Rare Earth Element Composition of Carbonate Rocks Afforded by LA-ICP-MS and Its Formation Environment of the Zhaidi Underground River in Guilin
-
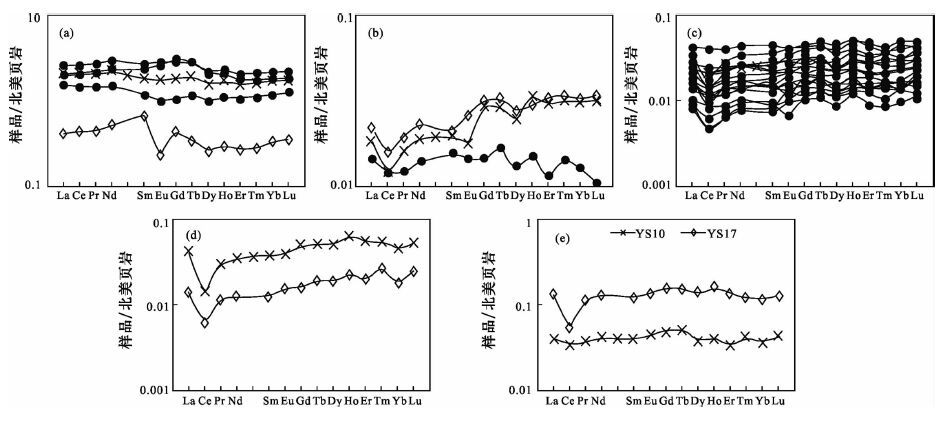
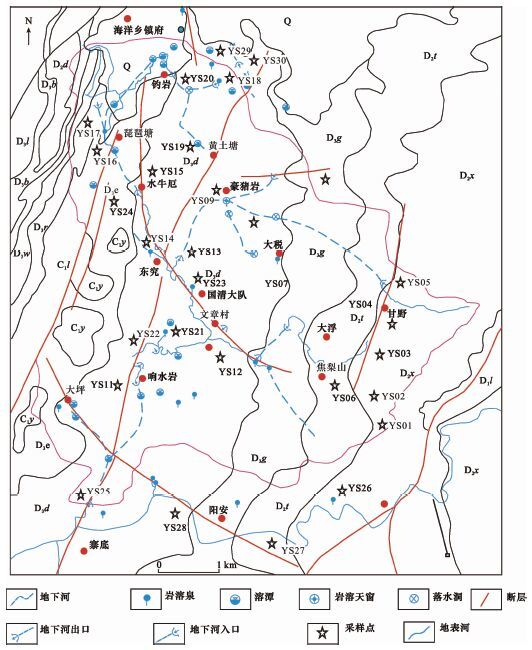
摘要: 稀土元素是研究沉积岩的形成条件及环境特征的重要指标,本文以桂林寨底地下河系统中岩石样品为研究对象,采用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱进行稀土元素测试分析,研究了该地区碳酸盐岩的形成环境。结果表明:碳酸盐岩的稀土总量(∑REEs)偏低,不同地层岩性间的∑REEs具有一定差异性,总体上信都组泥质粉砂岩(D2x)的∑REEs最高,其次为融县组(D3r)厚层灰岩和桂林组灰岩(D3g),东村组厚层灰岩(D3d)和额头村组灰岩及白云质灰岩(D3e)的∑REEs较低。整体上表现为重稀土元素相对于轻稀土元素富集的特征,且Ce具有较明显的负异常,而Eu无异常或异常不明显,不同于碎屑岩的轻稀土相对富集、Eu负异常、Ce无异常或异常不明显的特征。这些特征表明研究区碳酸盐岩的形成环境为氧化-海相碳酸盐岩沉积环境,可为定量化判别岩溶区碳酸盐岩形成环境提供依据。
-
关键词:
- 岩溶地区 /
- 碳酸盐岩形成环境 /
- 稀土元素 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract: Rare earth elements are an important indicator for studying the formation condition and environmental characteristics of sedimentary rocks. The REEs of limestone samples in the Zhaidi underground river in Guilin were determined by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and the formation environment is discussed in this paper. Results show that the total rare earth elements (REEs) content of carbonate rocks is low. There are differences in the concentrations of rare earth elements for carbonate rocks of different strata. Total REEs (ΣREEs) of sandstone in Xindu formation is the highest, followed by thick limestone of Rongxian formation (D3r) and limestone of Guilin formation (D3g). Thick-layer limestone of Dongcun formation (D3d) and limestone and dolomite limestone of Etoucun formation (D3e) contain low REEs. In general, heavy rare earth elements are relatively enriched, with negative Ce anomalies and no Eu anomalies. The REE patterns of carbonate rocks are completely different from negative Eu anomalies and no Eu anomalies for clastic rock. These characteristics of rare earth elements indicate that the sedimentary environment is an oxidative marine carbonate sedimentary environment, which provides a baseline for the formation environment of carbonate rocks in the Karst region. -

-
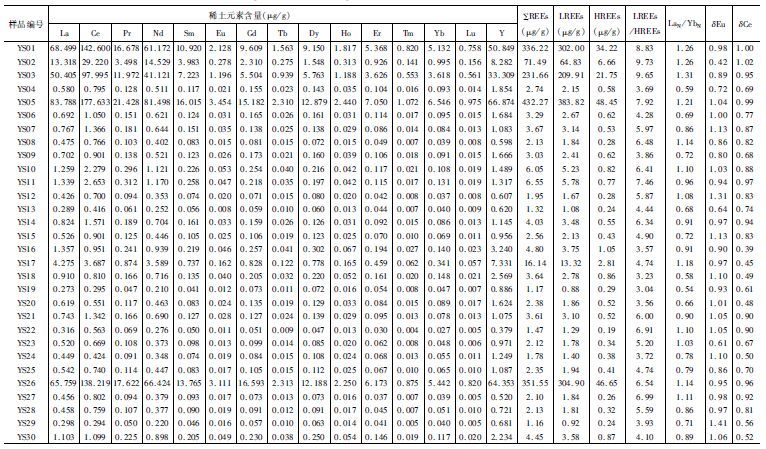
表 1 桂林寨底岩石样品中稀土元素含量及其特征参数
Table 1. Rare earth elements and their characteristic parameters of rock samples from Zhaidi in Guilin district
-
[1] 赵振华编著.微量元素地球化学原理[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:56-187.
Zhao Z H.Principle of Trace Element Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Science Press,1997:56-187.
[2] Henderson P.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1989:195-213.
[3] 张虎才,张文翔,常凤琴,等.稀土元素在湖相沉积中的地球化学分异——以柴达木盆地贝壳堤剖面为例[J].中国科学(D辑),2009,39(8):1160-1168.
Zhang H C,Zhang W X,Chang F Q,et al.Geochemical Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Lacustrine Deposits from Qaidam Basin[J].Science Chinese D-Earth Science,2009,39(8):1160-1168.
[4] 李军,桑树勋,林会喜,等.渤海湾盆地石炭二叠系稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J].沉积学报,2007,25(4):589-596.
Li J,Sang S Y,Lin H X,et al.REE Characteristics and Its Geological Significance of the Permo-carboniferous in Bohaiwan Basin[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2007,25(4):589-596.
[5] Bolhar R,Vankranendonk M.A Non-marine Depositional Setting for the Northern Fortescue Group,Pilbara Craton,Inferred from Trace Element Geochemistry of Stromatolitic Carbonates[J].Precambrian Research,2007,155(3-4):229-250.
[6] Han R S,Liu C Q,Emmanuel J M C,et al.REE Geochemistry of Altered Tectonites in the Huize Base-metal District,Yunnan,China[J].Geochemistry:Exploration,Environment,Analysis,2012,12:127-146.
[7] 秦燕,王登红,梁婷,等.广西大厂锡多金属矿区深部碳酸盐岩的稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J].岩矿测试,2014,33(2):296-302.
Qin Y,Wang D H,Liang T,et al.Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in the Deep Carbonate Rocks and Their Geological Significance in the Dachang Tin-polymetallic Deposit of Guangxi[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis,2014,33(2):296-302.
[8] Lai X D,Yang X Y,Sun W D.Geochemical Constraints on Genesis of Dolomite Marble in the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe Deposit,Inner Mongolia:Implications for REE Mineralization[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,57:90-102.
[9] 伊海生,林金辉,赵西西,等.西藏高原沱沱河盆地渐新世-中新世湖相碳酸盐岩稀土元素地球化学特征与正铕异常成因初探[J].沉积学报,2008,26(1):1-10.
Yi H S,Lin J H,Zhao X X,et al.Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements and Origin of Positive Europium Anomaly in Miocene-Oligocene Lacustrine Carbonates from Tuotuohe Basin of Tibetan Plateau[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2008,26(1):1-10.
[10] 蒋忠诚,裴建国,夏日元,等.我国"十一五"期间的岩溶研究进展与重要活动[J].中国岩溶,2010,29(4):349-354.
Jiang Z C,Pei J G,Xia R Y,et al.Progresses and Important Activities of Karst Research During the 11th Five-year Plan in China[J].Carsologica Sinica,2010,29(4):349-354.
[11] 熊平生,袁道先,谢世友.我国南方岩溶山区石漠化基本问题研究进展[J].中国岩溶,2010,29(4):355-362.
Xiong P S,Yuan D X,Xie S Y.Progress of Research on Rocky Desertification in South China Karst Mountain[J].Carsologica Sinica,2010,29(4):355-362.
[12] Klindworth C,Schneider W,刘效曾.桂林唐家湾剖面中-上泥盆统碳酸盐岩沉积相和成岩作用[J].岩相古地理,1993,13(3):9-17. Klindworth C,Schneider W,Liu X Z.Sedimentary Facies and Diagenesis of the Middle and Upper Devonian Carbonate Rocks in the Tangjiawan Section,Guilin[J].Lithofacies and Paleo Geography,1993,13(3):9-17.
[13] 何红蓼,李冰,韩丽荣,等.封闭压力酸溶-ICP-MS法分析地质样品中47个元素的评价[J].分析试验室,2002,21(5):8-12.
He H L,Li B,Han L R,et al.Evaluation of Determining 47 Elements in Geological Samples by Pressurized Acid Digestion-ICPMS[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2002,21(5):8-12.
[14] 张莉,季宏兵,高杰,等.贵州碳酸盐岩风化壳主元素、微量元素及稀土元素的地球化学特征[J].地球化学,2015,44(4):323-336.
Zhang L,Ji H B,Gao J,et al.Geochemical Characteristics of Major,Trace and Rare Earth Elements in Typical Carbonate Weathered Profiles of Guizhou Plateau[J].Geochimica,2015,44(4):323-336.
[15] 杨瑞东.贵阳地区碳酸盐岩风化红黏土剖面稀土、微量元素分布特征[J].地质论评,2008,54(3):409-418.
Yang R D.The Distribution of Rare Elements and Trace Elements in Latecritic Profile:Implication for Karst Environment[J].Geological Review,2008,54(3):409-418.
[16] 余新亚,李平平,邹华耀,等.川北元坝气田二叠系长兴组白云岩稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J].古地理学报,2015,17(3):309-320.
Yu X Y,Li P P,Zhou H Y,et al.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Dolostones and Its Indicative Significance of the Permian Changxing Formation in Yuanba Gasfield,Northern Sichuan Basin[J].Journal of Palaeogeography,2015,17(3):309-320.
[17] Bau M,Dulski P.Distribution of Yttrium and Rare-earth Elements in the Penge and KurumanIron-formations,Transvaal Supergroup,South Africa[J].Precambrian Research,1996,79:37-55.
[18] Zhang J,Nozaki Y.Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium in Seawater:ICP-MS Determinations in the East Caroline,Coral Sea,and South Fiji Basins of the Western South Pacific Ocean[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1996,60:4631-4644.
[19] Goldstein S J,Jacobsen S B.Rare Earth Elements in River Waters[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1988,89:35-47.
[20] Nothdurft L D,Webb G E,Kamber B S.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Late Devonian Reefal Carbonates,CanningBasin,Western Australia:Confirmation of a Seawater REE Proxy in Ancient Limestones[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2004,68(2):263-283.
[21] Olivier N,Boyet M.Rare Earth and Trace Elements of Microbialites in Upper Jurassic Coral-and Sponge-Microbialite Reefs[J].Chemical Geology,2006,230:105-123.
[22] 席明杰,马生明,朱立新,等.内蒙古准苏吉花铜钼矿床稀土元素特征及对成矿作用的约束[J].中国稀土学报,2013,31(4):503-512.
Xi M J,Ma S M,Zhu L X,et al.Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements and Constraints on Mineralization from Zhunsujihua Copper-Molybdenum Deposit in Inner Mongolia[J].Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths,2013,31(4):503-512.
[23] Lai X D,Yang X Y,Sun W D.Geochemical Constraints on Genesis of Dolomite Marble in the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe Deposit,Inner Mongolia:Implications for REE Mineralization[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,57:90-102.
-



 下载:
下载: