APPLICATION OF EXTREME LEARNING MACHINE IN ANALYSIS OF CLAY MINERALS
-
摘要:
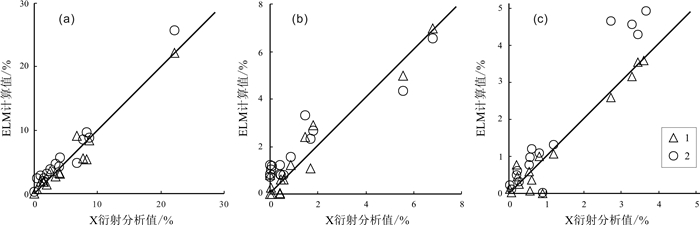
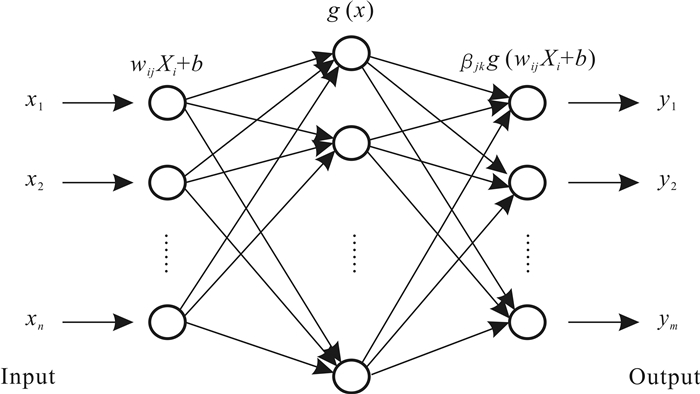
对鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格北部上古生界盒8段低渗透储层研究发现,成岩作用是控制气藏分布的主要因素之一,而黏土矿物又影响着成岩作用类型及强度,在成岩作用划分中具有重要指示作用.本研究尝试利用自然伽马能谱测井结合神经网络(极限学习机)准确计算储层中黏土矿物含量,为全井自动成岩作用识别提供支撑.在黏土矿物分析过程中,为避免测井信息受岩石骨架颗粒成分差异的影响,针对研究区沉积的岩屑砂岩和岩屑石英砂岩分别建立黏土矿物分析神经网络,提高计算精度.神经网络采用了参数不易陷入局部最优的极限学习机,保证了分析结果的速度和稳定性.在此基础上,利用苏里格北部地区上古生界盒8段15个X衍射分析样本,将分岩性计算结果与及未分岩性分析结果进行比较,证明了方法的有效性.
Abstract:The study on low permeability reservoirs in the 8th member of Lower Shihezi Formation, Upper Paleozoic in northern Sulige of Ordos Basin show that diagenesis is one of the main factors controlling the distribution of gas reservoirs, while clay minerals affect the type and intensity of diagenesis and serve as an important indicator in the classification of diagenesis. This study attempts to use natural gamma-ray spectral logging combined with neural network (extreme learning machine, ELM) to accurately calculate the content of clay minerals in reservoir, providing support for automatic identification of diagenesis in the whole well. In the analysis of clay minerals, to avoid the influence of difference of rock skeleton and particle compositions on logging information, the neural network of clay mineral analysis is established respectively for lithic sandstone and lithic quartz sandstone in the study area to improve calculation accuracy. The neural network adopts the ELM with lower probability of trapping into low efficiency and local optimum to ensure the speed and stability of analysis result. On this basis, 15 X-ray diffraction analysis samples from the 8th member of Lower Shihezi Formation in northern Sulige area are used to compare the calculated results of differential and indifferential lithology, proving the effectiveness of the method.
-

-
表 1 不同黏土矿物及岩性自然伽马能谱测井特征对照表
Table 1. Comparison of natural gamma-ray spectral logging characteristics by clay minerals and lithology
放射性元素 岩屑石英砂岩 岩屑砂岩 高岭石 蒙脱石 伊利石 绿泥石 Th/10-6 7.16 8.28 6~19 0.8~2 10~25 0~8 K/% 1.41 1.74 0~0.5 0~1.5 3.51~8.31 0~0.3 Th/K 5.07 4.75 11~30 3.7~8.7 1.7~3.5 11~30 U/10-6 1.6 1.56 4.4~7 4.3~7.7 8.7~12.4 17.4~36.2 表 2 黏土矿物计算结果对照表
Table 2. Comparison of clay mineral calculation results
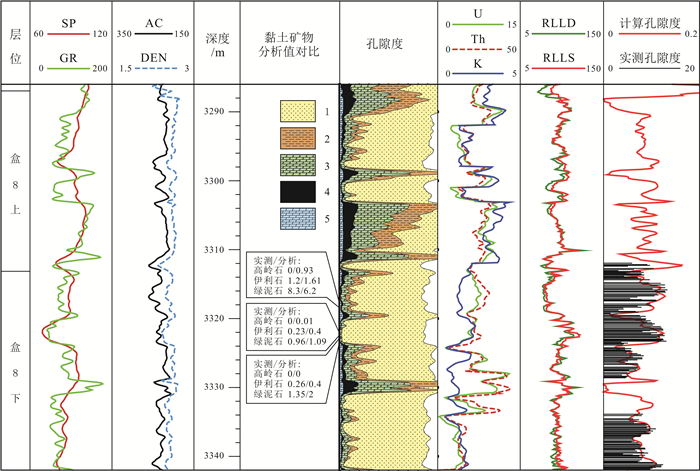
井名 深度/m 绿泥石 高岭石 伊利石+伊/蒙混层 实测 未分岩性 分岩性 实测 未分岩性 分岩性 实测 未分岩性 分岩性 苏74 3237.92 0.49 0.92 0.7 0.07 1.2 0 0.07 0.11 0.02 苏77 3148.89 2.01 3.1 1.43 0.57 0.8 0.6 0.56 0.98 0.07 苏77 3152.46 7.69 6.52 5.57 1.48 3.32 2.39 2.72 4.67 2.58 召23 3064.39 2.48 3.77 3.61 1.69 2.32 0.53 0.61 1.2 0.37 召23 3071.17 22.2 25.68 22.12 6.8 6.56 6.96 3.44 4.3 3.54 召36 3090.06 6.66 4.8 8.1 5.57 4.35 3.59 3.6 5.02 3.59 召36 3098.93 3.89 4.2 3.32 0.85 1.56 1.22 0.81 1.08 0.99 召36 3101.6 1.48 2.36 1.78 0.45 0.8 0.6 0.2 0.51 0.77 召48 2908.69 8.64 8.87 8.41 1.8 2.65 2.39 3.28 4.56 3.16 召51 2817.28 0 0.31 0 0.03 1.03 0.27 0.03 0.22 0.12 苏53 3318.35 8.32 9.68 5.37 0 0.52 0.39 1.2 1.31 1.07 苏53 3321.53 0.96 1.18 1.09 0 0.85 0 0.23 0.62 0.45 苏53 3323.07 1.35 1.96 1.81 0 0.74 0 0.26 0.31 0.26 苏53 3346.06 4.07 5.65 3.15 0.4 1.23 0.03 0.53 0.78 0.58 苏53 3347.55 3.41 4.66 2.71 0.4 0.85 0 0.89 0.02 0 含量单位:%. -
[1] 白烨, 薛林福, 石玉江, 等. 测井成岩相自动识别及其在鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格地区的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(1): 35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.01.006
Bai Y, Xue L F, Shi Y J, et al. An automatic identification method of log diagenetic facies and its application in Sulige area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2013, 37(1): 35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.01.006
[2] 张海涛, 时卓, 石玉江, 等. 低渗透致密砂岩储层成岩相类型及测井识别方法——以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田下石盒子组8段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(2): 256-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202015.htm
Zhang H T, Shi Z, Shi Y J, et al. Diagenetic facies types and logging identification methods for low-permeability tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study on the 8th member of Xiashihezi Formation in Sulige Gasfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(2): 256-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202015.htm
[3] 牟传龙, 王秀平, 王启宇, 等. 关于苏里格气田东二区盒8段储层成岩相的再认识[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(2): 346-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201602013.htm
Mou C L, Wang X P, Wang Q Y, et al. The recognition of diagenetic facies on the case from the reservoir in He8 section of Shihezi Formation, East Ⅱ part of Sulige gas field, Qrdos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(2): 346-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201602013.htm
[4] 王秀平, 牟传龙, 贡云云, 等. 苏里格气田Z30区块下石盒子组8段储层成岩演化与成岩相[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(5): 883-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201305009.htm
Wang X P, Mu C L, Gong Y Y, et al. Diagenetic evolution and facies of reservoirs in Member 8 of Permian Xiashihezi Formation in the Z30 block of Sulige gasfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(5): 883-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201305009.htm
[5] 徐同台, 王行信, 张有瑜, 等. 中国含油气盆地粘土矿物[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003: 20-53.
Xu T T, Wang X X, Zhang Y Y, et al. Clay minerals of petroliferous basins in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 20-53. (in Chinese)
[6] 刘菁华, 王祝文, 易清平. 利用自然γ能谱测井资料确定粘土矿物的含量及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(1): 215-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201001036.htm
Liu J H, Wang Z W, Yi Q P. Determinating clay mineral content by natural gamma-ray spectral logging data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(1): 215-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201001036.htm
[7] 石强. 利用自然伽马能谱测井定量计算粘土矿物成分方法初探[J]. 测井技术, 1998, 22(5): 349-352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS805.009.htm
Shi Q. Preliminary investigation on quantitative analysis of the composition of clay minerals using NGS log[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1998, 22(5): 349-352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS805.009.htm
[8] 郭影文. 自然伽马能谱测井在粘土矿物含量分析中的应用[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 2008, 30(6): 268-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200806067.htm
Guo Y W. Application of natural gamma ray spectroscopy log for analysis of clay mineral content[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 2008, 30(6): 268-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200806067.htm
[9] 谭廷栋. 测井解释粘土矿物[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 1987, 4(6): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZC198706006.htm
Tan T D. Log interpretation of clay minerals[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 1987, 4(6): 25-32. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZC198706006.htm
[10] 孙建孟, 李召成. 应用自然伽马能谱测井确定粘土矿物类型和含量[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 23(4): 29-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.1999.04.008
Sun J M, Li Z C. Determination of clay types and contents by natural gamma-ray spectrum logging[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 1999, 23(4): 29-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.1999.04.008
[11] Schlumberger Wireline & Testing. Schlumberger log interpretation charts[M]. Houston: Schlumberger, 1997: 4-30.
[12] 张立明. 人工神经网络的模型及其应用[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 1993: 32-47.
Zhang L M. Models and applications of artificial neural networks[M]. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 1993: 32-47.
[13] 桂现才. BP神经网络在MATLAB上的实现与应用[J]. 湛江师范学院学报, 2004, 25(3): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4702.2004.03.021
Gui X C. Realization of BP networks and their applications on MATLAB[J]. Journal of Zhanjiang Normal College, 2004, 25(3): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4702.2004.03.021
[14] 苏高利, 邓芳萍. 论基于MATLAB语言的BP神经网络的改进算法[J]. 科技通报, 2003, 19(2): 130-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2003.02.012
Su G L, Deng F P. On the improving backpropagation algorithms of the neural networks based on MATLAB language: A review[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2003, 19(2): 130-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2003.02.012
[15] 黄丽. BP神经网络算法改进及应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2008.
Huang L. BP neural network algorithm improvement and application research[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2008.
[16] 王娜娜. 神经网络在测井岩性识别中的应用[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2009.
Wang N N. The application of neural network in logging lithology identification[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2009.
[17] 蔡磊, 程国建, 潘华贤. 极限学习机在岩性识别中的应用[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2010, 31(9): 2010-2012. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201009035.htm
Cai L, Cheng J G, Pan H X. Lithologic identification based on ELM[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2010, 31(9): 2010-2012. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201009035.htm
[18] Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks[C]//Proceedings of 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2004.
[19] 白烨, 薛林福, 潘保芝, 等. 多方法融合判别复杂砂砾岩岩性[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(S2): 442-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ2012S2050.htm
Bai Y, Xue L F, Pan B Z, et al. Multi-methods combined identify lithology of glutenite[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(S2): 442-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ2012S2050.htm
[20] 黄隆基. 放射性测井原理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1985: 66-79.
Huang L J. Principle of radioactive logging[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1985: 66-79. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: