Research on Occurrence State of Iron and Rare Earth in Mica Type Iron Ore in Bayan Obo
-
摘要:
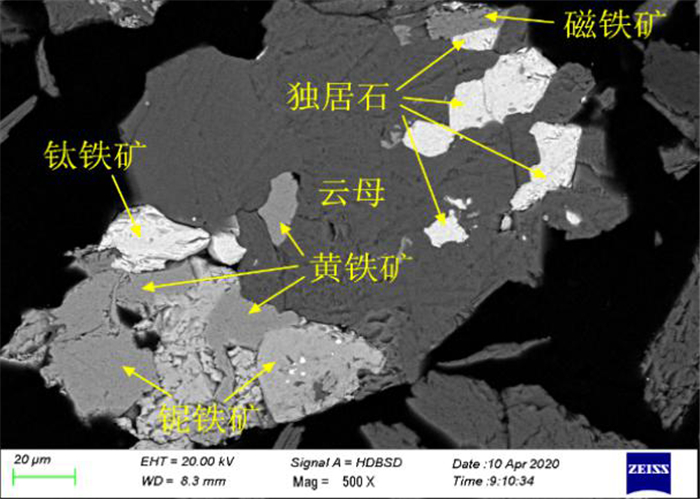
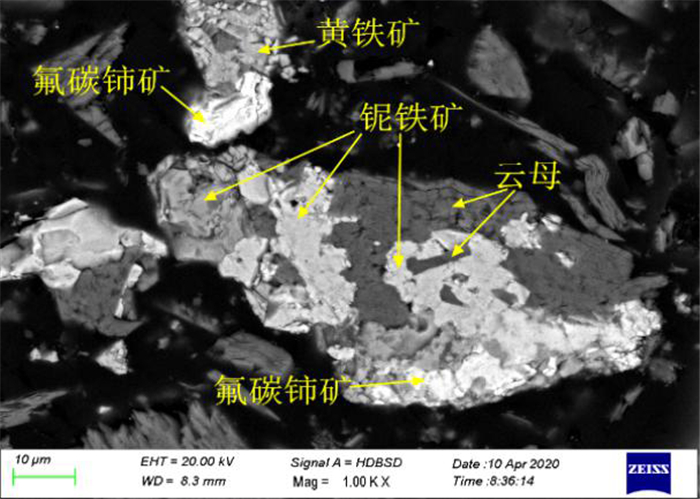
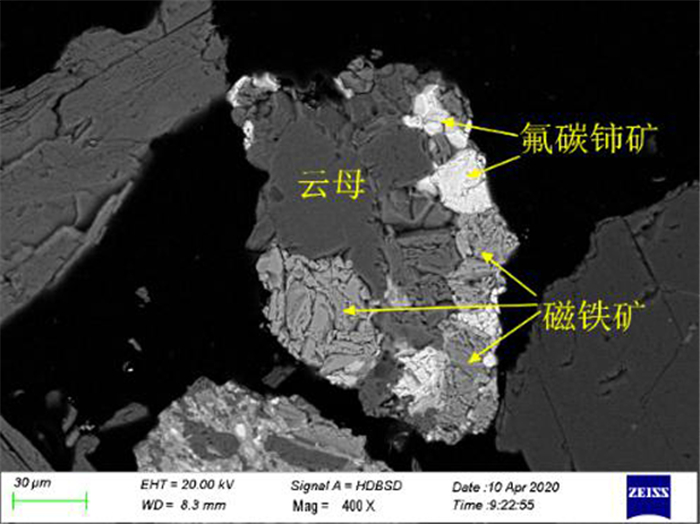
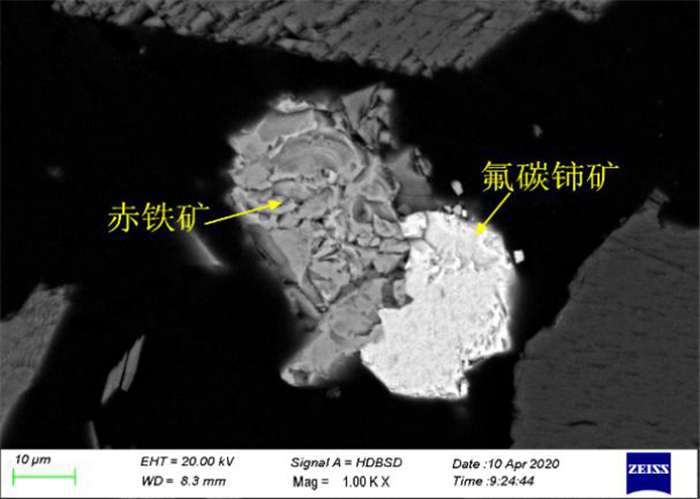
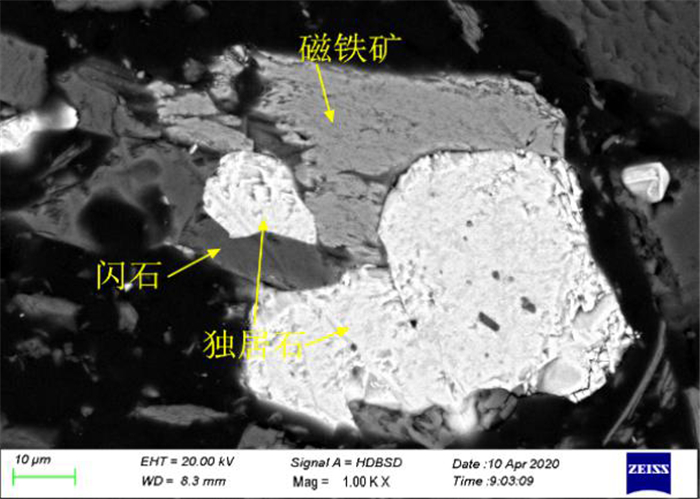
白云鄂博云母型铁矿石中TFe品位为17.48%,稀土REO品位为2.46%。矿石中矿物组成复杂,含铁矿物主要是磁铁矿和赤铁矿,含有少量铌铁矿、黄铁矿等,稀土矿物以氟碳铈矿和独居石为主。矿石构造主要由黑云母定向排列而成的片状构造、斑杂状构造及浸染状构造;矿物主要为自形-半自形粒状结构、他形粒状结构、尖角状结构、交代残余结构、细脉状结构。磁铁矿多呈半自形至他形粒状变晶结构形式出现,部分呈角砾状集合体与云母共生;赤铁矿多呈半自形和他型粒状结构,也有部分赤铁矿呈微细粒粒状嵌布在脉石矿物中;氟碳铈矿和独居石呈粒状,与周边其它矿物紧密共生、镶嵌关系复杂。磁铁矿和赤铁矿的嵌布粒度不均,氟碳铈矿和独居石的嵌布粒度较细,部分细粒铁矿石和稀土矿物嵌布在脉石矿物中,部分铁矿石中也含有细粒稀土矿物。磨矿细度-0.074 mm占90%下磁铁矿、赤铁矿、氟碳铈矿和独居石的单体解离度仅为51.54%、58.36%、52.27%和63.64%。因此,强化矿石细磨和微细粒高效分选是解决精矿品位和回收率低的有效途径。
Abstract:The grade of TFe and REO in Bayan Obo mica type iron ore is 17.48% and 2.46%, respectively. The mineral composition of the ore is complex. The iron minerals are mainly magnetite and hematite, with a small amount of niobium, pyrite, etc. The rare-earth minerals are mainly bastnaesite and monazite. The ore structure is mainly composed of schistose structure, patchy structure and disseminated structure formed by directional arrangement of biotite. The minerals are mainly automorphic and semi automorphic granular structure, allomorphic granular structure, angular structure, metasomatic residual structure and veinlet structure. The magnetite is mostly in the form of semi automorphic to allomorphic granular crystalloblastic structure, some of which are in the form of breccia aggregate and mica. The hematite is mostly in the form of half automorphic and other granular structure, and some of hematite is embedded in gangue minerals in the form of fine grains. The bastnaesite and monazite are granular, which are closely associated with other surrounding minerals and have complex inlaying relationship. The distribution granularity of magnetite and hematite is uneven. The distribution granularity of bastnaesite and monazite is finer. Some fine-grained iron ores and rare-earth minerals are embedded in gangue minerals. Some iron ores also contain fine-grained rare-earth minerals. When the grinding fineness of -0.074 mm accounts for 90%, the monomer dissociation of magnetite, hematite, bastnaesite and monazite is only 51.54%, 58.36%, 52.27% and 63.64%, respectively. Therefore, it is an effective way to solve the problem of low concentrate grade and recovery rate by strengthening fine grinding and high efficiency separation of fine particles.
-
Key words:
- Bayan Obo /
- mica type /
- iron /
- rare earth /
- occurrence state
-

-
表 1 矿石多元素分析结果
Table 1. Multi-element analysis results of the ore
/% 成分 TFe REO Nb2O5 F Na2O K2O MgO CaO BaO SiO2 ThO2 Sc2O3 P S 含量 17.48 2.46 0.54 4.81 1.32 3.04 5.12 8.96 2.39 28.62 0.04 0.01 0.46 1.44 表 2 矿石的主要矿物组成及相对含量
Table 2. Mineral composition and the relative content of the ore
/% 名称 磁黄铁矿 赤铁矿 磁铁矿 黄铁矿 菱铁矿 氟碳铈矿 萤石 铌铁矿 独居石 绿泥石 重晶石 辉石 云母 长石 闪石 褐帘石 磷灰石 黄河矿 方解石 白云石 含量 0.45 11.04 9.18 1.19 0.68 1.40 4.55 1.31 0.62 8.19 3.91 3.25 43.03 10.12 1.28 0.83 0.86 0.02 0.64 0.56 表 3 原矿铁化学物相分析结果
Table 3. Iron phase analysis results of raw ore
/% 铁物相 含量 分布率 磁铁矿中铁 7.12 41.08 赤铁矿中铁 7.70 44.43 菱铁矿中铁 0.33 1.91 硫化铁中铁 0.74 4.27 硅酸铁中铁 1.44 8.31 合计 17.33 100.00 表 4 稀土在矿物中的分布
Table 4. Distribution of rare earths in minerals
/% 矿物种类 w(REO) 分布率 铁矿物 磁铁矿/假象磁铁矿 1.10 1.61 赤铁矿/假象赤铁矿 0.99 3.65 黄铁矿 0.11 0.01 铌矿物 铌铁矿 1.35 0.04 稀土矿物 氟碳铈矿/氟碳钙铈矿 69.02 47.43 黄河矿 0.01 0.03 独居石 75.76 43.60 其他矿物 萤石 0.42 0.76 云母 40.01 1.29 磷灰石 3.19 0.44 石英/长石 2.36 0.48 钠辉石 0.25 0.03 钠闪石 0.05 0.17 重晶石 0.35 0.28 绿泥石 0.28 0.03 白云石/方解石 0.09 0.15 总和 100.00 表 5 主要矿物的粒度分布
Table 5. Particle size distribution of major minerals
/% 粒度(mm) 磁铁矿 赤铁矿 氟碳铈矿 独居石 个别 累计 个别 累计 个别 累计 个别 累计 +0.20 11.26 100.00 14.06 100.00 0.10~0.20 8.51 88.74 11.67 85.94 0.074~0.10 15.23 80.23 14.49 74.27 0.043~0.074 17.74 65.00 19.47 59.78 14.46 100.00 3.19 100.00 0.02~0.043 12.87 47.26 16.38 40.31 29.67 85.54 25.89 96.78 0.01~0.02 26.31 34.39 18.54 23.93 29.52 55.87 42.42 70.89 -0.01 8.08 8.08 5.39 5.39 26.35 26.35 28.47 28.47 表 6 主要矿物的单体解离度
Table 6. Monomer dissociation degree of major minerals
/% 样品名称 连生特征 单体解离度 与铁矿物连生 与碳酸盐矿物连生 与硅酸盐矿物连生 与稀土矿物连生 与其它矿物连生 磁铁矿 51.54 - 1.70 39.27 2.16 5.33 赤铁矿 58.36 - 0.47 34.96 1.03 5.18 氟碳铈矿 52.27 7.38 0.21 31.14 - 9.00 独居石 63.64 4.02 0.79 28.43 - 3.30 -
[1] 林东鲁, 李春龙, 邬虎林.白云鄂博特殊矿采选冶工艺攻关与技术进步[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2007:103-106.
[2] 余永富, 陈泉源.白云鄂博中贫氧化矿弱磁-强磁-浮选联合流程综合回收稀土研究[J].矿冶工程, 1992, 12(1):58-61.
[3] 李俐.白云鄂博铁矿矿产资源的现状及其开发利用前景[J].包钢科技, 2003, 29(2):1-4.
[4] 马鹏起, 高永生, 徐自来.包头白云鄂博资源的综合利用与环境保护[J].决策咨询通讯, 2009(2):88-91.
[5] 池汝安, 王淀佐.稀土选矿与提取技术[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1996:316.
[6] 柳建勇, 陈林, 马文亮.浅谈白云鄂博铁矿石入选品位降低的可行性[J].中国矿业, 2010(19):367-369.
[7] 樊丽琴, 贾艳.提高白云鄂博氧化矿铁精矿品位的试验研究[J].金属矿山, 2010(11):71-74
[8] 康德伟, 李解, 李保卫.白云鄂博磁选铁精矿提铁降氟试验[J].金属矿山, 2017(9):78-81.
[9] 陈杏婕, 倪文, 范敦城.白云鄂博铁矿石工艺矿物学研究[J].金属矿山, 2015(5):109-113.
[10] 黄小宾, 杨占峰, 王振江.白云鄂博深部稀土尾矿的工艺矿物学[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2019(4):6-8.
[11] 付强, 金建文, 李磊.白云鄂博尾矿库中铁的赋存状态研究[J].矿冶, 2017, 26(3):94-98.
-




 下载:
下载: