FLUID INCLUSION CHARACTERISTICS AND GENESIS OF SHIWULIQIAO GOLD DEPOSIT IN NORTHERN DAXINGANLING MOUNTAINS
-
摘要:
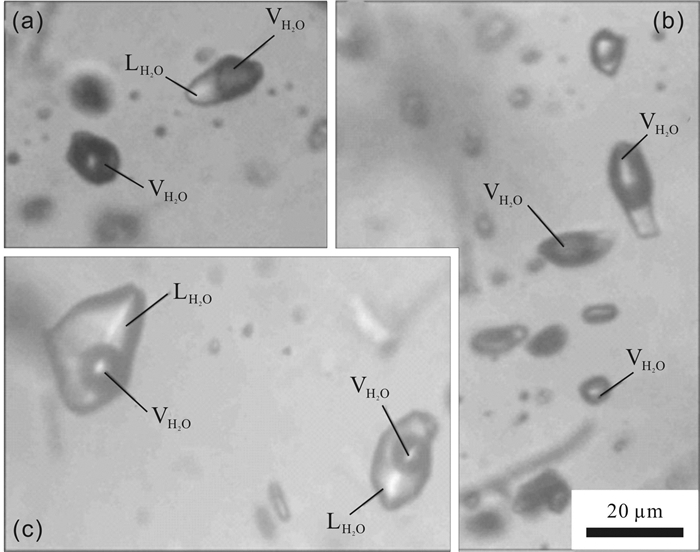
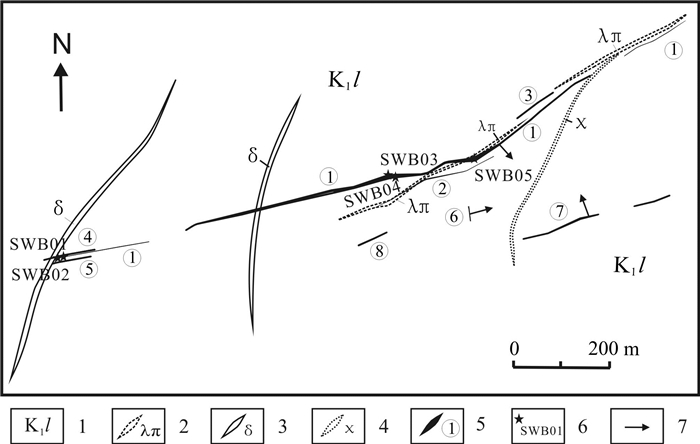
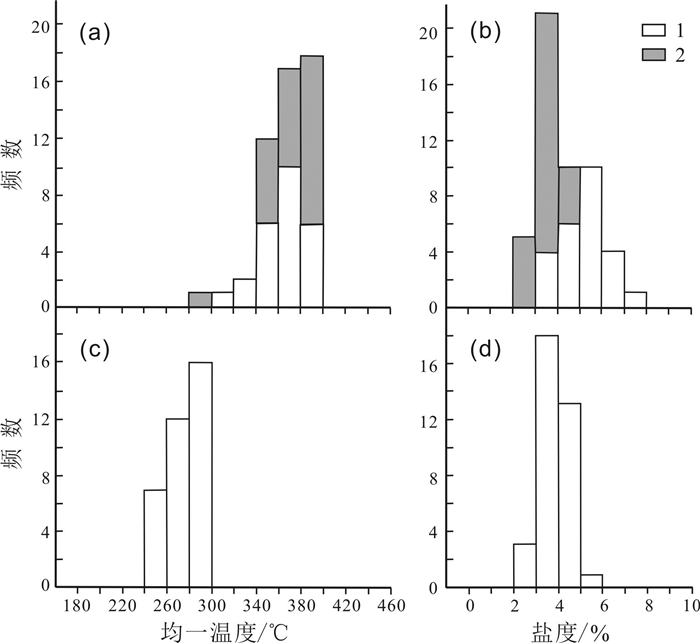
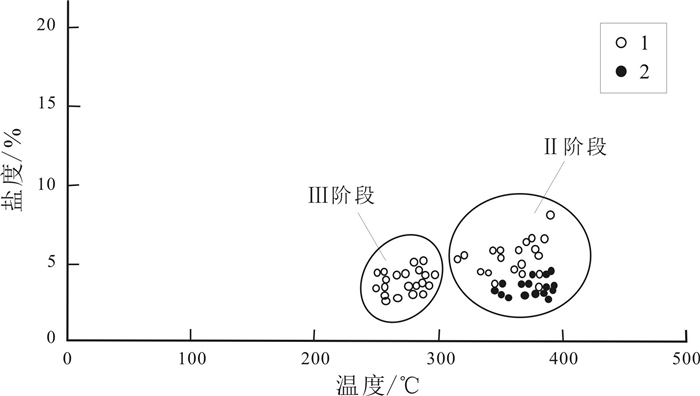
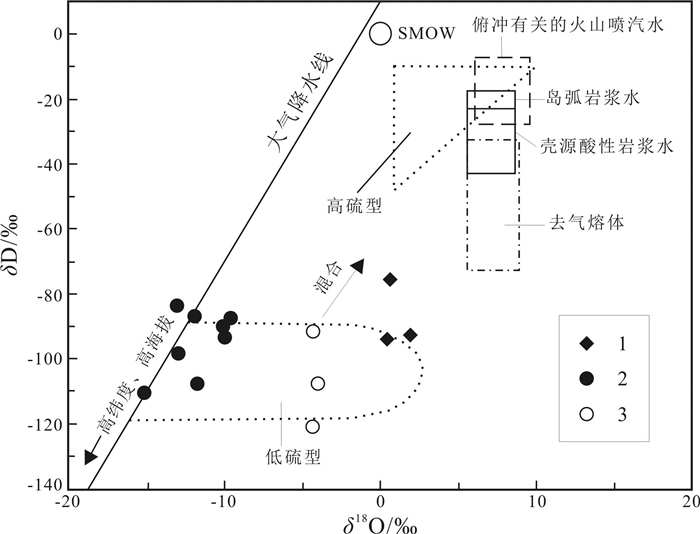
十五里桥金矿床位于上黑龙江Au(Cu-Mo)成矿带内,上黑龙江盆地南缘、腰站断陷北缘与二十二站隆起南缘交接地带. 矿床可划分为4个成矿阶段:Ⅰ—脉状黄铁矿-石英阶段;Ⅱ—浸染状黄铁矿±黄铜矿-石英阶段;Ⅲ—浸染状黄铁矿±黄铜矿±闪锌矿±方铅矿-石英阶段;Ⅳ—少硫化物-碳酸盐阶段. 其中多金属硫化物-石英阶段为主成矿阶段. 流体包裹体研究表明,Ⅱ、Ⅲ阶段发育富气相和富液相型流体包裹体,Ⅱ阶段流体发生不混溶,均一温度介于283~394 ℃之间,盐度介于2.56%~7.99%(NaCl当量,质量分数)之间;Ⅲ阶段均一温度介于251~298 ℃,盐度介于2.56%~5.09%(NaCl当量,质量分数),属于简单的NaCl-H2O体系. H-O同位素指示成矿流体主要为大气降水;S同位素指示成矿物质主要来自深源岩浆硫. 十五里桥金矿床为火山岩容矿的浅成中温热液型矿床.
Abstract:The Shiwuliqiao gold deposit is located in the junction zone between the southern margin of Upper Heilongjiang Basin, the northern margin of Yaozhan fault depression and the southern margin of Ershierzhan uplift within the Upper Heilongjiang Au-Cu-Mo metallogenic belt. The metallogenesis of the deposit can be divided into four stages, i.e. I) vein pyrite-quartz stage, Ⅱ) disseminated pyrite±chalcopyrite-quartz stage, Ⅲ) disseminated pyrite±chalcopyrite±sphalerite±galena-quartz stage and IV) low sulfide-carbonate stage, among which the polymetallic sulfide-quartz is the main metallogenic stage. The study of fluid inclusions shows that gas-rich and liquid-rich fluid inclusions are developed in stages Ⅱ and Ⅲ. The fluid in stage Ⅱ is immiscible, with the homogenization temperature of 283-394 ℃ and salinity of 2.56%-7.99%, while the homogenization temperature in stage Ⅲ is 251-298 ℃ with the salinity of 2.56%-5.09%, belonging to simple NaCl-H2O system. The H-O isotope indicates that the ore-forming fluid is dominated by atmospheric precipitation, and the S isotope suggests that the metallogenic materials mainly come from deep magmatic sulfur. The Shiwuliqiao gold deposit is of volcanic rock-hosted epi-mesothermal type.
-
Key words:
- gold deposit /
- fluid inclusion /
- deposit genesis /
- mesothermal type /
- Daxinganling Mountains
-

-
图 7 十五里桥金矿床δDW-δ18OW体系图(据文献[11])
Figure 7.
图 8 十五里桥金矿床流体包裹体P-T-W相图(据文献[26])
Figure 8.
表 1 十五里桥金矿床流体包裹体特征及参数
Table 1. Fluid inclusion characteristics and parameters of Shiwuliqiao gold deposit
成矿阶段 包裹体类型 测试数量 大小/μm 气液比/% Tm/℃ Th/℃ 盐度/% 密度/(g/cm3) Ⅱ 富气相型 26 7~15 55~90 -1.5~-2.7 283~394 2.56~4.48 0.55~0.77 富液相型 25 5~10 20~40 -2.0~-5.1 317~392 3.37~7.99 0.58~0.73 Ⅲ 富液相型 35 6~15 20~25 -1.5~-3.1 251~298 2.56~5.09 0.75~0.83 -
[1] 刚绪军, 宋丙剑. 上黑龙江盆地火山岩分布控矿因素分析[J]. 甘肃冶金, 2010, 32(4): 89-91, 146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2010.04.030
Gang X J, Song B J. On Heilongjiang Basin the volcanic rock divided bringing under control ore factor analysis[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 2010, 32(4): 89-91, 146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2010.04.030
[2] 李向文, 杨言辰, 叶松青, 等. 黑龙江省塔河县十五里桥金矿床地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014, 50(1): 77-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201401009.htm
Li X W, Yang Y C, Ye S Q, et al. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Shiwuliqiao gold deposit in Tahe, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(1): 77-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201401009.htm
[3] 陈卓, 李向文, 张胜江, 等. 黑龙江十五里桥金矿龙江组火山岩地球化学特征及构造背景分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(5): 413-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.002 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8415.shtml
Chen Z, Li X W, Zhang S J, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of the volcanic rocks of Longjiang Formation in Shiwuliqiao gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(5): 413-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.002 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8415.shtml
[4] 张顺, 林春明, 吴朝东, 等. 黑龙江漠河盆地构造特征与成盆演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(3): 411-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.03.011
Zhang S, Lin C M, Wu C D, et al. Tectonic characteristics and basin evolution of the Mohe Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2003, 9(3): 411-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.03.011
[5] 李向文, 张志国, 王可勇, 等. 大兴安岭北段宝兴沟金矿床成矿流体特征及矿床成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(4): 1071-1084. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20170169
Li X W, Zhang Z G, Wang K Y, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid and genesis of Baoxinggou gold deposit in north of Great Xing'an Range[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2018, 48(4): 1071-1084. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20170169
[6] Potter R W Ⅱ, Brown D L. The volumetric properties of aqueous sodium chloride solutions from 0 ℃ to 500 ℃ at pressures up to 2000 bars based on a regression of available data in the literature[C]. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin, 1978, 1421-C3, 6.
[7] Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(1): 197-202. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197
[8] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 147-282.
Lu H Z, Fan H R, Ni P, et al. Fluid inclusions[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 147-282. (in Chinese)
[9] Wang Z L, Yang L Q, Guo L N, et al. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A fluid inclusion study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 701-717. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.006
[10] Clayton R N, O'Neil J R, Mayeda T K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(17): 3057-3067. doi: 10.1029/JB077i017p03057
[11] Hedenquist J W, Lowenstern J B. The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature, 1994, 370(6490): 519-527. doi: 10.1038/370519a0
[12] 李春诚, 吕新彪, 杨永胜, 等. 大兴安岭北段古利库金(银)矿床流体包裹体特征与成矿机制[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(2): 152-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602032.htm
Li C C, Lü X B, Yang Y S, et al. Fluid inclusions and metallogenic mechanism of Guliku Au-Ag deposit in Northern Daxinganling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(2): 152-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602032.htm
[13] 吕军, 王建民, 岳帮江, 等. 三道湾子金矿床流体包裹体及稳定同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005, 41(3): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200503008.htm
Lü J, Wang J M, Yue B J, et al. Fluid inclusion and stable isotope geochemistry of Sandaowanzi gold deposit[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2005, 41(3): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200503008.htm
[14] Ohmoto H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67(5): 551-578. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551
[15] Chaussidon M, Lorand J P. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): An ion microprobe study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10): 2835-2846. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90018-G
[16] 郑永飞, 陈江峰. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 218-247.
Zheng Y F, Chen J F. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 218-247. (in Chinese)
[17] 闫永生, 李向文, 聂春雨, 等. 黑龙江富克山地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿远景预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(1): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201301005.htm
Yan Y S, Li X W, Nie C Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospective prognosis of Fukeshan region in Heilongjiang Province based on stream sediment survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(1): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201301005.htm
[18] Urusova M A. Volume properties of aqueous solutions of sodium chloride at elevated temperatures and pressures[J]. Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 1975, 20(11): 1717-1721.
[19] Haas J L Jr. Physical properties of the coexisting phases and thermochemical properties of the H2O component in boiling NaCl solutions[R]. Washington DC: United States Department of the Interior, Geological Survey, 1976: 75-674.
[20] Bodnar R J, Burnham C W, Sterner S M. Synthetic fluid inclusions in natural quartz. Ⅲ. Determination of phase equilibrium properties in the system H2O-NaCl to 1000 ℃ and 1500 bars[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(9): 1861-1873.
[21] 辛存林, 徐明儒, 安国堡, 等. 川西南马头山铜金矿床地质和流体包裹体特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(6): 1556-1572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201906021.htm
Xin C L, Xu M R, An G B, et al. Deposit geology, fluid inclusion characteristics and ore genesis of the Matoushan Cu-Au deposit in southwest Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(6): 1556-1572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201906021.htm
[22] Ramboz C, Pichavant M, Weisbrod A. Fluid immiscibility in naturalprocesses: Use and misuse of fluid inclusion data: Ⅱ. Interpretation of fluid inclusion data in terms of immiscibility[J]. Chemical Geology, 1982, 37(1/2): 29-48.
[23] 代军治. 辽宁青城子地区金、银矿床成矿流体特征及成因探讨[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2005.
Dai J Z. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids and discussion on the genesis of Au, Ag deposits in Qingchengzi region, Liaoning Province [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2005.
[24] Roedder E. Fluid inclusions. Volume 12: Reviews in mineralogy[M]. Washington DC: Mineralogical Society of America, 1984: 1-644.
[25] Roedder E, Bodnar R J. Geologic pressure determinations from fluid inclusion studies[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1980, 8(1): 263-301.
[26] Bouzari F, Clark A H. Prograde evolution and geothermal affinities of a major porphyry copper deposit: The Cerro Colorado hypogene protore, Iregion, Northern Chile[J]. Economic Geology, 2006, 101 (1): 95-134.
-




 下载:
下载: