CHARACTERISTICS, MINERALIZATION AND RESOURCE POTENTIAL OF ENDOGENOUS GOLD DEPOSITS IN LIAODONG PENINSULA
-
摘要:
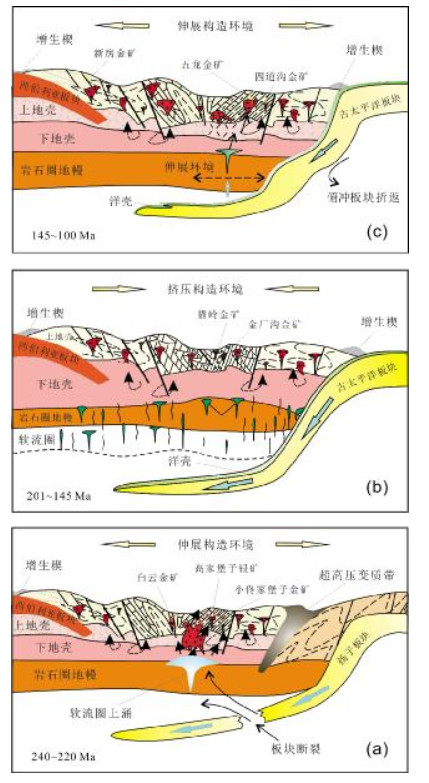
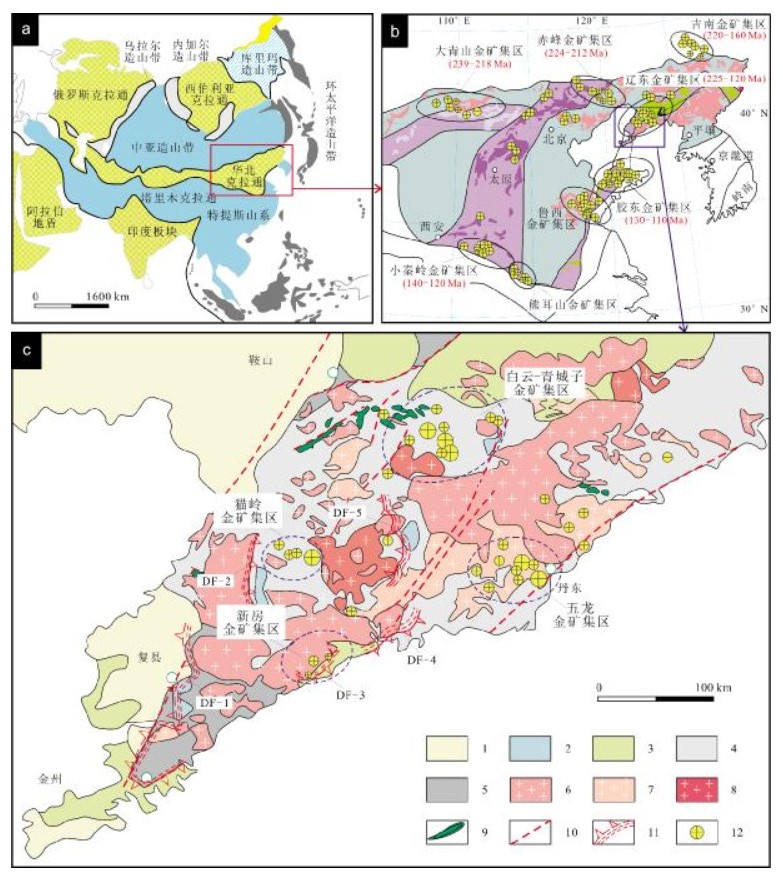
辽东半岛是华北克拉通重要组成部分, 中生代发生强烈的构造、岩浆活动和金矿成矿作用, 其内部产有不同规模的金矿床, 并具有明显的地域特色. 通过系统总结辽东半岛金矿床的空间分布、赋矿围岩、控矿构造类型、矿化蚀变等基本特征和成矿作用, 分析金矿的资源潜力. 根据金矿床的空间分布, 划分4个金矿集区, 即: 猫岭、白云-青城子、五龙-四道沟和新房金矿集区. 猫岭和白云-青城子矿集区赋矿围岩为古元古代沉积变质岩系, 矿化类型分为蚀变岩型和石英脉型, 矿体主要受低角度层间断裂控制; 五龙-四道沟矿集区赋矿围岩分别为中侏罗世片麻状黑云母花岗岩和古元古代沉积变质岩系, 矿化类型以石英脉型为主, 蚀变岩型次之, 矿体受高角度断裂和低角度层间断裂控制; 新房矿集区赋矿围岩为太古宙片麻岩和新元古界青白口系变质砂岩、变粒岩和大理岩, 矿化类型为石英脉型和蚀变岩型, 矿体多呈脉状受变质核杂岩剥离断层下盘发育的韧-脆性次级断裂和上部新元古界青白口系盖层构造裂隙控制. 年代学研究表明, 金矿成矿时代可分为晚三叠世(约220 Ma)、早侏罗世(约190 Ma)和早白垩世(约120 Ma). 流体包裹体研究显示, 流体不混溶是金矿成矿的主要机制; 氢-氧同位素显示, 成矿流体主要来自岩浆水, 后期有大气降水加入; 氦-氩同位素数据揭示, 成矿流体主要来自壳源, 少量来自幔源; 硫-铅-锶同位素显示, 成矿物质主要来自中生代岩浆. 同时, 赋矿地层起到不可或缺的作用. 矿床地质特征及同位素数据显示, 辽东半岛金矿为与岩浆热液有关的金矿床. 结合区域构造大地构造演化, 认为, 辽东半岛晚三叠世金矿形成与扬子板块向华北板块深俯冲背景有关, 早侏罗世金矿形成与古太平洋板块向欧亚板块俯冲挤压构造背景有关, 早白垩世金矿形成于古太平洋板块向欧亚板块俯冲折返伸展环境. 结合典型矿床地质特征、区域地球化学和地球物理特征, 圈定找矿靶区23处, 预测3 000 m以浅金资源量2 414.56 t.
Abstract:Liaodong Peninsula is an important part of North China Craton, where intense tectonic movement, magmatic activities and gold mineralization occurred in Mesozoic, and gold deposits of different scales are distributed with typical regional characteristics. Through the systematic summary of basic characteristics such as spatial distribution, ore-bearing wall rock, ore-controlling structures and mineralized alteration, as well as the metallogenesis of gold deposits, the paper analyzes the resources potential of gold deposits in Liaodong Peninsula. According to the spatial distribution of gold deposits, four gold deposit concentration areas are divided, including Maoling, Baiyun-Qingchengzi, Wulong-Sidaogou and Xinfang gold deposit concentration areas. The ore-bearing wall rocks of Maoling and Baiyun-Qingchengzi concentration areas are Paleoproterozoic sedimentary metamorphic rock series, with the mineralization of altered rock type and quartz vein type, and the orebodies mainly controlled by low-angle interlayer faults. The wall rocks of Wulong-Sidaogou concentration area are Middle Jurassic gneissic biotite granite and Paleoproterozoic sedimentary metamorphic rock series respectively, with the main mineralization of quartz vein type, followed by altered rock type, and the orebodies controlled by high-angle fault and low-angle interlayer fault. The wall rocks of Xinfang concentration area are Archean gneisses and Neoproterozoic Qingbaikouan metamorphic sandstone, granulite and marble, with the mineralization of quartz vein type and altered rock type. The orebodies are mostly in veins and controlled by the ductile-brittle secondary faults developed in the foot wall of metamorphic core complex detachment fault and by the structural fractures in the Neoproterozoic Qingbaikouou cap rock. The geochronological study shows that the gold mineralization epoch can be divided into Late Triassic (~220 Ma), Early Jurassic (~190 Ma) and Early Cretaceous (~120 Ma). The study on fluid inclusions indicates that fluid immiscibility is the main mechanism of gold mineralization. The H-O isotopes reveal the ore-forming fluid mainly comes from magmatic water, with atmospheric precipitation added in later period. The He-Ar isotopes show that the ore-forming fluid is mainly derived from crustal source and a little from mantle source. The S-Pb-Sr isotopes indicate that the metallogenic materials mainly come from the Mesozoic magma. Besides, the ore-bearing strata play an indispensable role. The geological characteristics and isotopic data show that the gold deposits in Liaodong Peninsula are of magmatic hydrothermal origin. Combined with regional tectonic evolution, it is believed that the Late Triassic gold deposits in the area are related to the deep subduction of Yangtze plate to North China plate, the Early Jurassic gold deposits related to the subduction and compression of Paleo-Pacific plate to Eurasian plate, and the Early Cretaceous gold deposits were formed in the subduction and exhumation extensional setting of Paleo-Pacific plate to Eurasian plate. According to the geological, regional geochemical and geophysical characteristics of typical deposits, 23 prospecting targets are delineated and 2 414.56 t of gold resources at 3 000 m below surface are predicted.
-

-
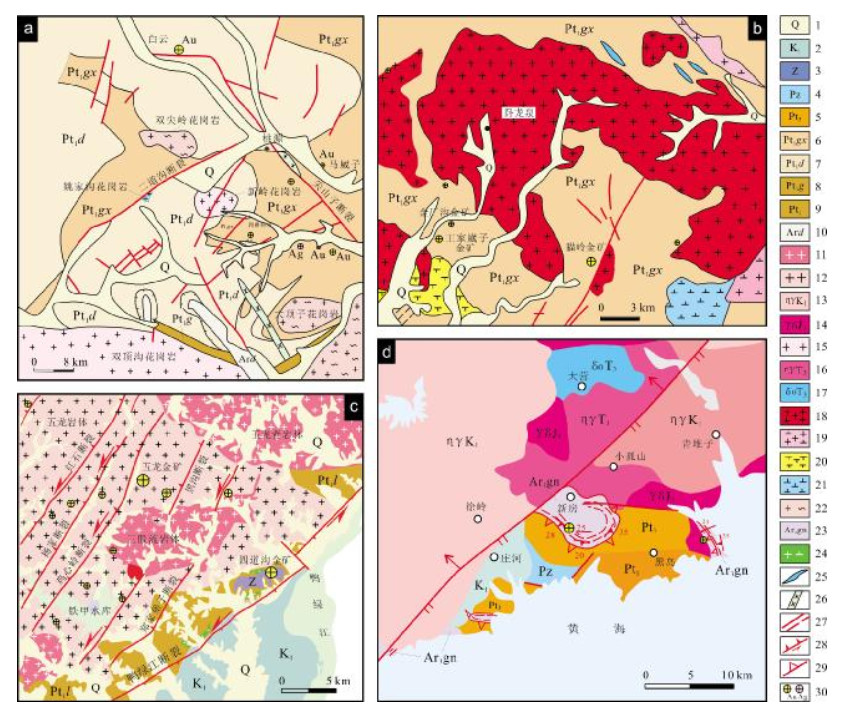
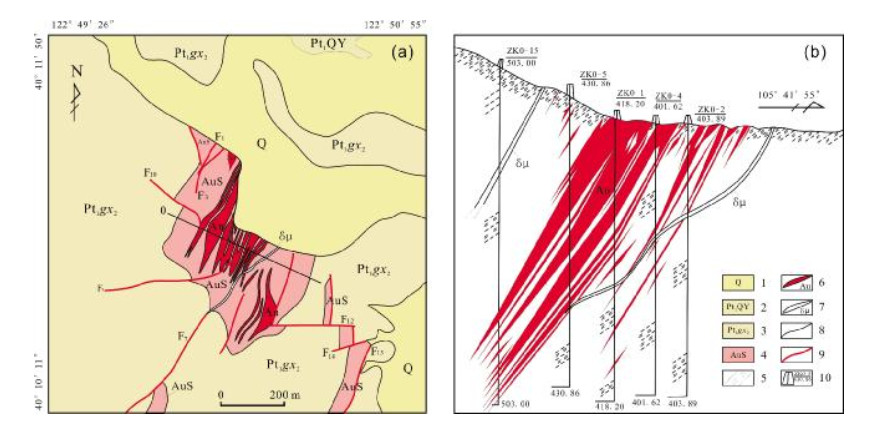
图 3 白云金矿地质简图(据文献[3])
Figure 3.
图 5 猫岭金矿地质简图(据文献[28])
Figure 5.
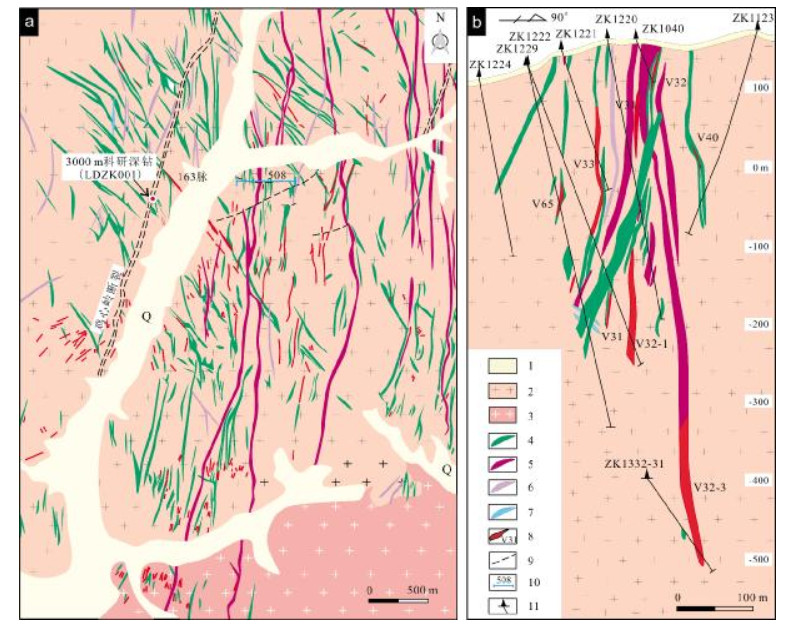
图 6 五龙金矿地质简图(据文献[36])
Figure 6.
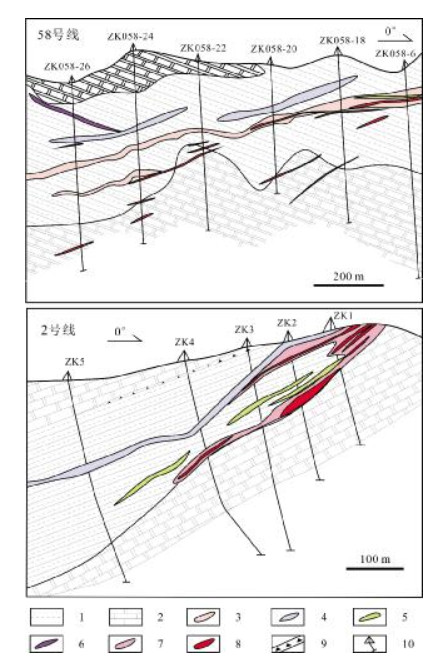
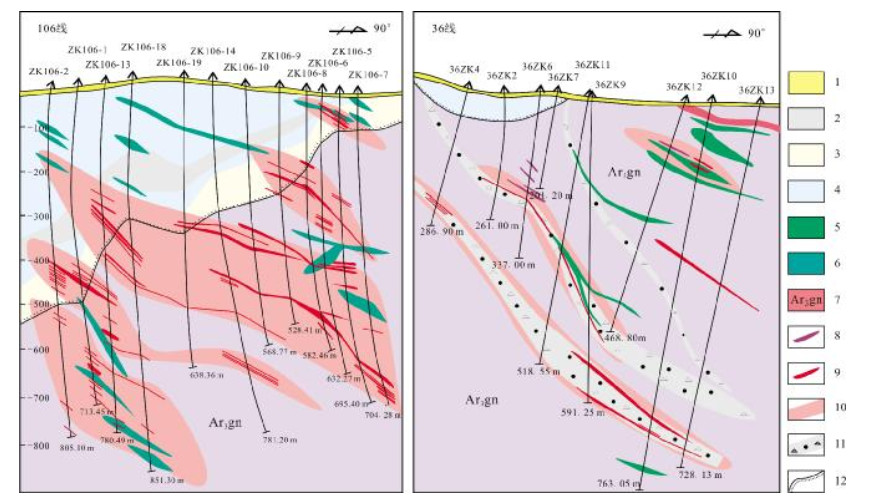
图 8 新房金矿106线和36线勘探线剖面图(据文献[49])
Figure 8.
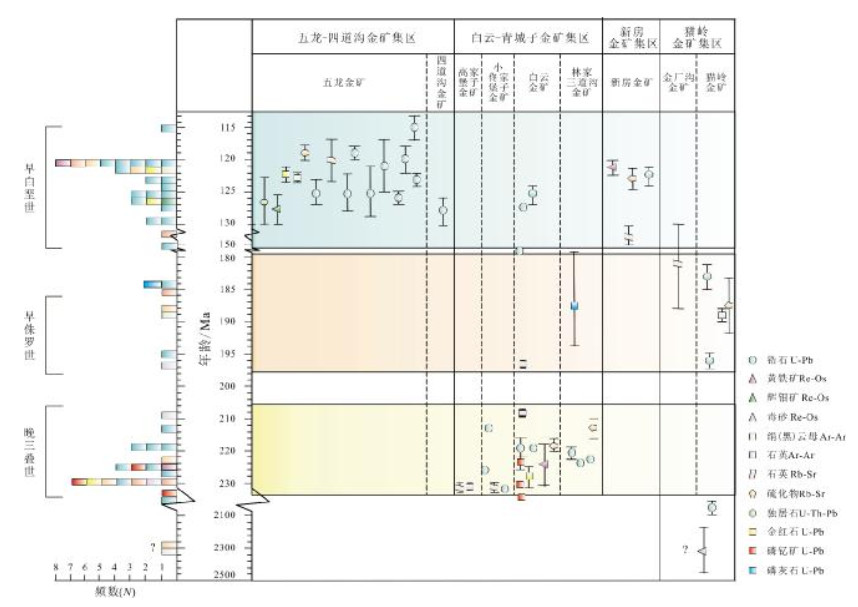
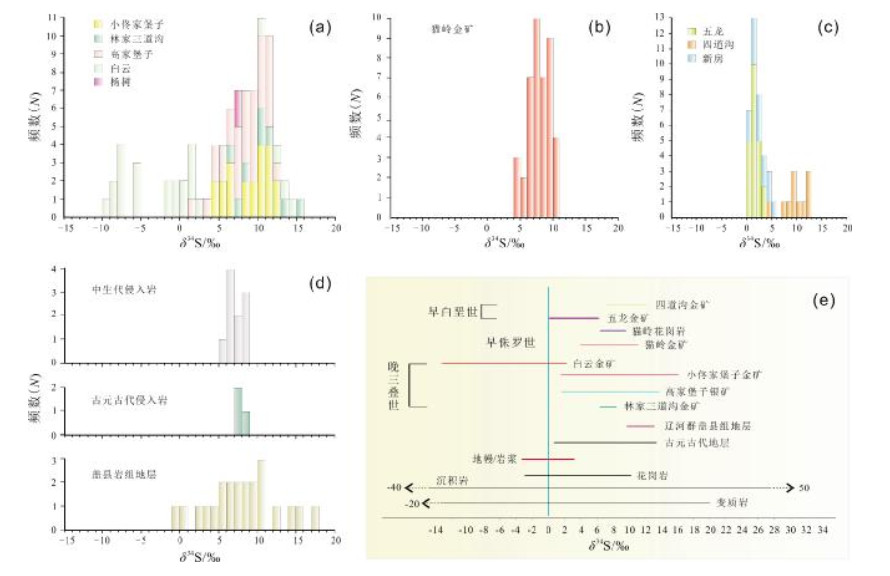
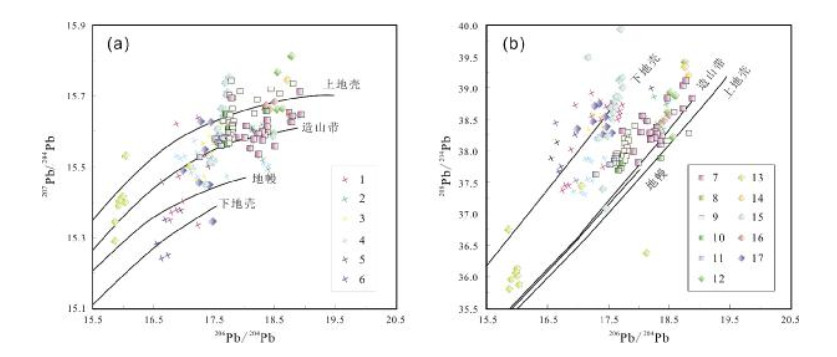
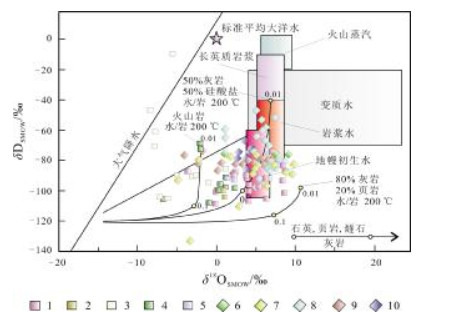
图 12 辽东半岛主要金矿床年龄锶同位素组成(底图据文献[80])
Figure 12.
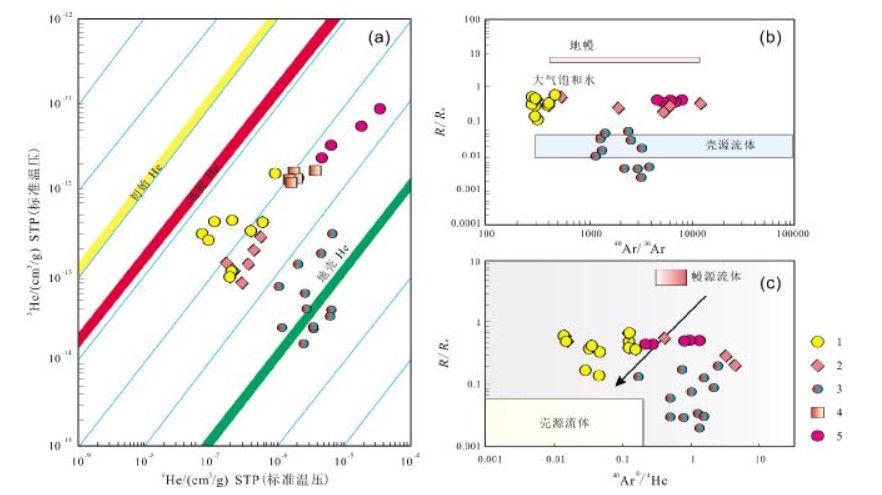
图 14 辽东半岛主要金矿氦-氩同位素组成(底图据文献[83])
Figure 14.
表 1 辽东半岛主要金矿床地质特征
Table 1. Geological features of significant gold deposits in Liaodong Peninsula
矿集区 地区 矿床 矿化 赋矿围岩 控矿构造 与成矿有关的侵入岩 蚀变类型 矿石矿物 脉石矿物 规模 参考文献 白云青城子金矿集区 凤城 林家三道沟金矿 蚀变岩型 盖县岩组片岩、大理岩, 晚三叠世煌斑岩和花岗斑岩 E-W向断裂构造 煌斑岩和花岗斑岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铁矿化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿、毒砂 石英、方解石、绢云母等 大型 [4, 35] 凤城 杨树金矿 蚀变岩型 盖县岩组片岩和大理岩 NNW向断裂构造 煌斑岩和花岗岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铁矿化 黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、毒砂 石英、白云石、绢云母和方解石等 中型 [4, 36] 凤城 白云金矿 蚀变岩、石英脉型 盖县岩组片岩和大理岩 NE、EW向断裂构造 闪长玢岩和花岗斑岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铁矿化绿泥石化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、辉钼矿、黄铁矿和自然金 石英、方解石、钾长石等 大型 [27, 37, 38] 凤城 小佟家堡子金矿 蚀变岩型 盖县岩组片岩和大石桥岩组大理岩 E-W向断裂构造 煌斑岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、毒砂 石英、方解石等 大型 [35, 39] 凤城 桃源金矿 蚀变岩、角砾岩型 盖县岩组片岩和大理岩 NE、E-W向断裂构造 煌斑岩和花岗斑岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铁矿化 黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、毒砂 石英、白云石、绢云母等 中型 [40] 五龙四道沟金矿集区 丹东 五龙金矿 石英脉型 片麻状花岗岩 NW、NE、N-S向断裂构造 花岗闪长岩、煌斑岩和闪长岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铁矿化 黄铜矿、辉钼矿、自然金、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿 石英、方解石、绢云母等 大型 [13, 41-42] 丹东 四道沟金矿 蚀变岩型 盖县岩组片岩和大理岩 NE向断裂构造 煌斑岩和闪长玢岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、钠长石化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿、毒砂、白钨矿 石英、方解石、绢云母等 大型 [29, 43] 猫岭金矿集区 大石桥 猫岭金矿 蚀变岩、石英脉型 盖县岩组千枚岩 NE向断裂构造 二长花岗岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铜矿化、黄铁矿化 磁黄铁矿、自然金、毒砂、黄铁矿、方铅矿、白钨矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿 石英、白云石、绢云母、方解石、黑云母等 超大型 [6, 28, 44] 大石桥 金厂沟金矿 石英脉型 盖县岩组片岩 NW向断裂构造 黑云母二长花岗岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铜矿化、黄铁矿化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿 石英、方解石、绢云母等 小型 [45] 大石桥 王家崴子金矿 石英脉型 盖县岩组片岩 NW向断裂构造 二长花岗岩和闪长玢岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铜矿化、黄铁矿化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、毒砂辉铜矿 石英、白云石、绢云母、方解石、黑云母、绿帘石、绿泥石等 中型 [45, 46] 新房金矿集区 庄河 新房金矿 蚀变岩、石英脉型 新太古代黑云二长片麻岩和新元古代石英砂岩 NE向拆离断层带 花岗斑岩 硅化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、黄铜矿化、钠长石化 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、自然金 石英、钾长石、方解石、绿帘石、绿泥石等 中型 [47-49] 表 2 辽东半岛金矿成岩、成矿年代学表
Table 2. Diagenetic and metallogenic chronology of gold deposits in Liaodong Peninsula
矿床 测试对象 方法 年龄/Ma 参考文献 高家堡子银矿 石英 Ar-Ar 234±1 [2] 石英 Rb-Sr 237±1 [2] 小佟家堡子金矿 含金硅质岩 Rb-Sr 233±3 [2] 煌斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 226±1 [34] 闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 214±2 [22] 白云金矿 黄铁矿 Re-Os 225±7 [3] 金红石 SIMS U-Pb 229±4 [8] 磷钇矿 SIMS U-Pb 224±2、231±1、1816±6 [8] 石英 Ar-Ar 207~209 [59] 石英 Ar-Ar 196~197 [59] 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 219 [60] 石英斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 219±3 [60] 二长斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 164 [60] 石英斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 127.8±0.8 [61] 闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 125.6±1.3 [61] 黄铁矿 Rb-Sr 218.5±2.6 作者待发表 林家三道沟沟金矿 热液磷灰石 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 184.78±9.35 [62] 矿化花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 220.7±2.1 [62] 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 224±1.5 [62] 蚀变闪长玢岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 226.4±2.8 [62] 黄铁矿 Rb-Sr 213.0±3.1 作者待发表 猫岭金矿 毒砂 Re-Os 2316±140 [6] 黑云母 Ar-Ar 189±1 [28] 卧龙泉花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 194±1 [28] 猫岭花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 196±1 [28] 毒砂、磁黄铁矿 Rb-Sr 2287±95 [44] 卧龙泉花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 1888.4±5.3 [51] 毒砂、磁黄铁矿 Rb-Sr 188.7±4.5 [63] 金厂沟金矿 石英 Rb-Sr 159±29 [64] 五龙金矿 成矿浅闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 123±1 [13] 煌斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 115±2 [13] 花岗闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 124±1 [13] 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 126±1 [13] 与成矿密切花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 120±1 [13] 辉长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 119±2 [13] 黄铁矿 Rb-Sr 119±1 [13] 辉钼矿 Re-Os 127.6±2.3 [42] 热液独居石 SIMS U-Th-Pb 126.7±3.2 [42] 三股流花岗岩 Single zircon U-Pb 129±3 [65] 石英 Rb-Sr 120±3 [65] 花岗斑岩 SHRIMP U-Pb 125±4 [56] 片理化闪长岩 SHRIMP U-Pb 125±2 [56] 未变形闪长岩 SHRIMP U-Pb 121±4 [56] 斑状花岗岩 SHRIMP U-Pb 125±3 [56] 斑状花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 120±2 [56] 花岗岩 TIMS U-Pb 129±3 [56] 绢云母 Ar-Ar 122.8±0.8 [66] 热液金红石 SIME U-Pb 122.3±1.1 [67] 成矿后闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 114.5±1.9 作者待发表 成矿前闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 124.8±2.5 作者待发表 四道沟金矿 矿化的煌斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 132.2±3.3 作者待发表 新房金矿 石英 Rb-Sr 143.0±5.8 [47] 黄铁矿、方铅矿 Rb-Sr 122.6±2.1 [48] 黄铁矿 Re-Os 121.1±1.2 [49] 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 123.0±1.4 作者待发表 -
[1] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿床: 基本特征和主要争议[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(4): 406-422.
Song M C, Song Y X, Ding Z J, et al. Jiaodong gold deposits: Essential characteristics and major controversy[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2018, 26(4): 406-422.
[2] 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 路远发, 等. 辽东青城子矿集区金、银成矿时代及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(2): 177-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.02.009
Xue C J, Chen Y C, Lu Y F, et al. Metallogenic epochs of Au and Ag deposits in Qingchengzi ore-clustered area, eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2003, 22(2): 177-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.02.009
[3] 张朋, 李斌, 李杰, 等. 辽东裂谷白云金矿载金黄铁矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(4): 731-738.
Zhang P, Li B, Li J, et al. Re-Os isotopic dating and its geological implication of gold bearing pyrite from the Baiyun gold deposit in Liaodong Rift[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2016, 40(4): 731-738.
[4] 曾庆栋, 陈仁义, 杨进辉, 等. 辽东地区金矿床类型、成矿特征及找矿潜力[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7): 1939-1963.
Zeng Q D, Chen R Y, Yang J H, et al. The metallogenic characteristics and exploring ore potential of the gold deposits in eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(7): 1939-1963.
[5] 孙立民, 孙文涛, 赵广繁. 青城子矿田小佟家堡子金银矿床地质特征及成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 黄金, 1997, 18(12): 13-18.
Sun L M, Sun W T, Zhao G F. Geological characteristics of Xiaotongjiabaozi gold-silver deposit of Qingchengzi ore field and it source of mineralized matter[J]. Gold, 1997, 18(12): 13-18.
[6] Yu G, Yang G, Chen J F, et al. Re-Os dating of gold-bearing arsenopyrite of the Maoling gold deposit, Liaoning Province, Northeast China and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(14): 1509-1514. doi: 10.1360/04wd0229
[7] 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 1153-1168.
Zhu R X, Fan H R, Li J W, et al. Decratonic gold deposits[J]. Science China Earth Science, 2015, 58(9): 1523-1537.
[8] Feng H X, Shen P, Zhu R X, et al. Precise ages of gold mineralization and pre-gold hydrothermal activity in the Baiyun gold deposit, northeastern China: In situ U-Pb dating of hydrothermal xenotime and rutile[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2022, 57(6): 1001-1022. doi: 10.1007/s00126-021-01082-z
[9] Liu S J, Chen B, Zheng J H, et al. Genesis of the Xinfang gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula: Insights from fluid inclusions and S-Sr isotopic constraints[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2021, 32(1): 68-80. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1074-7
[10] Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A. Paleotectonics of Asia: Fragments of a synthesis[C]//Yin A, Harrison T M. The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996: 486-640.
[11] Deng J, Wang Q F. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 36: 219-274. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
[12] Li Y J, Li S R, Santosh M, et al. Isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Niujuan silver deposit, northern North China Craton: Implications for magmatism and metallogeny in an extensional tectonic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90: 36-51. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.10.004
[13] Zhang P, Kou L L, Zhao Y, et al. Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, Liaoning Province, NE China: Constrains from noble gases, radiogenic and stable isotope studies[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(2): 547-563. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.05.012
[14] Zhang P, Kou L L, Zhao Y. Three periods of gold mineralization in the Liaodong Peninsula, North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2022, 64(20): 2922-2940. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2021.2009046
[15] Wu F Y, Zhang Y B, Yang J H, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic constraints on the Early Archean crustal evolution in Anshan of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 167(3/4): 339-362.
[16] 孟恩, 刘福来, 刘平华, 等. 辽东半岛东北部宽甸地区南辽河群沉积时限的确定及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(7): 2465-2480.
Meng E, Liu F L, Liu P H, et al. Depositional ages and tectonic implications for South Liaohe Group from Kuandian area in northeastern Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(7): 2465-2480.
[17] Xu W, Liu F L. Geochronological and geochemical insights into the tectonic evolution of the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 193: 162-198. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.04.019
[18] Lu X P, Wu F Y, Guo J H, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological constraints on the Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution of the eastern block in the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 146(3/4): 138-164.
[19] Luo Y, Sun M, Zhao G C, et al. A comparison of U-Pb and Hf isotopic compositions of detrital zircons from the North and South Liaohe groups: Constraints on the evolution of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2018, 163(3/4): 279-306.
[20] Wang H Z, Mo X X. An outline of the tectonic evolution of China[J]. Episodes, 1995, 18(1/2): 6-16.
[21] Yang J H, Wu F Y, Wilde S A, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic granitoids and their enclaves with implications for post-collisional lithospheric thinning of the Liaodong Peninsula, North China Craton[J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 242(1/2): 155-175.
[22] Wu F Y, Yang J H, Wilde S A, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Jurassic granites in the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 221(1/2): 127-156.
[23] Yang J H, Sun J F, Zhang J H, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic intrusive rocks in the northern Liaodong Peninsula related to decratonization of the North China Craton: Zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotope evidence[J]. Lithos, 2012, 153: 108-128. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.023
[24] Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Late Triassic intrusive rocks in the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China: Petrogenesis and implications for Early Mesozoic tectonic evolution[J]. International Geology Review, 2023, 65(2): 219-235. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2022.2042743
[25] 裴福萍. 辽南-吉南中生代侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学: 对华北克拉通破坏时空范围的制约[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008: 1-186.
Pei F P. Zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic intrusive rocks in southern Liaoning and Jilin provinces: Constraints on the spatial-temporal extent of the North China Craton destruction[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008: 1-186.
[26] 王玉往, 解洪晶, 李德东, 等. 矿集区找矿预测研究——以辽东青城子铅锌-金-银矿集区为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2017, 36(1): 1-24.
Wang Y W, Xie H J, Li D D, et al. Prospecting prediction of ore concentration area exemplified by Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Au-Ag ore concentration area, eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(1): 1-24.
[27] Zhang P, Kou L L, Zhao Y, et al. Fluid inclusions, H-O, S, Pb, and noble gas isotope studies of the Baiyun gold deposit in the Qingchengziorefield, NE China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 200: 37-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.01.016
[28] Zhang P, Zhao Y, Chai P, et al. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb analysis, and biotite 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Maoling gold deposit, Liaodong rift, NE China[J]. Resource Geology, 2017, 67(4): 426-441. doi: 10.1111/rge.12133
[29] Feng H X, Shen P, Zhu RX, et al. Geology and He-Ar-S-Pb isotope constraints on thegenesis of the Sidaogou gold deposit in Liaodong Peninsula, northeastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 113: 103080. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103080
[30] 仲米山, 张国仁, 杨中柱, 等. 辽东半岛南部早白垩世变质核杂岩时空分布及动力学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(5): 411-418. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.05.002
Zhong M S, Zhang G R, Yang Z Z, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and dynamic characteristics of the Early Cretaceous metamorphic core complexes in southern Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(5): 411-418. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.05.002
[31] 宋运红, 杨凤超, 闫国磊, 等. 辽东地区古元古代花岗岩SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(10): 2620-2636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.10.006
Song Y H, Yang F C, Yan G L, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic compositions of paleoproterozoic granites from the eastern part of Liaoning Province and their tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(10): 2620-2636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.10.006
[32] Yu G, Chen J F, Xue C J, et al. Geochronological framework and Pb, Sr isotope geochemistry of the Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Ag-Au orefield, northeastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 35(3/4): 367-382.
[33] 张朋, 杨宏智, 李斌, 等. 辽东青城子矿集区姚家沟钼矿床成矿物质来源、成矿年代及成矿动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(6): 1684-1696.
Zhang P, Yang H Z, Li B, et al. Ore source, ore-forming age and geodynamic setting of Yaojiagou molybdenum deposit in Qingchengzi ore-clustered area, eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1684-1696.
[34] 张朋, 赵岩, 寇林林, 等. 辽东青城子矿田煌斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(7): 1056-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.07.030
Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and its geological significance of lamprophyres from Qingchengzi Orefield, Liaodong[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2016, 37(7): 1056-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.07.030
[35] 张森, 张迪, 沙德喜, 等. 辽东林家三道沟-小佟家堡子地区金(银)矿成矿特征及成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(3): 725-732.
Zhang S, Zhang D, Sha D X, et al. Metallogenetic characteristics and genesis of the gold (silver) mineralization in Linjiasandaogou-Xiaotongjiapuzi area, eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(3): 725-732.
[36] 孙文涛, 孙吉国, 孙红云, 等. 青城子矿田杨树区超大型金银铅锌矿床地质特征及成矿机理[J]. 地质与勘探, 2008, 44(4): 24-30.
Sun W T, Sun J G, Sun H Y, et al. Geology and mineralization of superlarge Yangshuqu Au-Ag-Pb-Zn deposit in the Qinchengzi mine field[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2008, 44(4): 24-30.
[37] Liu J, Liu F X, Li S H, et al. Formation of the Baiyun gold deposit, Liaodong gold province, NE China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, fluid inclusion, and C-H-O-Pb-He isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Review, 2019, 104: 686-706. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.006
[38] Sun G T, Zeng Q D, Zhou L L, et al. Trace element contents and in situ sulfur isotope analyses of pyrite in the Baiyun gold deposit, NE China: Implication for the genesis of intrusion-related gold deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118: 103330. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103330
[39] Liu J, Liu F X, Li S H, et al. Genesis of the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit of the Liaodong gold province, Northeast China: Fluid inclusion thermometry and S-Pb-H-O-He isotope constraints[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(1): 1023-1040. doi: 10.1002/gj.3454
[40] 孙国强, 孙启明, 郑廷. 辽宁青城子矿田桃源金矿床地质特征及成矿机制探讨[J]. 甘肃冶金, 2008, 30(6): 49-51.
Sun G Q, Song Q M, Zheng T. Geological characteristics and causes of Taoyuan gold deposit in Liaoning Qingchengzi[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 2008, 30(6): 49-51.
[41] Yu B, Zeng Q D, Frimmel H E, et al. Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, northeastern North China Craton: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and pyrite trace element concentrations[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 102: 313-337.
[42] Yu B, Zeng Q D, Frimmel H E, et al. The 127 Ma gold mineralization in the Wulong deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China: constraints from molybdenite Re-Os, monazite U-Th-Pb, and zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 121: 103542. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103542
[43] Chen C, Li D T, Wu T T, et al. Genesis of gold deposits in the Wulong orefield, Liaodong Peninsula, North China Craton: Constraints from ore deposit geology, REE, and C-H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(8): 5914-5933. doi: 10.1002/gj.3661
[44] 刘军, 李铁刚, 段超. 辽宁猫岭大型金矿床成岩成矿年龄及同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(7): 1325-1337.
Liu J, Li T G, Duan C. Geochronology and isotopic geochemistry characteristics of the Maoling large gold deposit, Liaoning Province, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(7): 1325-1337.
[45] 孙宝亮, 梁俊红, 姚玉增, 等. 猫岭-王家崴子金成矿带铅同位素地球化学特征[J]. 辽宁地质, 2000, 17(4): 259-262.
Sun B L, Liang J H, Yao Y Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of lead isotope in Maoling-Wangjiawaizi gold metallogenic belt[J]. Liaoning Geology, 2000, 17(4): 259-262.
[46] 郝瑞霞, 彭省临. 辽宁王家崴子金矿床地球化学研究[J]. 黄金地质, 1999, 5(2): 47-51.
Hao R X, Peng S L. Geochemical study of Wangjiawaizi gold deposit in Liaoning[J]. Gold Geology, 1999, 5(2): 47-51.
[47] 郭大招, 魏俊浩, 张可清, 等. 辽东庄河金矿同位素地球化学特征及成矿时代[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(5): 671-678.
Guo D Z, Wei J H, Zhang K X, et al. The isotope geochemical characteristics and ore-forming time of Zhuanghe gold deposit, eastern Liaoning[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(5): 671-678.
[48] Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. Genesis of the Xinfang gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, pyrite trace element concentrations, and chronology[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 113: 210-231. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.11.002
[49] Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. Genesis of the Xinfang magmatic-hydrothermal gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from pyrite Re-Os isotopes, C, O, S, Pb, Si, He and Ar isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 148: 105025.
[50] 冯啸宇. 辽南盖县组地层中金矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与资源, 2011, 20(1): 36-69. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2011.01.002
Feng X Y. Geologic characteristics and prospecting direction of gold deposits in Gaixian formation in southern Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2011, 20(1): 36-69. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2011.01.002
[51] 张朋, 陈冬, 寇林林, 等. 辽东卧龙泉岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(10): 1762-1772.
Zhang P, Chen D, KouL L, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes of the Wolongquan intrusion in Liaodong and its tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(10): 1762-1772.
[52] 刘文彬, 彭游博, 赵辰, 等. 辽南盖州卧龙泉岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2018, 27(6): 531-539. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/id/8503
Liu W B, Peng Y B, Zhao C, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of Wolongquan intrusion in Gaizhou, Southern Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2018, 27(6): 531-539. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/id/8503
[53] 杨进辉, 吴福元, 谢烈文, 等. 辽东矿洞沟正长岩成因及其构造意义: 锆石原位微区U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 263-276.
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Xie L W, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Kuangdonggou syenites in the Liaodong Peninsula, east North China Croton: Constraints from in-situ zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(2): 263-276.
[54] 徐山. 辽东地区金矿矿产资源评价[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013: 1-158.
Xu S. The mineral resources assessment of gold deposits in eastern Liaoning[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013: 1-158.
[55] 余昌涛, 贾斌, 刘斌. 辽宁省盖县猫岭金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 贵金属地质, 1992, 1(1): 37-47.
Yu C T, Jia B, Liu B. Geological characteristic and genesis of Maoling gold deposit in Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 1992, 1(1): 37-47.
[56] 吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明. 辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3): 305-317.
Wu F Y, Yang J H, LiuX M. Geochronological framework of the Mesozoic granitic magmatism in the Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(3): 305-317.
[57] 张朋, 赵岩, 寇林林, 等. 辽东半岛丹东地区中生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(10): 3297-3313.
Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotope sand geological significance of Mesozoic granites in Dandong area, Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(10): 3297-3313.
[58] 仲米山, 张国仁, 高福亮, 等. 辽南新房变质核杂岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(1): 272-287.
Zhong M S, Zhang G R, Gao F L, et al. Discovery and geological implication of Xinfang metamorphic core complex in southern Liaoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(1): 272-287.
[59] 刘国平, 艾永富. 辽宁白云金矿床成矿时代探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(4): 627-632.
Liu G P, Ai Y F. Studies on the mineralization age of Baiyung old deposit in Liaoning[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2000, 16(4): 627-632.
[60] 周国超, 王玉往, 李德东, 等. 辽东白云金矿区脉岩锆石的U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36(4): 620-627.
Zhou G C, Wang Y W, Li D D, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of dykes from the Baiyun gold deposit in eastern Liaoning[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2017, 36(4): 620-627.
[61] Sun G T, Zeng Q D, Li T Y, et al. Ore genesis of the Baiyun gold deposit in Liaoning Province, NE China: Constraints from fluid inclusions and zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2019, 12(9): 299.
[62] Sun G T, Zeng Q D, Zhou J X. Jurassic Au-Ag mineralization of the Linjiasandaogou deposit in the Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China: Evidence from apatite U-Pb dating and the in situ geochemistry of sulfides[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 251: 107242.
[63] Zhang P, Kou L L, Zhao Y, et al. Genesis of the Maoling gold deposit in the Liaodong Peninsula: Constraints from a combined fluid inclusion, C-H-O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic and geochronological studies[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2022, 13(4): 101379.
[64] 张朋. 辽宁省东南部典型有色、贵金属矿床成矿特征、成因与成岩成矿地球动力学过程[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018: 62-67.
Zhang P. Metallogeniccharacteristics, oregenesis, diagenesis and metallogenic geodynamic process of precious and nonferrous metals ore deposits in southeast Liaoning Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018: 62-67.
[65] 魏俊浩, 刘丛强, 李志德, 等. 论金矿床成矿年代的确定——以丹东地区成岩成矿Rb-Sr、U-Pb同位素年代为例[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(1): 113-119.
Wei J H, Liu C Q, Li Z D, et al. U-Pb, Rb-Sr isotopic dating of the diagenesis and mineralization of gold deposits in the Dandong area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2003, 77(1): 113-119.
[66] Liu J, Zhang L J, Wang S L, et al. Formation of the Wulong gold deposit, Liaodong gold province, NE China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, sericite Ar-Ar age, and H-O-S-He isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 109: 130-143.
[67] Feng H X, Shen P, Zhu R X, et al. SIMS U-Pb dating of vein-hosted hydrothermal rutile and carbon isotope of fluids in the Wulong lode gold deposit, NE China: Linking gold mineralization with craton destruction[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 127: 103838.
[68] 马玉波, 邢树文, 张增杰, 等. 辽吉裂谷区铅锌金矿床S、Pb同位素组成特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(9): 1399-1410.
Ma Y B, Xing S W, Zhang Z J, et al. Characteristics of the sulfur and lead isotope compositions of the polymetallic deposit in the Liaoji rift and their geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(9): 1399-1410.
[69] 赵鸿志, 杨沈生, 李辉. 白云金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 有色矿冶, 2009, 25(3): 4-7.
Zhao H Z, Yang S S, Li H. Geologic features of Baiyun gold ore deposit and discussion of the genesis[J]. Non-Ferrous Miningand Metallurgy, 2009, 25(3): 4-7.
[70] 关广岳, 金成洙. 白云金矿床的成因[J]. 地质与勘探, 1983(10): 12-20.
Guan G Y, Jin C Z. Genesis of Baiyun gold deposit[J]. Geology and Exploration, 1983(10): 12-20. (in Chinese)
[71] 郝立波, 赵昕, 赵玉岩. 辽宁白云金矿床稳定同位素地球化学特征及矿床成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(2): 442-451.
Hao L B, Zhao X, Zhao Y Y. Stable isotope characteristics and ore genesis of the Baiyun gold deposit, Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(2): 442-451.
[72] 刘先利, 姜瑛, 刘志远. 青城子矿田高家堡子大型金银矿床地质特征及成矿机制[J]. 辽宁地质, 2000, 17(2): 121-127.
Liu X L, Jiang Y, Liu Z Y. Geological characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of Gaojiapuzi large-scale Au-Ag deposits in Qingchengzi orefield[J]. Liaoning Geology, 2000, 17(2): 121-127.
[73] 杨凤超, 宋运红, 张朋, 等. 辽宁青城子矿集区金银矿成矿流体特征和成矿物质来源示踪[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(10): 2775-2785.
Yang F C, Song Y H, Zhang P, et al. Forming fluid characteristics and tracing of ore-forming source materials of gold-silver deposit in the Qingchengzi ore concentration area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(10): 2775-2785.
[74] 刘辉, 金成洙, 关广岳. 辽南猫岭金矿床的成矿物质来源及金的活化、迁移及富集机理[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1990, 5(4): 57-68.
Liu H, Jin C Z, Guan G Y. A mechanism study on the source of minerogenic material and the activation transportation and concentration of gold in Maoling gold deposit[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1990, 5(4): 57-68.
[75] 成曦晖. 辽东中生代岩浆活动及金铀成矿作用[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2017: 1-207.
Cheng X H. Integrated research on Mesozoic magmatism and gold-uranium metallogenesis in the Liaodong Peninsula, Liaoning Province[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology, 2017: 1-207.
[76] 吴兴华. 辽南马蹄形带金矿床层控-多因成矿模式[D]. 沈阳: 东北工学院, 1990: 1-99.
Wu X H. Stratabound-polygenetic metallogenic model of the C-shaped gold deposit belt in southern Liaoning[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern Institute of Technology, 1990: 1-99. (in Chinese)
[77] Chen J F, Yu G, Xue C J, et al. Pb isotope geochemistry of lead, zinc, gold and silver deposit clustered region, Liaodong rift zone, northeastern China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(4): 467-476.
[78] Yao X F, Yan T J, Lü Z C, et al. Ore-forming age and tectonic setting of the Linjiasandaogou gold deposit in the Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2022, 41(2): 244-266.
[79] 李兆龙, 许文斗, 秦敏琪, 等. 辽宁五龙金矿地质特征及矿床成因[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1987, 2(3): 31-39.
Li Z L, Xu W D, Qin M Q, et al. Geological characteristics and ore genesis of Wulong gold deposits, Liaoning Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1987, 2(3): 31-39.
[80] 刘国平, 艾永富. 辽宁白云金矿床某些基本问题探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 1999, 18(3): 219-225.
Liu G P, Ai Y F. A discussion on some major problems of the Baiyun gold deposit, eastern Liaoning[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1999, 18(3): 219-225.
[81] Faure G. Principles of isotope geology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1986: 1-589.
[82] 赵岩, 张朋, 吕骏超, 等. 辽宁青城子矿田高家堡子银矿成矿流体特征及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(3): 441-450.
Zhao Y, Zhang P, Lü J C, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids in the Gaojiapuzi Ag deposit of the Qingchengzi orefield, Liaoning Province and geological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(3): 441-450.
[83] Stuart F M, Burnard P G, Taylor R P, et al. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(22): 4663-4673.
[84] Burnard P G, Hu R, Turner G, et al. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(10): 1595-1604.
-



 下载:
下载: