GEOCHEMICAL ANOMALIES AND METALLOGENIC PROSPECT IN CHAHAXILI AREA OF DULAN COUNTY, QINGHAI PROVINCE
-
摘要:
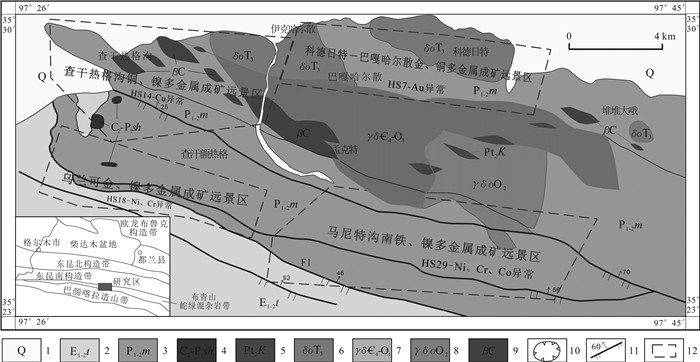
通过1:5万水系沉积物的地球化学测量,对查哈西里地区Au、Cu等16种元素的地球化学特征进行了初步分析.综合元素富集程度、分异程度、叠加强度,发现Au、Cu、Ni、Cr、Co在研究区内有富集成矿的可能,是研究区主要成矿元素.根据异常特征与成矿地质条件,推断区内为构造蚀变岩型Au-Cu多金属矿床及热液蚀变型Cu-Ni多金属矿床.优选出4处成矿远景区,即科德日特-巴嘎哈尔散金铜多金属成矿远景区、查干热格沟铜多金属成矿远景区、乌兰可镍多金属成矿远景区和马尼特沟南铁镍多金属成矿远景区.
Abstract:Through the 1:50 000 geochemical survey of stream sediments in Chahaxili area, the paper analyzes the geochemical characteristics of 16 elements such as Au and Cu. Combined with the enrichment, differentiation, and superposition degree of elements, it is found that Au, Cu, Ni, Cr and Co have the possibility of enrichment and mineralization, and serve as the main ore-forming elements in the study area. Based on the anomaly characteristics and metallogenic geological conditions, it is inferred that there are structural altered rock type Au-Cu polymetallic deposits and hydrothermal alteration type Cu-Ni polymetallic deposits in the area. Four metallogenic prospective areas are optimized, including Kederite-Bagahaersan Au-Cu polymetallic prospective area, Chaganregegou Cu polymetallic prospective area, Wulanke Ni polymetallic prospective area and Manitegounan Fe-Ni polymetallic prospective area.
-

-
表 1 查哈西里地区元素异常下限统计
Table 1. Statistics of element anomaly threshold in Chahaxili area
元素 理论计算值 实际使用值 元素 理论计算值 实际使用值 Au 3.37 3 Ti 4702.16 3800 As 30.16 25 Pb 29.66 25 Sb 2.93 4.5 Zn 115.05 95 Hg 67.55 45 Ag 82.73 70 Cu 47.93 41 W 2.40 2 Ni 57.97 47 Sn 4.18 3.45 Co 21.63 17 Bi 0.52 0.45 Cr 111.78 90 Mo 1.07 0.90 异常值单位:Au、Ag、Hg为10-9;其他元素为10-6. 表 2 查哈西里地区元素分布及富集特征参数统计
Table 2. Statistics of element distribution and enrichment characteristic parameters in Chahaxili area
元素 均值 标准方差 东昆仑平均值* 富集系数 变化系数 叠加系数 Ag 61.93 58.14 51 1.21 0.94 4.98 As 16.18 15.34 12.3 1.32 0.95 2.20 Au 2.97 28.92 1.61 1.84 9.74 60.94 Bi 0.33 0.33 0.33 1.00 1.00 3.27 Co 14.53 17.63 9.55 1.52 1.21 4.62 Cr 77.41 70.67 48.7 1.59 0.91 3.59 Cu 45.81 412.73 20.2 2.27 9.01 68.61 Hg 31.42 93.91 20 1.57 2.99 8.26 Mo 0.7 0.63 0.8 0.88 0.90 3.25 Ni 39.3 50.97 22.7 1.73 1.30 4.85 Pb 19.65 9.46 18.7 1.05 0.48 1.85 Sb 2.58 3.23 0.96 2.69 1.25 7.85 Sn 2.68 0.89 2.36 1.14 0.33 1.17 Ti 2932.53 959.87 3040 0.96 0.33 1.08 W 1.54 0.92 1.9 0.81 0.60 2.04 Zn 72.15 54.61 58.3 1.24 0.76 2.51 *东昆仑元素平均值据《青海省东昆仑地球化学说明书(1∶ 500000)》.含量单位:Au、Ag、Hg为10-9,其他为10-6. 表 3 查哈西里地区元素分布类型统计
Table 3. Statistics of element distribution types in Chahaxili area
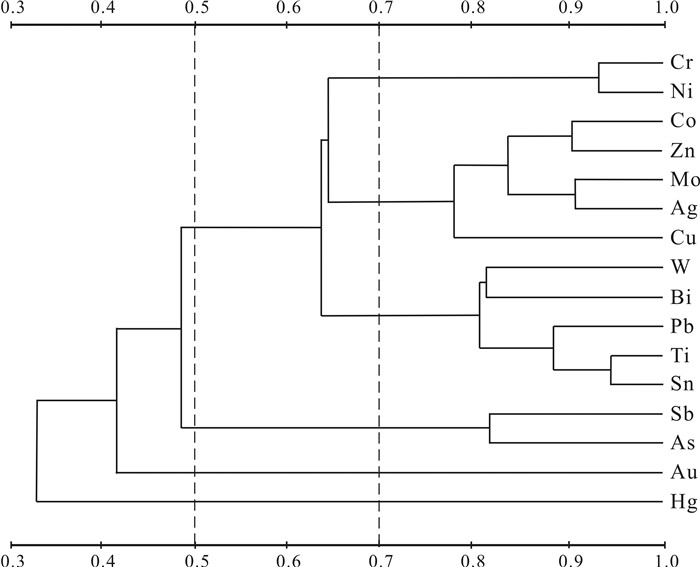
参数 范围 等级划分 研究区化学元素 Cv <0.7 均匀型 Pb、Sn、Ti、W [0.7,1.0) 分异型 Ag、As、Cr、Mo、Zn ≥1.0 强分异型 Au、Bi、Co、Cu、Hg、Ni、Sb K <0.8 贫化型 [0.8,1.2) 背景型 Bi、Mo、Pb、Sn、Ti、W ≥1.2 富集型 Ag、As、Au、Co、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Sb、Zn D <1.5 同生型 Sn、Ti [1.5,3.5) 改造型 As、Bi、Mo、Pb、W、Zn [3.5,7.0) 叠加型 Ag、Co、Cr、Ni [7.0,14.0) 强叠加型 Hg、Sb ≥14.0 极强叠加型 Au、Cu 表 4 HS7综合异常特征
Table 4. Characteristics of HS7 integrated anomaly
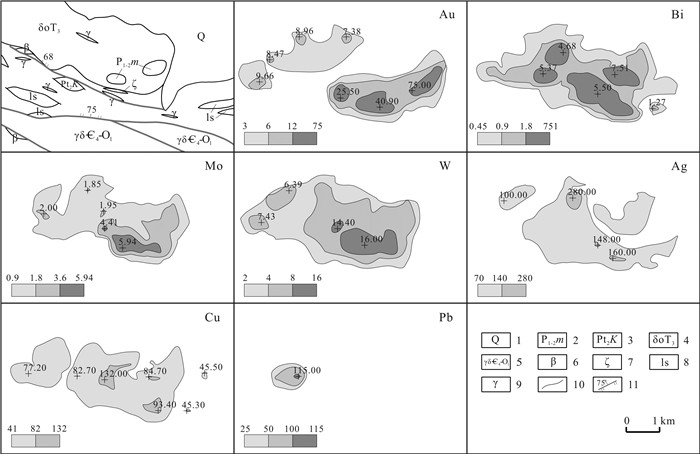
元素 异常下限 异常点数 面积/km2 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变化系数 衬度 规模 Ag 70.00 45 6.82 280.00 99.11 35.00 0.35 1.42 9.66 As 25.00 7 0.92 43.30 32.30 6.92 0.21 1.29 1.19 Au 3.00 43 7.26 75.00 11.26 13.20 1.17 3.75 27.25 Bi 0.45 53 9.35 7.51 1.76 1.72 0.98 3.91 36.57 Co 17.00 18 2.41 28.40 21.48 2.78 0.13 1.26 3.05 Cr 90.00 17 2.02 242.00 117.19 33.93 0.29 1.30 2.63 Cu 41.00 40 7.06 132.00 68.49 18.84 0.28 1.67 11.79 Mo 0.90 42 7.03 5.94 2.04 1.29 0.63 2.27 15.93 Ni 47.00 19 1.90 76.90 58.05 9.05 0.16 1.24 2.35 Pb 25.00 2 0.66 115.00 83.6 31.4 0.38 3.34 2.21 Sn 3.45 4 0.62 4.32 4.06 0.25 0.06 1.18 0.73 W 2.00 60 9.96 16.00 5.44 3.26 0.60 2.72 27.09 异常值单位: Au、Ag为10-9; 其他元素为10-6. 表 5 HS14综合异常特征
Table 5. Characteristics of HS14 integrated anomaly
元素 异常下限 异常点数 面积/km2 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变化系数 衬度 规模 Ag 70.00 8 2.78 1890.00 926.25 773.37 0.83 13.23 36.79 As 25.00 7 0.92 69.40 41.77 17.44 0.42 1.67 1.54 Au 3.00 14 2.60 99.90 26.82 34.13 1.27 8.94 23.24 Bi 0.45 6 1.98 2.54 1.67 0.72 0.43 3.71 7.35 Co 17.00 23 4.30 568.00 126.29 181.68 1.44 7.43 31.94 Cr 90.00 25 4.35 507.00 164.30 88.70 0.54 1.83 7.94 Cu 41.00 23 3.87 14902.00 2585.04 4630.31 1.79 63.05 244.00 Hg 45.00 23 2.19 575.00 108.05 167.01 1.55 2.40 5.26 Mo 0.90 7 2.42 18.40 10.99 7.51 0.68 12.21 29.55 Ni 47.00 21 3.74 332.00 96.18 55.31 0.58 2.05 7.65 Pb 25.00 6 1.07 133.00 73.92 42.94 0.58 2.96 3.16 Sn 3.45 8 1.28 8.97 5.11 1.89 0.37 1.48 1.90 W 2.00 9 1.28 3.66 2.78 0.44 0.16 1.39 1.78 Zn 95.00 12 2.74 1850.00 624.09 629.45 1.01 6.57 18.00 Sb 4.50 2 0.17 6.26 6.15 0.10 0.02 1.37 0.23 异常值单位: Au、Ag、Hg为10-9; 其他元素为10-6. 表 6 HS18综合异常特征
Table 6. Characteristics of HS18 integrated anomaly
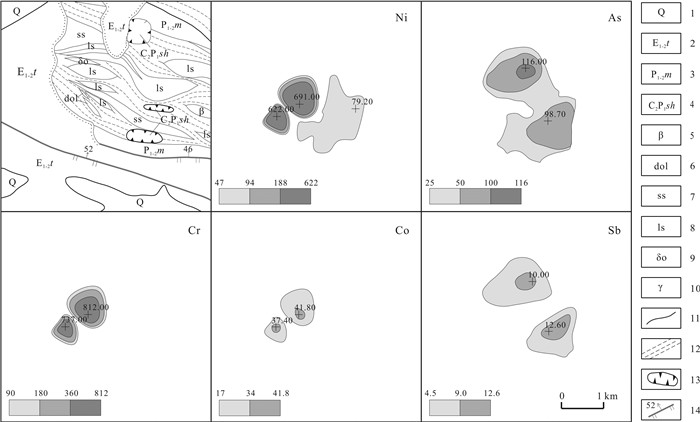
元素 异常下限 异常点数 面积/km2 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变化系数 衬度 规模 As 25.00 16 3.58 116.00 58.32 29.63 0.51 2.33 8.35 Bi 0.45 6 1.22 1.07 0.67 0.26 0.39 1.49 1.82 Co 17.00 2 0.75 41.80 39.60 2.20 0.06 2.33 1.75 Cr 90.00 3 1.02 812.00 533.13 342.71 0.64 5.92 6.04 Hg 45.00 5 0.97 93.8 73.6 15.73 0.21 1.64 1.59 Mo 0.90 5 0.36 1.20 1.02 0.10 0.10 1.13 0.41 Ni 47.00 10 2.51 691.00 176.14 241.03 1.37 3.75 9.41 Sn 3.45 5 0.67 6.33 4.25 1.06 0.25 1.23 0.83 W 2.00 5 0.72 2.74 2.46 0.27 0.11 1.23 0.89 Sb 4.50 8 2.19 12.60 9.15 2.28 0.25 2.03 4.45 异常值单位: : Hg为10-9;其他元素为10-6. 表 7 HS29综合异常特征
Table 7. Characteristics of HS29 integrated anomaly
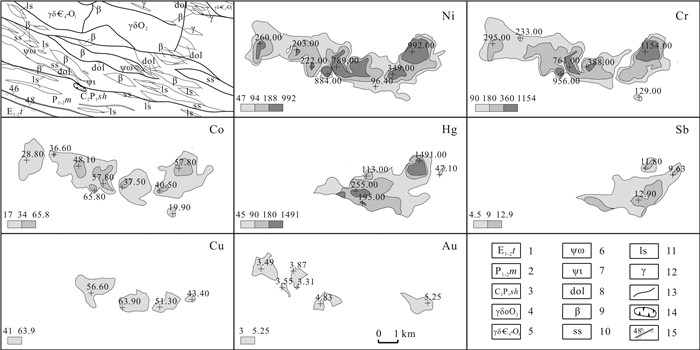
元素 异常下限 异常点数 面积/km2 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变化系数 衬度 规模 As 25.00 40 5.26 48.70 35.91 5.87 0.16 1.44 7.56 Au 3.00 31 3.24 5.25 3.50 0.60 0.17 1.17 3.78 Co 17.00 76 12.66 65.80 27.32 11.17 0.41 1.61 20.35 Cr 90.00 92 15.48 1154.00 236.94 206.17 0.87 2.63 40.75 Cu 41.00 26 3.97 63.90 46.77 5.97 0.13 1.14 4.53 Hg 45.00 63 9.19 1491 135.79 226.54 1.67 3.02 27.73 Mo 0.90 40 4.95 1.41 1.05 0.13 0.12 1.17 5.78 Ni 47.00 94 17.08 992.00 172.85 199.31 1.15 3.68 62.81 Sn 3.45 40 5.76 5.69 4.33 0.63 0.15 1.26 7.23 W 2.00 40 5.78 3.10 2.35 0.23 0.10 1.18 6.79 Zn 95.00 37 4.29 114.00 101.65 5.23 0.05 1.07 4.59 Sb 4.50 47 6.47 12.90 8.26 2.3 0.28 1.84 11.88 异常值单位: : Au、Hg为10-9; 其他元素为10-6. -
[1] 潘彤, 罗才让, 伊友昌, 等. 青海省金属矿产成矿规律及成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 1-214.
Pan T, Luo C R, Yi Y C, et al. Metallogenic laws and prospecting of metal depoist in Qinghai Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 1-214. (in Chinese)
[2] 薛顺荣, 肖克炎, 丁建华. 香格里拉地区勘查地球化学信息找矿应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(5): 537-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200805020.htm
Xue S R, Xiao K Y, Ding J H. The application of geochemical information to ore exploration in Shangri-La area, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(5): 537-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200805020.htm
[3] 王磊, 杨建国, 王小红, 等. 甘肃北山炭山子-黄草泉一带水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1276-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.009
Wang L, Yang J G, Wang X H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in the Tanshanzi-Huangcaoquan Area of Beishan, Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(6): 1276-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.009
[4] 张晶, 杨博, 李宝强, 等. 中国西北地区成矿元素区域地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(5): 1042-1052 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201805017.htm
Zhang J, Yang B, Li B Q, et al. Regional geochemical characteristics of metallogenic elements in northwest China[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(5): 1042-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201805017.htm
[5] 崔晓亮, 刘婷婷, 王文恒, 等. 东昆仑布青山地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(5): 573-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201105002.htm
Cui X L, Liu T T, Wang W H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and ore search prospects of Buqingshan area in Qinghai Province based on stream sediment survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(5): 573-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201105002.htm
[6] 颜自给, 李学彪. 青海省都兰县阿拉克湖地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 矿产与地质, 2014, 28(1): 58-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2014.01.011
Yan Z J, Li X B. Geochemical characteristics of the stream sediment and prospecting direction in Alake Lake area, Dulan County in Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2014, 28(1): 58-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2014.01.011
[7] 胡兆国, 张少鹏, 连国建, 等. 青海省纳日宗地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 481-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803006.htm
Hu Z G, Zhang S P, Lian G J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting in the Narizong area, Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 481-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803006.htm
[8] 高永伟, 郭周平, 赵辛敏, 等. 青海北祁连冷龙岭地区水系沉积物元素地球化学特征及异常圈定[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 468-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803005.htm
Gao Y W, Guo Z P, Zhao X M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and anomalies identification of elements in the stream sediments from the Lenglongling area of North Qilian Mountains, Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 468-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803005.htm
[9] 赵娟, 王泰山, 李德彪, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区1: 5万水系沉积物测量方法技术及应用成果[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(4): 739-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201704013.htm
Zhao J, Wang T S, Li D B, et al. The techniques and application achievements in 1: 50000 stream sediment survey of the Qimantage area, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(4): 739-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201704013.htm
[10] 邵继, 刘会文, 刘江峰, 等. 阿尔金牛鼻子梁地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5): 176-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805025.htm
Shao J, Liu H W, Liu J F, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments in the Niubiziliang area, Altyn: Implication for mineralization and prospecting direction[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(5): 176-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805025.htm
[11] 祝大伟, 何玉燕, 郝延海, 等. 新疆塔什库尔干县赞坎铁矿外围水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(10): 1867-1873. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.10.017
Zhu D W, He Y Y, Hao Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting orientation in the periphery of the Zankan iron ore deposit, Taxkorgan, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(10): 1867-1873. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.10.017
[12] 朱有光, 蒋敬业, 李泽九, 等. 试论我国重要景观区中景观、表生因素对金、铜区域地球化学异常标志的影响[J]. 物探与化探, 2001, 25(6): 418-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2001.06.003
Zhu Y G, Jiang J Y, Li Z J, et al. A Tentative discussion on the influence of landscape and epigenetic factors upon indicators of copper and gold geochemical anomalies in important landscape regions of China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2001, 25(6): 418-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2001.06.003
[13] 戴慧敏, 代雅键, 马振东, 等. 大兴安岭查巴奇地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 1043-1050. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.025
Dai H M, Dai Y J, Ma Z D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in the Chabaqi area of Da Hinggan Mts[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 1043-1050. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.025
[14] 魏小林, 康波, 甘承萍, 等. 东昆仑马尼特地区晚三叠世侵入岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(1): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201901006.htm
Wei X L, Kang B, Gan C P, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of late Triassic intrusive rock in the Manite area, East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(1): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201901006.htm
[15] 边千韬, 罗小全, 李涤徽, 等. 青海省阿尼玛卿带布青山蛇绿混杂岩的地球化学性质及形成环境[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(1): 45-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.01.005
Bian Q T, Luo X Q, Li D H, et al. Geochemistry and formation environment of the Buqingshan ophiolite complex, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(1): 45-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.01.005
[16] 刘战庆, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂岩带的地质特征及大地构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(8): 1182-1195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.08.002
Liu Z Q, Pei X Z, Li R B, et al. Geological characteristics of the Buqingshan tectonic melange belt in the southern margin of East Kunlun and its tectonic implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(8): 1182-1195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.08.002
[17] 刘战庆, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑南缘阿尼玛卿构造带布青山地区两期蛇绿岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(2): 185-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201102005.htm
Liu Z Q, Pei X Z, Li R B, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of the two suites of ophiolites at the Buqingshan area of the A'nyemaqen orogenic belt in the southern margin of East Kunlun and its tectonic implication[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(2): 185-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201102005.htm
[18] 李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂带得力斯坦南MOR型玄武岩地质、地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(7): 1148-1162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201507004.htm
Li R B, Pei X Z, Li Z C, et al. Geological and geochemical features of Delisitannan basalts and their petrogenesis in Buqingshan tectonic mélange belt, southern margin of East Kunlun orogen[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(7): 1148-1162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201507004.htm
[19] 郭世珍, 赵寿, 保正岳, 等. 马尼特金矿控矿因素及找矿前景分析[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 28(2): 47-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8996.2010.02.012
Guo S Z, Zhao S, Bao Z Y, et al. Analysis on the ore-controlling factor and ore-searching prospect in the Manife gold deposit[J]. Journal of Qinghai University (Nature Science), 2010, 28(2): 47-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8996.2010.02.012
[20] 周红智, 徐崇文, 张松涛, 等. 青海都兰沟里金矿整装勘查1: 100000地质矿产数据集[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(S1): 93-104. doi: 10.12029/gc2019Z111
Zhou H Z, Xu C W, Zhang S T, et al. The 1: 100000 Mineralogical Dataset of the Gouli Gold Deposit Integrated Exploration Area in Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(S1): 93-104. doi: 10.12029/gc2019Z111
[21] 李欢, 徐国志, 孙璐, 等. 化探综合异常图定量编制方法及应用[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(6): 1062-1070. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201906016.htm
Li H, Xu G Z, Sun L, et al. A quantitative method for integrated anomaly map of geochemical prospecting and application[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2019, 38(6): 1062-1070. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201906016.htm
[22] 严己宽, 玉强忠. 地球化学勘查固体样品采集的野外质量评价指标[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(6): 1112-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201806002.htm
Yan J K, Yu Q Z. The field quality evaluation index of solid sampling in geochemical exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6): 1112-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201806002.htm
[23] 柳坤峰, 冯昌荣, 翟黎明, 等. 新疆乌恰县吾合沙鲁地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 759-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201904009.htm
Liu K F, Feng C R, Zhai L M, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in the Wuheshalu area, Wuqia County, Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(4): 759-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201904009.htm
[24] 史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2): 234-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602005.htm
Shi C Y, Liang M, Feng B. Average background values of 39 chemical elements in stream sediments of China[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(2): 234-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602005.htm
[25] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-148.
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 1-148.
[26] 戴慧敏, 鲍庆中, 宫传东, 等. 因子分析法对内蒙古查巴奇地区水系沉积物地球化学分区的应用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(2): 245-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.02.007
Dai H M, Bao Q Z, Gong C D, et al. Study of applying factor analysis method to the geochemical division in stream sediments in the Chabaqi area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(2): 245-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.02.007
-



 下载:
下载: