Process Mineralogy Study of a Low-grade Rare and Polymetallic Ore of Tantalum-niobium-rubidium-beryllium from Guangdong
-
摘要:
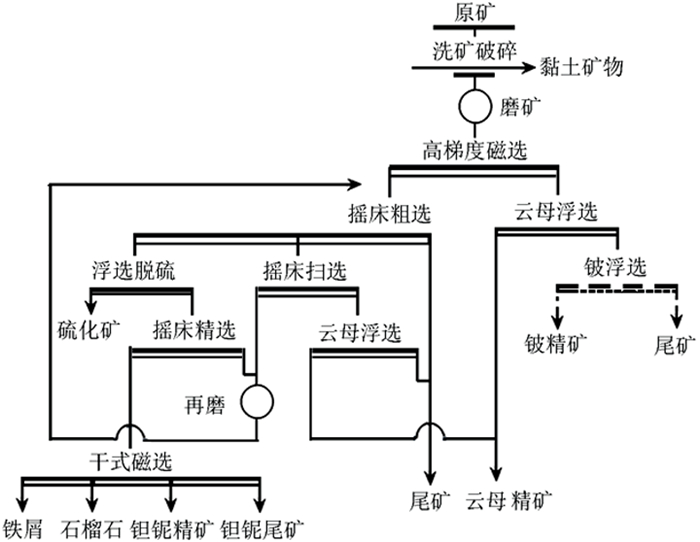
以广东省某低品位钽铌铍铷多金属矿为研究对象,采用先进矿物定量检测技术与传统工艺矿物学研究手段相结合的方法,对矿石进行工艺矿物学研究,以期为多金属矿石综合回收提供指导。结果表明,本矿石属强钠长石化和云英岩化花岗岩型钽铌铍铷矿石,原矿中主要有价金属为钽、铌、铍、铷、镓和银。以钽铌铁矿矿物形式存在的钽和铌分别占总含量的68.51%、62.72%;以绿柱石和硅铍石矿物形式存在的铍分别占原矿总含量的71.01%和20.29%;赋存于云母和长石中的铷分别占总含量的74.94%和20.24%;镓主要富集在黏土矿物中,银主要以螺状硫银矿形式赋存于硫化矿物中。采用重磁浮联合选矿流程,可实现有用元素和尾矿的综合回收。
Abstract:The rare metals, tantalum and niobium, beryllium and rubidium, are commonly associated with each other on earth. They have been recognized as important strategic resources in recent years. In this paper, the occurrence research of niobium-tantalum-beryllium-rubidium on a low-grade and micro-fine disseminated rare metals deposit from Guangdong province was carried out, by combining advanced mineralogical determination technology with traditional process mineralogy methods. In order to provide a clarified guidance to process selection of subsequent mineral separation and comprehensive recovery of the ore. As a result, the ore is classified into tantalum-niobium-beryllium-rubidium granite type ore with strong alteration of albitzation and greisenization. In the ore, the valuable metals include tantalum, niobium, rubidium, beryllium, gallium and silver. Tantalum and niobium in the form of columbite-tantalite account for 68.51% and 62.72%, respectively. The beryllium in the form of beryl and phenacite account for 71.01% and 20.29%, respectively. The rubidium occurred in muscovite and feldspar account for 74.94% and 20.24%, respectively. While gallium in the ore is mainly concentrated in clay minerals, and silver is mainly present in sulfide minerals in the form of acanthite. The comprehensive recovery of valuable metals and tailing can be achieved by using combined process of gravity separation, magnetic separation and flotation.
-
Key words:
- rare metals deposit /
- process mineralogy /
- tantalum /
- niobium /
- rubidium /
- beryllium
-

-
表 1 原矿多元素化学分析结果 /%
Table 1. Results of multi-element chemical analysis
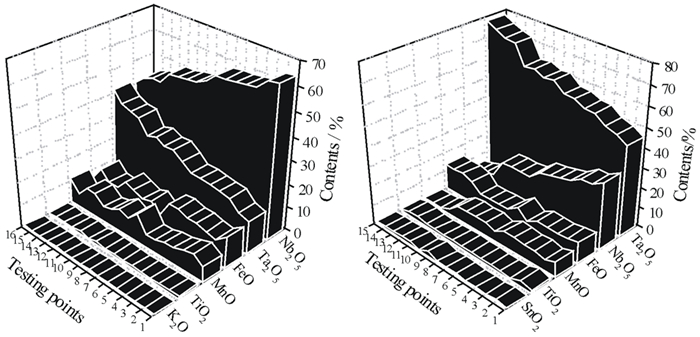
元素 Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Rb2O BeO Ag Ga2O3 Sn 含量 0.009 0.011 0.14 0.044 1.33 48 0.012 元素 WO3 Cu Zn Li2O Cs2O Fe S 含量 < 0.01 0.017 0.012 0.008 0.005 0.28 0.016 元素 K2O Na2O Al2O3 SiO2 CaO MgO 含量 3.36 3.35 18.06 70.87 0.13 0.16 注:Ag、Ga2O3单位为g/t,参考《矿产资源工业要求手册》2014年修订版,铷的工业品位为Rb2O 0.1%~0.2%。参考《选矿工程师手册(第四册)》2015年版,钽铌的工业品位为(Ta, Nb)2O5 0.024%~0.028%,铍的工业品位为BeO 0.10%~0.14%。 表 2 原矿矿物组成及含量
Table 2. The mineralogical composition of raw ore
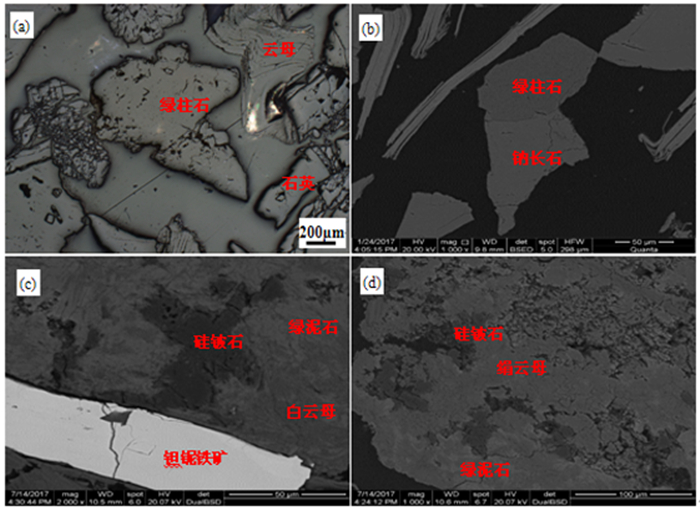
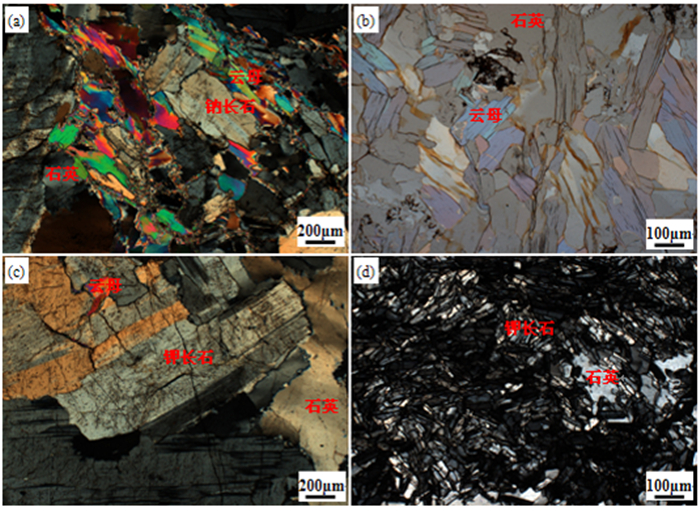
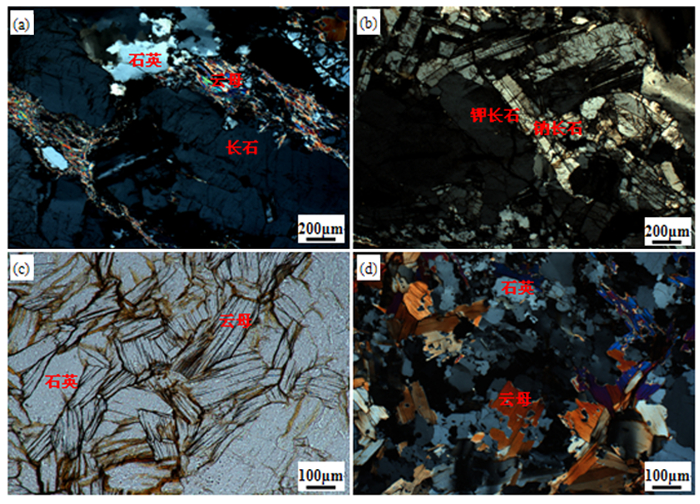
矿物 含量/% 钽铌铁矿 0.017 绿柱石 0.241 硅铍石 0.020 硫化物 0.052 石英 34.872 钾长石 10.434 钠长石 28.397 云母 16.427 高岭土 4.443 三水铝石 3.776 其他 1.319 合计 100.000 表 3 有价元素的磁性分布
Table 3. The magnetic distribution of valued elements
磁级/mT 产率/% 品位/% 回收率/% Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Rb2O BeO Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Rb2O BeO 250 2.87 0.010 0.018 0.10 0.037 2.99 3.18 2.85 2.58 450 1.13 0.019 0.022 0.091 0.039 2.22 1.52 1.01 1.06 650 1.11 0.44 0.63 0.091 0.042 50.77 43.04 1.00 1.13 1 100 1.24 0.18 0.21 0.094 0.066 23.10 15.96 1.15 1.98 2 000 2.36 0.008 0.018 0.23 0.081 1.96 2.62 5.38 4.64 Nonmagnetic 91.29 0.002 0.006 0.098 0.04 18.96 33.68 88.61 88.61 Total 100.00 0.010 0.016 0.101 0.041 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 表 4 原矿重液试验结果
Table 4. Results of heavy liquid test
粒级/mm 产率/% 品位/% 产率/% 轻 品位/% 重 品位/% 重 回收率/% Ta2O5 Nb2O5 轻 重 Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Ta2O5 Nb2O5 +0.32 2.75 0.007 0.022 88.48 11.52 0.006 0.017 0.012 0.060 20.76 31.63 -0.32+0.2 6.36 0.007 0.013 84.69 15.31 0.004 0.007 0.021 0.046 48.67 51.33 -0.2+0.1 23.03 0.006 0.009 92.44 7.56 0.001 0.002 0.071 0.092 85.33 78.99 -0.1+0.074 15.60 0.009 0.011 94.87 5.13 0.001 0.001 0.149 0.196 88.97 91.38 -0.074+0.043 17.62 0.009 0.013 93.78 6.22 0.001 0.002 0.128 0.179 89.46 85.57 -0.043* 34.64 0.012 0.018 / / / / / / / / Total 100.00 0.009 0.014 60.43 4.93 0.002 0.003 0.083 0.117 44.70 42.12 *注:-0.043 mm粒级重矿物颗粒不易沉降,重液分离效果较差。 表 5 原矿中有价元素的平衡分配表
Table 5. Allocation rates of valued elements in the ore
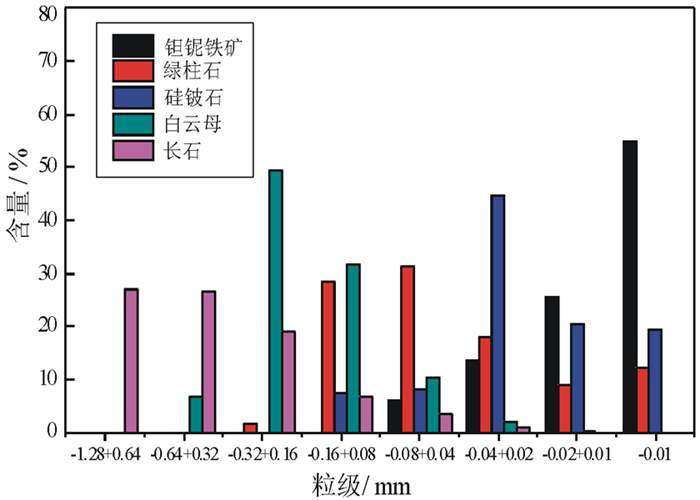
矿物 含量/% 品位/% 分布率/% Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Rb2O BeO Ta2O5 Nb2O5 Rb2O BeO 钽铌铁矿 0.017 34.21 46.06 / / 68.51 62.72 / / 绿柱石 0.241 / / 0.064 13.46 / / 0.10 71.01 硅铍石 0.020 / / / 44.89 / / / 20.29 云母 16.427 0.010 0.023 0.700 0.001 19.66 30.75 74.94 0.36 长石 38.830 0.001 0.000 5 0.080 0.003 4.65 1.58 20.24 2.57 黏土 8.398 0.003 0.006 0.082 0.027 3.01 4.10 4.49 5.00 石英 34.872 0.001 0.000 3 0.001 0.001 4.17 0.85 0.23 0.77 其他 1.196 / / / / / / / / 合计 100.00 0.008 0.012 0.153 0.045 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 -
[1] 程征, 伍喜庆, 杨平伟.我国钽铌资源的特征及选矿技术[J].金属矿山, 2013, 445(7):97-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2013.07.027
[2] 高玉德, 邹霓, 董天颂.钽铌矿资源概况及选矿技术现状和进展[J].材料研究与应用, 2004, 14(2):87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2004.02.001
[3] Gong W J, Wu C F, Tian H, et al. Corrosion behavior of Zr-Nb-Cr cladding alloys[J]. Rare metals, 2009, 32(5):480-485. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/85314X/201305/47836302.html
[4] 丘德镳.钽铌选矿理论与实践[J].世界有色金属, 2001, 11(1):27-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjysjs200111008
[5] Xu Kuangdi, Ren Zhongming, Li Chuanjun. Progress in application of rare metals in superalloys[J]. Rare metals, 2014, 33(2):111-126. doi: 10.1007/s12598-014-0256-9
[6] 梁冬云, 何国伟.蚀变花岗岩型钽铌矿石的工艺矿物学研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2004, 1(1):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2004.01.001
[7] 梁冬云, 李波.稀有金属工艺矿物学[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2015:138-140.
[8] 陈勇, 宋永胜, 温建康, 等.某含稀土、锆复杂铌矿的选矿试验研究[J].稀有金属, 2013, 37(3):429-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2013.03.016
[9] 吕子虎, 卫敏, 吴东印, 等.钽铌矿选矿技术研究现状[J].矿产保护与利用, 2010(5):44-47. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=6c931916-91bf-488e-8d1d-280316a0f6c1
[10] 梁冬云, 喻莲香, 张永进, 等.花岗伟晶岩型铌钽矿石的工艺矿物学研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2004(5):1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2004.05.001
[11] 熊玉旺.云南某钽铌矿中钽、铌的赋存状态研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2014, 1(1):1-4, 20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2014.01.001
[12] Yuan Z T, L J W, Wu H F, et al. Mineralogical characterization and comprehensive utilization of micro-fine tantalum-niobium ores from songzi[J]. Rare metals, 2015, 34(4):282-290. doi: 10.1007/s12598-014-0428-7
-



 下载:
下载: