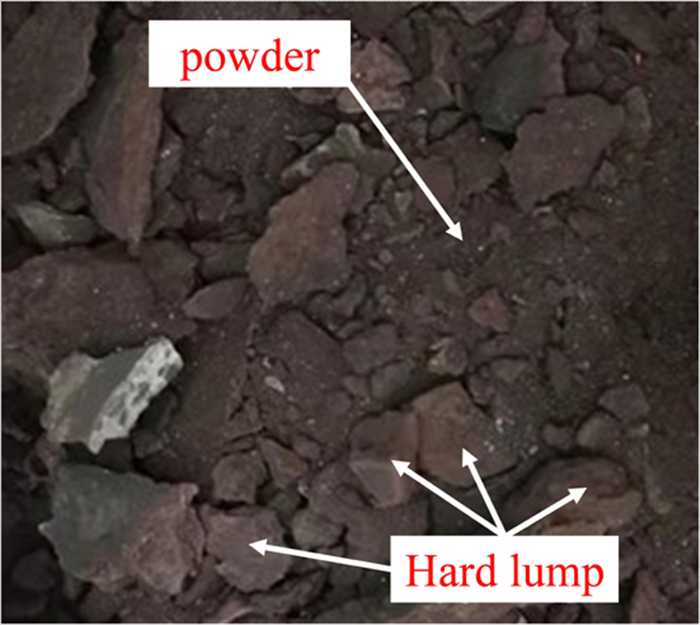
Process Mineralogy Study on Hard Lump Forming in Copper Smelting Flue of ISA Furnace
-
摘要:
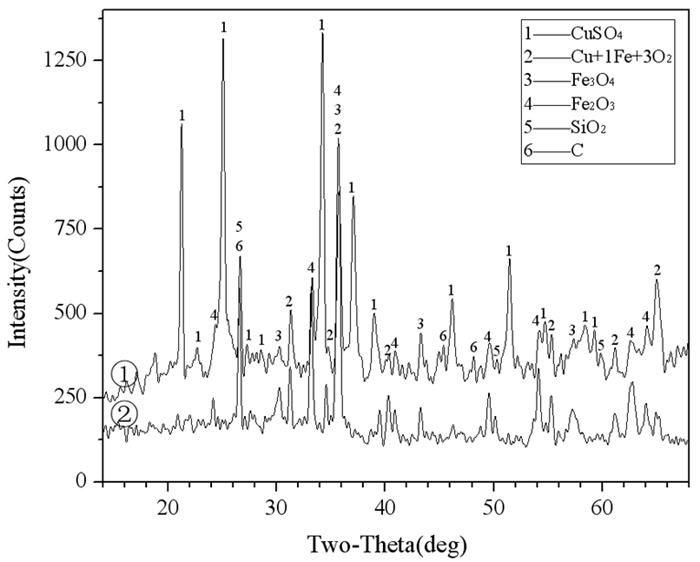
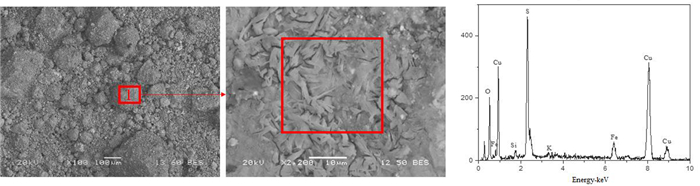
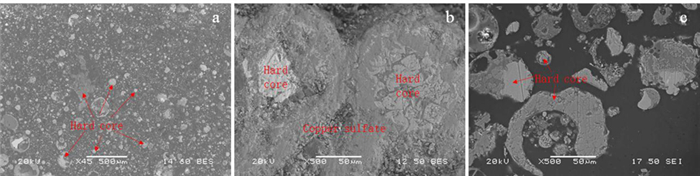
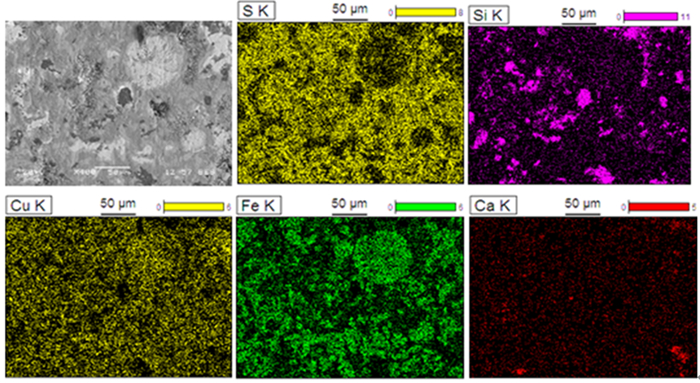
艾萨炉铜熔炼过程中因烟道结渣造成刮板磨损严重,烟气流通受阻,影响生产效率和稳定性。从工艺矿物学角度,通过考察艾萨炉余热锅炉水平烟道产物中主要元素铜、铁、硫等的赋存状态,以及结渣的物相组成和结构特征,对烟道结渣原因进行分析。结果表明,烟道结渣中铁酸铜、赤铁矿、磁铁矿、冰铜及硅酸盐玻璃相含量明显偏高,且常以核的形式黏附并胶结硫酸铜形成硬度相对较高的结渣,这主要由生产过程炉渣、冰铜的强烈喷溅所致,又因烟道气流温度及含氧量偏高,使结渣反复黏附并二次反应而不断长大。依据研究结果,通过在生产中控制艾萨炉喷枪流量及炉内负压,适当降低烟尘温度,并扩大垂直烟道直径等措施,有效改善烟道结渣问题。
Abstract:During the process of copper smelting in Isa furnace, the scraper was worn badly due to hard lump formed in flue, and the flue gas circulation was blocked, which affected the production efficiency and stability. In this paper, from the perspective of process mineralogy, the occurrence state of copper, iron, sulfur and other main elements from the residual heat boiler flue products of the Isa furnace, as well as the mineral phase composition and structure characteristics of hard lump were examined. And the factors leading to the formation of hard lump in flue were analyzed. The results show that the content of copper ferrite, hematite, magnetite, matte and silicate glass phase in hard lump is obviously high. And these mineral phases often adhere and cement copper sulfate in the form of nuclei to form slags with relatively high hardness, which was related to the strong splashing of slag and matte during smelting. Due to the high temperature and oxygen content of the flue gas flow, the slagging continues to grow accompanied by repeated adhesion and secondary reactions. According to the research results, the slagging problem in the flue can be effectively improved by controlling the flow of the spray gun and the negative pressure in the furnace, appropriately reducing the temperature of the dust and expanding the diameter of the vertical flue.
-
Key words:
- isa furnace /
- copper smelting /
- dust /
- flue hard lump /
- process mineralogy
-

-
表 1 原料(A)、可溶物蒸干物质(B)及水浸渣(C)的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of the sample, water-soluble substance and water leaching residue
/% 样品 Cu S Fe Bi SiO2 Al2O3 CaO K2O MgO A 26.14 11.76 15.06 1.95 7.36 1.25 1.56 0.97 0.75 B 35.21 15.27 3.55 < 0.1 < 0.1 < 0.1 0.87 0.85 0.53 C 11.21 2.57 34.72 7.89 7.78 1.31 1.04 < 0.1 0.87 -
[1] 易光明, 李熹. 艾萨炉在铜冶炼过程中的应用[J]. 有色金属文摘, 2016, 31(1): 141-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJW201601079.htm
[2] 付江, 王华. 艾萨熔池熔炼的应用与优化[J]. 工业加热, 2007(1): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYJR200701010.htm
[3] 张鑫, 惠兴欢, 朱江, 沈强华. 控制艾萨炉余热锅炉过渡段结渣的生产实践[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2013, 42(3): 12-14+18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL201303004.htm
[4] 赵璧, 李发彪, 葸军, 张宇云. 艾萨铜熔炼高温段烟道结渣处理[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019(8): 19-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201908008.htm
[5] 杨毓和. 控制艾萨炉余热锅炉结渣探讨[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2007(5): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL200705005.htm
-




 下载:
下载: