5 ):1231 −1244 .[50] 席海洋, 冯起, 司建华, 等 . 黑河下游绿洲NDVI对地下水位变化的响应研究[J]. 中国沙漠,2013 ,33 (2 ):574 −582 .XI Haiyang, FENG Qi, SI Jianhua, et al . Response of NDVI to Groundwater Level Change in the Lower Reaches of the Heihe River, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2013 ,33 (2 ):574 −582 .[51] 杨锦 . 石羊河流域荒漠绿洲区植被与地下水埋深的关系研究[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术,2018 ,54 (12 ):1 −4 .[52] 杨丽娟, 黄峰, 潘若云, 等 . 青土湖绿洲植被指数适用性及优选研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020 (19 ):65 −68 .YANG Lijuan, HUANG Feng, PAN Ruoyun, et al . Study on the Applicability and Optimization of Vegetation Index in Qingtu Oasis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020 (19 ):65 −68 .[53] 易学睿, 王强, 田华, 等 . 我国煤化工产业水资源短缺问题分析与建议[J]. 现代化工,2023 ,43 (11 ):10 −14 .YI Xuerui, WANG Qiang, TIAN Hua, et al . Analysis and suggestion of water shortage in China's coal chemical industry[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2023 ,43 (11 ):10 −14 .[54] 尹立河, 张俊, 王哲, 等 . 西北内陆河流域地下水循环特征与地下水资源评价[J]. 中国地质,2021 ,48 (4 ):1094 −1111 .YIN Lihe, ZHANG Jun, WANG Zhe, et al . Groundwater circulation patterns and its resources assessment of inland rivercatchments in northwestern China[J]. Geology in China,2021 ,48 (4 ):1094 −1111 .[55] 于静洁 . 李亚飞. 稳定氢氧同位素定量植物水分来源的不确定性解析[J]. 生态学报,2018 ,38 (22 ):7942 −7949 .YU Jingjie, LI Yafei . Uncertainties in the usage of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes for the quantification of plant water sources[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018 ,38 (22 ):7942 −7949 .[56] 于茜茜, 宋新英, 杨敏生, 等 . 胡杨耐盐分子机制研究进展[J]. 林业与生态科学,2012 ,27 (4 ):402 −404 .YU Xixi, SONG Xinying, YANG Minsheng, et al . Research on molecular mechanisms of salt tolerance in Populus euphratica[J]. Hebei Journal of Forestry and Orchard Research,2012 ,27 (4 ):402 −404 .[57] 张高强, 聂洪峰, 肖春蕾, 等 . 浑善达克沙地东南缘地下水埋深对植被盖度的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2022 ,36 (7 ):147 −153 .ZHANG Gaoqiang, NIE Hongfeng, XIAO Chunlei, et al . Effect of groundwater depth on vegetation coverage in southeastern margin of Otindag Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2022 ,36 (7 ):147 −153 .[58] 张天曾 . 中国干旱区水资源利用与生态环境[J]. 资源科学,1981 (1 ):62 −70 .[59] 张晓, 魏青军, 刘亮 . 吐鲁番盆地地下水与植被的关系研究[J]. 山东国土资源,2016 ,32 (7 ):42 −48 .ZHANG Xiao, WEI Qingjun, LIU Liang . Research on Relation between Groundwater and Vegetation in Turpan Basin[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2016 ,32 (7 ):42 −48 .[60] 张阳阳, 陈喜, 高满, 等 . 基于元数据分析的西北干旱区生态地下水位埋深及其影响因素[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2020 ,18 (5 ):57 −65 .ZHANG Yangyang, CHEN Xi, GAO Man, et al . Meta-analysis of ecological depth to groundwater table and its influencing factors in aird region of northwest China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020 ,18 (5 ):57 −65 .[61] 张宇, 张明军, 王圣杰, 等 . 基于稳定氧同位素确定植物水分来源不同方法的比较[J]. 生态学杂志,2020 ,39 (4 ):1356 −1368 .ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Mingjun, WANG Shengjie, et al . Comparison of different methods for determining plant water sources based on stable oxygen isotope[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020 ,39 (4 ):1356 −1368 .[62] 翟家齐, 董义阳, 祁生林, 等 . 干旱区绿洲地下水生态水位阈值研究进展[J]. 水文,2021 ,41 (1 ):7 −14 .ZHAI Jiaqi, DONG Yiyang, QI Shenglin, et al . Advances in Ecological Groundwater Level Threshold in Arid Oasis Regions[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2021 ,41 (1 ):7 −14 .[63] 赵文智, 任珩, 杜军, 等 . 河西走廊绿洲生态建设和农业发展的若干思考与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2023 ,38 (3 ):424 −434 .ZHAO Wenzhi, REN Hang, DU Jin, et al . Thoughts and suggestions on oasis ecological construction and agricultural development in Hexi Corridor[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2023 ,38 (3 ):424 −434 .[64] 曾祥明, 徐宪立, 钟飞霞, 等 . MixSIAR和IsoSource模型解析植物水分来源的比较研究[J]. 生态学报,2020 ,40 (16 ):5611 −5619 .ZENG Xiangming, XU Xianli, ZHONG Feixia, et al . Comparative study of MixSIAR and IsoSource models in the analysis of plant water sources[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020 ,40 (16 ):5611 −5619 .[65] 朱成刚, 艾克热木·阿布拉, 李卫红, 等 . 塔里木河下游生态输水条件下胡杨林生态系统恢复研究[J]. 干旱区地理,2021 ,44 (3 ):629 −636 .ZHU Chenggang, AIKEREMU Abula, LI Weihong, et al . Ecosystem restoration of Populus euphratica forest under the ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Tarim River[J]. Arid Land Geograph,2021 ,44 (3 ):629 −636 .[66] Au T F, Maxwell J T, Robeson S M, et al . Younger trees in the upper canopy are more sensitive but also more resilient to drought[J]. Nature Climate Change,2022 ,12 (12 ):1168 −1174 .[67] Bajgain R, Xiao X, Wagle P, et al . Sensitivity analysis of vegetation indices to drought over two tallgrass prairie sites[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2015 ,108 :151 −160 .[68] Barbeta A, Jones S P, Clave L, et al. Unexplained hydrogen isotope offsets complicate the identification and quantification of tree water sources in a riparian forest[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2019, 23(4): 2129–2146. [69] Bennett A C, McDowell N G, Allen C D, et al. Larger trees suffer most during drought in forests worldwide[J]. Nature Plants, 2015, 1(10): 1-5. [70] Brown J, Bach L, Aldous A, et al . Groundwater-dependent ecosystems in Oregon: An assessment of their distribution and associated threats[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment,2011 ,9 (2 ):97 −102 .[71] Callahan R P, Riebe C S, Sklar L S, et al . Forest vulnerability to drought controlled by bedrock composition[J]. Nature Geosciences,2022 ,15 :714 −719 .[72] Camarero J J, Colangelo M, Rodríguez-González P M . Tree growth, wood anatomy and carbon and oxygen isotopes responses to drought in Mediterranean riparian forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management,2023 ,529 :120710 .[73] Canham C A, Duvert C, Beesley L S, et al . The use of regional and alluvial groundwater by riparian trees in the wet-dry tropics of northern Australia[J]. Hydrological Processes,2021 ,35 (5 ):e14180 .[74] Castellazzi P, Doody T, Peeters L . Towards monitoring groundwater-dependent ecosystems using synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. Hydrological processes,2019 ,33 (25 ):3239 −3250 .[75] Condon L E, Maxwell R M . Simulating the sensitivity of evapotranspiration and streamflow to large-scale groundwater depletion[J]. Science Advances,2019 ,5 (6 ):eaav4574 .[76] Doody T M, Barron O V, Dowsley K, et al . Continental mapping of groundwater dependent ecosystems: A methodological framework to integrate diverse data and expert opinion[J]. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies,2017 ,10 :61 −81 .[77] Doolittle J A, Miller W F. Use of ground-penetrating radar techniques in archaeological investigations[J]. NASA. Stennis Space Center, Applications of Space-Age Technology in Anthropology, 1991. [78] Duran-Llacer I, Arumí J L, Arriagada L, et al . A new method to map groundwater-dependent ecosystem zones in semi-arid environments: A case study in Chile[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2022 ,816 :151528 .[79] Eamus D, Zolfaghar S, Villalobos-Vega R, et al . Groundwater-dependent ecosystems: Recent insights from satellite and field-based studies[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2015 ,19 (10 ):4229 −4256 .[80] Ehleringer J R, Dawson T E. Water uptake by plants: perspectives from stable isotope composition[J]. Plant, cell & environment, 1992, 15(9): 1073-1082. [81] Fan G, Liang H, Zhao Y, et al . Automatic reconstruction of three-dimensional root system architecture based on ground penetrating radar[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2022 ,197 :106969 .[82] Fan Y, Miguez-Macho G, Jobbágy E G, et al . Hydrologic regulation of plant rooting depth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2017 ,114 (40 ):10572 −10577 .[83] Fildes S G, Doody T M, Bruce D, et al . Mapping groundwater dependent ecosystem potential in a semi-arid environment using a remote sensing-based multiple-lines-of-evidence approach[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth,2023 ,16 (1 ):375 −406 .[84] Giehl R F H, von Wirén N . Hydropatterning-how roots test the waters[J]. Science,2018 ,362 (6421 ):1358 −1359 .[85] Glanville K, Sheldon F, Butler D, et al . Effects and significance of groundwater for vegetation: A systematic review[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2023 ,875 :162577 .[86] Gou S, Gonzales S, Miller G R . Mapping potential groundwater-dependent ecosystems for sustainable management[J]. Groundwater,2015 ,53 (1 ):99 −110 .[87] Goulden M L, Bales R C. California forest die-off linked to multi-year deep soil drying in 2012–2015 drought[J]. Nature Geosciences,2019 ,12 :632 −637 .[88] Gupta A, Rico-Medina A, Caño-Delgado A I . The physiology of plant responses to drought[J]. Science,2020 ,368 (6488 ):266 −269 .[89] Harbaugh A W, Banta E R, Hill M C, et al. MODFLOW-2000, the US Geological Survey Modular Groundwater Mode—User Guide to Modularization Concepts and the Ground-water Flow Process[J]. Open-File Report 00-92, Reston, Virginia, 2000. [90] Hernandez J O . Ecophysiological effects of groundwater drawdown on phreatophytes: research trends during the last three decades[J]. Land,2022 ,11 (11 ):2061 .[91] Holling C S . Resilience and stability of ecological systems[J]. Annual review of ecology and systematics,1973 ,4 (1 ):1 −23 .[92] Hou C, Tian D, Xu B, et al . Use of the stable oxygen isotope method to evaluate the difference in water consumption and utilization strategy between alfalfa and maize fields in an arid shallow groundwater area[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2021 ,256 :107065 .[93] Howard J, Merrifield M . Mapping groundwater dependent ecosystems in California[J]. Plos One,2010 ,5 (6 ):e11249 .[94] Isbell F, Craven D, Connolly J, et al . Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes[J]. Nature,2015 ,526 (7574 ):574 −577 .[95] Jasechko S, Seybold H, Perrone D, et al . Rapid groundwater decline and some cases of recovery in aquifers globally[J]. Nature,2024 ,625 (7996 ):715 −721 .[96] Kibler C L, Schmidt E C, Roberts D A, et al . A brown wave of riparian woodland mortality following groundwater declines during the 2012–2019 California drought[J]. Environmental research letters,2021 ,16 (8 ):084030 .[97] Kuang X, Liu J, Scanlon B R, et al . The changing nature of groundwater in the global water cycle[J]. Science,2024 ,383 (6686 ):eadf0630 .[98] Liang M, Cao R, Di K, et al . Vegetation resistance and resilience to a decade-long dry period in the temperate grasslands in China[J]. Ecology and Evolution,2021 ,11 (15 ):10582 −10589 .[99] Liu C, Liu H, Yu Y, et al. Mapping groundwater-dependent ecosystems in arid Central Asia: Implications for controlling regional land degradation[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 797: 149027. [100] Liu D, Wang T, Peñuelas J, et al . Drought resistance enhanced by tree species diversity in global forests[J]. Nature Geoscience,2022 ,15 (10 ):800 −804 .[101] Liu S, Xu G, Chen T, et al . Quantifying the effects of precipitation exclusion and groundwater drawdown on functional traits of Haloxylon ammodendron-How does this xeric shrub survive the drought?[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2023 ,904 :166945 .[102] Maan C, ten Veldhuis M C, van de Wiel B J H . Dynamic root growth in response to depth-varying soil moisture availability: a rhizobox study[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2023 ,27 (12 ):2341 −2355 .[103] Martinez-Santos P, Díaz-Alcaide S, De la Hera-Portillo A, et al . Mapping groundwater-dependent ecosystems by means of multi-layer supervised classification[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021 ,603 :126873 .[104] Matos I S, Menor I O, Rifai S W, et al . Deciphering the stability of grassland productivity in response to rainfall manipulation experiments[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography,2020 ,29 (3 ):558 −572 .[105] Miller G R, Chen X, Rubin Y, et al. Groundwater uptake by woody vegetation in a semiarid oak savanna[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(10). [106] Münch Z, Conrad J. Remote sensing and GIS based determination of groundwater dependent ecosystems in the Western Cape, South Africa[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2007, 15: 19-28. [107] Naumburg E, Mata-Gonzalez R, Hunter R G, et al . Phreatophytic vegetation and groundwater fluctuations: a review of current research and application of ecosystem response modeling with an emphasis on Great Basin vegetation[J]. Environmental Management,2005 ,35 (6 ):726 −740 .[108] Olsson L, Jerneck A, Thoren H, et al . Why resilience is unappealing to social science: Theoretical and empirical investigations of the scientific use of resilience[J]. Science advances,2015 ,1 (4 ):e1400217 .[109] Orellana F, P Verma, S P Loheide II, et al . Monitoring and modeling water-vegetation interactions in groundwater-dependent ecosystems[J]. Rev. Geophys.,2012 ,50 :RG3003 .[110] Pandey H K, Singh V K, Singh S K, et al . Map** and validation of groundwater dependent ecosystems (GDEs) in a drought-affected part of Bundelkhand region, India[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development,2023 ,23 :100979 .[111] Pérez Hoyos I C, Krakauer N Y, Khanbilvardi R, et al . A review of advances in the identification and characterization of groundwater dependent ecosystems using geospatial technologies[J]. Geosciences,2016 ,6 (2 ):17 .[112] Pritchett D, Manning S J . Response of an intermountain groundwater-dependent ecosystem to water table drawdown[J]. Western North American Naturalist,2012 ,72 (1 ):48 −59 .[113] Qiu D, Zhu G, Bhat M A, et al . Water use strategy of nitraria tangutorum shrubs in ecological water delivery area of the lower inland river: Based on stable isotope data[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023a ,624 :129918 .[114] Qiu Y, Wang D, Yu X, et al . Effects of Groundwater Table Decline on Vegetation in Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystems[J]. Forests,2023b ,14 (12 ):2326 .[115] Rampheri M B, Dube T, Dondofema F, et al . Identification and delineation of groundwater-dependent ecosystems (GDEs) in the Khakea–Bray transboundary aquifer region using geospatial techniques[J]. Geocarto International,2023a ,38 (1 ):2172217 .[116] Rampheri M B, Dube T, Dondofema F, et al . Progress in the remote sensing of groundwater-dependent ecosystems in semi-arid environments[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C,2023b ,130 :103359 .[117] Rohde M M, Biswas T, Housman I W, et al . A machine learning approach to predict groundwater levels in California reveals ecosystems at risk[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021 ,9 :784499 .[118] Rohde M M, Froend R, Howard J . A global synthesis of managing groundwater dependent ecosystems under sustainable groundwater policy[J]. Groundwater,2017 ,55 (3 ):293 −301 .[119] Schwalm C R, Anderegg W R L, Michalak A M, et al . Global patterns of drought recovery[J]. Nature,2017 ,548 (7666 ):202 −205 .[120] Schymanski S J, Sivapalan M, Roderick M L,et al . An optimality-based model of the coupled soil moisture and root dynamics[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2008 ,12 (3 ):913 −932 .[121] Simunek J I R K A, M Th Van Genuchten, M Sejna. The HYDRUS software package for simulating two-and three-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media[J]. Technical manual, version 1 (2006): 241. [122] Sperry J S, Hacke U G, Oren R, et al . Water deficits and hydraulic limits to leaf water supply[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment,2002 ,25 (2 ):251 −263 .[123] Wang J, Song C, Reager J T, et al . Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages[J]. Nature Geoscience,2018 ,11 (12 ):926 −932 .[124] Wang T Y, Wang P, Wang Z L, et al . Drought adaptability of phreatophytes: insight from vertical root distribution in drylands of China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2021 ,14 (6 ):1128 −1142 .[125] Wang T, Wang P, Wu Z, et al . Modeling revealed the effect of root dynamics on the water adaptability of phreatophytes[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2022 ,320 :108959 .[126] Wang T, Wu Z, Wang P, et al . Plant-groundwater interactions in drylands: A review of current research and future perspectives[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2023 ,341 :109636 .[127] Xu C, McDowell N G, Fisher R A, et al . Increasing impacts of extreme droughts on vegetation productivity under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change,2019 ,9 (12 ):948 −953 .[128] Xu W, Kong F, Mao R, et al . Identifying and mapping potential groundwater-dependent ecosystems for a semi-arid and semi-humid area in the Weihe River, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022 ,609 :127789 .[129] Yang J, He Z, Du J, et al . Uncertainty in ecohydrological modeling in an arid region determined with Bayesian methods[J]. Plos One,2016 ,11 (3 ):e0151283 .[130] Yin L, Zhou Y, Xu D, et al. Response of phreatophytes to short-term groundwater pumping in a semiarid region: Field experiments and numerical simulations[J]. Ecohydrology, 2018, 11: e1948. [131] Zhang Q, Kong D, Singh V P, et al . Response of vegetation to different time-scales drought across China: Spatiotemporal patterns, causes and implications[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2017 ,152 :1 −11 .[132] Zhou Y, Wenninger J, Yang Z, et al . Groundwater–surface water interactions, vegetation dependencies and implications for water resources management in the semi-arid Hailiutu River catchment, China – a synthesis[J]. Hydrology & Earth System Sciences,2013 ,17 (7 ):2435 −2447 .[133] Zimmerman O R, Pearce D W, Woodman S G, et al . Increasing contribution of alluvial groundwater to riparian cottonwood forest water use through warm and dry summers[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2023 ,329 :109292 . -



 下载:
下载: