Study on Microwave-assisted Grinding Mechanism of Cassiterite-polymetallic Sulfide Ore
-
摘要:
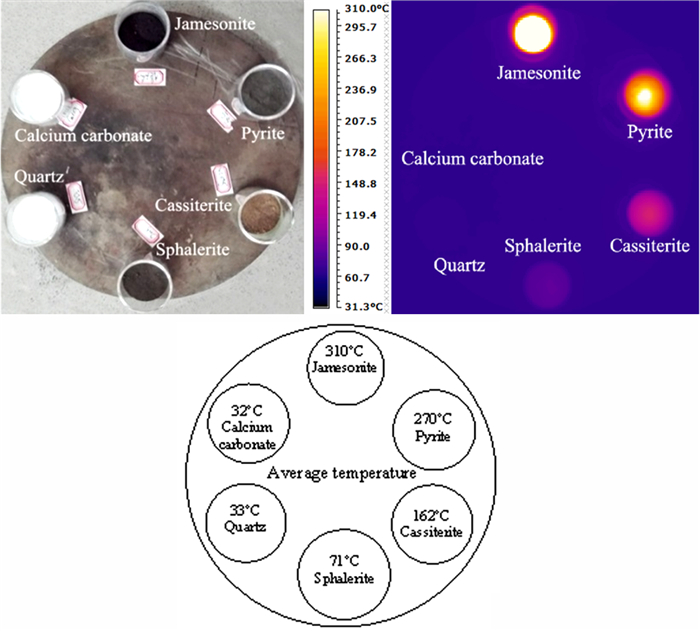
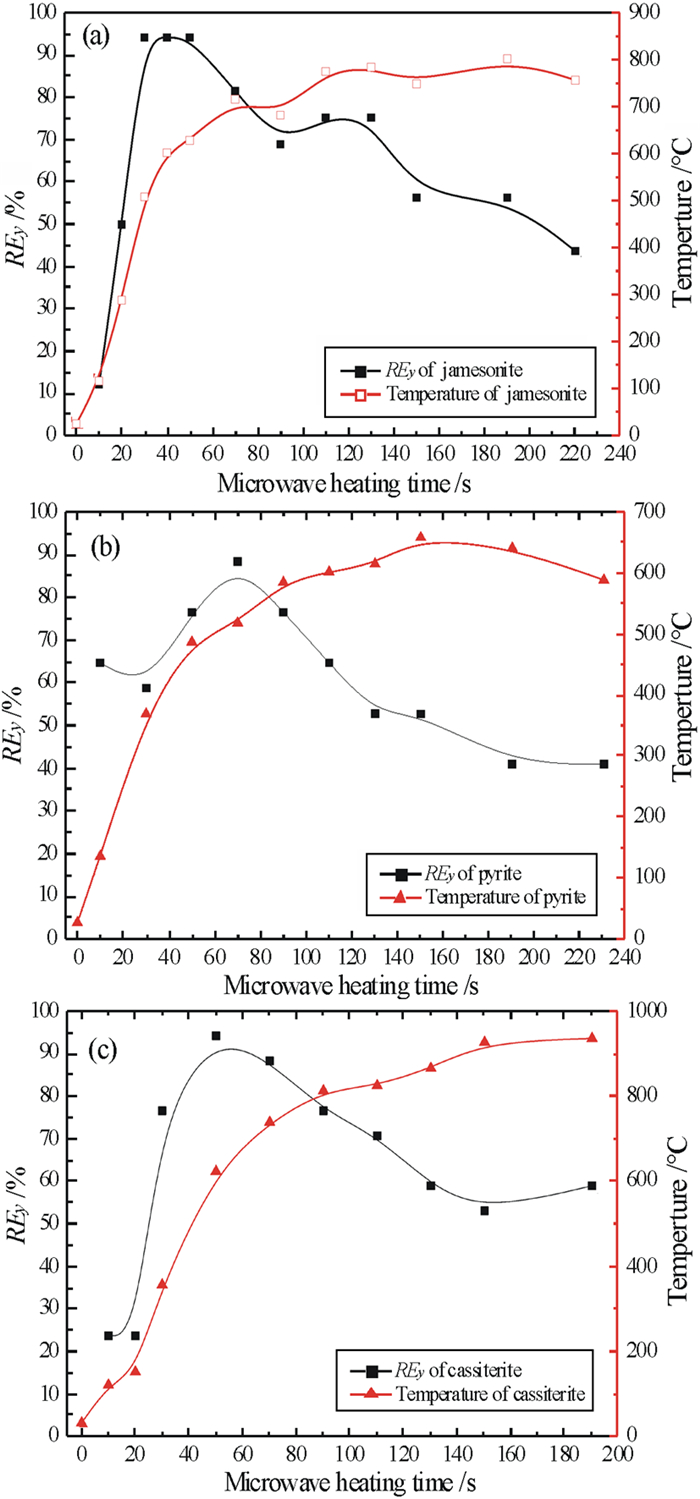
以锡石多金属硫化矿作为研究对象,通过微波加热预处理矿石,考察矿石预处理前后和不同冷却方式对磨矿产品可磨度等指标的影响。结果表明,经微波加热预处理后,矿石可磨度提高,邦德功指数下降。这是因为微波辐射致使锡石多金属硫化矿中的脆硫锑铅矿、黄铁矿、闪锌矿、锡石等金属矿物温度升高,而脉石矿物升温并不明显,致使金属矿物和脉石的温度梯度大,产生不均匀热膨胀,导致在矿石内部出现应力集中对矿物与脉石产生破坏,强化锡石多金属硫化矿磨矿效果。
Abstract:Taking cassiterite polymetallic sulphide ore as the research object, the effects of preheating and different cooling methods on the grindability of grinding products were investigated after pretreatment of microwave heating. The results showed that after microwave heating, the grindability increased and the Bond work index decreased. This is mainly due to the fact that the microwave radiation increases the temperature of the metal minerals such as jamesonite, pyrite, sphalerite, cassiterite, etc. in the cassite polymetallic sulfide ore, and has less effect on the gangue minerals. The large temperature gradient between the metallic metal minerals and gangue minerals could produce uneven thermal expansion and promote the dissociation of metallic minerals and gangue minerals due to the high stress concentration inside the ore, thereby strengthening the grinding effect.
-
Key words:
- microwave /
- cassiterite /
- polymetallic sulfide ore /
- grinding /
- Bond's work index /
-

-
表 1 试验样品粒度分布
Table 1. Particle size distribution of ore sample
粒度/mm 产率/% 筛下累积产率/% -3.2+3 19.08 100.00 -3+2 43.12 80.92 -2+1.5 29.54 37.80 -1+0.425 8.08 8.26 -0.425 0.18 0.18 合计 100.00 - 表 2 试验样品各粒级中主要金属元素分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of main metallic elements in each size fraction of ore sample
粒度/mm 金属品位/% 金属分布率/% Fe Sn Pb Sb Zn Fe Sn Pb Sb Zn -3.2+3 10.9 0.87 0.32 0.18 2.16 21.20 19.45 22.12 20.20 19.37 -3+2 10.04 0.85 0.30 0.19 2.10 44.12 42.94 46.86 48.19 42.57 -2+1 8.56 0.76 0.22 0.14 2.26 25.77 26.30 23.54 24.32 31.38 -1 10.60 1.17 0.25 0.15 1.72 8.922 11.32 7.48 7.29 6.68 合计 - - - - - 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 表 3 试验样品的化学成分分析
Table 3. Chemical composition analysis of the ore sample
化学成分 SiO2 CaCO3 Fe2O3 SO3 Al2O3 其他 含量/% 45.9 28.2 8.4 7.2 4.1 6.2 表 4 微波加热预处理后冷却方式对磨矿产品粒度分布的影响
Table 4. Effect of the cooling pattern on the particle size distribution after microwave pretreatment
粒级/mm 产率/% 筛下累计产率/% Untreated MW-N MW-W Untreated MW-N MW-W -3.2+2 3.24 2.78 1.84 100.00 100.00 100.00 -2+1 20.36 19.20 12.94 96.76 97.22 98.16 -1+0.425 35.04 32.21 34.06 76.40 78.02 85.22 -0.425+0.15 17.22 18.47 20.79 41.36 45.81 51.15 -0.15+0.074 5.66 6.64 7.84 24.13 27.34 30.36 -0.074+0.038 4.59 5.59 5.71 18.47 20.70 22.52 -0.038 13.88 15.11 16.81 13.88 15.11 16.81 注:Untreated未经微波加热预处理;MW-N微波辐射后,经自然冷却处理;MW-W微波辐射后,经水冷却处理,以下各表均相同。 表 5 原矿的邦德功球磨试验数据
Table 5. Experiment data of Bond ball mill of raw ore
次序 新给料Fi/g 转数Ni/r 新生成合格产品量qi/g 循环负荷Ci/% 可磨度Grpi/(G/r) 1 1 173.00 100 109.97 3.17 1.100 2 109.97 305 345.19 2.47 1.132 3 345.19 296 355.01 2.44 1.199 4 355.01 279 387.83 2.34 1.390 5 387.83 242 333.77 2.50 1.379 6 333.77 249 314.78 2.56 1.264 7 314.78 246 342.43 2.48 1.392 8 342.43 241 322.15 2.54 1.337 9 322.15 244 323.87 2.53 1.327 表 6 微波处理后矿样邦德功球磨试验数据
Table 6. The experiment data of Bond ball mill after microwave pretreatment
次序 新给料Fi/g 转数Ni/r 新生成合格产品量qi/g 循环负荷Ci/% 可磨度Grpi/(G/r) 1 1173.00 100 163.18 3.01 1.632 2 163.18 205 191.16 2.93 0.932 3 191.16 236 321.63 2.54 1.363 4 321.63 246 338.80 2.49 1.377 5 338.80 243 338.67 2.49 1.394 6 338.67 240 346.60 2.47 1.444 7 346.6 232 340.38 2.48 1.467 表 7 金属矿物和脉石矿物的吸波能力
Table 7. Microwave absorption ability of metallic minerals and gangue minerals
名称 脆硫锑铅矿 黄铁矿 锡石 闪锌矿 石英 碳酸钙 REc/% 33.96 28.04 18.87 2.44 0 2.12 表 8 矿物密度及比热容
Table 8. Density and specific heating capacity of minerals
矿物 密度/(kg·m-3) 比热/(J·kg-1·K-1) 298 K 500 K 1000 K 黄铁矿 5 016 517.08 600.42 683.83 石英 2 648 740.50 991.17 1167.17 方解石 2 712 817.70 1051 1 238.5 表 9 矿物热膨胀系数
Table 9. Thermal expansion coefficients of minerals
矿物 热膨胀系数(α) : (1/K)(10-6) 373K 473 K 673 K 873 K 黄铁矿 27.3 29.3 33.9 -- 石英 45.0 43.3 49.7 77.9 方解石 13.1 15.8 20.1 24 -
[1] 石政威.锡石多金属硫化矿球介质磨矿规律试验研究[J].南宁:广西大学, 2009. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1598983
[2] Napier-Munn T. J., Morrell S., Morrison R. D., et al. Mineral comminution circuits:their operation and optimization[M]. Julius kruttschnitt mineral research centre, University of Queensland, 2005:1-2.
[3] Amankwah R. K., Ofori-Sarpong G. Microwave heating of gold ores for enhanced grindability and cyanide amenability[J]. Minerals engineering, 2011, 24(6):541-544. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2010.12.002
[4] 付润泽, 朱红波, 彭金辉, 等.采用微波助磨技术处理惠民铁矿的研究[J].矿产综合利用, 2012(2):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2012.02.007
[5] 付润泽.微波辅助磨细惠民铁矿实验研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1012263253.htm [6] Schmuhl R., Smit J. T., Marsh J. H. The influence of microwave pre-treatment of the leach behaviour of disseminated sulphide ore[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108(3):157-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fbc6f6f33c54d022e010a374e1c6cbfc
[7] Omran M., Fabritius T., Abdel-Khalek N., et al. Microwave assisted liberation of high phosphorus oolitic iron ore[J]. Journal of minerals and materials characterization and engineering, 2014, 2(5):414-427. doi: 10.4236/jmmce.2014.25046
[8] Omran M., Fabritius T., Mattila R. Thermally assisted liberation of high phosphorus oolitic iron ore:a comparison between microwave and conventional furnaces[J]. Powder technology, 2015, 269:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.073
[9] Lester E., Kingman S., Dodds C., et al. The potential for rapid coke making using microwave energy[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(14):2057-2063. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6e63bf999b69bd0830db3610ef225146
[10] Han L. C., Li E., Guo, G. F., et al. Application of transmission/reflection method for permittivity measurement in coal desulfurization[J]. Progress in electromagnetics research letters, 2013, 37:177-187. doi: 10.2528/PIERL12123002
[11] Walkiewicz J W, Kazonich G, McGill S L. Microwave heating characteristics of selected minerals and components[J]. Mineral and metallurgical processing, 1988, 5(1):39-42.
[12] McGill S L, Walkiewicz J W, Smyres G A. The effect of power level on microwave heating of selected chemicals and minerals[J]. Materials research society proceedings, 1988, 124:247-252. doi: 10.1557/PROC-124-247
[13] Connell L H, Moe L A. Apparatus for treatment of ore US: 3261959[P]. 1966-04-24.
[14] Ford J D, T Pei D C. High temperature chemical process via microwave absorption[J]. Microwave power, 1967, 2(2):61-64. doi: 10.1080/00222739.1967.11688647
[15] Whittles D N, Kingman S W, Reddish D J. Application of numerical modelling for prediction of the influence of power density on microwave-assisted breakage[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2003, 68(1):71-91. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5310b5cfc8d9bf0678b65cf12e4c9f38
[16] Jones D A, Kingman S W, Whittles D N, et al. Understanding microwave assisted breakage[J]. Minerals engineering, 2005, 18(7):659-669. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2004.10.011
[17] Ali A Y. Understanding the effects of mineralogy, ore texture and microwave power delivery on microwave treatment of ores[J]. Stellenbosch:University of Stellenbosch, 2010. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f7dab99632fbbfac18fe630e5cb208ab&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-



 下载:
下载: