High-temperature Phase Reconstruction Process of Typicalpolymetallic Ferruginous Manganese Ores and Preparation of Mnferrite Material
-
摘要:
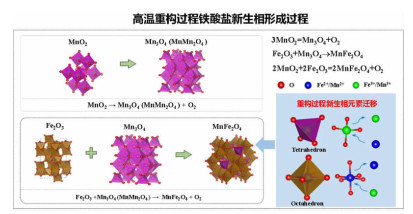
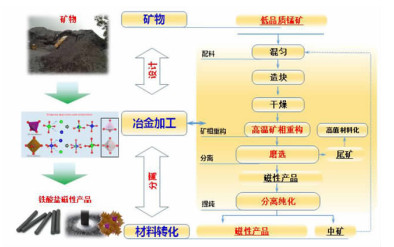
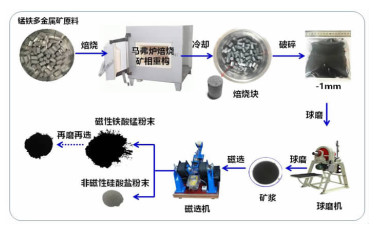
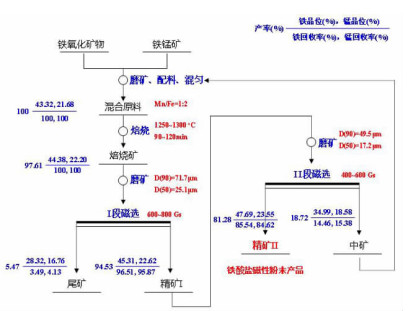
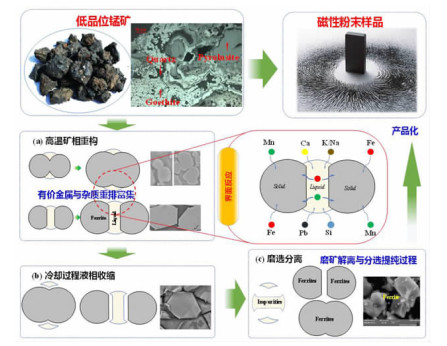
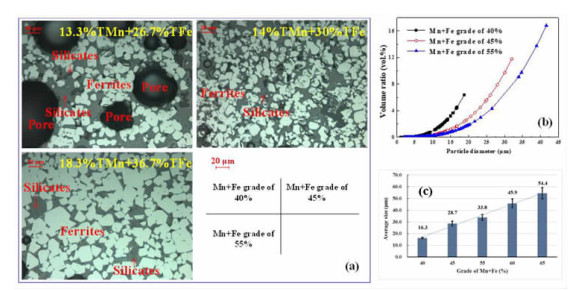
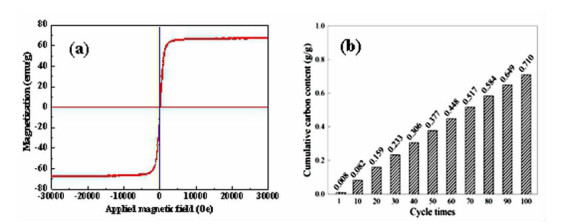
在典型金属矿产资源铁锰矿综合利用的过程中,锰、铁等成分易生成强磁性复合铁酸盐,导致其综合利用过程中有价组元分步分离难度大。本研究改变传统铁锰矿资源锰、铁需预先分离后分别利用的认识,提出铁锰矿高温矿相重构同步回收锰铁有价组元并制备铁酸盐材料的技术思路。本文对铁锰矿冶金材料化加工过程中的矿相重构原理、新生相颗粒尺寸表征、矿相重构-磨选机理、分选磁性样品的性能进行了综述与分析。本次课题为"资源-冶金-材料一体化"研究的典型案例,可为金属矿资源的短流程材料化高值利用提供新的途径,也可以为其它类型低品质资源的综合利用提供技术借鉴。
Abstract:During the existing comprehensive utilization methods of ferruginous manganese ore, it's found that the spinel-type composite ferrites with strong magnetism are readily generated from the Mnand Fe constitutes resulting in the poor separation of the valuable metals. In this study, thetraditionalseparationof Mnand Feischanged, andtheextraction of valuable components and preparation of manganese ferrites synchronously from the ferruginous manganeseore by mineral phase reconstructionis put forward. The principle of mineral phase reconstruction, the particle size characterization of new phase, the mechanism of mineral phase reconstruction and grinding and separation, and the performance of separated magnetic products are reviewed in this work. This study is a typical case research of mineral-metallurgy-materials integration research, which can provide a short process for the high-efficiency utilizationof metallic mineral resources, and it also provides a technical reference for the comprehensive utilization of other types of low-grade polymetallic ore resources.
-
Key words:
- ferruginous manganese ores /
- phase reconstruction /
- newphase /
- separation
-

-
[1] 曹新元, 吕古贤, 朱裕生. 我国主要金属矿产资源及区域分布特点[J]. 资源产业, 2004, 6(4): 20-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZIYU200404005.htm
[2] 孙宏伟, 王杰, 任军平, 等. 全球锰资源现状及对我国可持续发展建议[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(6): 169-174. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2021&filename=KCBH202006025&v=bWlZEyt9HxuHuEWARdIbKUlpPq8EeU66HMUo9gbwkU3sp%25mmd2FW9lOva1vXXLE7DXwYm
[3] 梅光贵, 张文山, 曾湘波, 等. 中国锰业技术[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2011.
[4] U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, Mineral commodity summaries 2021[R]. https: //doi.org/10.3133/mcs2021.
[5] 朱志刚. 中国锰矿资源开发利用现状[J]. 中国锰业, 2016, 34(2): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201602002.htm
[6] 刘陟娜, 许虹, 王秋舒, 等. 中国锰矿供需现状及可持续发展建议[J]. 资源与产业, 2015, 17(6): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZIYU201506010.htm
[7] LIU BINGBING, XUEYUBIN, HANGUIHONG, et al. An alternative and clean utilisation of refractory high-phosphorus oolitic hematite: P for crop fertiliser and Fe for ferrite ceramic[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 299, (2021): 126889. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652621011082
[8] NIYONZIMA1J. C., LUO LIQUN, EDO E. E., et al. Mineralogical characterization and optimization of Fe and Mnthrough roast-leaching of ferromanganese ore[J]. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-021-00390-2. doi: 10.1007/s42461-021-00390-2
[9] GAOLIHUA, LIU ZHENGGEN, PAN YUZHU, et al. Systematic study on separation of Mn and Fe fromferruginous manganese ores by carbothermicreduction roasting process: Phase transformationand morphologies[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(6): 5591-5609. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.028
[10] SINGH V, BISWAS A, SAHU N. Development of a smelting reduction process for low-gradeferruginous manganese ores to produce valuable syntheticmanganese ore and pig iron[J]. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration, 2020, 37: 1681-1692. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/343412220_Development_of_a_Smelting_Reduction_Process_for_Low-Grade_Ferruginous_Manganese_Ores_to_Produce_Valuable_Synthetic_Manganese_Ore_and_Pig_Iron
[11] TRIPATHY S. K, BANERJEE P. K, SURESH N. Effect of desliming on the magnetic separation of low-grade ferruginous manganese ore[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015, 22(7): 661-673. doi: 10.1007/s12613-015-1120-0
[12] BAFGHI M. S, ZAKERI A, GHASEMI Z, et al. Reductive dissolution of manganese ore in sulfuric acid in the presence of iron metal[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 90(2): 207-212. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X07001569
[13] NAIK P. K, SUKLA L. B, DAS S. C. Aqueous SO2 leaching studies on nishikhal manganese ore through factorial experiment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 54(s2/s3): 217-228. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X99000754
[14] SU H, WEN Y, WANG F, et al. Reductive leaching of manganese from low-grade manganese ore in H2SO4 using cane molasses as reductant[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(3/4): 136-139. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X08000054
[15] TIAN X, WEN X, YANG C, et al. Reductive leaching of manganese from low-grade manganese dioxide ores using corncob as reductant in sulfuric acid solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(3/4): 157-160. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X09002862
[16] HARIPRASAD D, DASH B, GHOSH M. K, et al. Leaching of manganese ores using sawdust as a reductant[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(14): 1293-1295. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2007.07.013
[17] MPHO M, SAMSON B, AYO A. Evaluation of reduction roasting and magnetic separation for upgrading Mn/Fe ratio of fine ferromanganese[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2013, 23(4): 537-541. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.07.012
[18] ZHANG YUANBO, LIU BINGBING, YOU ZHIXIONG, et al. Consolidation behavior of high-Fe manganese ore sinters with natural basicity[J]. Minerals Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2016, 37(5): 333-341. doi: 10.1080/08827508.2016.1218870
[19] AHMED A, GHALI S, EL-FAWAKHRY M. K, et al. Silicomanganese production utilising local manganese ores and manganese rich slag[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2014, 41(4): 310-320. doi: 10.1179/1743281213Y.0000000173
[20] ZHANG YUANBO, ZHAO YI, YOU ZHIXIONG, et al. Manganese extraction from high-iron-content manganese oxide ores by selective reduction roasting-acid leaching process using black charcoal as reductant[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(7): 2515-2520. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2780-7
[21] ZHANG YUANBO, YOU ZHIXIONG, LI GUANGHUI, et al. Manganese extraction by sulfur-based reduction roasting-acid leaching from low-grade manganese oxide ores[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 133: 126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.01.003
[22] YOU ZHIXIONG, LI GUNAGHUI, ZHANG YUANBO, et al. Extraction of manganese from iron rich MnO2 ores via selective sulfation roasting with SO2 followed by water leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015(156): 225-231. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X15300244
[23] GAO Y. B, OLIVAS-MARTINEZ M, SOHN H. Y, et al. Upgrading of low-grade manganese ore by selective reduction of iron oxide and magnetic separation[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 201243(6): 1465-1475. doi: 10.1007/s11663-012-9731-6
[24] 李献锐, 王娜, 焦留国, 等. 纳米级铁酸锰制备、表征及对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附作用[J]. 河北师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 37(6): 614-617. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1565.2013.06.011
[25] 王立民. 溶剂热法合成不同形貌MnFe2O4纳米颗粒及其在污水处理中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(7): 763-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WGCL201407017.htm
[26] CHEN Y, WANG Z, ZHONG Z. CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy production and foreign trade in China[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 131: 208-216. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.07.047
[27] RANJITH KUMAR E, SIVA P R P, SARALA DEVI G, et al. Structural, dielectric and gas sensing behavior of Mn substituted spinel MFe2O4 (M=Zn, Cu, Ni, and Co) ferrite nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Magnetism & Magnetic Materials, 2015, 398(1): 281-288.
[28] 张元波, 刘兵兵, 李光辉, 等. 一种制备锰铁尖晶石材料的方法: ZL201610801954.1[P]. 2017-12-15.
[29] 张元波, 刘兵兵, 苏子键, 等. 一种低品位铁锰矿火法选矿方法: ZL201710812352.0[P]. 2018-10-26.
[30] LIU BB, ZHANG L, ZHANG B, et al. Characterizations on phase reconstruction, microstructure evolution and separation of magnetic ferrite ceramics from low-grade manganese ores by novel uphill reaction diffusion and magnetic separation[J]. Mater. Charact. 2021, 175: 111028. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111028
[31] LIU BB, ZHANG L, ZHANG YB., et al. Innovative methodology for co-treatment of mill scale scrap and manganese ore via oxidization roasting-magnetic separation for preparation of ferrite materials[J]. Ceram. Inter. 2021, 47: 6139-6153. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.193
[32] LIU BB, ZHANG YB., WANG J, et al. New understanding on separation of Mn and Fe from ferruginous manganese ores by the magnetic reduction roasting process[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 444: 133-144. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.234
[33] LIU BB, ZHANG YB., SU ZJ, et al. Formation mechanism of MnxFe3-xO4 by solid-state reaction of MnO2 and Fe2O3 in air atmosphere: Morphologies and properties evolution[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 313: 201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.03.012
[34] LIU BB, ZHANG YB., WANG J, et al. Investigations on the MnO2-Fe2O3 system roasted in air atmosphere[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2017, 28: 2167-2176. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2017.05.023
[35] KELLERHALS R, SHAW J, ARORA V. K. On grain size from thin sections[J]. Journal of Geology, 1975, 83(1): 79-96. doi: 10.1086/628046
[36] SAHAGIAN D. L, PROUSSEVITCH A. A. 3D particle size distributions from 2D observations: stereology for natural applications[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1998, 84(3): 173-196. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377027398000432
[37] CHAYES F. On the bias of grain-size measurements made in thin section[J]. Journal of Geology, 1950, 58(2): 156-160. doi: 10.1086/625716
[38] LUO J, LI G, PENG Z, et al. Phase evolution and Ni-Fe granular growth of saprolitic laterite ore-CaO mixtures during reductive roasting[J]. JOM, 2016, 68(12): 3015-3021. doi: 10.1007/s11837-016-2118-4
[39] LI G, LUO J, PENG Z, et al. Effect of quaternary basicity on melting behavior and ferronickel particles growth of saprolitic laterite ores in Krupp-Renn process[J]. ISIJ International, 2015, 55(9): 1828-1833. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-058
[40] ZHANG YUANBO, WANG JIA, SU ZIJIAN, et al. Spinel MnFe2O4 nanoparticles (MFO-NPs) for CO2 cyclic decomposition prepared from ferromanganese ores[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46: 14206-14216. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.229
-




 下载:
下载: