-
摘要:
高岭土是一种天然的黏土矿物,具有典型的1:1层状硅酸盐晶体结构。首先介绍了高岭土资源背景、结构组成和物化特性,着重介绍了高岭土在节能环保、生物医药和新材料三个战略性新兴产业的研究现状。天然的层状结构、丰富的表面羟基、较大的比表面积以及良好的生物相容性为高岭土的功能化应用提供了多种选择。随着科学技术的发展和国家社会的进步,对高岭土的研究更加深入。未来高岭土将作为一种战略性非金属矿物,在更多的领域有更好的应用前景。
Abstract:Kaolin is a natural clay mineral with a typical 1:1 layered silicate crystal structure. This paper firstly introduces the background, composition and physicochemical characteristics of kaolinite resources, and emphatically introduces the research status of kaolinite in three strategic emerging industries of energy conservation and environmental protection, biomedicine and new materials. The natural layered structure, abundant surface hydroxyl groups, large specific surface area and good biocompatibility provide a variety of options for the functional application of kaolin. With the development of science and technology and the progress of national society, the research on kaolinite will be more in-depth.Kaolin will be a strategic non-metallic mineral in the future and will have better application prospects in more fields.
-
Key words:
- kaolin /
- environmental protection /
- energy saving /
- biological medicine /
- new material
-

-
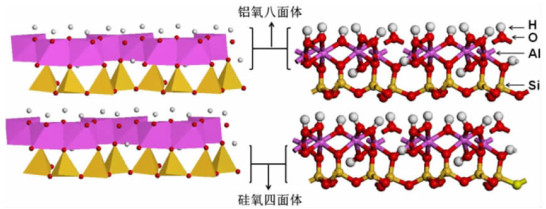
图 1 高岭石的晶体结构示意图(左图为多面体模型,右图为球棍模型)[50]
Figure 1.
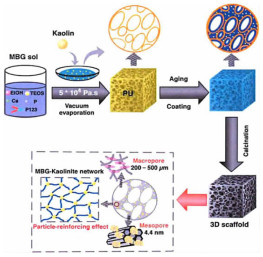
图 2 三维介孔生物玻璃-高岭石支架(MBG-XK)制备示意图[59]
Figure 2.
表 1 一些复合相变材料在文献中的热性能[33]
Table 1. Thermal characteristics of some composite PCMs in the literature[32]
Composite PCM Phase change
temperature/℃Latent heat phase
chang/(J·g-1)Lauric acid (60%)/expanded perlite 44.1 93.4 Lauric-capric acid+fire retardant/gypsum 17 28 Lauric-stearic acid(38%)/gypsum 34.0 50.4 Capric-myristic acid(20%)/VMT 19.8 27 Capric-myristic acid/expanded perlite 21.7 85.1 LA-LAL/kaolin 25.1 45.24 Sample Melting temperature/℃ Condensing temperature/℃ Latent heat of fusion/(J·g-1) Latent heat of condensation/(J·g-1) Sodium stearate/Kaolin 252.86 256.91 109.25 109.01 laurinol/Kaolin 19.10 17.10 48.08 46.65 Paraffin/kaolin 56.90 56.90 70.30 75.20 Al-Si metal/kaolin 573.80 588.70 102.50 102.50 -
[1] 李微微, 严春杰, 雷新荣.高岭土产业市场调查[J].化工矿物与加工, 2006(2):4-6, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7524.2006.02.002
[2] 汪先三.我国高岭土开发利用现状及应用前景[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2016(2):8-9, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2016.02.003
[3] 吴铁轮.我国高岭土行业现状及发展前景[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2001(4):3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2001.04.001
[4] 陈专, 蔡广超, 马驰, 等.高岭土的性质及应用[J].大众科技, 2013, 15(7):90-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2013.07.032
[5] 苗立锋, 包镇红, 宋福生, 等.几种高岭土的组成与可塑性研究[J].硅酸盐通报, 2014, 33(2):333-336. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201402018
[6] 王雪静, 张甲敏, 李晓波, 等.高岭土和煅烧高岭土的微观结构研究[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2007(5):18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2007.05.006
[7] 任伟.浅谈高岭土的成因类型及开发应用[J].西部探矿工程, 2015, 27(5):105-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2015.05.036
[8] 吴铁轮.我国高岭土行业现状剖析与展望[J].非金属矿, 2002, 25(2):8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2002.02.002
[9] 申继学, 马鸿文.高岭土资源及高岭石合成技术研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(4):1150-1158. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201604027
[10] 崔吉让, 方启学, 黄国智.一水硬铝石与高岭石的晶体结构和表面性质[J].有色金属工程, 1999, 51(4):25-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199901108677
[11] 赵杏媛, 张有瑜.黏土矿物与黏土矿物分析[M].山东:海洋出版社, 1990:22-23.
[12] 宋晓岚, 黄学辉.无机材料科学基础[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2005:57-65.
[13] Tombacz E, Szekeres M. Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite[J].Applied Clay Science, 2006, 34(1-4):105-124. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2006.05.009
[14] Hu P, Yang H. Insight into the physicochemical aspects of kaolins with different morphologies[J].Applied Clay Science, 2013, 74:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.10.003
[15] 杨二帅, 蔡晓君, 周梅, 等.重金属废水的处理技术研究[J].当代化工, 2018, 47(1):167-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2018.01.043
[16] 张丼娜, 裴强, 安亚明, 等.重金属污水处理的研究与发展[J].农业工程, 2012, 2(11):30-32. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygch201211012
[17] 田建民.生物吸附法在含重金属废水处理中的应用[J].太原理工大学学报, 2000, 31(1):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2000.01.022
[18] 卓艳婷, 郑志华.重金属污水处理新趋势-生物吸附[J].上海船舶运输科学研究所学报, 2012, 35(1):67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5949.2012.01.017
[19] 夏天华, 严金土, 姬玉鹏.离子交换法处理重金属废水的研究[C].环渤海表面精饰发展论坛, 2014, 2(1): 6-9.
[20] 唐楚寒, 李森, 尚凯, 等.高岭土负载改性壳聚糖重金属吸附剂性能研究[J].当代化工, 2019, 48(8):1664-1667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.08.007
[21] 张继义, 郭晶晶, 郭勇, 等.改性高分子多糖去除重金属离子研究进展[J].兰州交通大学学报, 2014, 33(4):172-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2014.04.035
[22] Wang H, Dong Y N, Zhu M, et al. Heteroaggregation of engineered nanoparticles and kaolin clays in aqueous environments[J].Water Research, 2015, 80:130-138. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.023
[23] 许令国, 万梦, 李诗瑶, 等.改性高岭土处理含铬废水的研究[J].山东化工, 2019, 48(15):230-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2019.15.106
[24] 张雨童, 李义连.富里酸-高岭土复合体对溶液中铀的吸附效果探究[J].安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(5):102-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzktaq201905014
[25] Ganguly Mainak, Tao Yuanyuan, Lee Bryan, et al. Natural Kaolin:Sustainable technology for instantaneous and energy neutral recycling of anthropogenic mercury emissions.[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201902955. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201902955
[26] 樊聪慧, 黄亚继, 夏志鹏, 等.改性高岭土捕集CdCl_(2)、PbCl_(2)蒸气[J/OL].化工进展, 2019: 1-12.
[27] Mohamed Khairy, Haytham A. Ayoub, Farouk A. Rashwan, et al. Chemical modification of commercial kaolin for mitigation of organicpollutants in environment via adsorption and generation of inorganicpesticides[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2018, 153:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.014
[28] Huang Q, Liu M, Chen J, et al. Enhanced removal capability of kaolin toward methylene blue by mussel-inspired functionalization[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2016, 51(17):8116-8130. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0082-6
[29] Olushola S. A Yanda, Kehinde O. Sodeinde, P. O. Okolo, et al. Adsorptive behavior of kaolin for amido black dyein aqueous solution[J]. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 34(3):1233-1239. doi: 10.13005/ojc/340305
[30] Zhang Q, Yan Z, Ouyang J, et al. Chemically modified kaolinite nanolayers for the removal of organic pollutants[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2018, 157:283-290. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.009
[31] Boge Z, Yanping H, Zebin Y, et al. Three-dimensional electro-Fenton degradation of Rhodamine B with efficient Fe-Cu/kaolin particle electrodes:Electrodes optimization, kinetics, influencing factors and mechanism[J].Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 210:60-68. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cc30b77a93f8374f2125daa72fabc3e0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] L.F.Cabeza, A.Castell, C. Barreneche, et al. Materials used as PCM in termal energy storage in buildings:A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15:1675-1695. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2010.11.018
[33] 仇影, 吴其胜, 黎水平, 等.二元有机/煤系高岭土复合相变储能材料的制备及其热性能[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2013, 31(2):268-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=clkxygc201302023
[34] Sari Ahmet. Fabrication and thermal characterization of kaolin-based composite phase change materials for latent heat storage in buildings[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2015, 96:193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.03.022
[35] Liu S, Yan Z, Fu L, et al. Hierarchical nano-activated silica nanosheets for thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 167:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.04.009
[36] 郝红, 职佳敏, 毛立功.严寒地区太阳能-地源热泵与热网互补供暖运行方式研究[J].可再生能源, 2016, 34(7):976-982. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncny201607005
[37] 姜洪殿, 董康银, 孙仁金, 等.中国新能源消费预测及对策研究[J].可再生能源, 2016, 34(8):1196-1202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncny201608015
[38] 陈祉如, 姚兴茂, 尹翔鹏.应用于太阳能热发电站的高岭土基相变储热材料的制备[J].可再生能源, 2019, 37(3):37-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ncny201903006
[39] 中科院大连化物所分子筛组.沸石分子筛[M].北京:科学出版社, 1978.
[40] 张金山, 周珊, 李侠, 等.煤系高岭土制备分子筛的研究进展[J].煤炭加工与综合利用, 2016(1):72-75, 8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtjgyzhly201601027
[41] Wang P, Zha F, Yao L, et al. Synthesis of light olefins from CO2 hydrogenation over (CuO-ZnO)-kaolin/SAPO-34 molecular sieves[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2018, 163:249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.06.038
[42] Yan Z, Yang H, Ouyang J, et al. In situ loading of highly-dispersed CuO nanoparticles on hydroxyl-group-rich SiO2-AlOOH composite nanosheets for CO catalytic oxidation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 316(Complete):1035-1046. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c1c54bdbd7d898f567e1b3395cfe2889
[43] Optimization of biodiesel production from transesterification of triolein using zeolite LTA catalysts synthesized from kaolin clay[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 79: 14-22.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876107017300949 [44] S N Khalifah, Z N aini, E K Hayati, et al.Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous NaY zeolite from natural Blitar's kaolin[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 333(1):012005.
[45] 沈耀生.利用高岭土制备4A分子筛[J/OL].云南化工, 2019, 46(10): 8-11.
[46] 刘明慧, 魏振浩, 周茁, 等.碱处理对高岭土微球上原位合成ZSM-5分子筛的影响[J].无机盐工业, 2016, 48(7):68-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjygy201607019
[47] 刘丽娜, 王鼎.内蒙煤系高岭土煅烧实验研究[J].科技展望, 2016, 26(20):271, 273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8289.2016.20.234
[48] 卢文彪, 曾元儿, 矿物药的研究及发展概况[J].广东微量元素科学, 2001(6):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-446X.2001.06.003
[49] 汤庆国, 沈上越.矿物药应用研究中的问题及对策[J].矿产综合利用, 2003, 4:32-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2003.04.008
[50] 龙梅.高岭石基复合材料的性能调控及其生物医学应用探索[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2019.
[51] Baker S E, Sawvel A M, Zheng N, et al. Controlling bioprocesses with inorganic surfaces:layered clay hemostatic agents[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(18):4390-4392. doi: 10.1021/cm071457b
[52] Liang Yuping, Xu Congcong, Li Guofeng, et al. Graphene-kaolin composite sponge for rapid and riskless hemostasis.[J]. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2018, 169:168-175. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.016
[53] Estela Chavez-Delgado M, Veronica Kishi-Sutto C, Albores de la-Riva X N, et al.Topic usage of kaolin-impregnated gauze as a hemostatic in tonsillectomy[J].Journal of Surgical Research, 2014, 192(2):678-685. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.05.040
[54] Bonina F P, Giannossi M L, Medici L, et al. Adsorption of salicylic acid onbentonite and kaolin and release experiments[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2007, 36(1-3):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2006.07.008
[55] Mallick S, Pattnaik S, Swain K, et al. Formation of physically stable amorphous phase of ibuprofen by solid state milling with kaolin[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2008, 68(2):346-351. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.06.003
[56] Tan D, Yuan P, Annabi-Bergaya F, et al. High-capacity loading of 5-fluorouracil on the methoxy-modified kaolinite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 100:60-65. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.02.022
[57] Hamilton A R, Hutcheon G A, Roberts M, et al. Formulation and antibacterial profiles of clay-ciprofloxacin composites[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 87:129-135. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2013.10.020
[58] Nik Ahmad Nizam Nik Malek, Nur Isti'anah Ramli. Characterization and antibacterial activity of cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) immobilized on kaolinite with different CPB loadings[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2015, 109:8-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1b8fd7b841110a1733581aceb80591b4
[59] Tang W, Yuan Y, Lin D, et al. Kaolin-reinforced 3D MBG scaffolds with hierarchical architecture and robust mechanical strength for bone tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2(24):3782-3790. doi: 10.1039/C4TB00025K
[60] 朱华.高岭土应用的工业进展及现状[J].矿业工程, 2005, 3(6):25-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8550.2005.06.013
-

| 引用本文: | 孟宇航, 尚玺, 张乾, 杨华明. 高岭土的功能化改性及其战略性应用[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(6): 69-76. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2019.06.011 |
| Citation: | MENG Yuhang, SHANG Xi, ZHANG Qian, YANG Huaming. Functional Modification of Kaolin and Its Strategic Application[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(6): 69-76. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2019.06.011 |


 下载:
下载: