STUDY ON THE CHANGES OF SOIL ENZYME ACTIVITY UNDER DIFFERENT LAND USE TYPES
-
摘要:
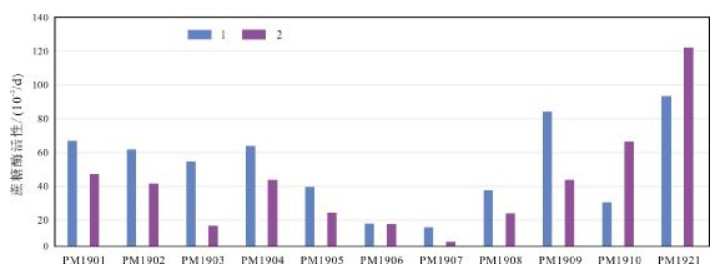
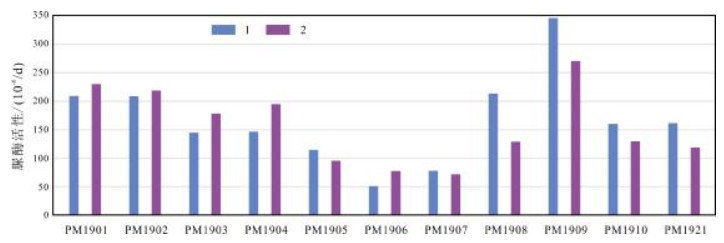
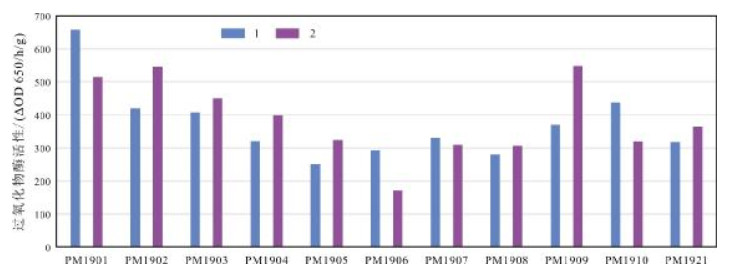
选择黑龙江省海伦市相邻耕地和林地作为研究对象,分析了土地利用方式、土壤深度以及部分地球化学特征等对土壤中蔗糖酶、脲酶、过氧化物酶活性的影响.结果表明:蔗糖酶受土壤深度影响较为明显,表层土壤中蔗糖酶活性显著高于深层土壤,而与土地利用方式无关;脲酶受土壤深度影响较小,但土地利用方式对其影响较大,如种植大豆可以显著提升土壤脲酶的活性,除此之外脲酶活性还受土壤黏粒含量的影响;过氧化物酶活性主要受控于土壤有机碳的含量,受土壤深度影响较小,但深层林地土壤中过氧化物酶活性显著高于深层耕地土壤.
Abstract:Focusing on the cultivated land and forest land in Hailun City of Heilongjiang Province, the paper analyzes the effects of land use types, soil depth and some geochemical characteristics on the activity of soil sucrase, urease and peroxidase. The results show that sucrase is significantly affected by soil depth, with the sucrase activity in surface layer obviously higher than that in deep layer, but not by land use types; while urease is less affected by soil depth than by land use types. Therefore soybean planting can drastically increase soil urease activity. Besides, urease activity is also affected by soil clay content. The peroxidase activity is mainly controlled by soil organic carbon (SOC) content, with less affection by soil depth, but the peroxidase activity in deep soil of forestland is significantly higher than that of cultivated land.
-
Key words:
- land use type /
- soil enzyme /
- sucrase /
- urease /
- peroxidase /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
表 1 土壤脲酶活性与理化指标
Table 1. Soil urease activity and physicochemical indexes for samples
土地利用方式 样品编号 脲酶活性/(10-6/d) Corg/10-2 pH CaO含量/10-2 砂粒含量/10-3 黏粒含量/10-3 杨树林 PM1909 308.31 3.92 6.26 1.62 75.75 293.4 杨树林 PM1901 219.86 3.23 6.49 1.52 94.41 311.76 玉米地 PM1902 213.85 3.14 6.56 1.44 68.09 341.56 大豆地 PM1908 171.29 1.88 6.42 1.36 96.17 212.46 玉米地 PM1904 170.7 2.97 6.35 1.53 66.48 247.67 杨树林 PM1903 161.79 2.49 6.65 1.47 74.19 258.47 玉米地 PM1910 144.93 2.28 6.11 1.42 69.53 283.37 松树林 PM1921 139.52 2.17 5.91 1.32 69.07 265.18 松树林 PM1905 105.08 1.86 6.55 1.29 97.38 182.3 杨树林 PM1907 75.17 2.47 6.4 1.36 86.15 229.59 玉米地 PM1906 64.7 1.77 6.2 1.23 92.74 214.77 表 2 土壤过氧化物酶活性与主要理化性质
Table 2. Soil peroxidase activity and physicochemical indexes for samples
土地利用方式 样品编号 过氧化物酶活性/(ΔOD 650/h/g) Corg/10-2 pH 黏粒含量/10-3 杨树林 PM1901 586.98 3.23 6.49 311.76 玉米地 PM1902 482.70 3.14 6.56 341.56 杨树林 PM1909 459.85 3.92 6.26 293.40 杨树林 PM1903 429.09 2.49 6.65 258.47 玉米地 PM1910 378.42 2.28 6.11 283.37 玉米地 PM1904 359.54 2.97 6.35 247.67 松树林 PM1921 341.33 2.17 5.91 265.18 杨树林 PM1907 320.26 2.47 6.4 229.59 大豆地 PM1908 293.66 1.88 6.42 212.46 松树林 PM1905 287.64 1.86 6.55 182.30 玉米地 PM1906 231.98 1.77 6.2 214.77 -
[1] Allison V J, Condron L M, Peltzer D A, et al. Changes in enzyme activities and soil microbial community composition along carbon and nutrient gradients at the Franz Josef chronosequence, New Zealand[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2007, 39(7):1770-1781. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.02.006
[2] Ajwa H A, Dell C J, Rice C W. Changes in enzyme activities and microbial biomass of tallgrass prairie soil as related to burning and nitrogen fertilization[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1999, 31(5):769-777. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00177-1
[3] Zornoza R, Guerrero C, Mataix-Solera J, et al. Assessing air-drying and rewetting pre-treatment effect on some soil enzyme activities under Mediterranean conditions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(8):2125-2134. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.01.010
[4] Max M C, Wood M, Jarvis S C. A microplatefluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2001, 33(12/13):1633-1640. http://europepmc.org/abstract/AGR/IND23266651
[5] Dick R P. Soil enzyme activities as indicators of soil quality[C]//Doran J W, Coleman D C, Bezdicek D F, et al. Defining Soil Quality for A Sustainable Environment. Madison WI: American Society of Agronomy, 1994: 107-124.
[6] Yao X H, Min H, Lü Z H, et al. Influence of acetamiprid on soil enzymatic activities and respiration[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2006, 42(2):120-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2005.12.001
[7] 樊军, 郝明德.黄土高原旱地轮作与施肥长期定位试验研究——Ⅰ.长期轮作与施肥对土壤酶活性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2003, 9(1):9-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2003.01.002
[8] 樊军, 郝明德.黄土高原旱地轮作与施肥长期定位试验研究Ⅱ.土壤酶活性与土壤肥力[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2003, 9(2):146-150. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2003.02.003
[9] Martens D A, Johanson J B, Frankenberger W T Jr. Production and persistence of soil enzymes with repeated addition of organic residues[J]. Soil Science, 1992, 153(1):53-61. http://journals.lww.com/soilsci/Abstract/1992/01000/Production_and_Persistence_of_Soil_Enzymes_With.8.aspx
[10] Chantigny M H, Angers D A, Beauchamp C J. Active carbon pools and enzyme activities in soils amended with de-inking paper sludge[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2000, 80(1):99-105. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036654121810_8c22.html
[11] Masto R E, Chhonkar P K, Singh D, et al. Changes in soil biological and biochemical characteristics in a long-term field trial on a sub-tropical inceptisol[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(7):1577-1582. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.11.012
[12] 王树起, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等.不同土地利用和施肥方式对土壤酶活性及相关肥力因子的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(6):1311-1316. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2009.06.010
[13] 李东坡, 武志杰, 陈利军, 等.长期不同培肥黑土磷酸酶活性动态变化及其影响因素[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2004, 10(5):550-553. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2004.05.019
[14] 王树起, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等.长期施肥对东北黑土酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2008, 19(3):551-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200803017.htm
[15] 杨春璐, 孙铁珩, 和文祥, 等.农药对土壤脲酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2006, 17(7):1354-1356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.07.040
[16] 闫颖.五种农药对土壤酶活性影响的研究[D].长春: 东北师范大学, 2004.
[17] 王艳.不同有机物料对有机磷农药污染土壤酶活性及土壤微生物量的影响[J].生态环境学报, 2014, 23(7):1205-1209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.07.018
[18] 闫雷, 李晓亮, 秦智伟, 等.农药对土壤酶活性影响的研究进展[J].农机化研究, 2009, 31(11):223-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJYJ200911069.htm
[19] 王光华, 金剑, 韩晓增, 等.不同土地管理方式对黑土土壤微生物量碳和酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2007, 18(6):1275-1280. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2007.06.018
[20] 王树起, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等.寒地黑土大豆轮作与连作不同年限土壤酶活性及相关肥力因子的变化[J].大豆科学, 2009, 28(4):611-615. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDKX200904010.htm
[21] 李文凤, 房翠翠, 牛玉昊, 等.高原地区不同农作物土壤酶活性与土壤养分关系研究[J].北方园艺, 2014, 38(12):159-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFYY201412046.htm
[22] 刘岚君, 何季, 文雪峰.间作不同农作物对刺梨园土壤微生物类群及酶活性的影响[J].山地农业生物学报, 2019, 38(6):8-13, 42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNS201906002.htm
[23] 徐华勤, 章家恩, 冯丽芳, 等.广东省典型土壤类型和土地利用方式对土壤酶活性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(6):1464-1471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF201006024.htm
[24] 陈大勋.福建省几种土壤类型酶活性的研究[J].福建农学院学报, 1986, 15(1):78-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJND198601011.htm
[25] Tu C M. Effect of four experimental insecticides on enzyme activities and levels of adenosine triphosphate in mineral and organic soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 1990, 25(6):787-800. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/19911154213.html
[26] 闫颖, 袁星, 樊宏娜, 等.五种农药对土壤转化酶活性的影响[J].中国环境科学, 2004, 24(5):588-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200405019.htm
[27] 王天元, 宋雅君, 滕鹏起.土壤脲酶及脲酶抑制剂[J].化学工程师, 2004, 18(8):22-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXGC200408009.htm
[28] 王涵, 王果, 黄颖颖, 等. pH变化对酸性土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态环境, 2008, 17(6):2401-2406. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200806057.htm
-



 下载:
下载: