The Harmless of Spent Refractory in Aluminum Electrolysis Cells and Summary of Its treatment
-
摘要:
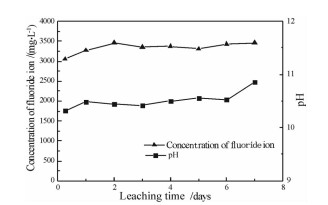
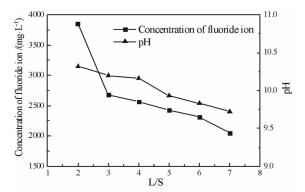
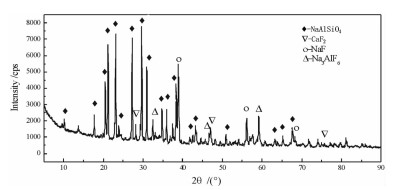
铝电解槽破损后产生大量的废耐火材料。通过对废耐火材料进行物相与成分分析及溶出试验研究,得出铝电解槽废耐火材料主要成分为霞石和氟化物电解质,溶出后溶液显碱性,氟离子大量进入溶液,废耐火材料的主要危害来自于其所含有的可溶氟化物组分。通过对现有的铝电解槽废耐火材料主要处理工艺的优缺点进行分析,得出真空还原蒸馏法在实现废耐火材料中氟化物电解质和金属钠回收的同时也实现了废耐火材料的再生,可实现废耐火材料的全组分回收利用,是一种经济环保的处理方法。
Abstract:A large number of spent refractory materialsis produced after overhaul of aluminum reduction cells. The XRD and composition of spent refractory materials was analysed, and dissolution experiments were studied in laboratory. The results show that the spent refractory materials is mainly consists of nepheline and flourides, and the leaching solution is alkaline. The concentration of fluoride ion in leaching solution is much higher indicating the main hazards of spent refractory materials is the soluble fluorides. The advantages and disadvantages of existing treatment methods of spent refractory materials are analyzed. The vacuum reduction and distillation process can not only recover fluoride electrolyte and sodium, but also regenerate refractory materials. It can recover all components of spent refractory materials with non-polluting and economic benefits.
-

-
表 1 废耐火材料的平均成分
Table 1. The chemical composition of spent refractory
Elements Al F SiO2 TFe Na C Ca Content /% 16.60 8.00 26.48 3.59 23.55 0.75 0.58 -
[1] 卢惠民, 邱竹贤.浮选法综合利用铝电解槽废阴极炭块的工艺研究[J].金属矿山, 1997(6):32-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700774740
[2] 詹磊, 牛庆仁, 贺华, 等.铝电解废阴极炭块无害化综合利用工业实践[J].轻金属, 2013(10):59-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS201310020.htm
[3] 吴巧玉.铝电解废阴极碳块无害化与资源化利用[J].环保科技, 2012(3):46-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0254.2012.03.013
[4] Barrillon E, Personnet P, Bontron J. Process for the thermal shock treatment of spent pot linings obtained from hall-heroult electrolytic cells: US5245115[P].1993-9-14.
[5] Pong T K, Adrien R J, Besida J, et al. A hazardous waste made safe[J]. Process safety and environmental protection, 2000, 78(3):204-208. doi: 10.1205/095758200530646
[6] 王再云, 肖亚明, 张凤炳.干式防渗透料在铝电解槽上应用的工业试验[J].有色冶金节能, 1999(4):25-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJJN199904009.htm
[7] O. Siljan, O. Junge, T. Svendsen. et al. Light Metals, February 15-19, 1998[C]. Warrendale: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2013.
[8] R. Pelletier, C. Allaire, O. J. Siljan, et al. The corrosion of potlining refractories:A unified approach[J]. JOM, 2001, 53(8):18-22. doi: 10.1007/s11837-001-0129-1
[9] C.Schöning, T. Grande, O.J Siljan. Light Metals, March 2-6, 1999[C]. San Diego, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1999.
[10] 赵更金, 吕风雷, 苗拥军, 等.YS/T 456-2014《铝电解槽用干式防渗料》修订介绍[J].耐火材料.2014, 48(6):478-480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1935.2014.06.024
[11] 王耀武, 狄跃忠, 蒿鹏程, 等.铝电解槽干式防渗料在电解过程中的反应机理探讨[J].化工学报.2019, 70(3):1035-1041. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201903027
[12] R.W.Peterson, L.C.Blayden, E.S.Martin.Light metals, March 2-6, 1985[C].New York, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1985.
[13] D.R.Augood, J.R.Keiser, Light Metals, February 27-March3, 1989[C].Las Vegas, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1989.
[14] F.Blanco, L.F.Verdeja, R.Zapico, et al. Light Metals, February 17-21, 1991[C]. New Orleans, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1991.
[15] P.B.Personnet.Light Metals, February 28-March 4, 1999[C]. San Diego, USA: Light Metals. 1999.
[16] D.G.Brooks, E.L.Cutshall, D.B.Banker, et al.Light Metals, March 1-5, 1992[C]. San Diego, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1992.
[17] Morten SΦrlie, HaraldA.Φye. Cathodes in Aluminum Electrolysis[M]. Dusseldorf:Aluminum-Verlag Marketing & kommunikation GmbH, 2010:611.
[18] W.Li, X.Chen. Light Metals, February 13-17, 2005[C].San Francisco, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2005.
[19] H.Fang, J.D. Smith, K.D. Pleaslee. Study of spent refractory waste recycling from metal manufacture in Missouri[J]. Resources, conservation and recycling, 1999, 25(2):111-124. doi: 10.1016/S0921-3449(98)00059-7
[20] 冯乃祥.铝电解[M].北京:化学工业出版社.2006:217-218.
[21] Laurent Birry, Simon Leclerc, Stephane Poirier. Light Metals, February 14-18, 2016[C]. Nashville, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2016.
[22] Kruger.Jorg, Thome. Roland, Moritz.Dieter, et al. Rotating apparatus for manufacturing hydrogen fluoride: US4362701[P]. 1982-12-07.
[23] James P. Mc Geer, Vladimir V. Mirkovich, Norman-W.F.Philips. Recovery of material from aluminum reduction cell lining: US2858198[P]. 1958-10-28.
[24] 冯乃祥, 王耀武.一种电解铝铝灰和耐火材料内衬废料的回收处理方法: CN104894382B[P].2017-05-17.
[25] 赵越飞.真空蒸馏处理铝电解槽废耐火材料的实验研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学.2017: 20-35.
[26] J.E.Deutschman, J.S.Lobos, D.O.Johnson, et al. Light Metals, February 24-26, 1987[C]. Denver, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1987.
-



 下载:
下载: