Green and High Efficiency Preparation of Silicon Fertilizer with Blast Furnace Slags
-
摘要:
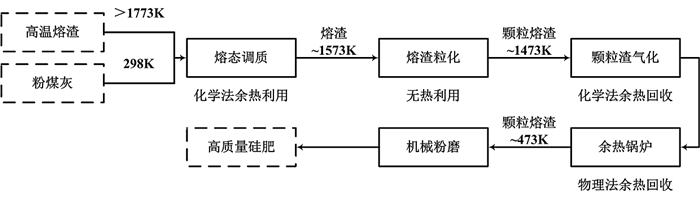
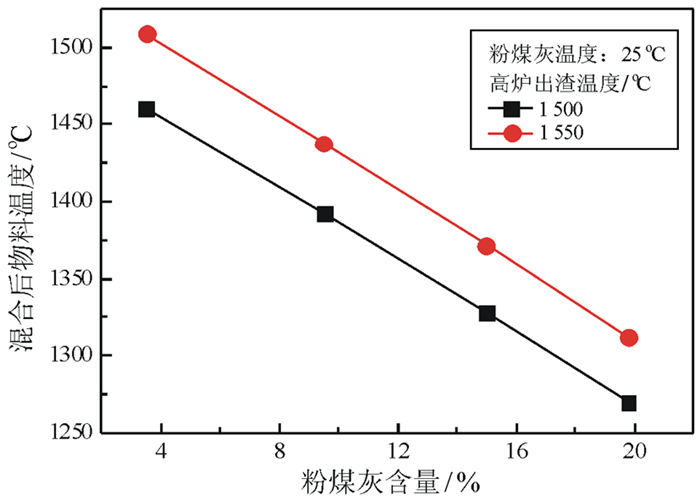
针对高炉熔渣含大量显热及粉煤灰中二氧化硅含量高的特点,进行高温炉熔渣混合加入粉煤灰制备高效硅肥研究。粉煤灰与熔渣按7.76:92.24质量比加入,经混合水淬后得到硅肥中有效硅含量最高,且随高炉熔渣温度升高,硅肥中有效硅含量提高,高炉熔渣温度为1 550℃,制备出高效硅肥有效硅含量达到22.4%,并提出高炉熔渣协同粉煤灰直接绿色制备高效硅肥技术。
Abstract:In view of the high content of silica in fly ash and abundant heat in blast furnace slag, high efficiency silicon fertilizer was prepared by mixing blast furnace slag with fly ash directly. When the fly ash and blast furnace slag were mixed with a mass ratio of 7.76:92.24, the effective silicon content in silicon fertilizer was highest after the condition of quenching. With increasing slag temperature, the effective silicon content in silicon fertilizer increased, and the effective silicon content of silicon fertilizer can reach up to 22.4% at the slag temperature of 1 550℃. Finally, the preparation technology for high efficiency silicon fertilizer with blast furnace slag and fly ash was raised.
-
Key words:
- blast furnace slag /
- heat recovery /
- fly ash /
- silicon fertilizer
-

-
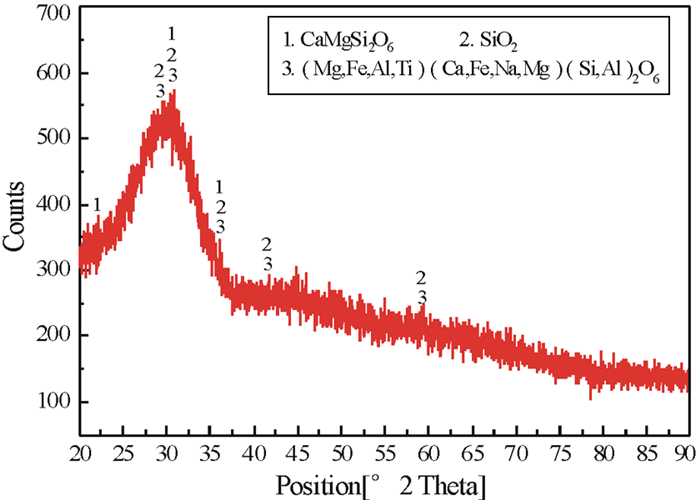
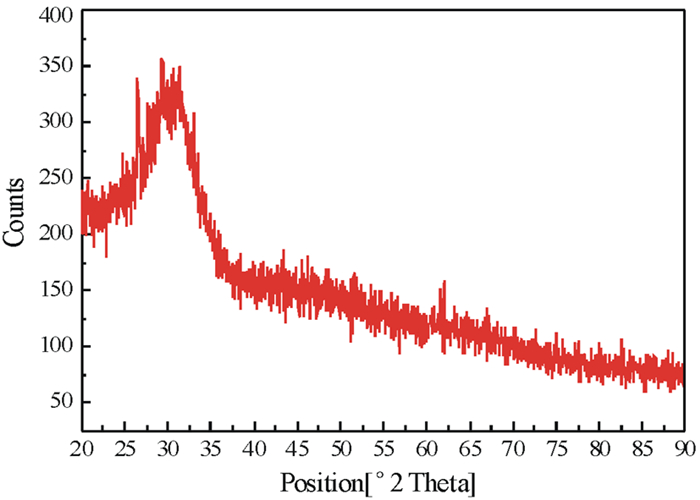
表 1 高炉渣、粉煤灰化学成分及有效硅含量 /%
Table 1. Chemical composition of raw materials and effective silicon content
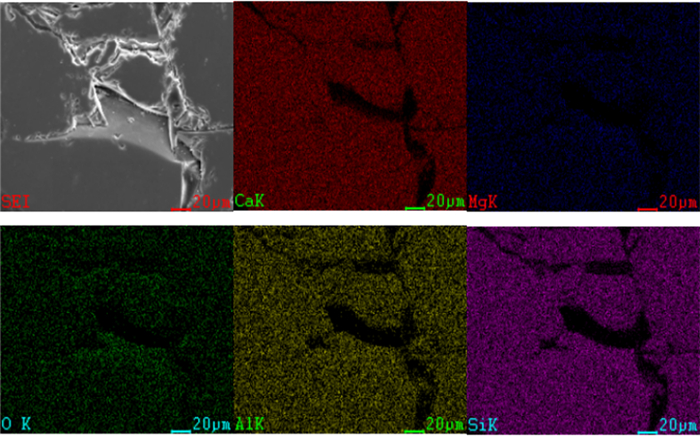
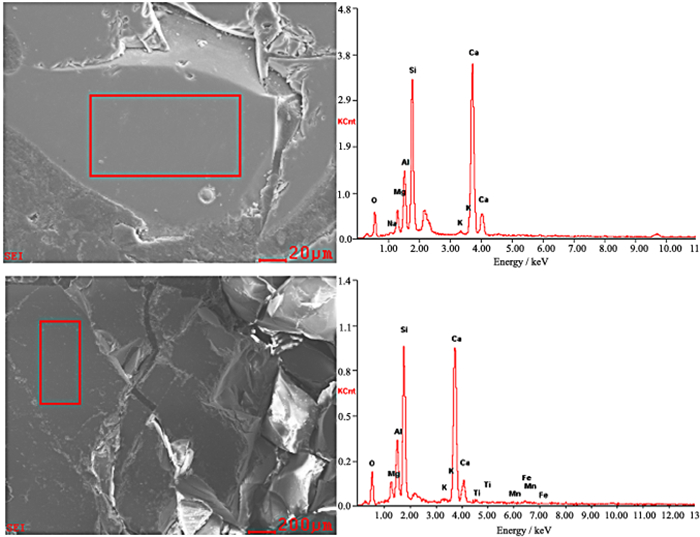
原料 CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO K2O 有效硅含量 高炉渣 43.03 35.92 11.99 5.35 0.62 15.14 粉煤灰 1.67 57.19 32.40 0.46 1.01 - 表 2 高炉渣和粉煤灰化学组成
Table 2. Chemical composition of blast furnace slag and fly ash
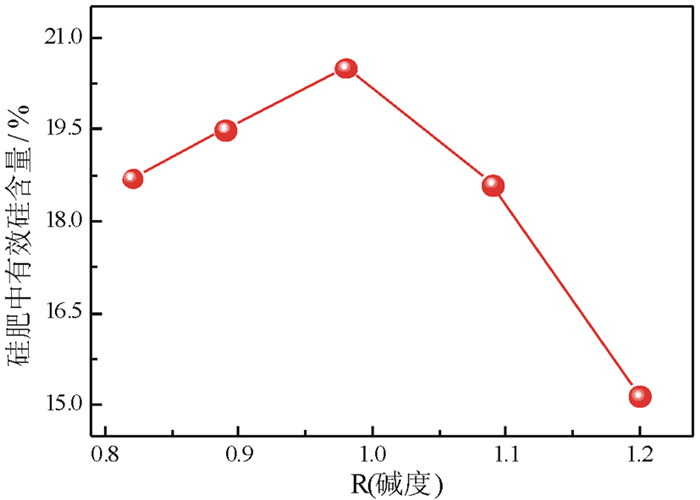
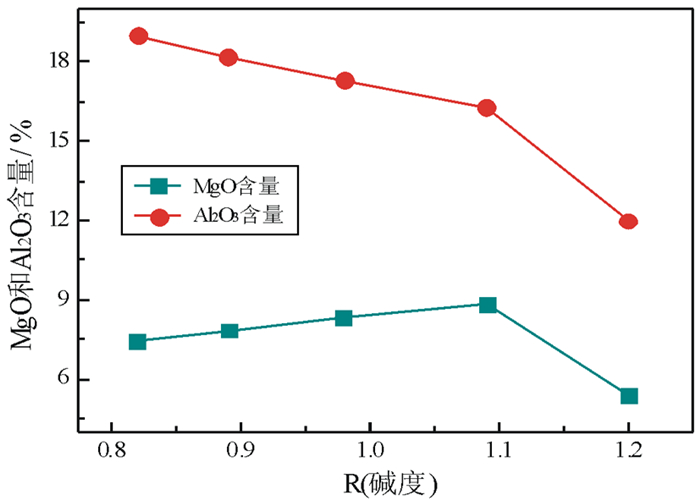
序号 R(碱度) 水淬高炉渣/g 粉煤灰/g a 1.20 100.00 0 b 1.09 98.39 1.61 c 0.98 92.24 7.76 d 0.89 86.74 13.26 e 0.82 81.79 18.21 -
[1] 汤优优, 涂玉国, 雷霆, 等.某高炉渣综合利用试验研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2011(3):34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0076.2011.03.009 http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=20c0899d-fec9-4b6d-b801-ec840e7c39f4
[2] 崔孝炜, 狄燕清, 南宁.钢渣的机械力粉磨特性[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(5):77-81. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=3a4c9951-d5bd-4e88-b51e-59a8dcf792e3
[3] 王海风, 张春霞, 齐渊洪, 等.高炉渣处理技术的现状和新的发展趋势[J].钢铁, 2007, 42(6):83-87. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt200706019
[4] 宋猛, 薛亚洲, 王雪峰, 等.矿产资源节约形势及监管途径探讨[J].矿产保护与利用, 2018(1):24-29. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c375ba24-c51e-4d8f-beac-0b1b65f377dd
[5] 宁东峰.钢渣硅钙肥高效利用与重金属风险性评估研究[D].北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014.
[6] 王海风, 张春霞, 齐渊洪.高炉渣处理和热能回收的现状及发展方向[J].中国冶金, 2008, 17(6):53-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyj200706013
[7] 戴晓天, 齐渊洪, 张春霞, 等.高炉渣急冷干式粒化处理工艺分析[J].钢铁, 2007, 19(5):14-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtyjxb200705004
[8] 周继程, 张春霞, 郦秀萍, 等.基于能级分析的钢厂余热资源回收利用方式的合理性[J].钢铁, 2013, 48(2):80-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt201302016
[9] Gan L, Zhang C X, Zhou J C, et al. Continuous cooling crystallization kinetics of a molten blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of non-crystalline solids, 2012, 358(1):20-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.08.008
[10] Gan L, Zhang C X, Shangguan F Q, et al. A differential scanning calorimetry method for construction of continuous cooling transformation diagram of blast furnace slag[J]. Metallurgical and materials transactions B, 2012, 43(3):460-467. doi: 10.1007/s11663-011-9631-1
[11] Richard J, Haynesl O. N, Belyaeval G, et al. Evaluation of industrial wastes as sources of fertilizer silicon using chemical extractions and plant uptake[J]. Journal of soil science and plant nutrition, 2013, 176(2):238-248. doi: 10.1002/jpln.v176.2
[12] Tasong W A, Wild S, Tilley R J D. Mechanism by which ground granulated blastfurnace slag prevents sulphate attack of lime-stabilised kaolinite[J]. Cement and concrete research, 1999, 29(7):975-982. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(99)00007-1
[13] Song S, Jennings H M. Pore solution chemistry of alkali-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag[J]. Cement and concrete research, 1999, 29:159-170. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00212-9
[14] Schmucker M, Schneider H, MacKenzie K J D, et al. AlO4/SiO4 distribution in tetrahedral double chains of mullite[J]. Journal of the American ceramic society, 2005, 88(10):2935-2937. doi: 10.1111/jace.2005.88.issue-10
[15] Mostafa N Y, Ei-Hemaly S A S, Al-Wakeel E I, et al. Characterization and evaluation of the hydraulic activity of water-cooled slag and air-cooled slag[J]. Cement and concrete research, 2001, 31:899-904. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00497-5
[16] Kato N, Owa N. Evaluation of Si availability in slag fertilizers by an extraction method using a cation exchange resin[J]. Soil science and plant nutrition, 1997, 43:351-359. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1997.10414759
-



 下载:
下载: