ELEMENT GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE TYPICAL BLACK SOIL SECTIONS IN BAIQUAN AREA, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE: Environmental Implication
-
摘要:
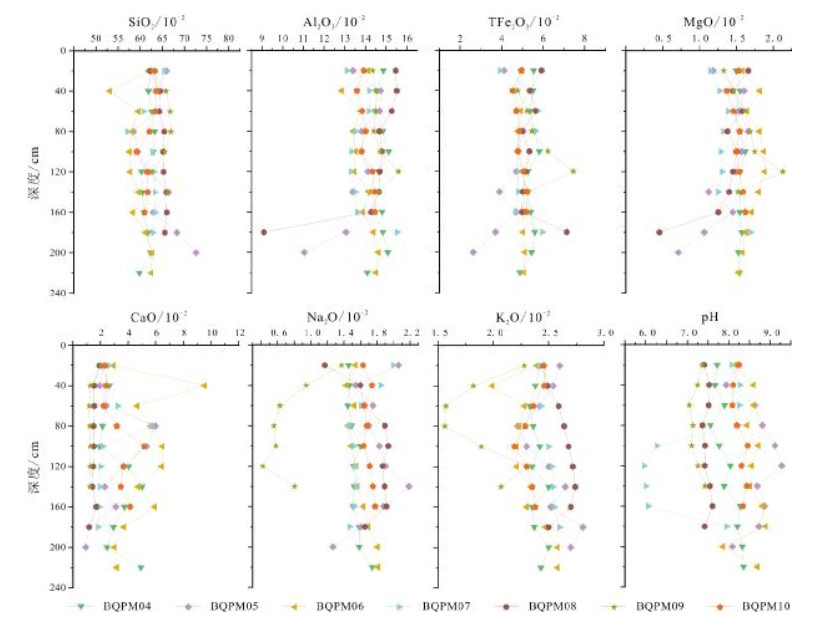
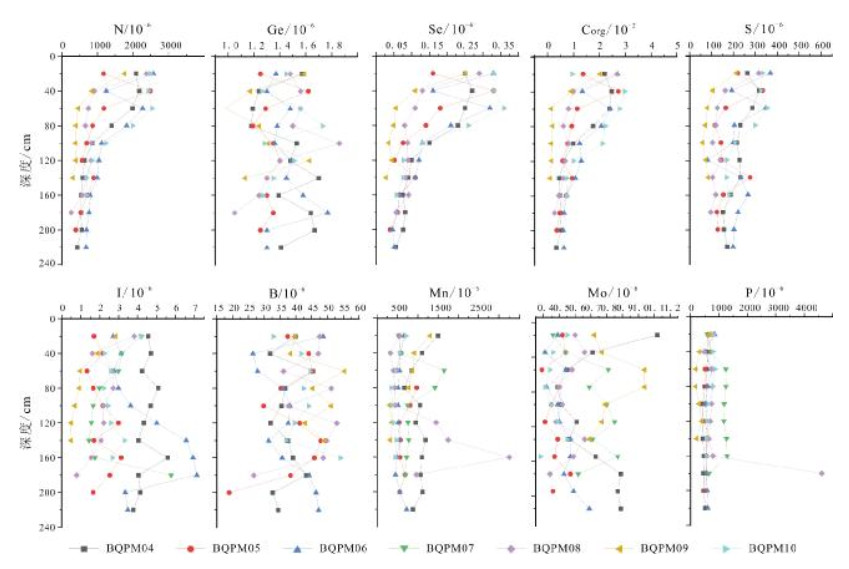
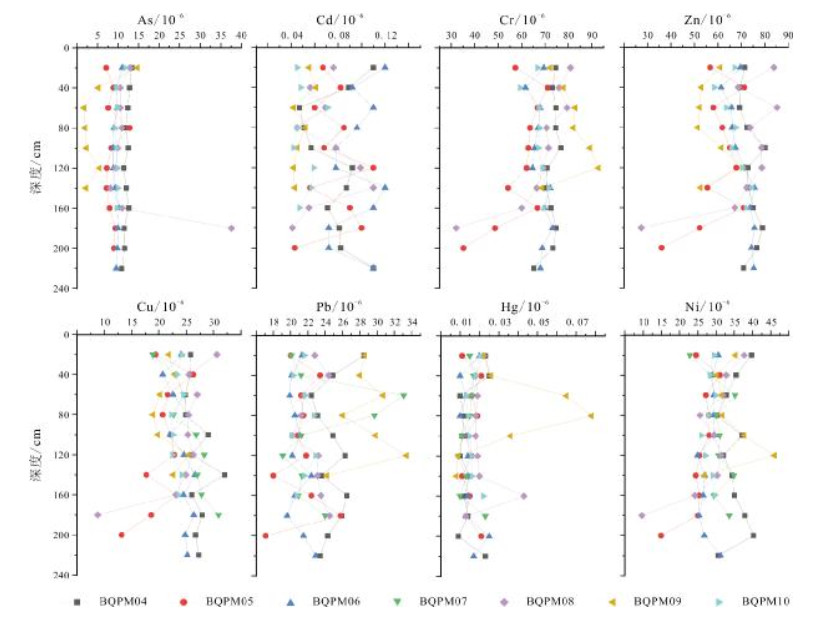
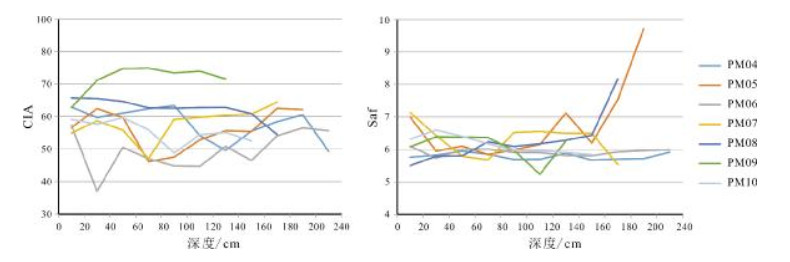
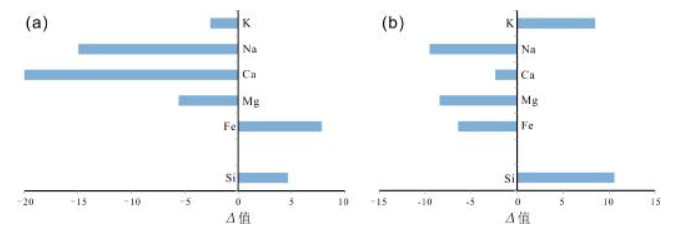
地表中元素的地球化学行为与自然环境密切相关,土壤中元素分布的变化记录了其形成时的环境特征.以拜泉地区典型黑土剖面为对象,对其常量、微量元素的分布规律及其蕴含的环境信息进行研究,探讨了研究区土壤剖面风化程度及剖面形成过程中气候演化特征.结果表明,拜泉土壤剖面常量元素含量除SiO2和Na2O外,总体上高于东北平原平均值;化学蚀变指数(CIA)平均值为58,硅铝铁率(Saf)值较高,属于弱风化强度.植物生长所必需的微量元素N、P、S、Mn、B、I、Ge、Se和Mo等在温暖气候条件下,在表层和淀积层积累,含量较高,在淋溶层和母质层含量较低;寒冷干燥条件下,在表层积累.金属微量元素与Fe元素具有较强的相关性,说明其垂向组分不仅受气候条件控制,同时受常量元素控制.常量元素迁移规律表明,剖面腐殖层土壤成熟度高,成土过程中以温暖湿润气候为主;淀积层可能处于脱Na、Ca阶段,成土过程中气候相对寒冷干燥.
Abstract:The geochemical behavior of elements in earth surface is closely related to natural environment, and the change of element distribution in soil records the environmental characteristics during its formation. Focusing on the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area, the paper studies the distribution rule of major and trace elements and its implied environmental information, and discusses the weathering degree of the soil sections and climatic evolution characteristics during the formation of section. The results show that except SiO2 and Na2O, the content of major elements in the soil sections is generally higher than that in Northeast Plain. The average chemical index of alteration (CIA) is 58, with high Saf value, belonging to weak weathering. The trace elements essential for plant growth, such as N, P, S, Mn, B, I, Ge, Se and Mo, accumulate under warm climatic condition, with high content in surface and illuvial layers, and low in eluvial layer and parent material layer; while under cold and dry conditions, they accumulate on the surface. The strong correlation between metal trace elements and Fe indicates that its vertical component is controlled not only by climatic conditions, but also by major elements. The migration rule of major elements reveals the soil in humus layer is of high maturity, mainly formed in a warm and humid climate. The illuvial layer may be at the removal stage of Na and Ca, with soil formed in a relatively cold and dry climate.
-
Key words:
- black soil section /
- major element /
- trace element /
- weathering /
- climate environment /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
表 1 拜泉土壤剖面常量元素参数
Table 1. Contents of major elements in the soil sections, Baiquan area
分层 含量/% SiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O 腐殖质层 最小值 47.87 11.51 2.64 0.52 0.77 0.95 1.76 最大值 69.54 15.52 5.50 1.82 13.14 1.91 3.49 平均值 62.91 14.05 5.27 1.42 2.32 1.48 2.40 标准差 6.45 1.08 0.79 0.35 4.00 0.30 0.47 淀积层 最小值 49.42 9.62 0.74 0.14 0.22 0.81 1.96 最大值 78.75 15.12 5.37 1.80 10.89 2.19 3.08 平均值 63.98 13.52 4.40 1.33 3.74 1.52 2.57 标准差 7.32 1.61 1.41 0.47 3.04 0.44 0.32 母质层 最小值 62.33 11.05 2.62 0.71 0.93 1.27 2.50 最大值 72.67 15.08 5.44 1.58 3.00 1.80 2.70 平均值 61.17 14.30 4.97 1.53 4.05 1.78 2.51 标准差 5.86 2.21 1.54 0.49 1.07 0.27 0.10 表 2 拜泉土壤剖面微量元素参数
Table 2. Contents of trace elements in the soil sections, Baiquan area
分层 含量/% SiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O 腐殖质层 最小值 47.87 11.51 2.64 0.52 0.77 0.95 1.76 最大值 69.54 15.52 5.50 1.82 13.14 1.91 3.49 平均值 62.91 14.05 5.27 1.42 2.32 1.48 2.40 标准差 6.45 1.08 0.79 0.35 4.00 0.30 0.47 淀积层 最小值 49.42 9.62 0.74 0.14 0.22 0.81 1.96 最大值 78.75 15.12 5.37 1.80 10.89 2.19 3.08 平均值 63.98 13.52 4.40 1.33 3.74 1.52 2.57 标准差 7.32 1.61 1.41 0.47 3.04 0.44 0.32 母质层 最小值 62.33 11.05 2.62 0.71 0.93 1.27 2.50 最大值 72.67 15.08 5.44 1.58 3.00 1.80 2.70 平均值 61.17 14.30 4.97 1.53 4.05 1.78 2.51 标准差 5.86 2.21 1.54 0.49 1.07 0.27 0.10 表 3 拜泉土壤剖面微量元素相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficient of trace elements in the soil sections, Baiquan area
元素 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn Fe As 1.00 0.52 -0.57 -0.12 0.98 0.02 0.27 -0.50 0.99 Cd 0.52 1.00 0.41 -0.91 0.35 0.86 0.96 0.48 0.38 Cr -0.57 0.41 1.00 -0.75 -0.72 0.81 0.64 1.00 -0.69 Cu -0.12 -0.91 -0.75 1.00 0.08 -0.99 -0.99 -0.80 0.04 Hg 0.98 0.35 -0.72 0.08 1.00 -0.17 0.08 -0.66 1.00 Ni 0.02 0.86 0.81 -0.99 -0.17 1.00 0.97 0.86 -0.14 Pb 0.27 0.96 0.64 -0.99 0.08 0.97 1.00 0.70 0.11 Zn -0.50 0.48 1.00 -0.80 -0.66 0.86 0.70 1.00 -0.63 Fe 0.99 0.38 -0.69 0.04 1.00 -0.14 0.11 -0.63 1.00 -
[1] 李艳华, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等.关中东部全新世黄土——古土壤序列微量元素分布特征及意义[J].土壤通报, 2012, 43(1):125-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201201025.htm
[2] 毛欣, 刘林敬, 李长安, 等.丰宁黄土-古土壤剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(10):1750-1759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201710010.htm
[3] 陆继龙, 周永昶, 周云轩.吉林省黑土某些微量元素环境地球化学特征[J].土壤通报, 2002(5):365-368. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2002.05.012
[4] 陆继龙, 周云轩, 周永昶, 等.黑土农业区常量和微量元素环境地球化学特征[J].农业环境与发展, 2002, 19(1):27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2002.01.014
[5] 周国华, 马生明, 喻劲松, 等.土壤剖面元素分布及其地质、环境意义[J].地质与勘探, 2002, 38(6):70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2002.06.017
[6] 马溶之.土壤剖面之研究及其地文意义[J].地质论评, 1948, 13(Z2):277-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1948Z2033.htm
[7] 崔明, 张旭东, 蔡强国, 等.东北典型黑土区气候、地貌演化与黑土发育关系[J].地理研究, 2008, 27(3):527-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.03.006
[8] 张明瑶, 刘月, 滕旭, 等.鸭绿江冲积平原土壤剖面常量元素的特征及其意义[J].辽东学院学报(自然科学版), 2019, 26(4):281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDFZ201904011.htm
[9] 佟宝辉, 张忠庆, 赵立刚, 等.吉林省中部黑土区土壤微量元素分布及空间变异特征研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(14):8143-8146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.14.049
[10] 李宁, 武洪峰, 林思伽.基于GIS的黑龙江省拜泉县耕地地力评价[J].现代化农业, 2012(6):63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2012.06.045
[11] 任为萍, 臧晓凡.明水-拜泉一带主要微量元素含量特征分析[J].黑龙江国土资源, 2010(7):59.
[12] 汤彦辉, 程岩, 孙玉龙.黑龙江省拜泉县耕地地力评价[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社, 2016.
[13] 石建凡, 施泽明, 吴鹏盛.四川万源大竹地区土壤垂向剖面硒的地球化学特征[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(Z1):38-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1020.htm
[14] 高宇, 杜亮亮, 海龙, 等.宁夏中宁县土壤硒元素垂向分布特征研究[J].资源环境与工程, 2017, 31(Z1):71-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK2017S1014.htm
[15] 韩晓凯, 高月, 娄翼来, 等.长期施肥对黑土中Cu、Cd含量及其剖面分布的影响[J].安全与环境学报, 2008, 8(3):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2008.03.003
[16] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2):295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[17] 王攀, 宁凯, 石迎春, 等.吴起全新世土壤剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].土壤通报, 2019, 50(6):1261-1268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201906001.htm
[18] 李徐生, 韩志勇, 杨守业, 等.镇江下蜀土剖面的化学风化强度与元素迁移特征[J].地理学报, 2007, 62(11):1174-1184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDE200803008.htm
[19] 徐树建, 倪志超, 丁新潮.山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(2):353-359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.017
[20] 刘银飞, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等.福建龙海土壤垂向剖面元素分布特征[J].物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):713-721. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201604013.htm
[21] 王海荣, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等.广东省典型花岗岩成土剖面元素垂向分布特征[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(2):619-628. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.025
[22] 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆鳞, 等.元素地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1984.
[23] 贾耀锋, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等.关中盆地全新世黄土-土壤剖面微量元素的地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J].土壤通报, 2012, 43(3):513-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201203002.htm
-




 下载:
下载: