Research Progress on the Interaction Mechanism of Typical Metal Ions with Sphalerite and Its Effect on Flotation
-
摘要:
典型金属离子对闪锌矿浮选行为具有显著影响。总结了闪锌矿浮选矿浆体系中金属离子的来源,综述了Cu2+、Pb2+、Fe2+、Fe3+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Zn2+等金属离子对闪锌矿浮选行为的影响及其作用机制。根据金属离子本身的性质和浮选环境的不同,其作用效果和作用机制也有不同,分析表明金属离子是通过取代、吸附和覆盖的方式对闪锌矿可浮性产生影响。展望了金属离子在闪锌矿浮选中的应用前景,并提出了闪锌矿与金属离子作用机制的研究方向。
Abstract:Typical metal ions have a significant effect on the flotation behavior of sphalerite. The sources of metal ions in flotation pulp system are summarized. The influence of metal ions such as copper, lead, calcium, magnesium, zinc, ferric and ferrous on the flotation behavior of sphalerite and its interaction mechanism are reviewed. According to the differences between metal ionic property and the flotation environment, the effect and functionary mechanism of metal ion are also different. The analysis shows that metal ions affect the floatability of sphalerite by substitution, adsorption and covering. The application prospect of metal ions in sphalerite flotation is prospected, and the research direction of interaction mechanism between sphalerite and metal ions is pointed out.
-
Key words:
- metal ions /
- sphalerite /
- flotation /
- adsorption /
- substitution
-

-
表 1 流体包裹体释放的离子的浓度
Table 1. The ion concentration of fluid inclusion releasing
-
[1] 刘建.闪锌矿表面原子构型及铜吸附活化浮选理论研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1015641661.htm [2] Kirjavainen V, Schreithofer N, Heiskanen K. Effect of calcium and thiosulfate ions on flotation selectivity of nickel-copper ores[J]. Minerals engineering, 2002, 15(1):1-5. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0892687501002138
[3] Dávila-Pulido G, Uribe-Salas A, álvarez-Silva M, et al. The role of calcium in xanthate adsorption onto sphalerite[J]. Minerals engineering, 2015, 71:113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.09.004
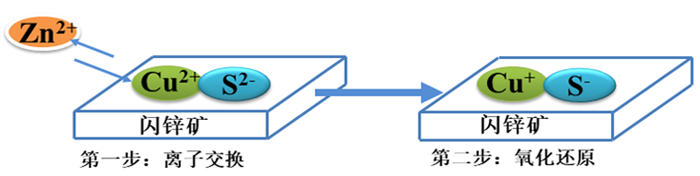
[4] Kartio I J, Basilio C I, Yoon R H. An XPS study of sphalerite activation by copper[J]. Langmuir, 1998, 14(18):5274-5278. doi: 10.1021/la970440c
[5] Sarvaramini A, Larachi F, Hart B. Collector attachment to lead-activated sphalerite-experiments and DFT study on pH and solvent effects[J]. Applied surface science, 2016, 367:459-472. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.213
[6] 胡熙庚.有色金属硫化矿选矿[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1987.
[7] Huston D L, Sie S H, Suter G F, et al. Trace elements in sulfide minerals from eastern Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits; Part Ⅰ, proton microprobe analyses of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite, and Part Ⅱ, selenium levels in pyrite; comparison with delta 34 S values and implications for the source of sulfur in volcanogenic hydrothermal systems[J]. Economic geology, 1995, 90(5):1167-1196. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.5.1167
[8] 陈建华, 曾小钦, 陈晔, 等.含空位和杂质缺陷的闪锌矿电子结构的第一性原理计算[J].中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(4):765-71. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgysjsxb201004027
[9] Basilio C I, Kartio I J, Yoon R H. Lead activation of sphalerite during galena flotation[J]. Minerals engineering, 1996, 9(8):870-879. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0892687596000787
[10] 黄福根, 肖鹂.方铅矿浮选时闪放的铅活化[J].国外选矿快报, 1997(16): 7-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199701079908
[11] Liu J, Wen S, Wu D, et al. Determination of the concentrations of calcium and magnesium released from fluid inclusions of sphalerite and quartz[J]. Minerals engineering, 2013, 45(3):41-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e1abfa77c5fbc081c0c5d5871fee42b9
[12] Deng J, Mao Y, Wen S, et al. New influence factor inducing difficulty in selective flotation separation of Cu-Zn mixed sulfide minerals[J]. International journal of minerals, metallurgy, and materials, 2015, 22(2):111-115. doi: 10.1007/s12613-015-1050-x
[13] Bai S, Wen S, Xian Y, et al. New source of unavoidable ions in galena flotation pulp: components released from fluid inclusions[J]. Minerals engineering, 2013, 45:94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.02.001
[14] Deng J, Wen S, Xian Y, et al. New discovery of unavoidable ions source in chalcopyrite flotation pulp: fluid inclusions[J]. Minerals engineering, 2013, 42:22-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2012.10.010
[15] Deng J, Wen S, Wu D, et al. Existence and release of fluid inclusions in bornite and its associated quartz and calcite[J]. International journal of minerals metallurgy & materials, 2013, 20(9):815-822. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/85313X/201309/47435951.html
[16] 孙昊, 孙体昌, 朱阳戈, 等.水质对十二酸浮选分离菱镁矿与白云石的影响研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2017(5):89-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2017.05.020
[17] Ikumapayi F, Makitalo M, Johansson B, et al. Recycling process water in sulphide flotation: effect of calcium and sulphate on sphalerite recovery[J]. Minerals engineering, 2012, 29(4):45-64. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0892687512002671
[18] 钟素姣.磨矿对方铅矿和闪锌矿浮选行为的影响研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2006.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y997676 [19] Grano S. The critical importance of the grinding environment on fine particle recovery in flotation[J]. Minerals engineering, 2009, 22(4): 386-394. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2008.10.008
[20] 黄凌云.闪锌矿晶体结构性质及其铜活化作用[J].矿产保护与利用, 2018(3):26-30. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=96b0acd6-ce96-4c98-b89f-9a2afe8128ad
[21] Sun S, Liu R, Song W. An electrochemical investigation on collectorless flotation of sphalerite in presence of Cu2+ ions[J]. Trans. nonferrous met. soc. China, 2000, 10(S1):56-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYSY2000S1010.htm
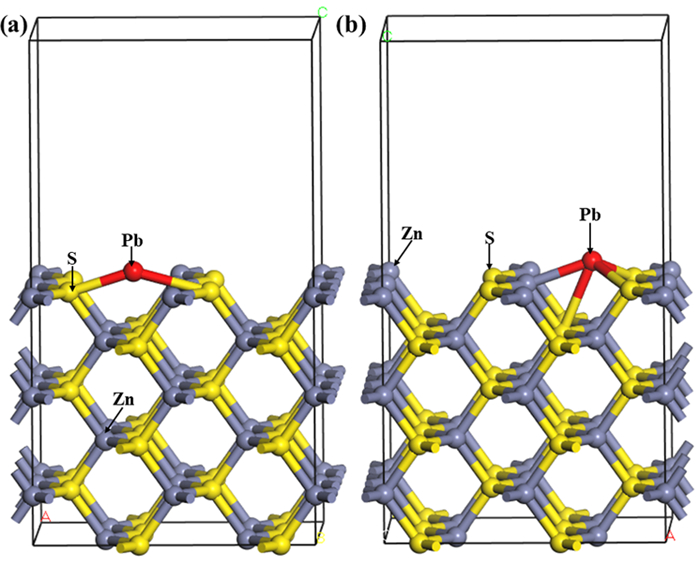
[22] Ravitz S F, Wall W A. The adsorption of copper sulfate by sphalerite and its relation to flotation[J]. J. phys. chem., 2002, 38(1):13-18. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/j150352a002
[23] 李宁.铜锌硫化矿浮选分离研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-1012477129.htm [24] 聂光华, 李帅, 邱盛华.某铁闪锌矿浮选试验研究[J].矿冶工程, 2012, 32(4):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2012.04.012
[25] Buckley A N, Woods R, Wouterlood H J. An XPS investigation of the surface of natural sphalerites under flotation-related conditions[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1989, 26(1-2):29-49. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(89)90041-0
[26] Finkelstein N P. The activation of sulphide minerals for flotation: a review[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1997, 52(2-3):81-120. doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(97)00067-7
[27] Gerson A R, Lange A G, Prince K E, et al. The mechanism of copper activation of sphalerite[J]. Applied surface science, 1999, 137(1-4):207-223. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(98)00499-1
[28] Gu G, Wang D, Liu R. Electrochemical mechanisms on cupric sulphate activating sphalerite[J]. Journal of central south university of technology, 1999, 30(4):374-377. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199901143630
[29] Ejtemaei M, Nguyen A V. Characterisation of sphalerite and pyrite surfaces activated by copper sulphate[J]. Minerals engineering, 2017, 100:223-232. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.11.005
[30] Laskowski J S, Liu Q, Zhan Y. Sphalerite activation: flotation and electrokinetic studies[J]. Minerals engineering, 1997, 10(8):787-802. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(97)00057-5
[31] 谢广元, 张明旭, 边炳鑫.选矿学[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社, 2001.
[32] Chandra A P, Gerson A R. A review of the fundamental studies of the copper activation mechanisms for selective flotation of the sulfide minerals, sphalerite and pyrite[J]. Adv colloid interface sci, 2009, 145(1):97-110. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a66874d08502a4c2f2613160a354b471
[33] Boulton A B, Fornasiero D, Ralston J. Characterisation of sphalerite and pyrite flotation samples by XPS and ToF-SIMS[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2003, 65(1):205-219. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=df8e9a419c881949d50514adb577df5c
[34] Ralston O C, King C R, Tartaron F X. Copper sulfate as flotation activator for sphalerite[J]. Trans. AIME, 1930, 87:389-400.
[35] Liu J, Zeng Y, Luo D, et al. Ab initio molecule dynamic simulation of Cu(OH)2 interaction with sphalerite (1 : 1 : 0) surface[J]. Minerals engineering, 2018, 122:176-178. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.04.003
[36] Fuerstenau D W, Metzger P H. Activation of sphalerite with lead ions in the presence of zinc salts[J]. Minerals engineering, 1960, 217:119-123.
[37] Popov S R, Vuini D R, Kaanik J V. Floatability and adsorption of ethyl xanthate on sphalerite in an alkaline medium in the presence of dissolved lead ions[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1989, 27(3-4):205-219. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(89)90065-3
[38] Trahar W J, Senior G D, Heyes G W, et al. The activation of sphalerite by lead a flotation perspective[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1997, 49(3-4):121-148. doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(96)00041-5
[39] Pattrick R A D, Charnock J M, England K E R, et al. Lead sorption on the surface of ZnS with relevance to flotation: a fluorescence reflexafs study[J]. Minerals engineering, 1998, 11(11):1025-33. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(98)00090-9
[40] Steele H M, Wright K, Hillier I H. A quantum-mechanical study of the (110) surface of sphalerite (ZnS) and its interaction with Pb2+ species[J]. Physics and chemistry of minerals, 2003, 30(2):69-75. doi: 10.1007/s00269-002-0296-9
[41] Morey M S, Grano S R, Ralston J, et al. The electrochemistry of Pb Ⅱ activated sphalerite in relation to flotation[J]. Minerals engineering, 2001, 14(9):1009-1017. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(01)00108-X
[42] Rashchi F, Sui C, Finch J A. Sphalerite activation and surface Pb ion concentration[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2002, 67(1):43-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029606750/
[43] Sui C, Lee D, Casuge A, et al. Comparison of the activation of sphalerite by copper and lead[J]. Minerals engineering, 1999, 16(3):53-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=76a20353e89f22e708c569c25390ff8b
[44] Zhang Q, Rao S R, Finch J A. Flotation of sphalerite in the presence of iron ions[J]. Colloids & surfaces, 1992, 66(2):81-89. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016666229280123J
[45] 童雄, 周庆华, 何剑, 等.铁闪锌矿的选矿研究概况[J]. 2006(6): 8-12.
[46] Chen Y, Chen J, Guo J. A DFT study on the effect of lattice impurities on the electronic structures and floatability of sphalerite[J]. Minerals engineering, 2010, 23(14):1120-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2010.07.005
[47] Ye C, Chen J, Lan L, et al. The influence of the impurities on the flotation behaviors of synthetic ZnS[J]. Minerals engineering, 2012, 27-28(1):65-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b56aff827b38f1140642eb342d0b05ea
[48] Liu J, Wang Y, Luo D, et al. Comparative study on the copper activation and xanthate adsorption on sphalerite and marmatite surfaces[J]. Applied surface science, 2018, 439:263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.032
[49] Chen Y, Chen J. The first-principle study of the effect of lattice impurity on adsorption of CN- on sphalerite surface[J]. Minerals engineering, 2010, 23(9):676-684. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2010.04.002
[50] Solecki J, 詹德俊.铜离子对不同铁含量混合闪锌矿的活化作用[J].国外金属矿选矿, 1982(1):19-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXK198201002.htm
[51] Szczypa J, Solecki J, Komosa A. Effect of surface oxidation and iron contents on xanthate ions adsorption of synthetic sphalerites[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1980, 7(2):151-157. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(80)90007-1
[52] Scott J L, Smith R W. Calcium ion effects in amine flotation of quartz and magnetite[J]. Minerals engineering, 1993, 6(12):1245-1255. doi: 10.1016/0892-6875(93)90102-S
[53] Liu Q, Zhang Y. Effect of calcium ions and citric acid on the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from galena using dextrin[J]. Minerals engineering, 2000, 13(13):1405-1416. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00122-9
[54] Zhang W, Honaker R Q, Groppo J G. Flotation of monazite in the presence of calcite part Ⅰ: calcium ion effects on the adsorption of hydroxamic acid[J]. Minerals engineering, 2017, 100:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.09.020
[55] Ejtemaei M, Plackowski C, Nguyen A V. The effect of calcium, magnesium, and sulphate ions on the surface properties of copper activated sphalerite[J]. Minerals engineering, 2016, 89: 42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.01.005
[56] Lascelles D, Finch J A, Sui C. Depressant action of Ca and Mg on flotation of Cu activated sphalerite[J]. Canadian metallurgical quarterly, 2013, 42(2):133-140. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1179/cmq.2003.42.2.133
[57] 孙伟, 胡岳华, 邱冠周, 等.闪锌矿(110)表面离子吸附的动力学模拟[J].中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(1):187-190. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2002.01.037
[58] Liu J, Wang Y, Luo D, et al. Use of ZnSO4, and SDD mixture as sphalerite depressant in copper flotation[J]. Minerals engineering, 2018, 121:31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.03.003
-



 下载:
下载: