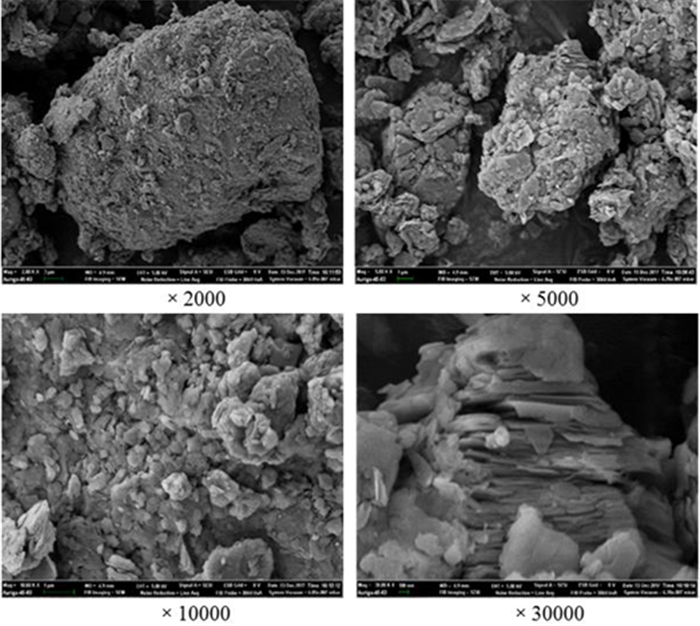
Mineralogical Characteristics and Calcination Composition Changes of Coal Gangue in Shuozhou Area of China
-
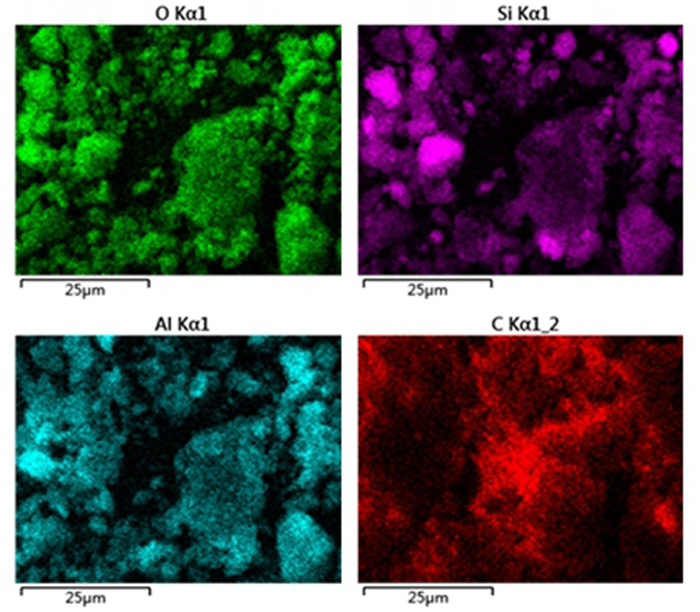
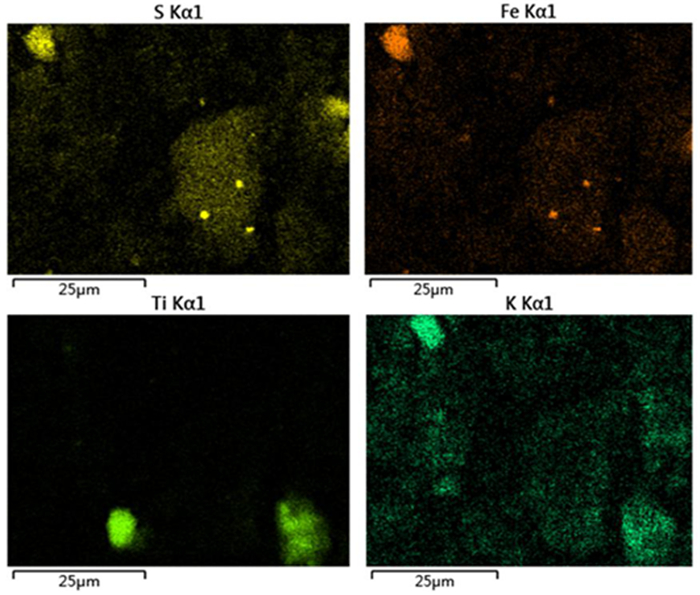
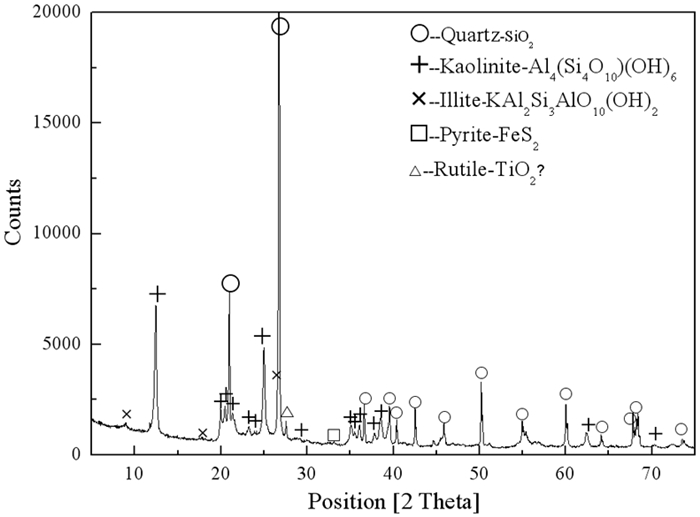
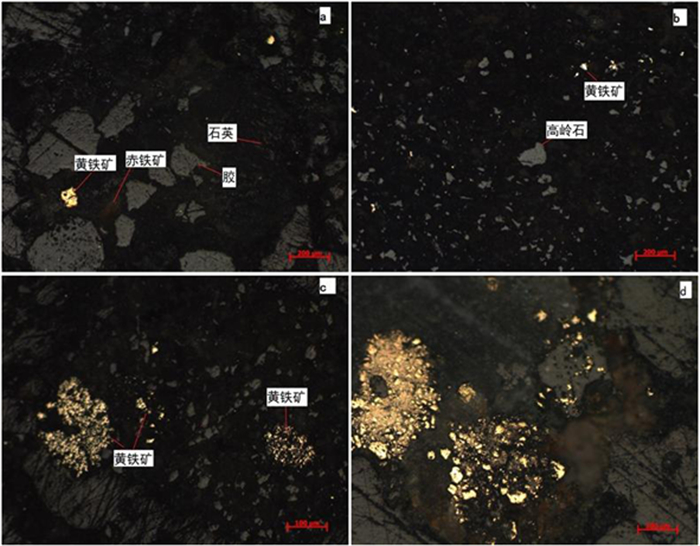
摘要: 目前,煤矸石利用是固废处置与利用的重要内容之一,煤矸石的综合利用与其矿石性质密切相关,但对煤矸石各组分的嵌布关系,元素分布、物相存在形式、微观形貌等相关研究较少。文章针对我国朔州地区煤矸石开展工艺矿物学研究,采用XRD、XRF、EDS、SEM等方法,查明了该煤矸石成分为石英、高岭土、黄铁矿、伊利石、金红石,且多为集合体形式存在,其颗粒微观形貌呈现层状或鳞片状。煤矸石中有用矿物高岭石的含量为56.3%,其次为石英21.1%,伊利石15%。铁杂质主要以黄铁矿存在,其含量为6.5%。煤矸石煅烧试验表明:黄铁矿在850℃左右开始被氧化,生成赤铁矿;在1 000℃煅烧2 h,煤矸石中碳降低到0.1%以下,硫含量也降低到1.74%。在900~1 000℃温度区间内,高岭石转变为无定型的偏高岭土。Abstract: At present, the utilization of coal gangue is one of the important contents of solid waste disposal and utilization. The comprehensive utilization of coal gangue is closely related to its ore properties, but there are few related researches on the distribution of elements, the existing forms of phases, and the micro-morphology of coal gangue components. In this paper, the process mineralogy of coal gangue in Shuozhou region of China was studied. XRD, XRF, EDS, SEM and other methods were used to find out that the coal gangue is composed of quartz, kaolin, pyrite, illite and rutile, and most of them exist in the form of aggregates, and the micro-morphology of its particles was lamellar or scaly. The content of useful mineral kaolinite in coal gangue was 56.3%., followed by quartz 21.1%, illite 15%. Iron impurities mainly existed in pyrite with a content of 6.5%.Calcination test of coal gangue shows that: Pyrite began to be oxidized at 850 ℃ to form hematite. When calcined at 1 000 ℃ for 2 hours, the carbon content in coal gangue was reduced to below 0.1%, and the sulfur content was also reduced to 1.74%. In the temperature range of 900~1 000 ℃, kaolinite was transformed into amorphous metakaolin.
-
Key words:
- coal gangue /
- composition /
- pyrite /
- calcination /
- impurity
-

-
表 1 煤矸石化学多样分析结果
/% Table 1. Chemical analysis results of coal gangue
Component Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 S C loss Content 21.02 55.01 6.04 4.58 1.81 13.74 表 2 煤矸石的X荧光分析结果
/% Table 2. X-ray fluorescence analysis results of coal gangue
Component SiO2 Al2O3 MnO Fe2O3 SO3 TiO2 Na2O MgO K2O P2O5 BaO ZnO LOI Fixed carbon Content 0.06 1.26 0.06 — — 11.40 4.52 51.69 21.59 0.04 5.94 6.12 0.76 0.08 表 3 煤矸石的化学成分能谱检测结果
/% Table 3. Chemical composition energy spectrum test results of coal gangue
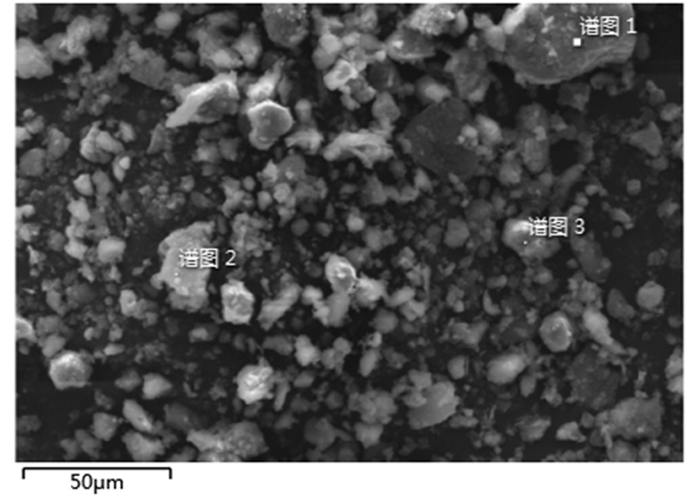
point O Al Si S K Ca Fe Ti Cu Zr 1 50.24 6.77 38.68 0.59 0.15 0.00 0.39 0.00 0.08 0.22 2 65.12 12.34 14.88 5.16 0.42 0.22 1.64 0.22 0.00 0.00 3 50.48 8.86 34.25 2.88 1.12 0.00 2.07 0.33 0.00 0.00 表 4 煤矸石物相组成
/% Table 4. Phase composition of coal gangue
phase Quartz Kaolinite Illite Pyrite Rutile Content 21.1 56.3 15 6.5 1.1 表 5 煤矸石焙烧前后的主要化学组成
/% Table 5. Main chemical composition of coal gangue before and after roasting
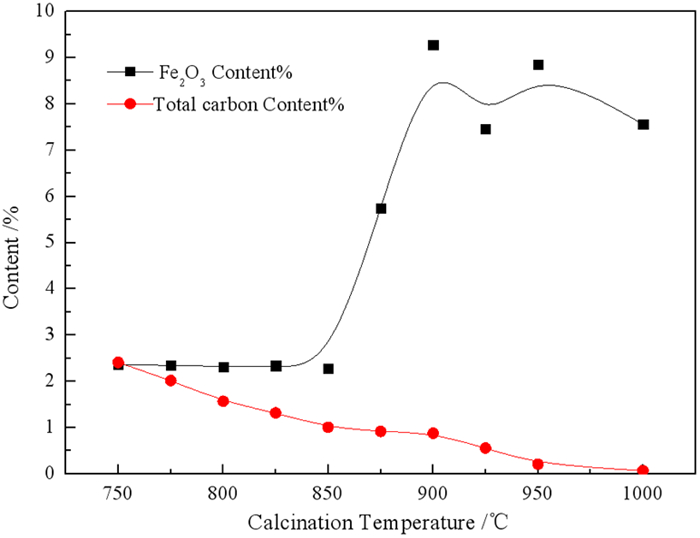
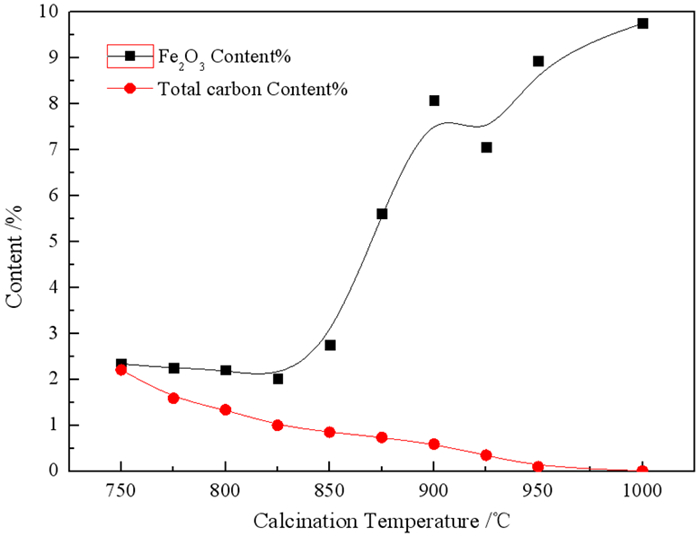
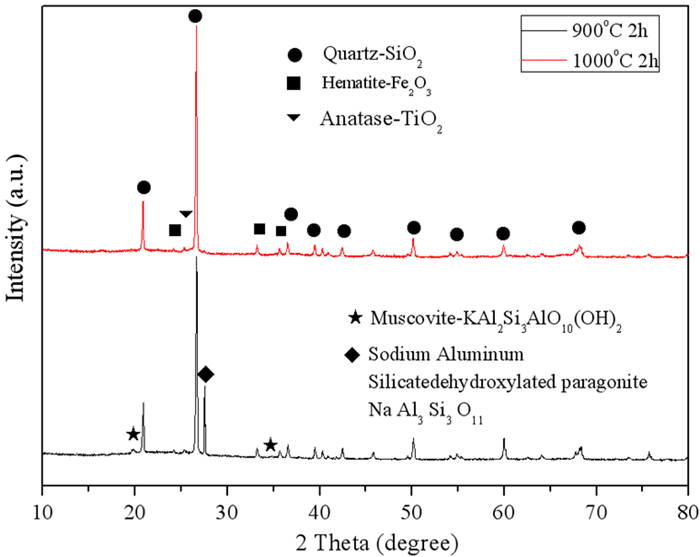
Component SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O SO3 TiO2 Original sample 51.69 21.59 5.94 1.26 6.12 0.76 900 ℃-2 h 50.23 22.82 9.28 2.61 5.12 1.90 1 000 ℃-2 h 52.17 26.85 7.46 1.24 1.74 0.78 -
[1] 李彤.中国煤炭产业对外依存度问题研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10004-1012355924.htm [2] 孙春宝, 董红娟, 张金山, 等.煤矸石资源化利用途径及进展[J].矿产综合利用, 2016(6):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.06.001
[3] 卞孝东.浅谈煤矸石的组成特征及综合利用途径[J].矿产综合利用, 2007(5):51-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcbhyly200705013
[4] 张拥军, 常鑫, 杨金花.浅析煤矿煤矸石山生态环境恢复治理技术[J].山西化工, 2019, 179(1):185-188. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shanxhg201901067
[5] JIAYAN LI, JINMAN WANG. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue:Areview[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 239:1-17. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652619328161
[6] 孙春宝, 董红娟, 张金山, 等.煤矸石及其国内外综合利用[J].煤炭技术, 2016, 35(3):286-288. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtjs201603114
[7] 梁效.煤矸石中高岭土的分选及煅烧增白试验研究[D].西安: 西安科技大学, 2018.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10704-1018882692.htm [8] 王占娥, 李辉、徐德龙, 等.煤系高岭土悬浮煅烧工艺试验研究[J].非金属矿, 2007, 30(2):45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2007.02.016
[9] 田钊.煤系高岭土煅烧与脱碳试验研究[D].武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2014.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/D617959 [10] 刘成俊.内蒙古乌海煤系高岭土低温快速煅烧试验[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2017, 125(1):12-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2017.01.005
[11] 黄腾.选矿提纯与低温焙烧降低煤系高岭土COD及机理研究[D].武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10497-1018807106.htm [12] 王相, 李金洪.准格尔露天煤矸石制备精细煅烧高岭土的试验研究[J].硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(6):1249-1253. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90627X/201106/40386410.html
[13] 宋旭艳, 宫晨琛, 李东旭.煤矸石活化过程中结构特性和力学性能的研究[J].硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(3):358-363. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2004.03.028
[14] 霍晨磊, 何亚波, 孟子浩.煤矸石资源化利用技术综述[J].山西焦煤科技, 2011(1):47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0652.2011.01.013
[15] 宋艳芳, 武学恒.高温煅烧提高煤矸石活性试验中煅烧温度的选择[J].地质评论, 2013, 59(S):818. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DXHD201304001361.htm
-



 下载:
下载: