THE SOURCE ROCKS OF MESOPROTEROZOIC TIELING FORMATION IN LINGYUAN-NINGCHENG BASIN: Biomarker Characteristics and Implication
-
摘要:
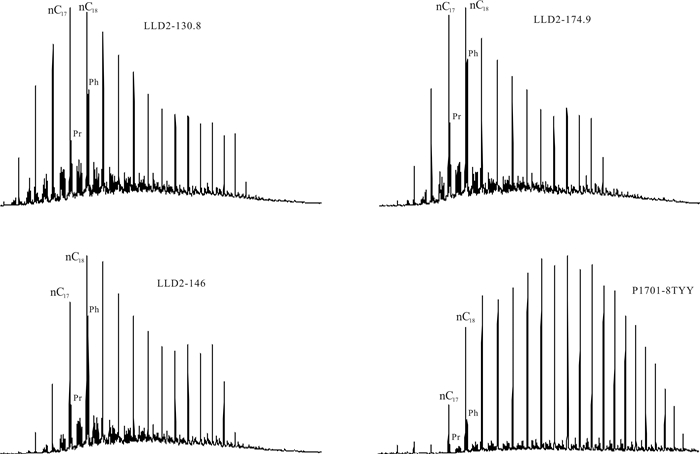
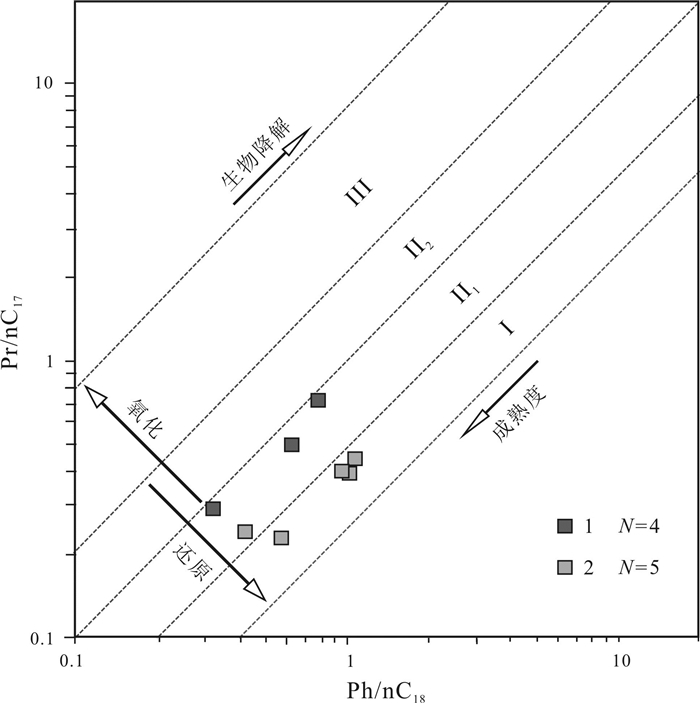
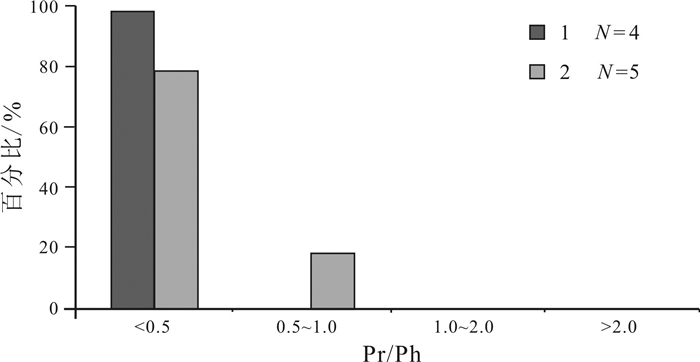
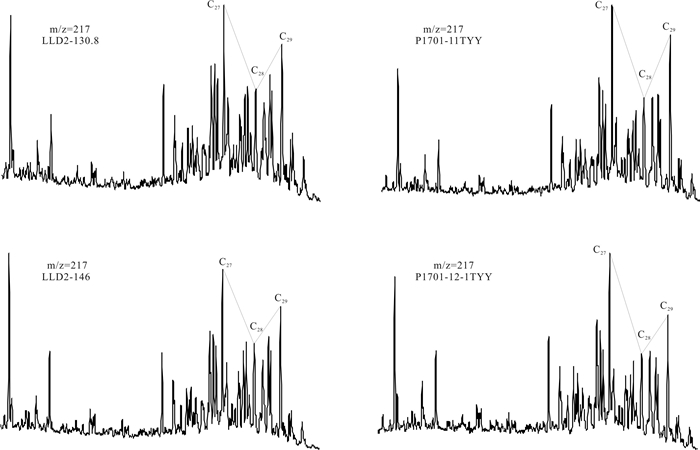
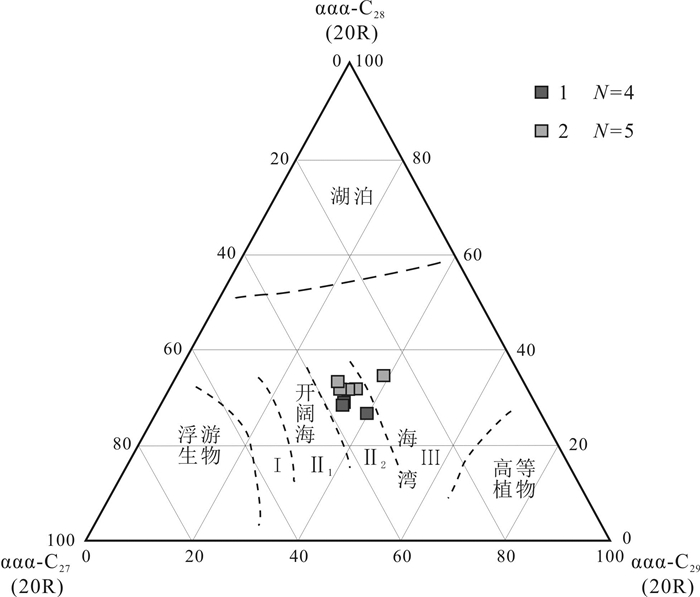
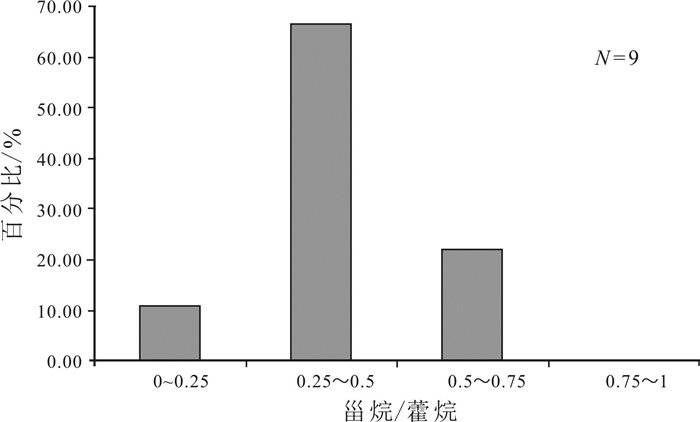
采用气相色谱、气相色谱-质谱技术, 对凌源-宁城盆地中元古界铁岭组烃源岩生物标志化合物特征进行研究, 剖析其蕴含有机质生源、沉积环境、有机质热演化程度等方面的信息及地球化学意义.铁岭组烃源岩饱和烃气相色谱以"前峰型"的单峰分布为主, 主峰碳多为nC18, 表明有机质来源以低等生物为主; Pr/Ph比值主要分布于0.16~0.73之间, 植烷优势较明显, 指示为强还原的沉积环境, 少部分为还原环境.铁岭组烃源岩具有长侧链三环萜烷丰富、伽马蜡烷含量高和C27甾烷分布占优势的分子化石组合特征, 伽马蜡烷指数(Ga/C30H)为0.10~0.31, 平均值0.19, 反映出铁岭组烃源岩形成于微咸水-半咸水环境; Ts/Tm比值为0.54~1.19, 平均值为0.88, 表明烃源岩热演化程度较高; 甾烷与藿烷的含量比值主要分布于0.24~0.59之间, 平均值0.42, 表明低等生物藻类的贡献较低, 而细菌等微生物的贡献相对较大.铁岭组烃源岩甾烷呈现C27甾烷占优势的"L"型, 表明生烃母质生源构成是低等水生生物来源的有机质特征.
Abstract:Based on gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, the paper studies the characteristics of biomarker compounds in the source rocks of Tieling Formation in Lingyuan-ningcheng Basin, and analyzes the organic source, sedimentary environment and thermal evolution degree of organic matter, as well as geochemical implication. The saturated hydrocarbon gas chromatography of source rocks is front-peak type unimodal distribution dominated, with the main peak carbon mostly nC18, indicating that the organic matter is mainly derived from lower organism. The Pr/Ph ratio mainly ranges from 0.16 to 0.73, with obviously more phytane, indicating a strongly reducing sedimentary environment. The source rocks of Tieling Formation are characterized by abundant long-side chain tricyclic terpane, high content of gamacerane and dominant distribution of C27 sterane, with Ga/C30H of 0.10-0.31, averagely 0.19, reflecting the source rocks were formed in slight saline water-brackish water environment. The Ts/Tm ratio of 0.54-1.19 (averagely 0.88) shows the thermal evolution degree of source rocks is relatively high. The ratio of sterane/hopane contents is mainly in the range of 0.24-0.59, averagely 0.42, reflecting the lower organism of algae contributes little to organic matter, while the microorganisms such as bacteria contribute a lot. The sterane in the source rocks are L-shape with dominant C27 sterane, indicating the hydrocarbon generating parent material is of lower aquatic biological organism origin.
-
Key words:
- biomarker compound /
- source rock /
- Tieling Formation /
- Mesoproterozoic /
- Lingyuan-Ningcheng Basin
-

-
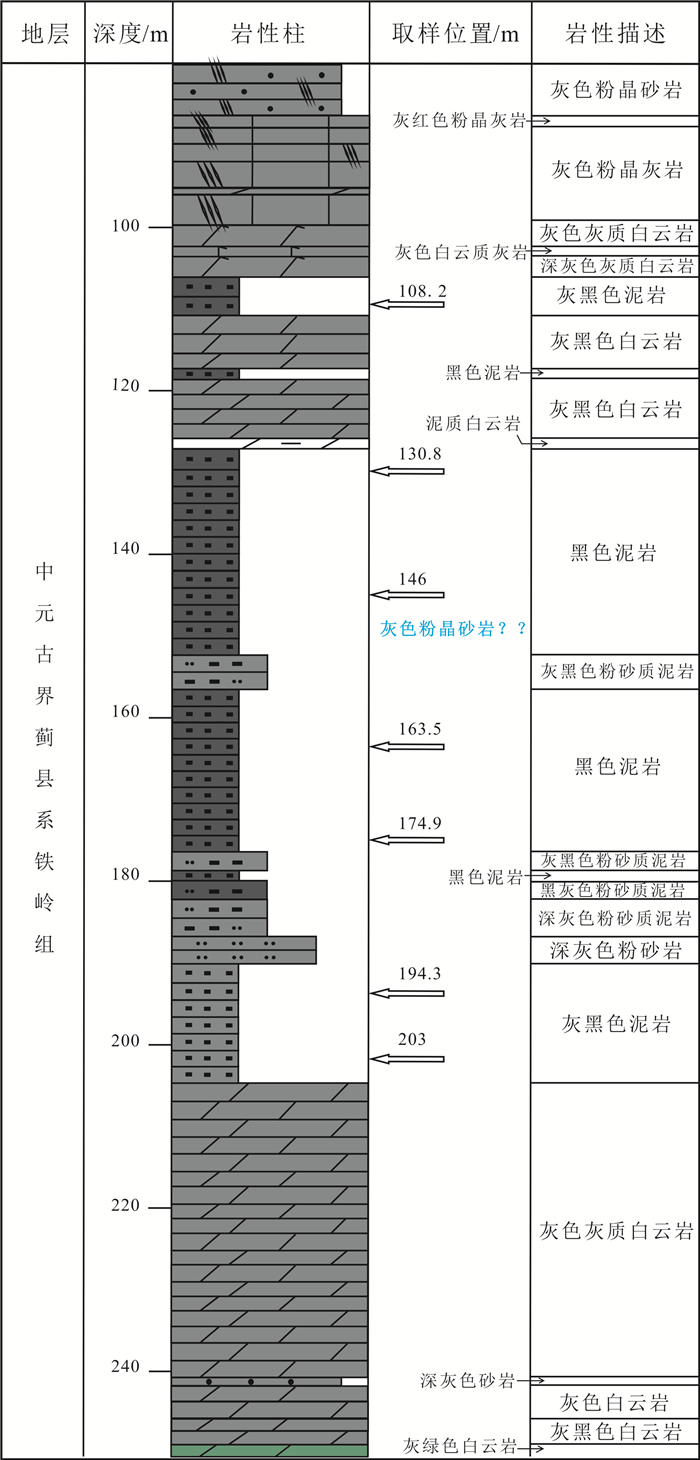
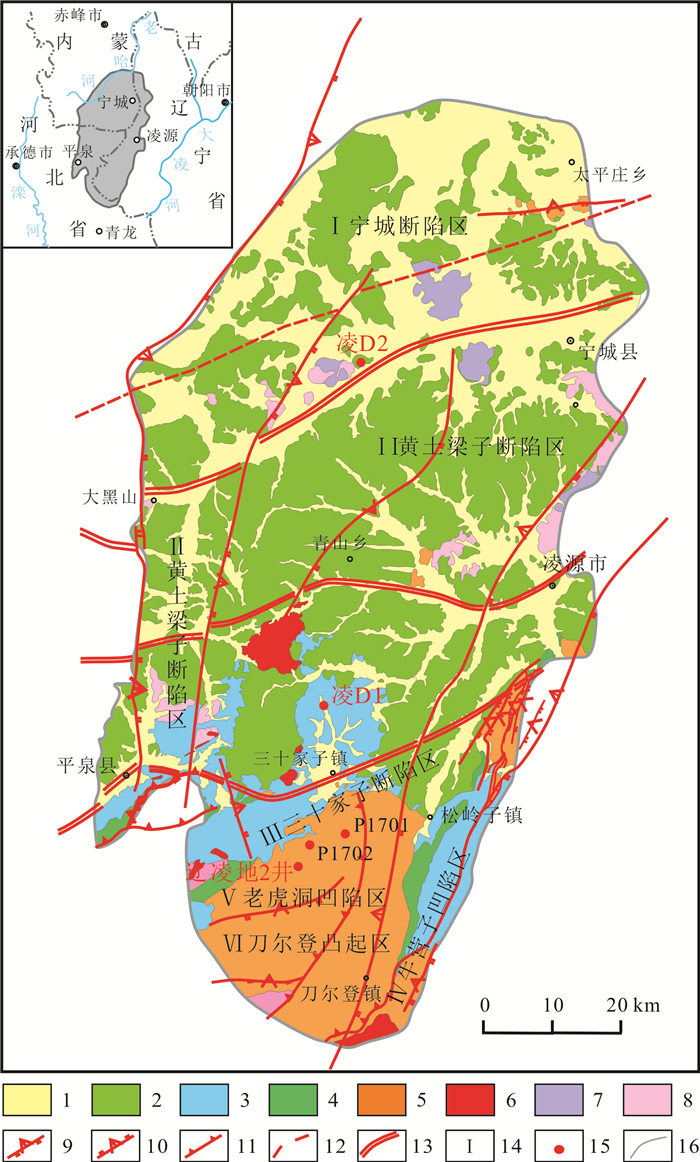
表 1 铁岭组样品基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of the samples from Tieling Formation
样品编号 位置 岩性 P1701-8TYY P1701 中段 粉砂质泥岩 P1701-11TYY P1701 中下段 粉砂质泥岩 P1701-12-1TYY P1701 中下段 粉砂质泥岩 P1701-12-2TYY P1701 中下段 粉砂岩 P1702-7TYY P1702 中段 页岩 LLD2-108.2 LLD2 108.q2 m 泥岩 LLD2-130.8 LLD2 130.8 m 泥岩 LLD2-146 LLD2 146 m 泥岩 LLD2-163.5 LLD2 163.5 m 泥岩 LLD2-174.9 LLD2 174.9 m 泥岩 LLD2-194.3 LLD2 94.3 m 泥岩 LLD2-203 LLD2 203 m 泥岩 表 2 凌源-宁城盆地铁岭组烃源岩地球化学分析数据
Table 2. Geochemical data of the source rocks from Tieling Formation in Lingyuan-Ningcheng Basin
样品号 TOC/% Ro/% ∑nC21-/∑nC22+ Pr/nC17 Ph/nC18 Pr/Ph 主峰碳数 Ts/Tm Ga/C30H P1701-8TYY 0.816 1.54 0.59 0.50 0.61 0.29 C21 0.54 0.00 P1701-11TYY 0.526 1.53 0.43 0.29 0.32 0.36 C23 0.82 0.18 P1701-12-1TYY 0.305 1.62 0.39 0.00 0.73 0.00 C23 0.82 0.18 P1701-12-2TYY 0.214 1.45 0.53 0.72 0.77 0.16 C22 0.65 0.11 P1702-7TYY 0.255 LLD2-108.2 0.674 4.18 0.24 0.42 0.73 C15 1.19 0.22 LLD2-130.8 0.533 2.08 1.75 0.40 0.96 0.46 C17 1.08 0.24 LLD2-146 0.755 2.08 1.27 0.39 1.01 0.30 C18 1.06 0.22 LLD2-163.5 0.829 2.15 LLD2-174.9 0.566 2.1 1.67 0.45 1.08 0.45 C17 1.06 0.21 LLD2-194.3 0.944 2.15 LLD2-203 0.625 2.18 1.25 0.23 0.57 0.38 C18 0.66 0.25 -
[1] 赵文智, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等. 中国元古界-寒武系油气地质条件与勘探地位[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801002.htm
Zhao W Z, Hu S Y, Wang Z C, et al. Petroleum geological conditions and exploration importance of Proterozoic to Cambrian in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801002.htm
[2] 叶云涛, 王华建, 翟俪娜, 等. 新元古代重大地质事件及其与生物演化的耦合关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(2): 203-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702001.htm
Ye Y T, Wang H J, Zhai L N, et al. Geological events and their biological responses during the Neoproterozoic Era[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(2): 203-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702001.htm
[3] 谢树成, 殷鸿福. 地球生物学前沿: 进展与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(6): 1072-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406002.htm
Xie S C, Yin H F. Progress and perspective on frontiers of geobiology[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(5): 855-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406002.htm
[4] 王鸿祯. 地球的节律与大陆动力学的思考[J]. 地学前缘, 1997, 4(3/4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY7Z2.001.htm
Wang H Z. Speculations on Earth's rhythms and continental dynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1997, 4(3/4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY7Z2.001.htm
[5] 沈树忠, 朱茂炎, 王向东, 等. 新元古代-寒武纪与二叠-三叠纪转折时期生物和地质事件及其环境背景之比较[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010, 40(9): 1228-1240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201009013.htm
Shen S Z, Zhu M Y, Wang X D, et al. A comparison of the biological, geological events and environmental backgrounds between the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian and Permian-Triassic transitions[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(12): 1873-1884. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201009013.htm
[6] Craig J, Thurow J, Thusu B, et al. Global Neoproterozoic petroleum systems: the emerging potential in North Africa[M]. London: Geological Society Special Publication, 2009: 1-25.
[7] 王铁冠, 韩克猷. 论中-新元古界的原生油气资源[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201101002.htm
Wang T G, Han K Y. On Meso-Neoproterozoic primary petroleum resources[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201101002.htm
[8] 王铁冠. 一种新发现的三环萜烷生物标志物系列[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1989, 11(3): 117-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX198903018.htm
Wang T G. A new series of tricyclic terpane biomarkers[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 1989, 11(3): 117-118. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX198903018.htm
[9] 王泽九, 苗培实, 马秀兰. 2001第七次李四光地质科学奖获得者主要科学技术成就与贡献[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 151-161.
Wang Z J, Miao P S, Ma X L. Achievements and contributions of the 7th Li Siguang prize for geoscience in 2001[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003: 151-161. (in Chinese)
[10] 卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 177-212.
Lu S F, Zhang M. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 177-212. (in Chinese)
[11] 唐友军, 陈践发. 内蒙古西部额济纳旗苦水沟地区下石炭统白山组烃源岩分子化石的特征[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(6): 888-894. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201106009.htm
Tang Y J, Chen J F. Characteristics of molecular fossils in source rocks of Lower Carboniferous Baishan Formation in Kushuigou area of Ejin Banner, western Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(6): 888-894. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201106009.htm
[12] 孙枢, 王铁冠. 中国东部中-新元古界地质学与油气资源[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 449-467.
Sun S, Wang T G. Meso-Neoproterozoic geology and petroleum resources in Eastern China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[13] 王晓梅, 张水昌, 王华建, 等. 烃源岩非均质性及其意义——以中国元古界下马岭组页岩为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701005.htm
Wang X M, Zhang S C, Wang H J, et al. Significance of source rock heterogeneities: A case study of Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling Formation shale in North China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701005.htm
[14] 博蒙特E A, 福斯特N H. 油气圈闭勘探[M]. 刘德来, 王永兴, 薛良清, 等译. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 201-215.
Beaumont E A, Foster N H. Exploring for oil and gas traps[M]. Liu D L, Wang Y X, Xue L Q, et al, trans. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 201-215.
[15] 侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011: 201-242.
Hou D J, Feng Z H. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011: 201-242. (in Chinese)
[16] Aquino Neot F R, Bjorφy M. Advances in Organic Geochemistry[C]. New York: Wiley, 1983: 659-667.
[17] 张立平, 黄第藩, 廖志勤. 伽马蜡烷-水体分层的地球化学标志[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htm
Zhang L P, Huang D F, Liao Z Q. Gammacerane-geochemical indicator of water column stratification[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htm
[18] Huang W Y, Meinschein W G. Sterols as ecological indicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 739-745.
[19] 唐友军, 马忠梅, 蒋兴超. 内蒙古扎鲁特盆地陶海营子剖面林西组烃源岩生物标志化合物特征及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(8): 1315-1321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201308021.htm
Tang Y J, Ma Z M, Jiang X C. Characteristics and significance of biomarker compounds of Linxi Formation hydrocarbon source rocks along Taohaiyingzi section in Zhalute basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(8): 1315-1321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201308021.htm
[20] 段云鹏, 包建平, 马安来, 等. 辽河双南油田油气地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(6): 496-501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200306015.htm
Duan Y P, Bao J P, Ma A L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of oil and gas from Shuangnan oilfield, Liaohe basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(6): 496-501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200306015.htm
-



 下载:
下载: