Experimental Study on Leaching of Valuable Metals from Purification Residue of Zinc Hydrometallurgy
-
摘要:
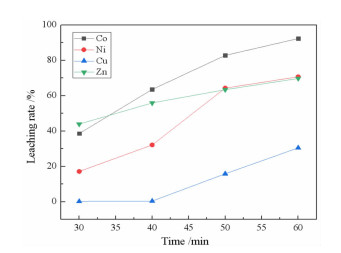
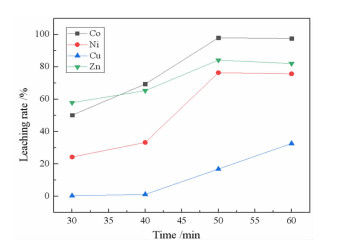
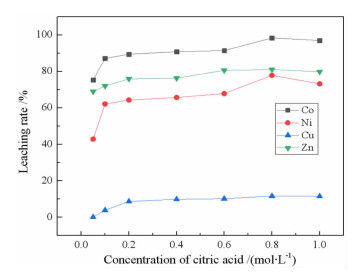
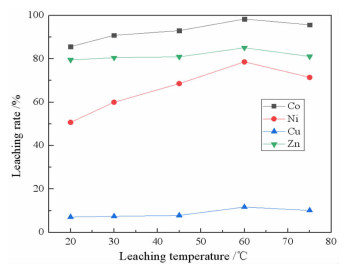
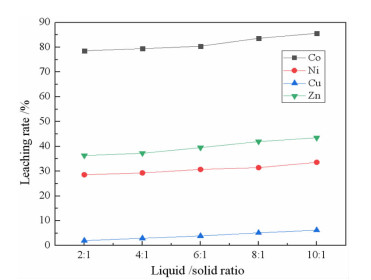
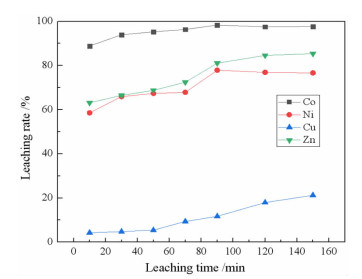
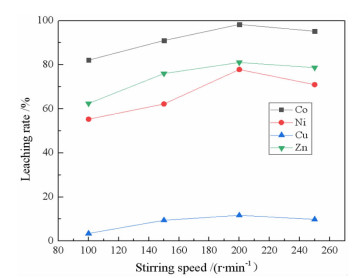
研究了用柠檬酸从湿法炼锌净化渣中回收有价金属的工艺方法。采用单因素浸出试验,探讨了净化渣中有价金属浸出的行为规律。分别考察了柠檬酸浓度、浸出温度、液固比、搅拌速度、pH值和浸出时间对有价金属浸出率的影响。结果表明:在柠檬酸浓度0.8 mol/L、浸出温度60℃、液固比10:1、搅拌速度200 r/min、pH 1.0、浸出时间90 min条件下,锌、镍、铜的浸出率分别为79.60%、75.09%、9.70%,钴的浸出率高达97.64%。本研究为湿法炼锌净化渣的综合回收利用提供了一种新的途径。
Abstract:The process of recovering valuable metals of purification residue from zinc hydrometallurgy with citric acid was studied. The leaching behavior of valuable metals from purification residue was analyzed by single factor test. The effects of citric acid concentration, leaching temperature, ratio of liquid to solid, stirring speed, pH value and leaching time on the leaching rate of valuable metals were investigated. The results showed that the leaching rates of zinc, nickel and copper were 79.60%, 75.09% and 9.70%, respectively, and that of cobalt was as high as 97.64%, under the conditions of citric acid concentration 0.8 mol/L, leaching temperature 60 ℃, ratio of liquid to solid 10:1, stirring speed 200 r/min, pH1.0 and leaching time 90 min. This research provides a new way for comprehensive recovery and utilization of purification residue from zinc hydrometallurgy.
-
Key words:
- zinc hydrometallurgy /
- purification residue /
- citric acid /
- valuable metals /
- leaching
-

-
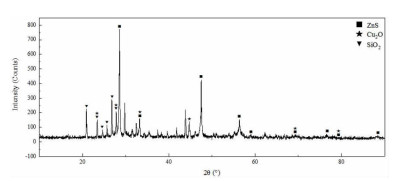
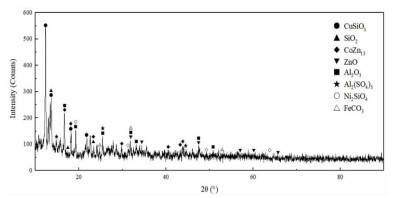
表 1 湿法炼锌净化渣主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical components of purification residue from zinc hydrometallurgy
/% 元素 Co Ni Cu Zn Fe Al 含量 5.98 1.40 0.82 11.04 1.77 0.058 表 2 优化条件下的综合试验结果
Table 2. Comprehensive experimental results under optimized conditions
序号 浸出率/% Co Ni Cu Zn 1 98.34 71.77 7.60 76.94 2 98.52 77.16 9.81 80.77 3 96.07 76.34 11.68 81.09 平均值 97.64 75.09 9.70 79.60 -
[1] 何耀. 锌冶炼工艺现状及有价金属高效回收利用新工艺[J]. 矿冶, 2020, 29(4): 73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2020.04.014
[2] 王振银, 高文成, 温建康, 等. 锌浸出渣有价金属回收及全质化利用研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(11): 1400-1410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD202011002.htm
[3] 汤裕源, 刘丽. 锌冶炼工艺综述与展望[J]. 云南冶金, 2020, 49(6): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2020.06.008
[4] TANG L, TANG C, XIAO J, et al. A cleaner process for valuable metals recovery from hydrometallurgical zinc residue[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 201: 764-773. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.096
[5] 雷霆, 陈利生, 余宇楠. 锌冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012: 6-7.
[6] 蓝碧波, 丁文涛, 申开榜, 等. 从湿法炼锌钴渣中回收锌富集钴试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2018, 37(6): 457-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ201806008.htm
[7] 马进, 何国才, 程亮, 等. 湿法炼锌净化镍钴渣全湿法回收新工艺[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2013, (12): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201312004.htm
[8] 李贺, 陈露露, 王海北, 等. 锌冶炼净化钴渣综合回收工艺研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019, (9): 69-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201909012.htm
[9] ASHTARI P, POURGHAHRAMANI P. Hydrometallurgical recycling of cobalt from zinc plants residue[J]. Journal of Material Cycles & Waste Management, 2018, 20: 155-166. doi: 10.1007/s10163-016-0558-0
[10] BEHNAJADY B, MOGHADDAM J. Selective leaching of zinc from hazardous As-bearing zinc plant purification filter cake[J]. Chemical Engineering Research Design, 2017, 117: 564-574. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2016.11.019
[11] 王艳, 周春山. 铅锌冶炼渣浸出液提取镓的研究[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2001, (4): 7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2001.04.002
[12] 周涛, 徐莉萍, 范百林, 等. 从废旧钴镍锰酸锂电池中回收有价金属的新工艺[J]. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(1): 6-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OXZG201701002.htm
[13] 方兆珩. 浸出[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007: 1-3.
[14] LI Q, ZHANG B, MIN X B, et al. Acid leaching kinetics of zinc plant purification residue[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 2786-2791. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62798-3
[15] RUSEN A, SUNKAR A S, TOPKAYA Y A. Zinc and lead extraction from Cinkur leach residues by using hydrometallurgical method[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93: 45-50. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.02.018
[16] PENG P, XIE H Q, LU L Z. Leaching of a sphalerite concentrate with H2SO4-HNO3 solutions in the presence of C2Cl4[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 80: 265-271. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2005.08.004
[17] 郑莹, 胡晨, 周洁, 等. 柠檬酸浸出废旧锂离子电池回收有价金属研究[J]. 电源技术, 2019, 43(10): 1653-1683. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2019.10.020
[18] 朱显峰, 赵瑞瑞, 常毅, 等. 废旧锂离子电池三元正极材料酸浸研究[J]. 电池, 2017, 47(2): 105-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DACI201702014.htm
[19] LI L, GE J, WU F, et al. Recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent lithium ion batteries using organic citric acid as leachant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 176(1/2/3): 288-293. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19954882
[20] GOLMOHAMMADZADEH R, FARAJI F, RASHCHI F. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs) using organic acids as leaching reagents: A review[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 2018, 136: 418-435. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921344918301629
[21] AHN J W, AHN H J, KIM M W. Chemical Leaching of Co, Cu, Ni, Al, Fe by Organic acid from Cobalt Concentrate[J]. Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling, 2011, 20(6): 63-70. doi: 10.7844/kirr.2011.20.6.063
[22] HUANG K, INOUE K, HARADA H, et al. Leaching of heavy metals by citric acid from fly ash generated in municipal waste incineration plants[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2011, 13: 118-126. doi: 10.1007/s10163-011-0001-5
[23] JIANG H, LI T Q, HAN X, et al. Effects of pH and low molecular weight organic acids on competitive adsorption and desorption of cadmium and lead in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2012, 184: 6325-6335. doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-2422-y
-



 下载:
下载: