STUDY ON THE DYNAMIC CHANGES OF SPRING FLOW, CONDUCTIVITY AND pH VALUE
-
摘要:
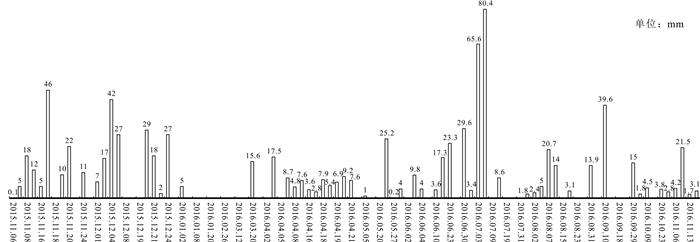
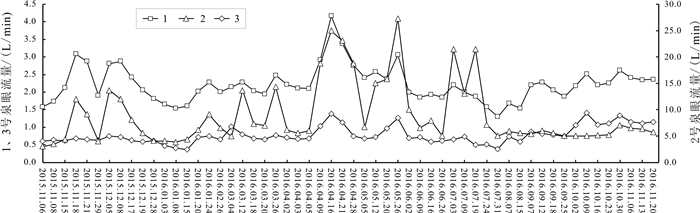
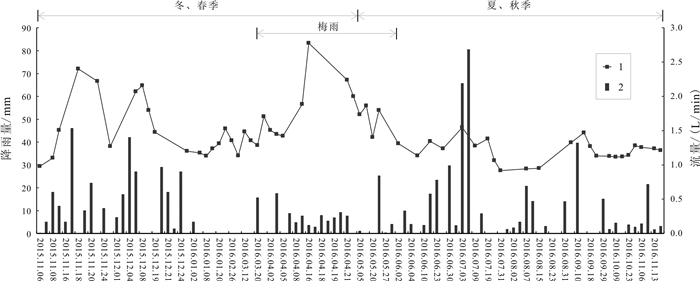
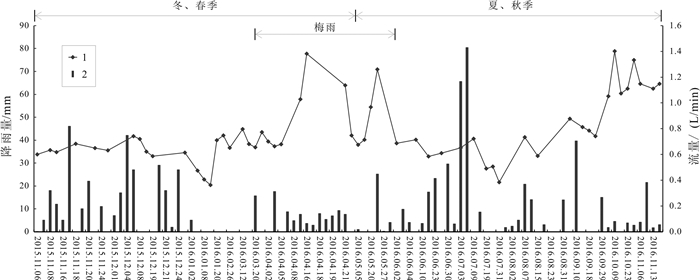
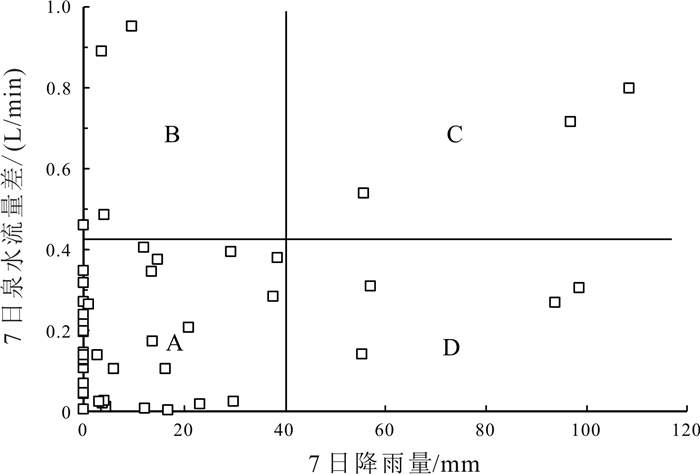
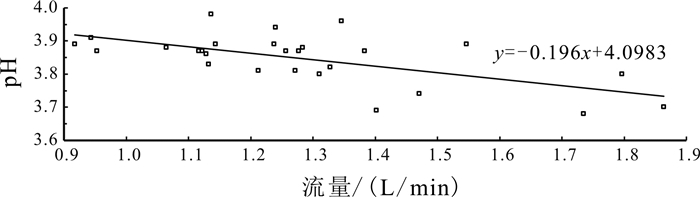
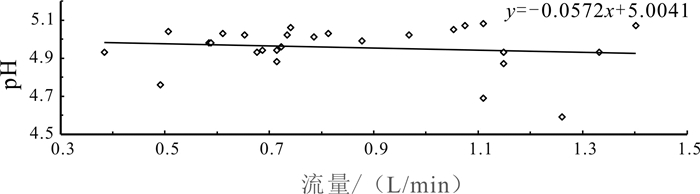
岩溶水是指赋存于岩溶孔隙中的地下水,是我国南方生产生活主要用水来源.随着社会对水资源需求的逐步扩大,岩溶水资源的开发利用越发重要.通过定期监测岳麓山泉水流量、电导率、pH值,结合岳麓山岩土层性质和长沙市降雨量,采用统计分析和Spearman秩相关系数法对泉水流量变化和泉水水质定性评价进行研究.研究结果表明,大气降雨对岩溶水进行补给从而使泉水流量增大,泉水流量的改变除与降雨量有关外,还受土壤入渗率和降雨时长的影响.采用Spearman秩相关系数法可定量计算电导率与时间的相关性,间接判断周围环境对泉水水质影响的难易程度,有利于识别电导率代表性位置泉眼,更好地监测和评价岩溶水.土壤酸沉降污染严重或酸雨频繁地区易导致岩溶水pH值呈酸性.对泉水流量和水质的研究有利于科学开发利用岩溶水资源.
Abstract:Karst water, referring to the groundwater that is hosted in karst pores, serves as the major water source for production and life in southern China. With the increasing social demand for water, the development and utilization of karst water resources is becoming more and more important. By regularly monitoring the spring flow, conductivity and pH value of Yuelu Mountain, combined with the rock-soil layer property of Yuelu Mountain and rainfall of Changsha City, the statistical analysis and Spearman rank correlation coefficient method are used to study the spring flow changes and qualitatively evaluate the water quality. The results show that rainfall replenishes karst water and increases spring flow. The spring flow is not only related to rainfall but also affected by soil infiltration rate and rainfall duration. The Spearman rank correlation coefficient method can be used to quantitatively calculate the correlation between conductivity and time, and indirectly judge the influence of surrounding environment on spring water quality, which is conducive to identify the representative location of conductivity, better monitor and evaluate karst water. The pH value of karst water tends to be acidic in areas with serious acid precipitation pollution of soil or frequent acid rain. The study of spring flow and water quality is beneficial to scientific development and utilization of karst water.
-
Key words:
- karst spring /
- water quality /
- infiltration rate /
- conductivity /
- pH value /
- Yuelu Mountain
-

-
表 1 根据电导率测定值对盐水进行分类
Table 1. Classification of brine by measured conductivity values
纯水 微含盐水 中含盐水 高含盐水 极高含盐水 卤水 <700 700~2000 2000~10000 10000~20000 20000~45000 >45000 电导率单位:μs/cm. 表 2 1号、3号泉眼Spearman秩相关系数计算数据
Table 2. Calculated result of Nos. 1 and 3 springs by Spearman rank correlation coefficient
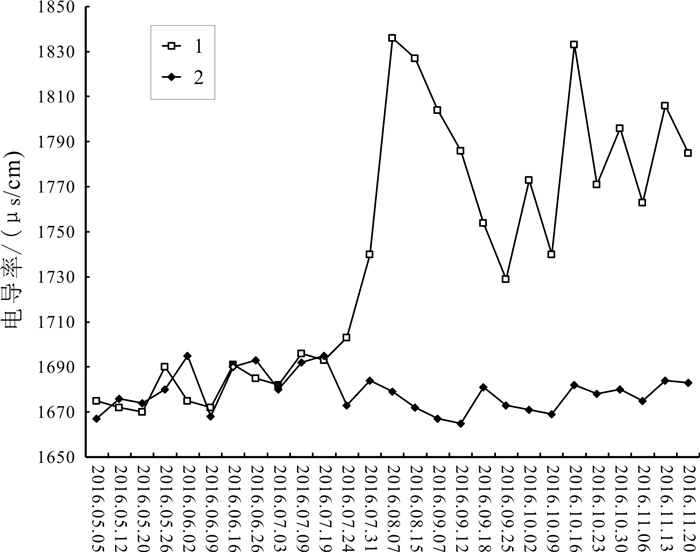
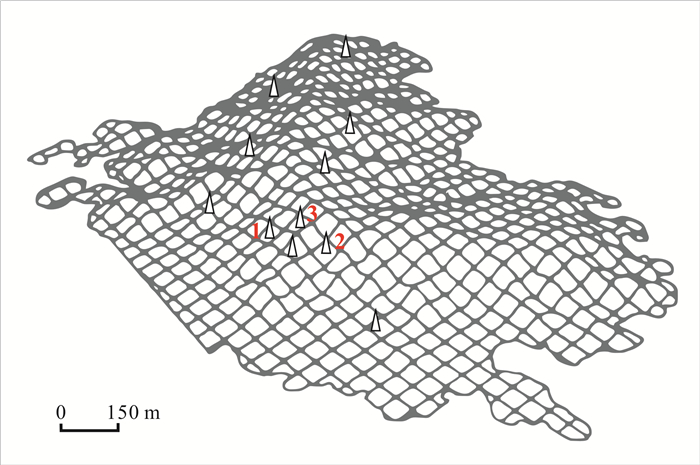
日期 1号泉眼 3号泉眼 电导率/μs/cm xi′ yi′ 电导率/μs/cm xi′ yi′ 2016.05.05 1675 1 22 1667 1 20 2016.05.12 1672 2 23 1676 2 12 2016.05.20 1670 3 24 1674 3 14 2016.05.26 1690 4 9 1680 4 9 2016.06.02 1675 5 22 1695 5 1 2016.06.09 1672 6 23 1668 6 19 2016.06.16 1691 7 18 1690 7 4 2016.06.26 1685 8 20 1693 8 2 2016.07.03 1682 9 21 1680 9 9 2016.07.09 1696 10 16 1692 10 3 2016.07.19 1693 11 17 1695 11 1 2016.07.24 1703 12 15 1673 12 15 2016.07.31 1740 13 13 1684 13 5 2016.08.07 1836 14 1 1679 14 10 2016.08.15 1827 15 3 1672 15 16 2016.09.07 1804 16 5 1667 16 20 2016.09.12 1786 17 7 1665 17 21 2016.09.18 1754 18 12 1681 18 8 2016.09.25 1729 19 14 1673 19 15 2016.10.02 1773 20 9 1671 20 17 2016.10.09 1740 21 13 1669 21 18 2016.10.16 1833 22 2 1682 22 7 2016.10.23 1771 23 10 1678 23 11 2016.10.30 1796 24 6 1680 24 9 2016.11.06 1763 25 11 1675 25 13 2016.11.13 1806 26 4 1684 26 5 2016.11.20 1785 27 8 1683 27 6 -
[1] 田辉, 郭晓东, 刘强, 等.大庆市地下水开采现状及环境地质问题探讨[J].地质与资源, 2012, 21(1):139-142. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201201021
[2] 缪晓宇, 郭昂青.黑龙江省松嫩平原地下水资源开发利用中主要问题及对策[J].地质与资源, 2010, 19(2):105-108, 113. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201002005
[3] 李强, 孙海龙, 韩军, 等.降水对广西马山兰电堂泉水化学动态变化观测研究[J].水科学进展, 2006, 17(5):733-737. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=skxjz200605024
[4] 姚昕, 夏日元, 唐健生, 等.湘西洛塔岩溶生态微景观结构对表层岩溶泉的影响[J].中国水土保持, 2006(11):35-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgstbc200611015
[5] 欧业成, 陈润玲, 黄喜新, 等.北海市滨海地下水天然偏酸性特征及其影响因素[J].桂林理工大学学报, 2009, 29(4):449-454. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=glgxy200904005
[6] 徐国策, 刘海波, 申震洲, 等.洛惠渠灌区地下水电导率时间稳定性分析[J].农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10):115-121. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nygcxb201510016
[7] 扈志勇, 杨平恒, 杨梅, 等.川东槽谷区岩溶泉水物理化学动态特征及其环境效应研究——以重庆青木关岩溶槽谷姜家泉为例[J].现代地质, 2009, 23(6):1167-1173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200906024
[8] 曹建文, 夏日元, 方尚武, 等.云贵高原斜坡地带典型地下水富硫酸盐地区"越层找水"模式及其机理研究[J].中国地质, 2019, 46(2):235-243. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201902003
[9] 何泽, 宁卓, 黄冠星, 等.太行山前平原浅层地下水污染的分子生物学响应特征——以滹沱河流域为例[J].中国地质, 2019, 46(2):290-301. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201902007
[10] 孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 等.哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1128-1141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201806005
[11] 许鹏, 谭红兵, 张燕飞, 等.特提斯喜马拉雅带地热水化学特征与物源机制[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1142-1154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201806006
[12] 孙跃, 岳运华, 刘中刚, 等.基于GMS的傍河应急水源地地下水资源评价[J].地质与资源, 2019, 28(1):72-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201901012
[13] 耿婷婷, 李颖智, 张涛, 等.西藏"一江三河"地区地下水环境背景值初步研究[J].地质与资源, 2018, 27(5):480-487. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GJSD201805011.htm
[14] 马立新, 吴丽.通辽市水资源承载能力的多层次多指标可变模糊评价研究[J].地质与资源, 2018, 27(1):83-88. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjsdz201801011
[15] Yadav S, Irfan M, Ahmad A, et al. Causes of salinity and plant manifestations to salt stress:a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2011, 32(5):667-685. http://www.bioone.org/servlet/linkout?suffix=bibr45&dbid=8&doi=10.2980%2F21-2-3705&key=22319886
[16] 王小娜, 王金生, 吴东杰, 等.北京市泉水变化状况及原因分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(4):28-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz201004006
[17] 杨平恒, 罗鉴银, 袁道先, 等.降雨条件下岩溶槽谷泉水的水文地球化学特征[J].水利学报, 2009, 40(1):67-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=slxb200901010
[18] 方至.长沙市酸雨现状分析[J].湖南农业大学学报, 1998, 24(1):43-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qyjskf200909046
[19] 杨宇红.长沙市市区近5年酸雨变化趋势及相关因素分析[J].湖南有色金属, 2005, 21(6):28-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnysjs200506010
[20] 李炳文.长沙岳麓山小流域水-土系统对酸沉降的响应研究[D].长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2009.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10537-2010061307.htm -



 下载:
下载: