GEOCHEMICAL STUDY ON SELENIUM IN ROCK-SOIL-PLANT IN NORTHERN LIAONING PROVINCE
-
摘要:
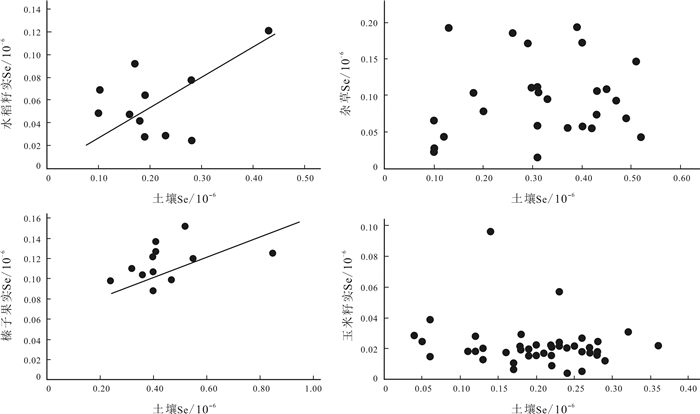
通过对辽宁北部地区岩石、土壤和植物中硒元素的地球化学研究,分析了硒元素在岩石-土壤-植物中的释放-迁移-吸收特征与数量变化规律.研究结果表明:岩石样品硒含量平均值为0.08×10-6,总体上岩石中硒质量分数呈现火山岩>碳酸盐岩>花岗岩/沉积岩>变质岩的规律;垂向上硒质量分数呈现土壤A层>土壤B层>成土母岩的变化规律;土壤表层硒平均含量0.24×10-6,土壤中硒质量分数总体上呈现棕壤(A、B层)>水稻土(A、B层)>草甸土(A、B层)>风砂土(A、B层)的规律;植物中硒平均含量0.07×10-6,植物对土壤中硒富集能力大小依次为杂草>榛子>水稻>玉米;土壤和水稻、土壤和榛子之间硒含量存在显著的正相关,土壤和杂草、土壤和玉米之间相关性不明显.
Abstract:Through the geochemical study of Se in rocks, soils and plants in northern Liaoning Province, the paper analyzes the release-migration-absorption of Se in rock-soil-plant. The results indicate that the average Se content in rocks is 0.08×10-6. For different rock types, the Se contents generally show the rule of volcanic rock > carbonate rock > granite/sedimentary rock > metamorphic rock. Vertically, the Se content shows the variation of soil layer A > soil layer B > pedogenic mother rock. The average Se content in topsoil is 0.24×10-6, with the general pattern of brown soil (A&B layers) > paddy soil (A&B layers) > meadow soil (A&B layers) > aeolian sandy soil (A&B layers); The average Se content in plants is 0.07×10-6, with the soil Se enrichment capacity of plants in the order of weeds > hazelnut > paddy rice > corn. There are significant positive correlations between soil and rice, soil and hazelnut, but no obvious correlations between soil and weeds, soil and corn.
-
Key words:
- selenium /
- geochemistry /
- rock-soil-plant /
- Liaoning Province
-

-
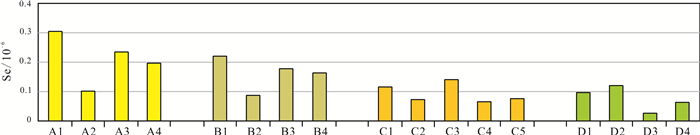
表 1 研究区岩石中硒元素含量特征表
Table 1. Characteristics of Se content in rocks of the study area
种类 样品数/件 平均值/10-6 最大值/10-6 最小值/10-6 极差(R) 标准偏差(SD) 变异系数(CV) 碳酸盐岩 11 0.11 0.62 0.01 0.61 0.17 1.55 花岗岩 13 0.07 0.22 0.02 0.20 0.05 0.75 火山岩 8 0.14 0.57 0.04 0.53 0.18 1.26 变质岩 15 0.05 0.44 0.01 0.43 0.10 1.81 沉积岩 13 0.07 0.31 0.02 0.29 0.07 0.97 表 2 研究区土壤中硒元素含量特征表
Table 2. Characteristics of Se content in soils of the study area
种类 样品数/件 平均值/10-6 最大值/10-6 最小值/10-6 极差(R) 标准偏差(SD) 变异系数(CV) 棕壤(A层) 86 0.30 0.85 0.05 0.80 0.13 0.44 风砂土(A层) 12 0.10 0.18 0.04 0.14 0.04 0.40 水稻土(A层) 19 0.23 0.43 0.14 0.29 0.07 0.33 草甸土(A层) 51 0.19 0.40 0.05 0.35 0.07 0.39 棕壤(B层) 87 0.22 0.71 0.06 0.65 0.10 0.46 风砂土(B层) 11 0.08 0.13 0.03 0.10 0.03 0.42 水稻土(B层) 19 0.18 0.45 0.08 0.37 0.07 0.43 草甸土(B层) 52 0.16 0.34 0.01 0.33 0.08 0.51 表 3 研究区植物中硒元素含量特征表
Table 3. Characteristics of Se content in plants of the study area
种类 样品数/件 平均值/10-6 最大值/10-6 最小值/10-6 极差(R) 标准偏差(SD) 变异系数(CV) 杂草 27 0.09 0.19 0.01 0.17 0.05 0.58 榛子 13 0.11 0.13 0.08 0.04 0.01 0.15 玉米 139 0.02 0.09 0.004 0.09 0.03 1.13 水稻 11 0.05 0.12 0.02 0.09 0.03 0.51 表 4 研究区不同土壤条件下植物硒富集系数参数表
Table 4. Se enrichment coefficients of plants by soil conditions in the study area
植物种类 棕壤(A层) 风砂土(A层) 草甸土(A层) 水稻土(A层) 平均值 杂草 0.27 0.63 0.45 榛子 0.26 0.26 玉米 0.12 0.38 0.11 0.15 0.19 水稻 0.20 0.30 0.25 -
[1] 孙梓耀, 王菲, 崔玉军. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部土壤硒元素的有效性与生态效应[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2016(9): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJN201609012.htm
Sun Z Y, Wang F, Cui Y J. Effectiveness and ecological Effects of Soil Selenium in southern of Songnen plain of Heilongjiang province[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016(9): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJN201609012.htm
[2] 戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1356-1364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201506015.htm
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in the northeast china plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6): 1356-1364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201506015.htm
[3] 付强, 王冬艳, 李月芬, 等. 吉林中部黑土区土壤硒元素土壤地球化学研究[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(1): 102-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201401011.htm
Fu Q, Wang D Y, Li Y F, et al. Pedogeochemiscal research on Se in black soil areas of central Jilin province[J]. Global Geology, 2014, 33(1): 102-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201401011.htm
[4] 张哲寰, 赵君, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤-作物系统Se元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(1): 38-43. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10147.shtml
Zhang Z H, Zhao J, Dai H M, et al. Geochemistry of selenium in soil-crop system of Nehe city, Heilongjiang province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(1): 38-43. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10147.shtml
[5] 杨立国, 马志超, 王鑫. 内蒙古通辽市科尔沁区土壤硒地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(4): 383-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.012 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8364.shtml
Yang L G, Ma Z C, Wang X. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in the soil of Horqin District Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(4): 383-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.012 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8364.shtml
[6] 迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201605017.htm
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in Soils of Heilongjiang province, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201605017.htm
[7] 龚河阳, 李月芬, 汤洁, 等. 吉林省西部土壤硒含量、形态分布及影响因素[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2015, 37(2): 177-184, 190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLNY201502011.htm
Gong H Y, Li Y F, Tang J, et al. Content, form distribution and influencing factors of soil selenium in western Jilin province[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2015, 37(2): 177-184, 190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLNY201502011.htm
[8] 王金达, 于君宝, 张学林. 黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地理科学, 2000, 20(5): 469-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200005013.htm
Wang J D, Yu J B, Zhang X L. Geochemical features of elements of selenium etc. in soil of Loess Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2000, 20(5): 469-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200005013.htm
[9] 朱建明, 梁小兵, 凌宏文, 等. 环境中硒存在形式的研究现状[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2003, 22(1): 75-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200301015.htm
Zhu J M, Liang X B, Ling H W, et al. Advances in studying occurrence modes of selenium in environment[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2003, 22(1): 75-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200301015.htm
[10] 马宝艳, 张学林. 吉林省区域环境中硒的生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2000, 20(1): 91-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200001035.htm
Ma B Y, Zhang X L. Ecological risk assessment of selenium in regional environment of Jilin Province[J]. China Environmental Science, 2000, 20(1): 91-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200001035.htm
[11] 廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 等. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1813-1825. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006018.htm
Liao Q L, Cui X D, Huang S S, et al. Element geochemistry of selenium-enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1813-1825. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006018.htm
[12] 赵燕, 栾文楼, 郭海全, 等. 河北省石家庄市藁城区富硒土壤特征、成因与生态环境健康评价[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(3): 764-776. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202103008.htm
Zhao Y, Luan W L, Guo H Q, et al. Characteristics, causes and ecological environment health evaluation of selenium-enriched soil in Gaocheng District of Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(3): 764-776. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202103008.htm
[13] 陈树旺, Zhukovskaya A A, 邢德和, 等. 铁岭地区生态地质研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 25-62.
Chen S W, Zhukovskaya A A, Xing D H, et al. Study on ecological geology in Tieling Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011: 25-62. (in Chinese)
[14] 黎彤, 倪守斌. 地球和地壳的化学元素丰度[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 1-136.
Li T, Ni S B. Abundance of chemical elements in the earth and crust[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990: 1-136. (in Chinese)
[15] Swaine J D. The trace-element content of soils[J]. Soil Science, 1956, 81(2): 144. http://journals.lww.com/soilsci/Citation/1956/02000/The_Trace_Element_Content_of_Soil.24.aspx
[16] 李家熙, 张光第, 葛晓云, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000: 1-204.
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X Y, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental character of human selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000: 1-204.
[17] 谭见安. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 39.
Tan J A. The Atlas of endemic diseases and their environments in the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 39.
[18] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 22499-2008, 富硒稻谷[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009: 1-3.
AQSIQ, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 22499-2008, Rich selenium paddy[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2009: 1-3.
[19] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 2762-2017, 食品安全国家标准——食品中污染物限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration of Food and Drug Administration. GB 2762-2017, Food safety national standard food pollutant limit[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017. (in Chinese)
[20] 张培毅, 宋鸿彬, 杨占田, 等. 硒对克山病病区人体红细胞免疫功能的影响[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 1998, 15(3): 12-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYJK803.006.htm
Zhang P Y, Song H B, Yang Z T, et al. Effects of Selenium on erythrocyte immunity function of residents in a Keshan disease area[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 1998, 15(3): 12-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYJK803.006.htm
[21] 张勇胜, 李仁兰, 刘妍, 等. 硒对人体健康作用的研究进展[J]. 内科, 2018, 13(4): 623-625, 662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKYT201804026.htm
Zhang Y S, Li R L, Liu Y, et al. Advances in research on the effects of selenium on human health[J]. Internal Medicine of China, 2018, 13(4): 623-625, 662. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKYT201804026.htm
[22] 李颂, 衣喆, 王春玲, 等. 微量元素硒的营养价值及应用[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2014, 35(20): 120-123, 132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPYK201420035.htm
Li S, Yi Z, Wang C L, et al. The nutritive value and application of trace element selenium[J]. ] Food Research and Development, 2014, 35(20): 120-123, 132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPYK201420035.htm
[23] 吴文斌, 杨鹏, 唐华俊, 等. 土地利用对土壤性质影响的区域差异研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(8): 1697-1702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNYK200708015.htm
Wu W B, Yang P, Tang H J, et al. Regional variability of effects of land use system on soil properties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2007, 40(8): 1697-1702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNYK200708015.htm
[24] 周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘-梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Selenium in soils of South Jiangxi province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
[25] 王秋爽, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等. 广东省揭西县土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1126-1133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806011.htm
Wang Q S, Luo J, Cai L M, et al. Distribution of soil selenium and its influential factors in Jiexi County, Guangdong Province[J]. Soil, 2018, 50(6): 1126-1133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806011.htm
[26] 蒋慧豪, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等. 广东省普宁市土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901015.htm
Jiang H H, Luo J, Cai L M, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Puning city, Guangdong province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(1): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901015.htm
[27] 谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区富硒土壤成因与土壤硒来源研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1373-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906027.htm
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of Selenium-enriched soils in Jizhou district of Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1373-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906027.htm
[28] 商翎, 提福魁, 王淑华, 等. 元素生态地球化学及其应用[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学出版社, 1997: 29-26.
Shang L, Ti F K, Wang S H, et al. Elemental ecological geochemistry and application[M]. Shenyang: Liaoning University Press, 1997: 29-26. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: