A Review on Recycling and Reuse of Rare Earth Metals
-
摘要:
稀土金属广泛应用于冶金、石油化工、玻璃陶瓷等领域,是当代高科技新材料(永磁材料、抛光材料、催化材料等)的重要组成部分。长期以来,中国稀土的高产量致使国际上普遍认为中国垄断了全球稀土金属生产和精炼供给,导致进口国面临着严重的供给风险,纷纷展开了稀土金属二次回收再利用的研究。本文概述了全球范围内稀土元素回收的当前和未来潜力,主要研究了从最终报废产品、生产过程中的工业废料、含稀土元素的工业固、液废弃物三方面回收稀土元素的研究现状以及未来回收潜力。
Abstract:Rare earth metals are widely used in metallurgy, petrochemical industry, glass ceramics and other fields, they are important components of modern high-tech new materials (permanent magnet materials, polishing materials, catalytic materials, etc.). The high output of rare earth in China has led the international community to generally believe that China has monopolized the global production and refining supply of rare earth metals, which has led to serious supply risks for importing countries. Therefore, research on recovery and reuse of rare earth metals has been carried out one after another. This paper reviews the current and future potential of rare earth element recovery. And mainly includes recovery of rare earth metals from scrap products, industrial waste in production process, industrial solid and liquid waste containing rare earth elements.
-
Key words:
- rare earth /
- recycling and reuse /
- recycling economy
-

-
表 1 稀土元素及其常见用途综述[7]
Table 1. Summary of the REEs and their common uses
稀土元素 常见用途 镧(La) 光学、电池、催化 铈(Ce) 化学应用、染色、催化 镨(Pr) 光学、磁铁、照明 钕(Nd) 光学、磁铁、照明、激光 钷(Pm) 由于放射性而限制使用,用于油漆和原子电池;自然界中非常罕见 钐(Sm) 磁铁、激光、微波激射器 铕(Eu) 激光、彩色电视、照明、医疗应用 钆(Gd) 磁铁、玻璃器皿、激光、X射线生成、计算机应用、医疗应用 铽(Tb) 激光、照明 稀土元素 常见用途 镝(Dy) 磁体、激光器 钬(Ho) 激光器 铒(Er) 激光,炼钢 铥(Tm) X射线生成 镱(Yb) 激光、化学工业应用 镥(Lu) 医疗应用、化学工业应用 钪(Sc) 航空航天工程、照明 钇(Y) 激光、超导体、微波滤波器、照明 表 2 稀土元素在循环利用过程中的潜在来源
Table 2. The potential sources of REEs during recycling
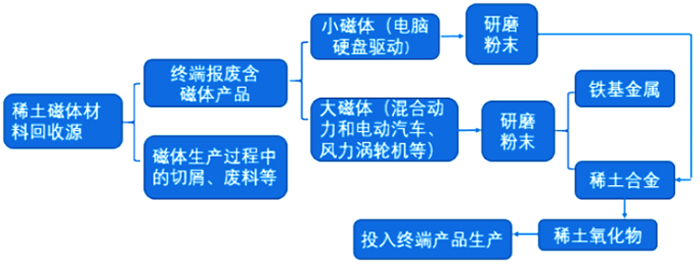
稀土元素回收来源 举例 可回收元素 方法 最终报废产品 报废电子产品、荧光材料 La, Tb, Nd, Eu, Dy, Pr, Y(Ce, Gd, La) 火法冶金(焙烧、煅烧);湿法冶金(浸出、溶剂萃取、选择性沉淀);气相萃取 工业生产废料 比如磁铁制造废料 Nd, Dy 湿法冶金过程(浸出、溶剂萃取、选择性沉淀) 工业固、液废弃物 赤泥、尾矿、冶金渣、热电厂和焚烧厂的灰渣 All REEs 湿法冶金(浸出、离子交换/溶剂萃取、沉淀、分离) 表 3 从荧光粉、永磁铁和催化剂中回收稀土元素的专利[20]
Table 3. Patents related to the REEs recovery from fluorescent powders, permanent magnets and FCCC
年份 名称 专利号 荧光粉 2016 利用废荧光粉生产红色荧光粉的方法 TW201638295 2016 从灯磷废料中回收钇和铕的工艺 WO2016065433 2016 废荧光粉中稀土元素钇的回收方法 CN106191446 2016 利用自蔓延反应回收废阴极射线管荧光粉中锌并富集稀土的方法 CN105755288 2016 利用废荧光粉回收稀土的方法 CN105568005 2015 利用废荧光粉制备稀土荧光上转换材料的方法 CN104388087 2015 从废荧光粉回收稀土金属的方法 CN105087934 2015 高效回收废阴极射线管荧光粉中稀土的方法 CN105039698 2014 有效回收荧光粉废料中稀土元素的方法 CN103667709 2014 废稀土荧光灯的综合回收处理方法 CN103627906 2012 超声波亚伏盐法回收稀土荧光粉中稀土元素的方法 CN102828030 2012 阴极射线管荧光粉中稀土的回收方法 CN102796872 2012 回收废弃荧光灯后接地元件的方法 CN102634667 2009 废阴极射线管荧光粉回收方法 TW200916552 2004 荧光粉回收方法 JP2004262978 永磁体 2017 再生烧结钕铁硼永磁体的制备方法 CN106971802 2016 烧结钕铁硼再生废料经扩散渗透处理制备高性能永磁体的方法 CN106158339 2016 烧结钕铁硼废料回收利用方法 CN105931781 催化裂化催化剂 2016 含钒废催化裂化平衡催化剂的回收利用方法 CN105251525 2014 稀土金属回收工艺 WO2014020626 2012 从催化剂废料中回收金属的工艺 WO2012082597 -
[1] Neil G. Connelly, Ture Damhas, Richard M, et al. Nomenclature of inorganic chemistry-IUPAC recommendations 2005[M]. Cambridge: RSC Publishing; 2005.
[2] Binnemans, K., Jones, PT., Blanpain, B., et al. Recycling of rare earths:a critical review[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2013(51):1-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy-e201904003
[3] Swain N., Mishra S.. A review on the recovery and separation of rare earths and transition metals from secondary resources[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2019(220):884-898. https://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000041588875499_d4e3.html
[4] Haque, N., Hughes A., Lim S., et al. Rare earth elements:overview of mining, mineralogy, uses, sustainability and environmental impact[J]. Resources, 2014(3):614-635. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301355638_Rare_Earth_Elements_Overview_of_Mining_Mineralogy_Uses_Sustainability_and_Environmental_Impact
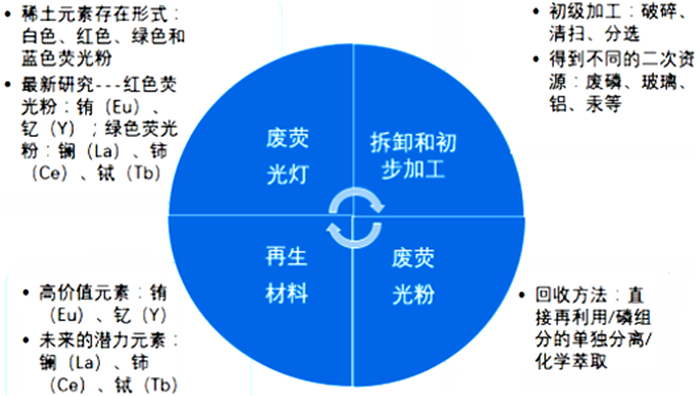
[5] Wu Y.F., Yin X.F., Zhang Q.J., et al. The recycling of rare earths from waste tricolor phosphors in fluorescent lamps:A review of processes and technologies[J]. Resources conservation and recycling, 2014(88):21-31.
[6] Jowitt S.M., Werner T.T., Weng Z.H., et al. Recycling of the rare earth elements[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2018(13):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzhg201810007
[7] Weng Z., Jowitt S.M., Mudd G.M., et al. A detailed assessment of global rare earth resources:opportunities and challenges[J]. Econ Geol, 2015(110):1925-1952.
[8] EC (European Commission). Report on critical raw materials for the EU[R]. Ad hoc working group on defining critical raw materials, Brussels: EC, 2010.
[9] EC (European Commission). Report on critical raw materials for the EU[R]. Ad hoc working group on defining critical raw materials, Brussels: EC, 2014.
[10] European commission. Study on the review of the list of critical raw materials, criticality assessments[R]. 2017, Table 18: 79-80.
[11] Department of the Interior office of the secretary. Final list of critical minerals 2018[EB/OL]. (2018-5-18)[2019-6-20]. https://www.usgs.gov/news/interior-releases-2018-s-final-list-35-minerals-deemed-critical-us-national-security-and.
[12] U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral commodity summaries 2018[EB/OL] [2019-5-21]. https://doi.org/10.3133/70194932.
[13] Sprecher B., Xiao Y., Walton A., et al. Life cycle inventory of the production of rare earths and the subsequent production of NdFeB rare earth permanent magnets[J]. Environ. sci. Technol., 2014(48):3951-3958. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6b4c93fad239406f753efb426bed085d
[14] Christmann P.. A forward look into rare earth supply and demand:a role for sedimentary phosphate deposits[J]. Proc Eng, 2014(83):19-26.
[15] Li J., He X., Zeng X.. Designing and examining e-waste recycling process:methodology and case studies[J]. Environ Technol, 2017(38):652-660. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27367434
[16] Kumari, A., Jha, M.K., Pathak, D.D.. Review on the processes for the recovery of Rare Earth Netals (REMs) from secondary resources[J]. In Rare metal technology. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society and Springer, 2018(1):53-65. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-72350-1_5
[17] Huang X. W., Long Z. Q., Wang L. S., et al. Technology development for rare earth cleaner hydrometallurgy in China[J]. Rare Metals, 2015, 34(4):215-222. doi: 10.1007/s12598-015-0473-x
[18] Chen Z. H.. Global rare earth resources and scenarios of future rare earth industry[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2011, 29(1):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxtxb-e201101001
[19] Ferron C. J., Henry P.. A review of the recycling of rare earth metals[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2016, 54(4):388-394. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy-e201904003
[20] Amato A., Becci A., Birloaga I., et al.. Sustainability analysis of innovative technologies for the rare earth elements recovery[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019(106):41-53.
[21] Shishkin, A., Mironovs, V., Goljandin, D., et al. Recycling of Al-W-B composite material[J]. Key Eng. Mater., 2013(527):143-147. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234842186_Recycling_of_Al-W-B_Composite_Material
[22] Shishkin, A., Mironovs, V., Vu, H., et al. Cavitation-dispersion method for copper cementation from wastewater by iron powder[J]. Metals, 2018(8):920-930.
[23] Loy S.V., Binnemans K., Gerven T.V.. Recycling of rare earths from lamp phosphor waste:enhanced dissolution of LaPO4:Ce3+, Tb3+ by mechanical activation[J]. J Clean Prod, 2017(156):226-234.
[24] Frhlich, P., Lorenz, T., Martin, G., et al. Valuable metals-recovery processes, current trends, and recycling strategies[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017(56):2544-2580.
[25] Schulze, R., Buchert, M.. Estimates of global REE recycling potentials from NdFeB magnet material[J]. Resour. Conserv. Recy., 2016(113):12-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ab4438045e7f9689c1ceda1c48300c71
[26] Zeng, X., Li, J.. Urban mining and its resources adjustment:characteristics, sustainability, and extraction[J]. Sci. Sin. Terrae, 2018(48):288-298.
[27] Al-Jabri K., Baawain M., Taha R., et al. Potential use of FCC spent catalyst as partial replacement of cement or sand in cement mortars[J]. Constr build mater, 2013(39):77-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_de865c70e09cfe79aa5958465317a80a
[28] Zhang H., Xiao R., Wang D., et al. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass in a fluidized bed with fresh and spent fluidized catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts[J]. Energy Fuels, 2009(23):6199-206. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ea6665a43d87eafa7f59da87e5918208
[29] Ferella F., D'Adamo I., Leone, S., et al. Spent FCC E-Cat:towards a circular approach in the oil refifining industry[J]. Sustainability, 2019b(11):1-19.
[30] Ujaczki, E., Zimmermann Y., Gasser C., et al. Red mud as secondary source for critical raw materials-Purification of rare earth elements by liquid/liquid extraction[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2017(92):2835-2844. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d9897aa7b110d168e498e8cce94e7752
[31] Borra, C.R., Pontikes Y., Binnemans K., Gerven, T.V.. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud)[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015(76):20-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a87d98d825b212d4f9e53c5a137ac2fc
[32] Davris P., Balomenos E., Panias D., et al. Selective leaching of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud), using a functionalized hydrophobic ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016(4):125-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fd4e1d6fd8ca1f8ebd7e2a1ae5e653fd
[33] Yang Q., Bin L.. Bioleaching of rare earth and radioactive elements from red mud using Penicillium tricolor RM-10[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013(136):16-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=303740d0cd3e09cdb558a4cd62836417
[34] Ponou J., Dodbiba G., Anh J.W., et al. Selective recovery of rare earth elements from aqueous solution obtained from coal power plant ash[J]. Journal of environmental chemical engineering, 2016(4):3761-3766. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343716303050
[35] Bogart J., Cole B., Boreen M., et al. Accomplishing simple, solubility based separations of rare earth elements with complexes bearing size-sensitive molecular apertures[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016(113):14887-14892. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f39777424cf5c585c794425f7eab9522
[36] Bogart J.A., Lippincott C.A., Carroll P.J., et al. An operationally simple method for separating the rare-earth elements neodymium and dysprosium[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015(54):8222-8225. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5a52c128fd17687c02509dd0f12913a1
[37] Peelman S., Sun Z.H.I., Sietsma J., et al. Hydrometallurgical extraction of rare earth elements from low grade mine tailings[J]. Rare metal technology, 2016(1):17-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bbdbee77bc60b4e61452f6606849928e
[38] López J., Reig M., Torres E., et al. Application of nanofiltration for acidic waters containing rare earth elements:influence of transition elements, acidity and membrane stability[J]. Desalination, 2018(430):33-44.
[39] Wilfong W.C., Kail B.W., Bank T.L., et al. Recovering rare earth elements from aqueous solution with porous amine-epoxy networks[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017(9):18283-18294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=897d707be5680b25e665334bc6cb993d
[40] Reed D.W., Fujita Y., Daubaras D.L., et al. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from waste phosphors and cracking catalysts[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016(166):34-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=39e7fbaf0303336f5219c4a5099d9c1d
[41] Wang J., Huang X., Cui D., et al. Recovery of rare earths and aluminum from FCC waste slag by acid leaching and selective precipitation[J]. Rare Earths, 2017(35):1141-1148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxtxb-e201711011
[42] Sprecher B., Daigo I., Murakami S., et al. Framework for resilience in material supply chains, with a case study from the 2010 rare earth crisis[J]. Environ Sci Technol., 2015(49):6740-6750. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=54ba015a5ef8d941bc9ea532150a7fbe
-



 下载:
下载: