Research Progress on Lithium Battery-class System for Lithium Extraction from Brine
-
摘要:
随着新能源汽车产业的迅速发展,锂及其化合物的需求量日益增长。世界锂资源中的65%都赋存于盐湖卤水中,从盐湖卤水中选择性提锂越来越受到人们的重视,实现盐湖卤水中锂的绿色、高效提取是新能源汽车产业和锂工业可持续发展的必然选择。锂离子电池材料由于其过渡金属的可氧化还原和锂的可逆循环脱嵌特性,越来越多地被用于盐湖提锂,由此开发出了系列不同的提锂新技术。该综述主要介绍了由不同锂离子电池正极材料所构成的盐湖卤水提锂体系的工作原理、工艺参数和提锂性能,并对利用锂离子电池正极材料从盐湖卤水中选择性提锂的发展及其应用前景进行了展望。
Abstract:As a result of the rapid development of the new energy material industry, the demand for lithium and its related compound sharply raised. As 65% of the lithium resources are restored in salt lake brine world widely, selectively extraction of lithium from salt lake brine has been treated valuable by the industry. It is necessary to make sure new energy industry and Lithium industry to become sustainable development industry by gain the technology of extract lithium from salt lake brine efficiently and eco-friendly. By drawing on the working principle of lithium-ion batteries, a wide variety of technologies for lithium extraction from salt lake brines using lithium-ion battery cathode materials has been developed. According to this paper, the following concept is covered: the working principle, process parameters and lithium extraction performance of lithium extraction system from salt lake brine composed of different lithium-ion battery cathode materials, as well as the development of selective extraction of lithium from salt lake brine using lithium-ion battery cathode materials and its application prospects have prospected.
-
Key words:
- salt lake brine /
- lithium extraction /
- lithium ion battery /
- cathode material
-

-
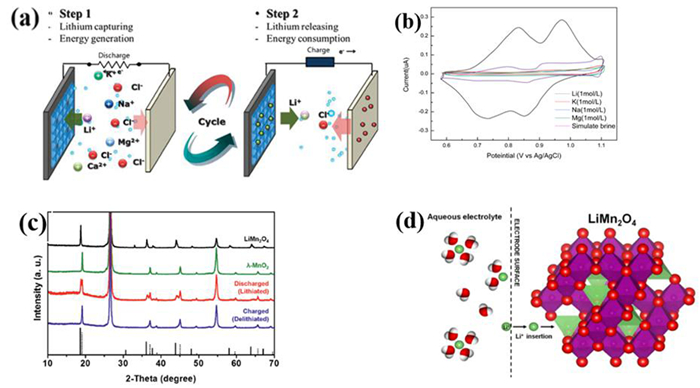
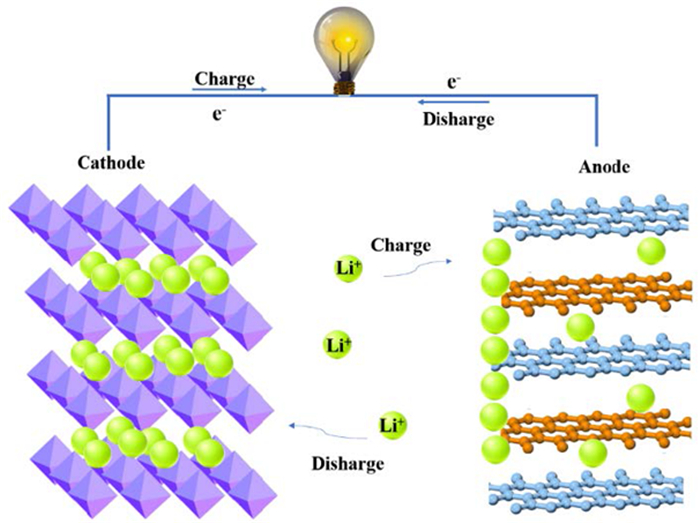
图 1 锰酸锂电池原理示意图[6]
Figure 1.
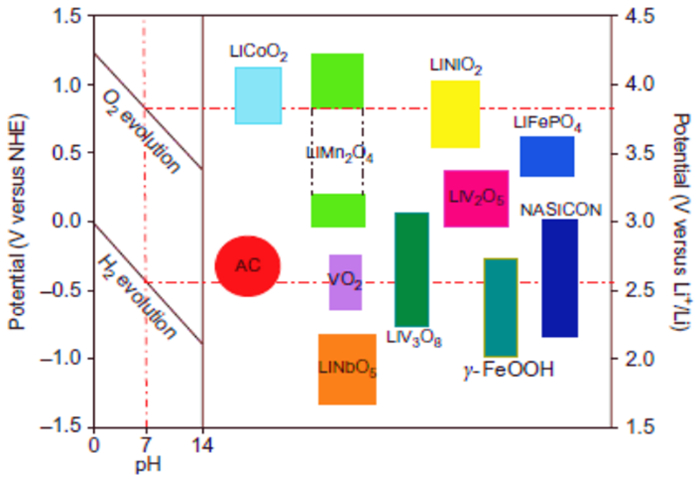
图 2 不同电极材料在水溶液中的稳定性[7]
Figure 2.
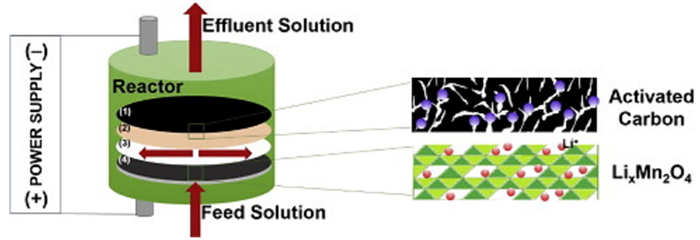
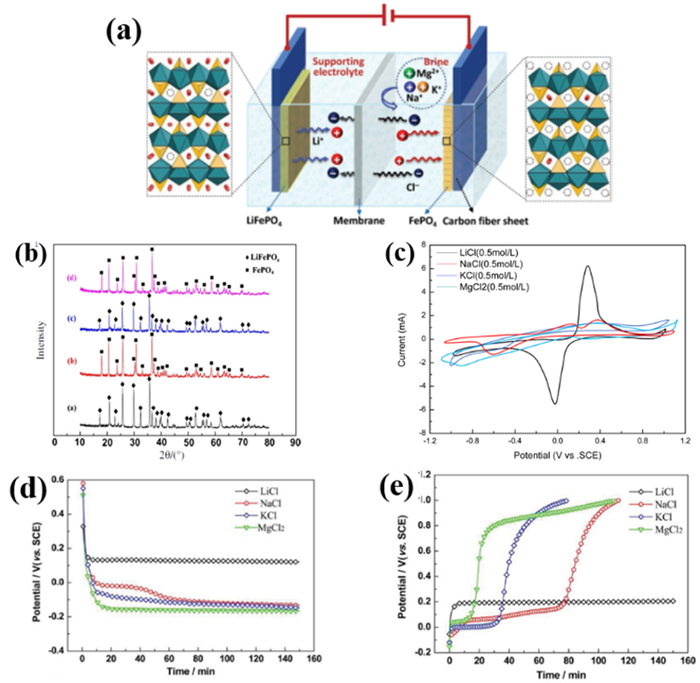
图 4 锰酸锂—活性炭体系盐湖提锂装置示意图[14]。其中(1)为活性碳电极,(2)为阴离子交换膜,(3)为尼龙垫圈,(4)λ-MnO2电极
Figure 4.
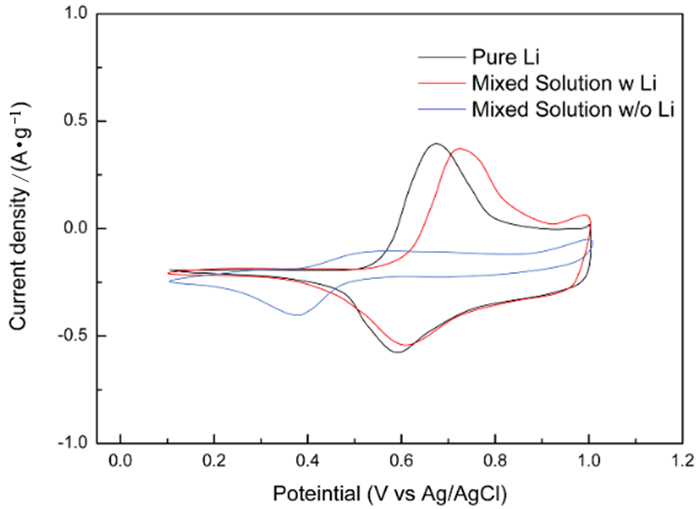
图 6 NCM材料在纯锂溶液,含锂以及不含锂的混合溶液的循环伏安曲线[22]
Figure 6.
-
[1] 吴荣庆.新能源材料锂:资源储量与供需形势分析[J].国土资源情报, 2017(1):4-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2017.01.002
[2] 杨卉芃, 柳林, 丁国峰.全球锂矿资源现状及发展趋势[J].矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(5):26-40. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=75498c57-431a-4720-8245-fa8040b638c4
[3] HUANG WEINONG, SUN ZHINAN, WANG XUEKUI, et al. Progress in industrialization for lithium extraction from salt lake[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2008, 28(2):14-17. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286997431_Progress_in_industrialization_for_lithium_extraction_from_salt_lake
[4] 王秋舒, 邱景智, 邵鹤楠, 等.全球盐湖卤水型锂矿床成矿特征与资源潜力分析[J].中国矿业, 2015, 24(11):82-88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGKA201511018.htm
[5] 谭秀民, 张永兴, 张利珍, 等.能源金属锂资源开发利用现状及发展建议[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(5):87-92. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=73769145-b053-4be2-a7d1-dc8e7f39d3e3
[6] 徐静.锂离子电池正极锰酸锂的制备[D].呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2019.
[7] LIHUA HE, WENHUA XU, YUNFENG SONG, et al. Lithium-Ion Batteries: New insights into the application of lithium-ion battery materials: selective extraction of lithium from brines via a rocking-chair lithium-ion battery system (global challenges 2/2018). 2018, 2(2): 1700079.
[8] KANOH H, OOI K, MIYAI Y, et al. Selective electroinsertion of lithium ions into a Pt/λ-MnO2 electrode in the aqueous phase[J]. Langmuir, 1991, 7(9):1841-1842. doi: 10.1021/la00057a002
[9] 杨卉芃.碳酸锂及钙镁杂质在扎布耶混盐碳化过程中的行为[J].矿产保护与利用, 2005(3):40-42. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=df2d57e4-91d1-4bf5-972e-46156d618ed8
[10] Lee Jaehan, Yu Seung-Ho, Kim Choonsoo, et al. Highly selective lithium recovery from brine using a λ-MnO2-Ag battery, 2013, 15(20): 7690-7695.
[11] ZHAO ALONG, LIU JINCHENG, AI XINPING, et al. Highly selective and pollution-free electrochemical extraction of lithium by a polyaniline/LixMn2O4 cell[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(7):1361-1367. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201803045
[12] KIM S, JOO H, MOON T, et al. Rapid and selective lithium recovery from desalination brine using an electrochemical system[J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2019, 21(4):667-676. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30799481
[13] MARCHINI, FLORENCIA, WILLIANMS, et al. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the LixMn2O4 interface with natural brine[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry:An International Journal Devoted to All Aspects of Electrode Kinetics, Interfacial Structure, Properties of Electrolytes, Colloid and Biological Electrochemistry, 2018, 819(SI):428-434. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=305c314af483637f67a560e777e5fc14
[14] SEONI KIM, JAEHAN LEE, JIN SOO KANG, et al. Lithium recovery from brine using a λ-MnO2/activated carbon hybrid supercapacitor system[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 125:50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.024
[15] 伏勇胜.纳米锰酸锂及锰酸锂/石墨烯复合物的制备与电化学性质研究[D].西安: 陕西科技大学, 2015.
[16] 丁伟, 王林霞, 胡天阳, 等.聚吡咯作为水系锂离子电池的负极材料[J].电源技术, 2019, 43(12):1933-1936. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DYJS201912009.htm
[17] PASTA M, BATTISTEL A, LA MANTIA F. Batteries for lithium recovery from brines[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(11):9487. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22977c
[18] KIM JOO-SEONG, LEE YONG-HEE, CHOI SEUNGYEON, et al. An Electrochemical Cell for Selective Lithium Capture from Seawater[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(16):9415-9422. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b00032
[19] SEONGSOO KIM, Dr. JAEHAN LEE, Dr. SEONI KIM, et al. Electrochemical Lithium Recovery with a LiMn2O4-Zinc Battery System using Zinc as a Negative Electrode[J]. Energy Technology, 2018, 6(2):340-344. doi: 10.1002/ente.201700488
[20] Dr. R. TróCOLI, A. BATTISTEL, Dr. F. LA MANTIA. Nickel hexacyanoferrate as suitable alternative to Ag for electrochemical lithium recovery. 2015, 8(15): 2514-2519.
[21] 桂阳海, 赵恒勤, 胡国荣.锂离子电池正极材料锂镍钴氧化物的研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2004(6):34-38. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=021fe691-2e4f-4957-a33b-c96ae83a15b1
[22] CHOSEL P. LAWAGON, GRACE M. NISOLA, ROSEMARIE ANN I. CUEVAS, et al. Li1-xNi0.3Co1/3Mn1/3O2/Ag for electrochemical lithium recovery from brine[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348:1000-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.030
[23] CHOSEL P. LAWAGON, GRACE M. NISOLA, ROSEMARIE ANN I, et al. Li1-xNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Ag for electrochemical lithium recovery from brine and its optimized performance via response surface methodology[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 212:416-426.
[24] ZHAO Z W, SI X F, LIANG X X, et al. Electrochemical behavior of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(4):1157-1164. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62578-9
[25] ZHONGWEI ZHAO, XIUFEN SI, XUHENG LIU, et al. Li extraction from high Mg/Li ratio brine with LiFePO4/FePO4 as electrode materials[J]. Hydrometallurgy. 2013, 133:75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.11.013
[26] LIU X, CHEN X, ZHAO Z, et al. Effect of Na+ on Li extraction from brine using LiFePO4/FePO4 electrodes[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 146:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.03.010
[27] INTARANONT N, GARCIA-ARAEZ N, HECTOR A L, et al. Selective lithium extraction from brines by chemical reaction with battery materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(18):6374-6377. doi: 10.1039/C4TA01101E
[28] 尚玺, 孟宇航, 张乾, 杨华明.富锂矿物的锂提取与战略性应用[J].矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(6):152-158. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=aa61359c-cf07-4fd6-967c-910b3d3e71d6
-



 下载:
下载: