VERTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF MAJOR NUTRIENT ELEMENTS IN TYPICAL BLACK SOIL SECTIONS IN HAILUN, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE: Before and After Reclamation
-
摘要:
垦殖前后典型黑土主要养分元素特征研究对东北黑土资源的可持续利用和保护东北大粮仓具有重要作用.在松嫩平原东部海伦地区对比研究了典型黑土区40年间土地利用未发生改变的地区(本次对比研究林地和耕地),布设了4条典型黑土剖面,对垦殖前后典型黑土剖面中土壤肥力的主要指标元素(有机质、全氮、全磷、C:N及pH值)分别对比分析.结果表明:有机质、全氮、全磷含量表现为随土壤深度急剧下降—缓慢下降—基本稳定的变化趋势;垦殖虽然改变了各土层土壤中养分元素的含量,但是并未改变其随土壤深度的变化规律;垦殖在一定程度上影响了表层黑土土壤的pH值,导致耕地表层黑土土壤慢慢酸化.研究结果可为黑土资源的可持续利用、保护及修复提供科学依据.
Abstract:The study on the characteristics of major nutrient elements in typical black soil areas before and after reclamation is important for sustainable utilization of black soil resources and protection of the breadbasket in Northeast China. Four sections are laid out in the typical black soil areas where land use has not changed for the past 40 years in Helen area, eastern Songnen Plain, to make a comparative study on the main index elements for soil fertility (organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, C:N and pH value) in the sections before and after reclamation. The results indicate that the contents of organic matter, total nitrogen and total phosphorus show a change trend of rapid decrease through slow decrease to basically stable with soil depth. Although reclamation has changed the content of nutrient elements in soil, it does not change the content variation rule with soil depth. Reclamation affects the pH value of black topsoil to a certain extent, which led to slow acidification of cultivated land. The research results will expectedly provide scientific basis for sustainable utilization, protection and restoration of black soil resources.
-
Key words:
- typical black soil /
- soil nutrient /
- soil pH /
- reclamation /
- Hailun area /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
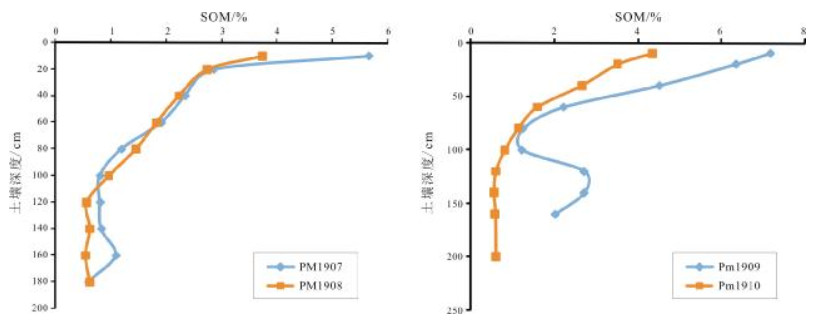
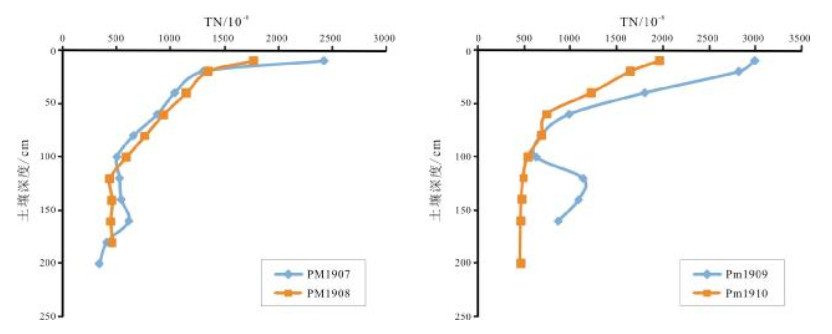
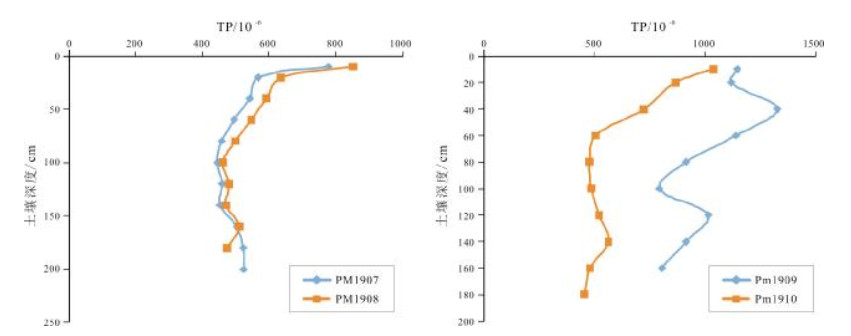
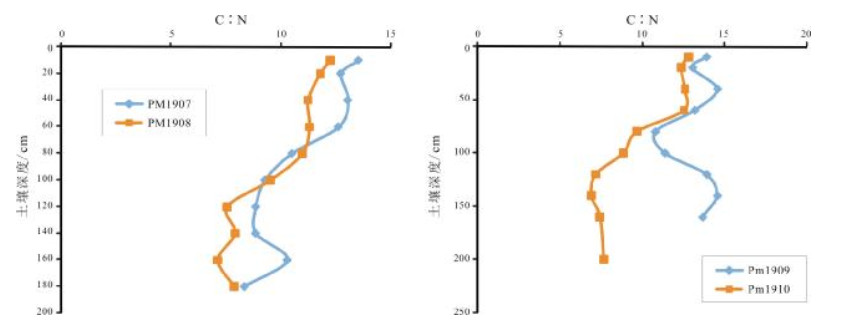
表 1 海伦地区典型黑土开垦前后土壤PM1907、PM1908剖面养分含量表
Table 1. Nutrient contents before and after reclamation in typical black soil sections PM1907 and PM1908
土层深度/cm SOM/% TN/10-6 C:N TP/10-6 pH值 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 0~10 5.66 3.75 2423 1770 13.55 12.27 777 851 6.40 6.05 10~20 2.86 2.74 1302 1347 12.74 11.82 567 635 6.40 6.79 20~40 2.34 2.23 1041 1149 13.06 11.26 542 592 6.39 6.59 40~60 1.92 1.83 880 937 12.63 11.33 495 546 6.45 6.48 60~80 1.19 1.46 659 768 10.52 11.01 457 498 6.49 6.39 80~100 0.81 0.97 505 591 9.28 9.54 445 461 6.47 6.13 100~120 0.81 0.57 528 438 8.87 7.56 459 479 6.51 6.56 120~140 0.83 0.63 544 460 8.86 7.93 452 471 6.69 6.49 140~160 1.09 0.55 615 446 10.30 7.13 503 510 6.64 6.60 160~180 0.59 0.63 411 463 8.35 7.88 523 474 6.57 6.52 180~200 0.42 341 7.17 524 6.55 SOM:有机质; TN:全氮; TP:全磷. 表 2 海伦地区典型黑土开垦前后土壤PM1909、PM1910剖面养分含量表
Table 2. Nutrient contents before and after reclamation in typical black soil sections PM1909 and PM1910
土层深度/cm SOM/% TN/10-6 C:N TP/10-6 pH值 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 林地 耕地 0~10 7.17 4.35 2990 1964 13.90 12.84 1148 1041 6.09 5.95 10~20 6.35 3.52 2818 1645 13.07 12.40 1119 867 6.42 6.26 20~40 4.52 2.66 1799 1223 14.56 12.61 1328 724 6.61 6.54 40~60 2.23 1.60 980 740 13.19 12.55 1141 506 6.64 6.69 60~80 1.26 1.14 674 685 10.83 9.68 915 479 6.64 6.26 80~100 1.23 0.82 625 539 11.41 8.86 795 487 6.61 6.36 100~120 2.72 0.61 1132 490 13.92 7.18 1016 522 6.46 6.65 120~140 2.72 0.56 1082 471 14.55 6.90 916 564 6.67 6.60 140~160 2.03 0.59 861 464 13.67 7.43 807 481 6.80 6.46 160~180 0.61 458 7.67 456 6.58 SOM:有机质; TN:全氮; TP:全磷. -
[1] Powlson D S, Gregory P J, Whalley W R, et al. Soil management in relation to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem services[J]. Food Policy, 2011, 36:S72-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2010.11.025
[2] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等.东北松辽平原典型黑土-古土壤剖面AMS14C年龄首次报道[J/OL].中国地质, 2019, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20191225.1615.006.html.
[3] 段轶仁, 杨忠芳, 杨琼, 等.广西北部湾地区土壤锗分布特征、影响因素及其生态环境评价[J/OL].中国地质. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/11.1167.P.20200407.1753.004.html, 2020-04-08.
[4] 张哲寰, 赵君, 戴慧敏, 等.黑龙江省讷河市土壤-作物系统Se元素地球化学特征[J].地质与资源, 2020, 29(1):38-43. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10147.shtml
[5] 张玉芬, 李长安, 熊德强, 等.长江三峡巫山黄土稀土元素特征及古气候环境意义[J/OL].中国地质, https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/11.1167.P.20200421.1251.004.html, 2020-04-21.
[6] 张哲寰, 宋运红, 赵君, 等.黑龙江省讷河市土壤某些微量元素地球化学特征[J].地质与资源, 2019, 28(4):378-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.011 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8363.shtml
[7] 贾树海, 张佳楠, 张玉玲, 等.东北黑土区旱田改稻田后土壤有机碳、全氮的变化特征[J].中国农业科学, 2017, 50(7):1252-1262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNYK201707008.htm
[8] 韩晓增, 李娜.中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J].地理科学, 2018, 38(7):1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
[9] Song Y H, Dai H M, Yang F C, et al. A preliminary study on soil degradation and nutrient imbalance of typical black soil in northeast China[C]//Proceedings of the 6th Academic Conference of Geology Resource Management and Sustainable Development. Beijing: Aussino Academic Publishing, 2018: 328-335.
[10] Song Y H, Dai H M, Yang F C, et al. Temporal and spatial change of soil organic matter and pH in Cultivated Land of the Songliao plain in northeast China during the Past 35 Years[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica:English Edition, 2019, 93(S3):142-143. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14271
[11] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等.东北松辽平原35年来耕地土壤全氮时空变化最新报道[J/OL].中国地质, 2019, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20191225.1612.004.html.
[12] Zhang Y, Zang S Y, Sun L, et al. Characterizing the changing environment of cropland in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China, from 1990 to 2015[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019, 29(5):658-674.
[13] 许士麒, 王义东, 郭长城, 等.天津咸化湿地土壤碳、氮特征对长期垦殖的响应[J].天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 37(1):63-68, 75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1114.2017.01.015
[14] 汪景宽, 张旭东, 王铁宇, 等.黑土土壤质量演变初探Ⅱ——不同地区黑土中有机质、氮、硫和磷现状及变化规律[J].沈阳农业大学学报, 2002, 33(4):270-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY200204008.htm
[15] Craft C, Redlinski I, Vymazal J, et al. Soil properties, carbon sequestration and nutrient (N, P) accumulation in wet meadows[R]. 2011: 35-43.
[16] 徐仁扣, Coventry D R.某些农业措施对土壤酸化的影响[J].农业环境保护, 2002, 21(5):385-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200205000.htm
[17] 侯立恒, 王熊飞, 王汀忠, 等.海南省耕地有机质和pH值变化分析[J].农业科技通讯, 2018(1):120-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTX201801042.htm
[18] 宋日, 刘利, 吴春胜, 等.东北松嫩草原土壤开垦对有机质含量及土壤结构的影响[J].中国草地学报, 2009, 31(4):91-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCD200904017.htm
[19] 迟美静, 侯玮, 孙莹, 等.东北黑土区荒地开垦种稻后土壤养分及pH值的变化特征[J].土壤通报, 2018, 49(3):546-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201803007.htm
[20] 霍莉莉.沼泽湿地垦殖前后土壤有机碳垂直分布及其稳定性特征研究[D].长春: 中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所, 2013: 40-44.
-



 下载:
下载: