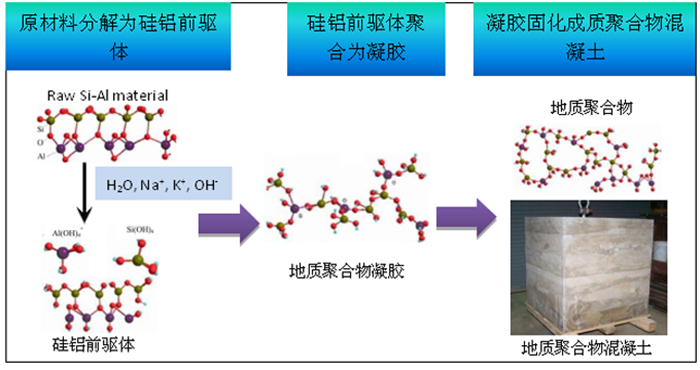
Research Progress on Solidification of Tailings by Alkali-activated Geopolymerization
-
摘要:
随着尾矿堆存量的不断增加,尾矿对人类安全、土壤及环境的危害也愈来愈严重,尾矿亟待处理。根据我国综合利用尾矿的现状,提出以碱激发地质聚合反应固化处理尾矿,着重介绍并论证了碱激发地质聚合反应固化尾矿的可行性,比较了碱激发反应和地质聚合反应在地质聚合反应理论的研究中的区别,指出地质聚合反应并不是碱激发反应的子集。同时,总结了表征碱激发地质聚合产物微观结构的技术,并展望了碱激发地质聚合反应固化尾矿的发展前景。
Abstract:With the continuous increase of tailings pile, tailings are becoming more and more harmful to human safety, soil and environment, so it is urgent to deal with tailings. Based on the present situation of comprehensive utilization of tailings in China, the paper proposed to deal with the tailings by alkali-activated geopolymerization. The feasibility of the solidification of tailings through alkali-excited geopolymerization was presented emphatically. Compared with the differences between alkaline-activated reaction and geopolymerization, the paper pointed out geopolymerization was not the subset of alkaline-activated reaction. Meanwhile, the techniques for characterizing the microstructure of alkali-activated geopolymer were summarized, and the development prospect of alkaline-activated geopolymerization was forecasted.
-
Key words:
- tailings /
- alkaline-activated reaction /
- geopolymerization /
- nuclear magnetic resonance /
- microstructure
-

-
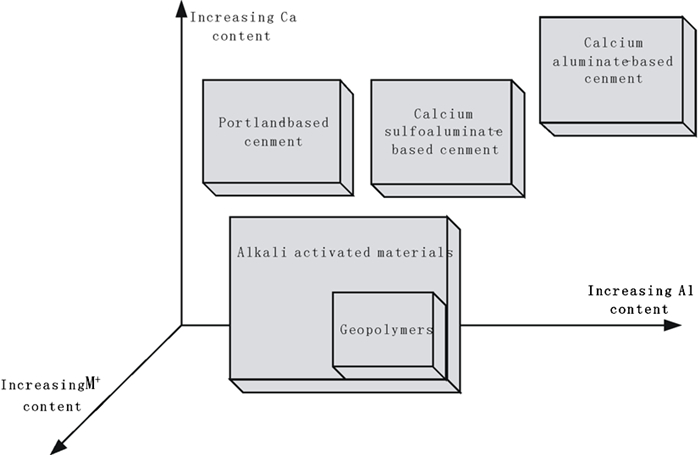
图 3 将地质聚合反应归类为碱激发反应子集的示意图[23]
Figure 3.
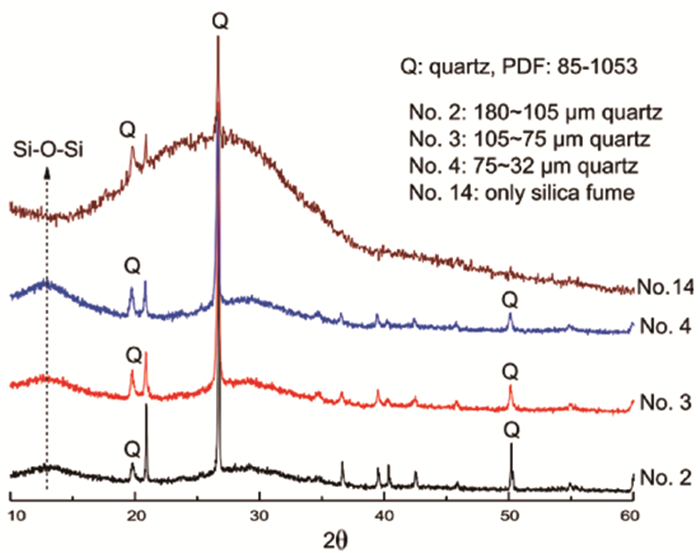
图 4 添加不同粒度石英的偏高岭土基地质聚合物XRD谱线图[39]
Figure 4.
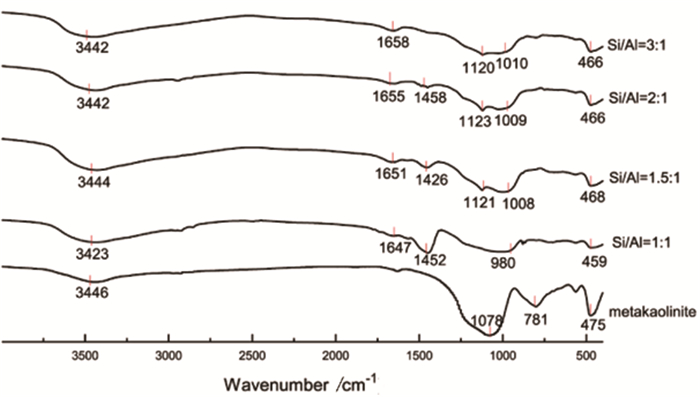
图 5 不同硅铝比的偏高岭土基地质聚合物FTIR谱线图[40]
Figure 5.
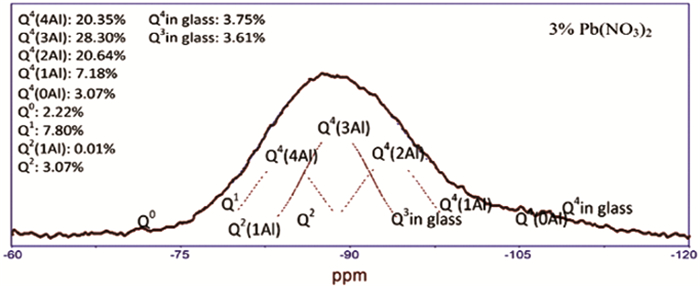
图 6 分峰计算尾矿基地质聚合物中各种微观结构百分比的示例[41]
Figure 6.
表 1 国外地质聚合物理论发展中的重要工作总结
Table 1. Summary of important work in the development of foreign geopolymer theory
作者 年份 描述 意义 Davidovits 1982 为一种新铝硅酸盐材料取得技术名称 为地质聚合物命名 Davidovits和Orlinski[10] 1988 “软矿物学”欧洲会议-第一本关于地质聚合物的论文集 总结了此前关于地质聚合物的工作 Wastiels等[13] 1993 通过碱激发粉煤灰制备地质聚合物 粉煤灰体系的地质聚合物 Rahier等[14-16] 1996
1997对偏高岭土体系的地聚合物进行了广泛和深入的基础研究 奠定偏高岭土体系地质聚合物理论基础 Xu和vanDeventer[17-18] 2000
2002研究了多种矿物的地质聚合反应 扩展了地质聚合物的原材料 Duxson等[19] 2007 综述论文“Geopolymer technology: the current state of the art” 全面总结了地质聚合物的发展 Davidovits[20] 2008 专著“Geopolymer chemistry & applications 2nd edition” Provis和Van Deventer[21] 2009 专著“Geopolymers: structure, processing, properties and industrial applications” Davidovits等[22] 2019 地质聚合物在南美古建筑上的应用 解释古建筑材料的形成原因 -
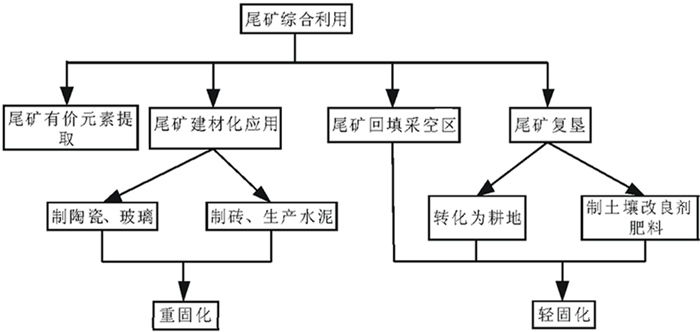
[1] 童雄.尾矿资源二次利用的研究与实践[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013.
[2] 秦玲玲, 杨海舟, 陈建平.尾矿综合利用充填采空区现状及展望[J].广东化工, 2018(16):130-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.16.057
[3] 张进德.我国矿山地质环境调查研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.
[4] 陈生水.尾矿库安全评价存在的问题与对策[J].岩土工程学报, 2016(10):1869-1873. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201610016
[5] 侯攀, 陈宇清, 樊宇姣.金属矿山尾矿综合利用现状[J].现代矿业, 2017(2):135-137. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdky201702035
[6] 刘志强, 郝梓国, 刘恋, 等.我国尾矿综合利用研究现状及建议[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(5):1277-1282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slsy201725171
[7] 徐帅.我国铁尾矿综合利用现状[J].职业技术, 2011(3):94. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kykb200807003
[8] 张大旺, 王栋民.地质聚合物混凝土研究现状[J].材料导报, 2018, 32(9):1519-1527. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cldb201809018
[9] Ahmari S, Zhang L. Durability and leaching behavior of mine tailings-based geopolymerbricks[J]. Construction and building materials, 2013, 44:743-750. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.075
[10] Shi C, Krivenko PV, Roy D. Alkali activated cement and concrete[M]. New York:Taylor & Francis; 2006.
[11] J. Davidovits. 30 years of successes and failures in geopolymer application. Market trends and potential breakthroughs. Geopolymer 2002 conference[C]. Melbourne, October 28-29, 2002.
[12] J. Davidovits, Transfer and exploitation of scientific and technical information, EUR 7716, Commission of the european communities[R]. Luxembourg, 1982.
[13] Bernal S A, Krivenko P V, Provis J L, et al. Other potential applications for alkali-activated materials[M]//Alkali activated materials. 2014(9): 339-379.
[14] J. Davidovits. Why alkali-activated materials (AAM) are not geopolymers[EB/OL].[2017-07-27]. https://www.geopolymer.org/faq/alkali-activated-materials-geopolymers/.
[15] Gualtieri M L, Romagnoli M, Gualtieri A F. Preparation of phosphoric acid-based geopolymer foams using limestone as pore forming agent-Thermal properties by in situ XRPD and rietveld refinements[J]. Journal of the european ceramic society, 2015, 35(11):3167-3178. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.04.030
[16] Davidovits.J, Orlinski J. Proceedings of the first european conference on soft mineralogy[J]. 1988, Compeigne, France.
[17] Wastiels J., Wu X., Faignet S., et al. Mineral polymer based on fly ash[C]. Proceeding of the 9th international conference on solid waste management, 1993, Philadelphia, Ameicia.
[18] Rahier H, Simons W, Mele B V, et al. Low-temperature synthesized aluminosilicate glasses:Part Ⅲ Influence of the composition of the silicate solution on production, structure and properties[J]. Journal of materials science, 1997, 32(9):2237-2247. doi: 10.1023/A:1018563914630
[19] Rahier H, Mele B V, Wastiels J. Low-temperature synthesized aluminosilicate glasses[J]. Journal of materials science, 1996, 31(1):80-85. doi: 10.1007/BF00355129
[20] Rahier H, Simons W, Mele B V, et al. Low-temperature synthesized aluminosilicate glasses:Part Ⅲ Influence of the composition of the silicate solution on production, structure and properties[J]. Journal of materials science, 1997, 32(9):2237-2247. doi: 10.1023/A:1018563914630
[21] Xu H, Deventer J S J V. The geopolymerisation of alumino-silicate minerals[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2000, 59(3):247-266. doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(99)00074-5
[22] Xu H, Deventer J S J V. Geopolymerisation of multiple minerals[J]. Minerals engineering, 2002, 15(12):1131-1139. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(02)00255-8
[23] Pacheco F. Investigations on mix design of tungsten mine waste geopolymericbinder[J]. Construction & building materials, 2008, 22(9):1939-1949.
[24] 李建平, 袁桂芳, 王坤英, 等.地质聚合物的制备及其在尾矿免烧制品中的应用[J].矿产综合利用, 2007(2):38-42. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kczhly200702011
[25] 和森, 罗钧耀, 郑森, 等.磷渣基地聚合物胶凝材料固化微细粒铁尾矿[J].过程工程学报, 2017, 17(4):785-790. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgyj201704019
[26] 李北星, 冯紫豪, 叶茂, 等.原状铅锌尾矿制备地聚物的研究[J].混凝土, 2018(1):68-71. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hnt201801018
[27] 焦向科, 张一敏, 陈铁军, 等.碱激发钒尾矿-矿渣基地聚合物的研究[J].新型建筑材料, 2012(2):1-4. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xxjzcl201202001
[28] Wan Q., Rao F., Song S., Leon-Patino C.A., Ma Y., Yin W. Consolidation of mine tailings through geopolymerization at ambient temperature[J]. Journal of the American ceramic society, 2019, 102(5):2451-2461. doi: 10.1111/jace.16183
[29] ZHANG Yunsheng, SUN Guowei. Synthesis and Heavy Metal Immobilization Behaviors of Fly Ash based Gepolymer[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of technology(materials science edition), 2009(5):819-825. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=whgydxxb-e200905030
[30] Perera D S, Aly Z, Vance E R, et al. Immobilization of Pb in a geopolymer matrix[J]. Journal of the American ceramic society, 2005, 88(9):2586-2588. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00438.x
[31] 金漫彤, 张琼, 楼敏晓, 等.粉煤灰用于土壤聚合物固化重金属离子的研究[J].硅酸盐通报, 2007, 26(3):467-471. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb200703011
[32] Zhang J, Provis J L, Feng D, et al. Geopolymers for immobilization of Cr6+, Cd2+, and Pb2+[J]. Journal of Hazardous materials, 2008, 157(2-3):587-598. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.053
[33] Jaarsveld J G S V, Deventer J S J V, Lorenzen L. Factors affecting the immobilization of metals in geopolymerized fly ash[J]. Metallurgical & materials transactions B, 1998, 29(1):283-291. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1007-s11663-998-0032-z/
[34] Phair J W, Deventer J S J V, Smith J D. Effect of Al source and alkali activation on Pb and Cu immobilisation in fly-ash based "geopolymers"[J]. Applied geochemistry, 2004, 19(3):423-434. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00151-3
[35] Palomo A, Palacios M. Alkali-activated cementitious materials:Alternative matrices for the immobilisation of hazardous wastes:Part Ⅱ. Stabilisation of chromium and lead[J]. Cement & concrete research, 2003, 33(2):289-295.
[36] Nikoliĉ V, Komljenoviĉ M, Marjanoviĉ N, et al. Lead immobilization by geopolymers based on mechanically activated fly ash[J]. Ceramics international, 2014, 40(6):8479-8488. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.059
[37] Guo B, Pan D, Liu B, et al. Immobilization mechanism of Pb in fly ash-based geopolymer[J]. Construction and building materials, 2017, 134:123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.139
[38] El-Eswed B I, Yousef R I, Alshaaer M, et al. Stabilization/solidification of heavy metals in kaolin/zeolite based geopolymers[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2015, 137:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.03.002
[39] Wan Q, Rao F, Song S, et al. Combination formation in the reinforcement of metakaolingeopolymers with quartz sand[J]. Cement and concrete composites, 2017, 80:115-122. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.03.005
[40] Wan Q, Rao F, Song S, et al. Geopolymerization reaction, microstructure and simulation of metakaolin-based geopolymers at extended Si/Al ratios[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2017, 79:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.01.014
[41] Qian W, Feng R, Shaoxian S, et al. Chemical forms of lead immobilization in alkali-activated binders based on mine tailings[J]. Cement and concrete composites, 2018, 92:198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.06.011
-



 下载:
下载: