Mechanism and Application of Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans in Leaching of Metal Sulfide Ores
-
摘要:
氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, T.f菌)在矿产资源全面节约和高效利用领域起着重要作用。概述了T.f菌生理学特性、浸出机理和及其浸矿过程影响因素,重点论述T.f菌浸矿的直接、间接机理,并梳理双氧化系统(铁氧化系统和硫氧化系统)的研究近况和细菌产生的胞外分泌物(Extracellular Polymeric Substances, EPS)在浸矿过程中的作用。最后阐述T.f菌在各类金属硫化物提取中的研究进展,评述了各类应用研究目前有待深入的方向,旨在为今后低品位矿产资源的高效提取与利用提供支撑。
Abstract:Theiobacillus ferrooxidans(T.f) plays an important role in the overall conservation and efficient use of mineral resources. There is a lot of research on the use of T.f bacteria to extract minerals with valuable metals, whereas there is a lack of systematic summary. Therefore, this paper introduces the physiological characteristics of T.f bacteria, the mechanism of immersion and the influencing factors of its immersion process. In addition, the direct and indirect mechanisms of T.f bacteria immersion are discussed, and the research status of the double oxidation system (iron oxidation system and sulfur oxidation system) and the role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances(EPS) produced by bacteria in the immersion process are discussed. Finally, the research progress of T.f bacteria in the extraction of various types of metal sulphides is expounded, and the direction of various kinds of applied research is still to be furthered, with the aim of providing a theoretical basis for the development direction of the efficient extraction and utilization of low-grade mineral resources in the future.
-

-
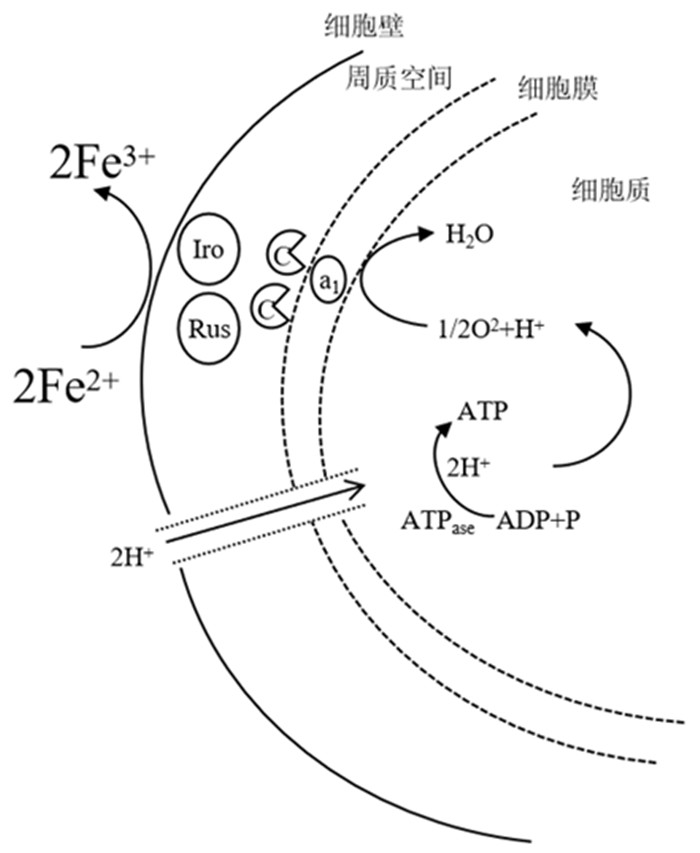
图 1 T.f菌浸出硫化矿的直接作用示意图(a)和电子传递示意图(b)[22]
Figure 1.
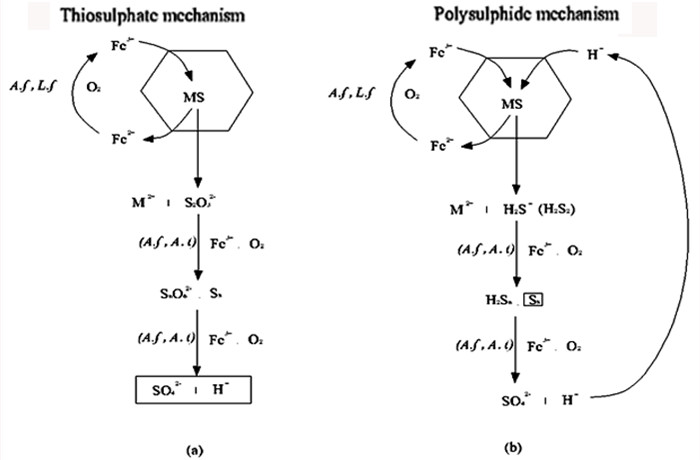
图 3 基于硫化矿性质的硫代硫酸盐溶解和多聚硫化氢溶解途径示意图[35]
Figure 3.
表 1 T.f菌在各类金属硫化矿浸出中的应用进展
Table 1. Research progress on Thiobacillus ferrooxidans of leaching of metal sulfide ores
浸矿类型 主要研究内容 小结 金矿 工艺参数调整[68]
浮选药剂影响[69]
浸矿机理研究[70]
诱变菌种(紫外线、X射线诱变等[71])研究从工艺到机理再到菌种诱变,旨在提高浸出效率。目前主要研究难点在于高温T.f菌的筛选以及各类浮选药剂的抑制机理尚不明确 铜矿 浸矿机理研究[72-73]
影响因素研究[64]
EPS研究[74]研究主要集中于影响因素和机理研究。其中直接作用在浸出中占主导,此外浸出金属离子会促进EPS的生成,但是EPS在浸出中具体起着什么作用还有待深入研究 钼镍矿 工艺参数和浸矿机理研究[75] 研究关注细菌驯化、工艺参数调整和浸矿机理研究。试验结果表明细菌对不同重金属的浸出率不同,初步证明细菌浸矿过程中存在直接和间接机理。但未深入研究EPS 铊矿 混合菌浸出[76] 初步探讨混合菌浸出铊矿效率更高 锑矿 工艺参数调整[77] 通过正交试验证明pH=3, t=25 ℃, 矿浆质量浓度c=20%时锑矿浸出量达到最大,但是没有研究浸出机理 锰矿 影响因素探究[78]
诱变菌种[79]
生物反应器构建[80]研究从化学诱变、紫外诱变驯化菌种,探讨浸出过程中的影响因素和以软性塑料纤维为填料构建固定化生物反应器高效浸出低品位锰矿。浸出机理方面研究欠缺 -
[1] 栾和林, 姚文, 吴萌. 湿法冶金中的一些污染新问题的探讨[J]. 矿冶, 2002, 11(z1): 281-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2002.z1.075
[2] 姜金龙, 戴剑峰, 冯旺军, 等. 火法和湿法生产电解铜过程的生命周期评价研究[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2006(1): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2006.01.005
[3] 周姗, 栗树珍, 钟慧, 等. 冶金模式微生物Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans表面质子吸附特性的研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(4): 1-8. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=6c1f8cab-ff72-4775-aaa6-a8b13e885eb1
[4] SAND W, GEHRKE T. Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iron(Ⅲ) ions and acidophilic bacteria[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2006, 157(1): 49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2005.07.012
[5] R.E. 布坎南, N.E. 吉本斯. 伯杰细菌鉴定手册(中文第八版)[M]. 中国科学院微生物研究所《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》翻译组. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.
[6] 庄贺, 沈俊剑, 黎俊, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌的分离鉴定及培养条件优化[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(7): 1131-1137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT201307002.htm
[7] 高健, 彭宏, 李邦梅, 等. 两株不同铁氧化细菌合成的沉淀差异性分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007(3): 453-458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2007.03.018
[8] 王艳锦, 郑正, 周培国, 等. 不同培养基中氧化亚铁硫杆菌生长及沉淀研究[J]. 生物技术, 2006, 16(4): 70-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-311X.2006.04.028
[9] JENSEN A B, WEBB C. Ferrous sulphate oxidation using thiobacillus ferrooxidans: a review[J]. Process Biochemistry, 1995, 30(3): 225-236. doi: 10.1016/0032-9592(95)85003-1
[10] 宋永伟, 王蕊, 杨琳琳, 等. 三种次生矿物固定A. ferrooxidans的Fe2+氧化及成矿性能比较[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(5): 2073-2080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.025
[11] 田祖源, 李浩东, 魏茜, 等. Cu2+、Fe2+和Fe3+对中等嗜热混合菌浸出黄铜矿的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(1): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ202101019.htm
[12] 邓明强, 白静, 白建峰, 等. 影响嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌生长及生物浸出效率的研究进展[J]. 湿法冶金, 2016, 35(3): 171-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ201603001.htm
[13] RAWLINGS D E, KUSANO T. Molecular genetics of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. [J]. Microbiological Reviews, 1994, 58(1): 39-55. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.39-55.1994
[14] LIU M, BRANION R, DUNCAN D W. The effects of ferrous iron, dissolved oxygen, and inert solids concentrations on the growth of thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1988, 66(3): 445-451. doi: 10.1002/cjce.5450660315
[15] 李先艳. 高性能氧化亚铁硫杆菌菌株的诱变与培育[D]. 西安: 西安工程大学, 2019.
[16] 陶语若. 抑制氧化亚铁硫杆菌作用下沉淀生成的研究[J]. 广州化工, 2012, 40(9): 111-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2012.09.039
[17] TUOVINEN O H, NIEMELA S I, GYLLENBERG H G. Effect of mineral nutrients and organic substances on the development of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 13(4): 517-527. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bit.260130406
[18] 刘欣伟, 冯雅丽, 李浩然, 等. 镁离子浓度对氧化亚铁硫杆菌生长动力学的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(8): 2353-2359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201208030.htm
[19] GOMEZ J M, GARO I. Kinetic equation for growth of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in submerged culture over aqueous ferrous sulphate solutions[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 1996, 48(1-2): 147-152. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(96)01504-0
[20] BOON M, RAS C, HEIJNEN J J. The ferrous iron oxidation kinetics of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in batch cultures[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1999, 51(6): 813-819. doi: 10.1007/s002530051467
[21] SHI J, WANG D S, ZOU K Y. Domestication and Kinetics Parameters of Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans in High Concentration of Uranium[J]. Journal of Nantong University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 13(3): 24-27. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7422499_Kinetics_of_Iron_Oxidation_by_Thiobacillus_ferrooxidans
[22] HUANG T, LI D W. Presentation on mechanisms and applications of chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching in biohydrometallurgy-a presentation[J]. Biotechnology Reports, 2014, 4(1): 107-119. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2215017X1400037X
[23] NT A, RSS B, CDH A. Microbial removal of sulphur from petroleum coke (petcoke)[J]. Fuel, 2019, 235: 1501-1505. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.072
[24] 伍赠玲. 黄铁矿对硫砷铜矿化学浸出的促进作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(11): 2376-2382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201811024.htm
[25] FOWLER T A, CRUNDWELL F K. Leaching of zinc sulfide by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: experiments with a controlled redox potential indicate no direct bacterial mechanism[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(10): 3570-3575. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.10.3570-3575.1998
[26] 梁方圆, 吴冉冉, 曹昌丽, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌的胞外电子传递研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(2): 372-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDXH201402030.htm
[27] 何正国, 李雅芹, 周培瑾. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌的铁和硫氧化系统及其分子遗传学[J]. 微生物学报, 2000(5): 563-566. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2000.05.021
[28] 田克立, 林建群, 张长铠, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌铁氧化系统分子生物学研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2002, 29(1): 85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2654.2002.01.021
[29] 武华平. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌及其在环境工程中的应用[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 2005, 22(4): 18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7162.2005.04.005
[30] VERA M, SCHIPPERS A, SAND W. Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation—part A[J]. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 2013, 97(17): 7529-7541. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4954-2
[31] LI Y, KAWASHIMA N, LI J, et al. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite[J]. Adv Colloid Interface, 2013, 197/198: 1-32. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23791420/
[32] NARULA N, REINICKE M, HAFERBURG G, et al. Plant-microbe interaction in heavy-metal-contaminated soils[C] // Kothe E, Varma A. Bio-geo interactions in heavy metal-contaminated soils. Springer, Heidelberg, 2012: 143-162.
[33] QUATRINI R, APPIA-AYME C, DENIS Y, et al. Insights into the iron and sulfur energetic metabolism of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by microarray transcriptome profiling[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/2/3/4): 263-272. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X06000971
[34] WANG R, LIN J, LIU X, et al. Sulfur oxidation in the acidophilic autotrophic acidithiobacillus spp[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019(9): 3290. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30687275/
[35] TAO H, LI D. Presentation on mechanisms and applications of chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching in biohydrometallurgy a presentation[J]. Biotechnology Reports, 2014, 4(1): 107-119. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2215017X1400037X
[36] WAGNER T, KOCH J, ERMLER U, et al. Methanogenic heterodisulfide reductase (HdrABC-MvhAGD) uses two noncubane[4Fe-4S] clusters for reduction[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6352): 699-703. doi: 10.1126/science.aan0425
[37] LIU L, STOCKDREHER Y, KOCH T, et al. Thiosulfate transfer mediated by DsrE/TusA homologs from acidothermophilic sulfur-oxidizing archaeon metallosphaera cuprina[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(39): 26949-26959. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.591669
[38] HOUGHTON J I, STEPHENSON T. Effect of influent organic content on digested sludge extracellular polymer content and dewaterability[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(14): 3620-3628. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00055-6
[39] HC A, JIA W B, BT A, et al. Generation behavior of extracellular polymeric substances and its correlation with extraction efficiency of valuable metals and change of process parameters during bioleaching of spent petroleum catalyst[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 275: 130006. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130006
[40] 皋德祥, 邓欢欢, 张明华, 等. 微生物胞外聚合物的研究进展[J]. 温州医学院学报, 2012, 42(3): 297-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2138.2012.03.030
[41] YI Q, WU S, SOUTHAM G, et al. Acidophilic iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, drives alkaline pH neutralization and mineral weathering in Fe ore Tailings. [J]. Environmental science & technology, 2021, 55: 8020-8034. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34043324/
[42] 余志波, 刘亚洁, 吴静琳, 等. 生物浸矿过程中细菌胞外聚合物的作用研究进展[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2016(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2016.02.001
[43] RAMÍREZ P, GUILIANI N, VALENZUELA L, et al. Differential protein expression during growth of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on ferrous iron, sulfur compounds, or metal sulfides[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(8): 4491-4498. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15294777/
[44] VARDANYAN A, VARDANYAN N, KHACHATRYAN A, et al. Adhesion to mineral surfaces by cells of leptospirillum, acidithiobacillus and sulfobacillus from armenian sulfide ores[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(2): 69. doi: 10.3390/min9020069
[45] SAAVEDRA A, AGUIRRE P, GENTINA J C. Climbing the hill: The implications of a two-step adaptation on biooxidation of ferrous ion at high total iron concentrations by At. ferrooxidans[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 197: 105486. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105486
[46] GAO X, LIU X, FU C, et al. Novel Strategy for Improvement of the Bioleaching Efficiency of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Based on the AfeI/R Quorum Sensing System[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(3): 222. doi: 10.3390/min10030222
[47] ZENG W, LI F, WU C, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) in toxicity response of soil bacteria Bacillus sp. S3 to multiple heavy metals[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 43(1): 153-167. doi: 10.1007/s00449-019-02213-7
[48] HARNEIT K, GÖKSEL A, KOCK D, et al. Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/2/3/4): 245-254. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X06000983
[49] 郑蕾, 丁爱中, 王金生, 等. 不同组成活性污泥胞外聚合物吸附Cd2+, Zn2+特征[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(10): 2850-2855. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.10.029
[50] 杨洪英, 王胜利, 佟琳琳, 等. 微生物胞外聚合物在浸矿过程中作用的研究进展[J]. 有色金属, 2010, 62(3): 103-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2010.03.024
[51] YUAN X, YUAN C, GONG W, et al. The depression of pyrite flotation by thibacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Materials ence Edition), 2000, 15(1): 60-65.
[52] PIROG T P, KORZHB Y V, SHEVCHUKB T A. The effect of cultivation conditions on the physicochemical properties of the exopolysaccharide ethapolan[J], 2009, 45(1): 50-55.
[53] DIGNAC M F, URBAIN V, RYBACKI D, et al. Chemical description of extracellular polymers: implication on activated sludge floc structure[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 38(8/9): 45-53. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0273122398006763
[54] 袁冬琴, 王毅力. 活性污泥胞外聚合物(EPS)的分层组分及其理化性质的变化特征研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(10): 3522-3528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201210036.htm
[55] 王利, 温建康. 嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌胞外聚合物浸矿作用研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2011, 40(7): 86-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201107027.htm
[56] 虞艳云. 胞外聚合物在含铁矿物同微生物界面过程中的作用研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014.
[57] DUNCAN D W, TRUSSELL P C, WALDEN C C. Leaching of Chalcopyrite with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Effect of Surfactants and Shaking[J]. Applied Microbiology, 1964, 12(2): 122-126. doi: 10.1128/am.12.2.122-126.1964
[58] 王超远. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌浸出硫化铜矿试验研究[D]包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2020.
[59] GUO Y, HUANG P, ZHANG W, et al. Leaching of heavy metals from Dexing copper mine tailings pond[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(10): 3068-3075. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62835-6
[60] LIZAMA H M, SUZUKI I. Rate equations and kinetic parameters of the reactions involved in pyrite oxidation by thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1989, 55(11): 2918-2923. https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC203191
[61] LIZAMA H M, SUZUKI I. Bacterial leaching of a sulfide ore by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans part Ⅱ: Column leaching studies[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1989, 33(3): 301-310.
[62] 邓蓉, 张小云, 张梦雪, 等. 嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌培养及其影响因素[J]. 湘潭大学自然科学学报, 2014(4): 67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5900.2014.04.013
[63] 金吉梅. 微生物强化浸出氧化铜矿的试验研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2010.
[64] 李靓洁, 董发勤, 谌书, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌浸取黄铜矿石影响因素的试验研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(3): 449-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201203015.htm
[65] PÉCOU E, MAASS A, REMENIK D, et al. A mathematical model for copper homeostasis in Enterococcus hirae[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2006, 203(2): 222-239. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.04.009
[66] 马骏, 汪菊香, 武彪, 等. 晶体结构对黄铜矿、黄铁矿生物浸出差异性影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(10): 2898-2904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201510029.htm
[67] NIE Z, ZHANG W, LIU H, et al. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite with different crystal phases by Acidianus manzaensis[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(3): 617-624. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64971-X
[68] 刘新艳, 刘丹丹, 张鸣昕. 提高金矿生物氧化细菌耐温性能试验研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2015(5): 48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2015.05.011
[69] 董颖博, 林海, 陆琳斐, 等. 浮选药剂对嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌活性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2011(6): 1662-1668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2011.06.028
[70] D·内斯托, 向平, 肖力子. 用氧化亚铁硫杆菌生物浸出难处理金矿物的机理[J]. 国外金属矿选矿, 2001, 38(11): 11-14+10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXK200111002.htm
[71] 剡倩, 张苗苗, 郭晓鹏, 等. X射线诱变选育嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌及其对难处理金矿浸出的研究[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2016, 34(5): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FYFG201605006.htm
[72] 苏贵珍, 陆建军, 陆现彩, 等. 微生物-矿物接触作用对金属硫化物溶解的影响—氧化亚铁硫杆菌参与黄铜矿溶解的初步研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(6): 100-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.06.013
[73] 项拥军. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌对黄铜矿的氧化作用[J]. 金属矿山, 2000, 10(10): 24-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2000.10.010
[74] 余润兰, 刘晶, 陈安, 等. 嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(ATCC 23270)浸出黄铜矿过程中的EPS、Cu2+和Fe3+的相互作用机制(英文)[J]. 中国有色金属学报: 英文版, 2013(1): 231-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYSY201301031.htm
[75] 薛洪其. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌对钼镍尾矿金属的浸出作用及其机理探讨[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学, 2017.
[76] 黎丹丹. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌和氧化硫硫杆菌联合浸出铊矿尾矿及浸出液毒性评价[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学.
[77] 张青青, 杨爱江, 姚维, 等. 硫氧化细菌对锑矿尾矿重金属浸出研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2014(5): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201405006.htm
[78] 张旭, 冯雅丽, 张小伟. 黄铁矿-微生物体系还原浸出低品位氧化锰矿工艺过程研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2018, 38(5): 106-108+112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201805027.htm
[79] 刘晓燕. 用于软锰矿脱硫的铁、锰氧化细菌的诱变育种及其对Fe、Mn的氧化动力学研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2005.
[80] 李志章, 徐晓军. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌对低品位锰矿浸出的试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2006(11): 50-53. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2006.11.014
-



 下载:
下载: