Study Progress on the Root Uptake Pathway of As, Cd and Pb and Its Influence Factors
-
摘要:
环境中的毒性元素被植物吸收后, 不仅危害植物生长, 还会通过生物链的传递危害人类健康。植物吸收毒性元素有根、茎、叶三种途径, 其中根系吸收最为重要。明晰毒性元素进入根细胞的途径和影响因素, 有助于阻控其进入植物, 降低食用风险。近年来, 在毒性元素根系吸收途径研究领域, 国际上主要开展了吸收动力学过程、转运蛋白识别和外界环境作用机制研究。本文从根系对As、Cd、Pb的吸收途径和影响因素两个方面, 对植物利用转运蛋白和离子通道跨膜转运过程、根际环境与共存元素的影响等进行了评述, 并认为在分子尺度下开展毒性元素细胞吸收动态过程、细胞响应机制和根际多因素作用机理研究是该领域未来发展方向, 同时推测As(Ⅲ)的外排机制与P类似, 且Pb2+利用了Ca2+通道转运至木质部。
Abstract:Toxic elements in the environment taken up by plants, not only damage plant growth, but also harm the health of human beings through the food chain. Toxic elements are taken up by plants commonly through root, stem and foliar, of which the foliar is the most important way. Knowing the ways of toxic elements entering the root cell and its influence factors would lower the uptake of toxic elements by plants and lower the edible danger. In recent years, uptake kinetic process, transport protein identification and action mechanism of external factors are carried out internationally in the field of root system uptake pathway of toxic elements. In this paper, we focus on the root uptake pathway of As, Cd and Pb and its influence factors. Transport processes by transport protein and ion channel of transmembrane protein, rhizosphere environment and the effects of coexisting elements are reviewed. It is concluded that the dynamic process of cellular uptake of As, Cd and Pb at the molecular scale, the cell response mechanism, and rhizosphere effect mechanism of many factors are the main research orientation in the future. Moreover, it is possible that the efflux mechanism of As(Ⅲ) is similar to P and Pb2+ is transported to xylem by Ca2+ channels.
-
Key words:
- Toxic element /
- plant root system /
- uptake pathway /
- influence factor /
- research progress
-

-
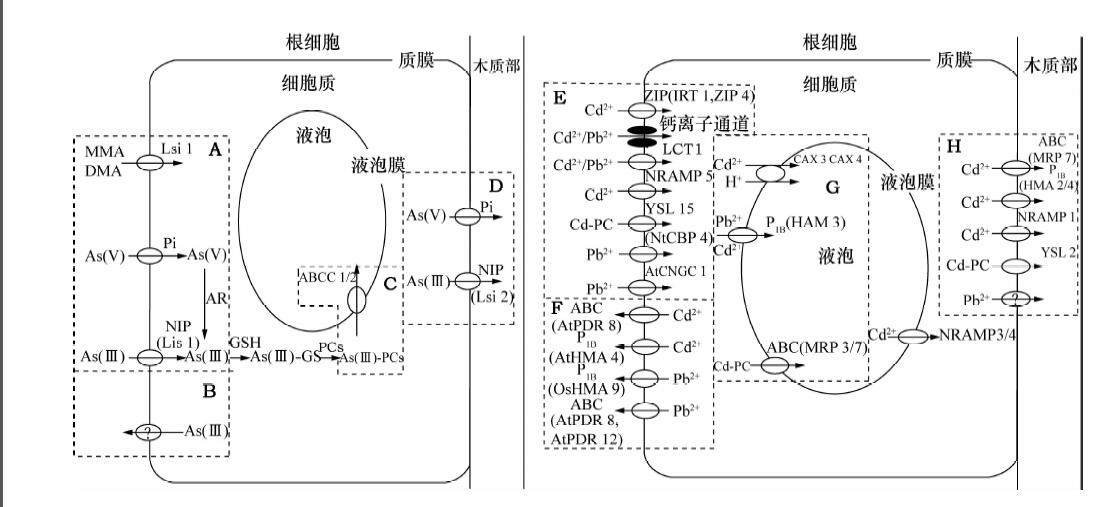
表 1 跨膜运输As、Cd、Pb的转运蛋白
Table 1. The transporter of As, Cd and Pb transmembrane transport
跨膜运输As 转运蛋白(TP)的名称 植物 TP在根细胞的位置 TP的作用 转运元素 文献 Pi转运蛋白 Pht1;1和Pht1;4 拟南芥 质膜 转运元素至细胞质 As(Ⅴ)、P [30] NIP转运蛋白 NIP2;1(Lsi1) 水稻 外侧质膜 转运元素至细胞质 As(Ⅲ)、MMA、DMA、Si [24, 27] AtNIP7;1 拟南芥 质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至细胞质 As(Ⅲ) [42] AtNIP5;1和AtNIP6;1 拟南芥 质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至细胞质 As(Ⅲ) [43] OsNIP2;1和OsNIP3;2 水稻 质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至细胞质 As(Ⅲ) [43] LjNIP5;1和LjNIP6;1 百脉根 质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至细胞质 As(Ⅲ) [43] Lsi2 水稻 内侧质膜 转运元素至木质部 As(Ⅲ)、Si [27] ABCC型转运蛋白 AtABCC1和AtABCC2 拟南芥 根细胞质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至液泡 As(Ⅲ) [26] BART 蜈蚣草 根细胞质膜 转运As(Ⅲ)至液泡 As(Ⅲ) [26] 跨膜运输Cd 转运蛋白(TP)的名称 植物 TP在根细胞的位置 TP的作用 转运元素 文献 ZIP蛋白 HvIRT1 大麦 质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Mn、Fe、Zn、Cd [44] OsIRT1 水稻 质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Fe、Zn、Cd [45] IRT1 拟南芥 表皮细胞质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Fe、Zn、Mn、Co、Cd [46] YSL蛋白 OsYSL15 水稻 质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Fe、Cd [33] AtYSL2 拟南芥 质膜 加载金属至木质部 Fe、Cd [37] 低亲和性阳离子转运蛋白 LCT1 烟草 质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Na、K、Ca、Cd [47] NRAMP蛋白 OsNRAMP1 水稻 质膜 转运金属至细胞质、木质部 Fe、Cd [48] AtNRAMP3和AtNRAMP4 拟南芥 液泡膜 从液泡排出金属 Fe、Cd [49] NRAMP5 水稻 质膜 转运金属至根细胞 Mn、Cd [32] H+/Cd2+逆向运输蛋白 AtCAX2、AtCAX4 拟南芥 液泡膜 转运Cd至液泡 Cd [34] ABC转运蛋白 AtMRP7 烟草 质膜、液泡膜 转运Cd至液泡、加载Cd至木质部 Cd [35] AtPDR8 拟南芥 质膜 排出金属至根际 Cd、Pb [15] P1B型ATPases HMA2 拟南芥 质膜 加载Cd至木质部 Cd [36] AtHMA4 拟南芥 质膜 加载金属至木质部、排出金属至根标 Cd、Zn [17] TcHMA3 天蓝遏蓝菜 液泡膜 转运Cd至液泡 Cd [50] AtHMA3 拟南芥 根尖液泡膜 转运金属至液泡 Cd、Zn、Co、Pb [16] OsHMA3 水稻 液泡膜 转运Cd至液泡 Cd [51] CDF蛋白 OsMTP1 洋葱 质膜 跨膜运输金属元素 Cd、Zn [52] 跨膜运输Pb 转运蛋白(TP)的名称 植物 TP在根细胞的位置 TP的作用 转运元素 文献 环核苷酸门控通道蛋白 AtCNGC1 拟南芥 质膜 转运Pb2+进入细胞 Pb [39] 钙调素结合蛋白 NtCBP4 烟草 质膜 转运金属至细胞质 Ca、Ni、Pb [38] 低亲和力阳离子转运蛋白 LCT1 烟草 质膜 转运Pb2+至细胞质 Pb [53] ABC转运蛋白 AtPDR12 拟南芥 质膜 排出Pb2+至根标 Pb [40] P1B型ATPases OsHMA9 单子叶植物 质膜 排出金属至根标 Cu、Zn、Pb [41] -
[1] [2] doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm119
[3] [4] [5] doi: 10.1021/jf4029859
[6] doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs039
[7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq085
[13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq281
[22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn207
[34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] [42] [43] [44] [45] [46] doi: 10.1105/tpc.001388
[47] [48] doi: 10.1093/jxb/err136
[49] [50] [51] [52] [53] [54] [55] [56] [57] [58] [59] [60] [61] [62] [63] [64] [65] [66] [67] [68] [69] [70] [71] [72] [73] -



 下载:
下载: