Study on Emerald-level Beryl from the Zhen'an W-Be Polymetallic Deposit in Shaanxi Province by Electron Probe Microanalyzer and Micro X-ray Diffractometer
-
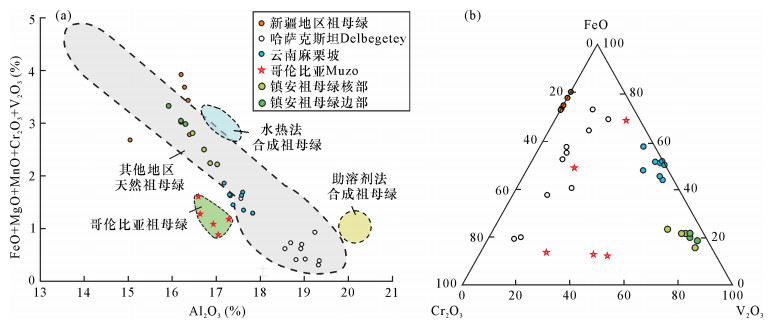
摘要: 南秦岭镇安地区发现了以白钨矿-绿柱石为矿石矿物组合的矿床新类型。为查明该矿床中首次发现的翠绿色祖母绿级绿柱石的致色机理并进一步揭示其成矿机制,本文在野外地质调查的基础上,对绿柱石开展了电子探针与微区X射线衍射等矿物学研究。结果表明:矿区中首次发现的祖母绿级绿柱石,呈自形晶产于石英(方解石)脉中并与白钨矿共(伴)生。祖母绿级绿柱石从核部至边缘V2O3含量较高,分别为0.64%~0.98%和1.04%~1.42%,且有增高趋势。X射线衍射数据表明区内祖母绿为“正常”绿柱石,同时存在Al↔Me2+和Be↔Li两种类质同象替换机制。V为本区祖母绿主要致色元素,来自于区内碳质板岩、金云母片岩及白云质大理岩等地层,Be、Si、Al等主要元素则来自于深部酸性岩浆岩。本次发现为该矿床中钨、铍矿产资源的综合开发利用提供了基础地质资料,并为南秦岭在区域及深部继续寻找稀有金属矿指出新的找矿方向。Abstract:
BACKGROUND A new deposit type with a scheelite-beryl-molybdenite assemblage was first discovered in the Zhen'an area of Shaanxi Province. BAOBJECTIVES The research on chromatic mechanism and genetic mechanism of emerald was carried out. METHODS Combined with the geological survey, Electron Microprobe and in-situ Micro X-ray Diffractomer were used to conduct mineral research. RESULTS The emerald mainly occurs in the quartz (calcite) veins as euhedral crystal and is associated with scheelite. Both the core and rim of the emerald with high V2O3 contents of 0.64%-0.98% and 1.04%-1.42%, respectively, show an increased V2O3 trend from core to rim. Diffraction data show that the emerald is normal beryl and has two kinds of isomorphous substitution mechanism, Al↔Me2+ and Be↔Li. Vanadium is the main coloring element of emerald and was mainly derived from carbonaceous slate, mica schist, and dolomitic marble, whereas Be, Si and Al were derived from deep acidic igneous rocks. CONCLUSIONS The discovery provides basic geological data for the comprehensive development and utilization of tungsten and antimony mineral resources in the deposit, and indicates new prospecting directions for continued searching for rare metal deposits in the region and deep areas of the South Qinling. -
Key words:
- emerald /
- mineralogy /
- coloring mechanism /
- W-Be polymetallics /
- Southern Qinling
-

-
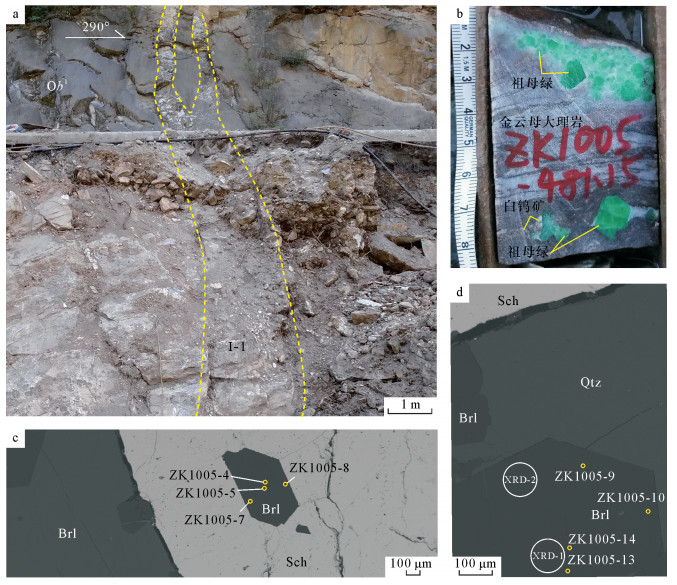
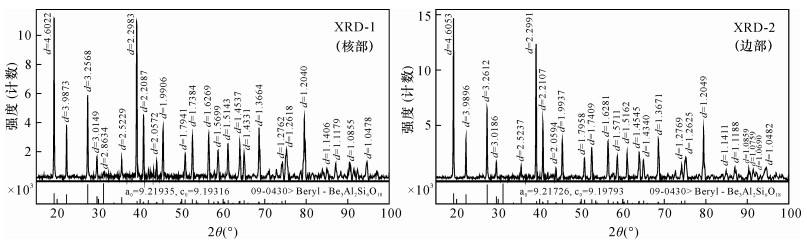
图 4 图 2d中单颗粒祖母绿级绿柱石核部及边部微区XRD分析
Figure 4.
表 1 陕西镇安某地绿柱石的电子探针分析结果
Table 1. EMPA data of beryl in Zhen'an area, Shaanxi Province
元素 核部 边部 ZK1005-4 ZK1005-5 ZK1005-13 ZK1005-14 平均值 ZK1005-7 ZK1005-8 ZK1005-9 ZK1005-10 平均值 SiO2 66.40 67.34 66.40 67.49 66.91 66.57 66.48 66.01 66.53 66.40 Al2O3 16.86 16.72 16.46 17.02 16.77 16.30 15.92 16.20 16.19 16.15 Na2O 0.71 0.80 0.76 0.69 0.74 0.80 0.85 0.74 0.82 0.80 K2O 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.03 CaO 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.01 / 0.01 0.02 0.01 TiO2 0.08 0.01 / 0.10 0.05 / 0.06 / / 0.02 P2O5 / 0.01 0.007 / / 0.01 / / 0.01 0.01 MgO 1.22 1.27 1.44 1.34 1.32 1.49 1.48 1.43 1.53 1.48 MnO 0.01 0.04 / 0 0.01 0.02 0 0.05 0 0.02 FeO 0.24 0.26 0.3 0.14 0.24 0.32 0.35 0.31 0.41 0.35 Rb2O / / / / / / / / / / Cs2O 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.07 V2O3 0.64 0.84 0.98 0.68 0.79 1.07 1.42 1.13 1.04 1.17 Cr2O3 0.13 0.10 0.09 0.06 0.10 0.08 0.07 0.09 0.07 0.08 BeO 12.93 12.81 12.61 13.08 12.86 12.47 12.18 12.44 12.39 12.37 Li2O 0.70 0.75 0.74 0.68 0.72 0.78 0.79 0.70 0.78 0.76 总计 100.01 101.15 100.02 101.48 100.67 100.06 99.76 99.27 99.96 99.76 元素 ZK1005-4 ZK1005-5 ZK1005-13 ZK1005-14 平均值 ZK1005-7 ZK1005-8 ZK1005-9 ZK1005-10 平均值 Si 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 Al 1.8 1.76 1.758 1.788 1.777 1.736 1.697 1.74 1.726 1.725 Na 0.124 0.138 0.134 0.12 0.129 0.14 0.148 0.131 0.143 0.141 K 0.003 0.001 0.004 0.003 0.003 0.005 0.004 0.002 0.004 0.004 Ca 0.002 0.002 0.001 0.003 0.002 0.001 / 0.001 0.001 0.001 Ti 0.005 0.001 / 0.007 0.004 / 0.004 / / 0.004 P / 0.001 0.001 / 0.001 0.001 / / 0.001 0.001 Mg 0.165 0.169 0.194 0.178 0.177 0.201 0.2 0.195 0.206 0.201 Mn 0.001 0.003 / / 0.002 0.002 / 0.004 / 0.003 Fe 0.018 0.019 0.023 0.01 0.018 0.024 0.026 0.024 0.031 0.026 Rb / / / / / / / / / / Cs 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.004 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.003 V 0.047 0.06 0.071 0.049 0.057 0.078 0.103 0.083 0.075 0.085 Cr 0.009 0.007 0.007 0.004 0.007 0.006 0.005 0.007 0.005 0.006 Li 0.13 0.141 0.139 0.125 0.134 0.149 0.154 0.135 0.149 0.147 Be 2.87 2.859 2.861 2.875 2.866 2.851 2.846 2.865 2.851 2.853 Mg+Fe+Mn+Cr+V 0.24 0.258 0.295 0.241 0.259 0.31 0.334 0.312 0.317 0.318 Mg+Mn+Fe 0.184 0.191 0.217 0.189 0.195 0.227 0.226 0.222 0.237 0.228 Na+K+Rb+Cs 0.13 0.141 0.139 0.125 0.134 0.149 0.154 0.135 0.149 0.147 注:①测试单位为中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所电子探针实验室;②“/”表示低于检测限;③绿柱石的晶体化学式以6个硅原子为基础计算,Li和Be原子数分别根据Li=Na+K+Rb+Cs和Be=3-Li。 -
[1] 胡荣荣, 张世涛.祖母绿矿床研究现状[J].化工矿产地质, 2006, 28(4):234-240. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HGKC200604009.htm
Hu R R, Zhang S T.Current research situation of the world emerald deposits and the existing problems[J].Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2006, 28(4):234-240. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HGKC200604009.htm
[2] 胡荣荣, 张世涛.世界祖母绿矿床研究现状及存在问题[J].矿产与地质, 2007, 21(1):94-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Navi/A.htm
Hu R R, Zhang S T.Status of worldwide emerald deposit research and some problems[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2007, 21(1):94-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Navi/A.htm
[3] Gavrilenko E, Pérez B C, Bolibar R C, et al.Emeralds from the Delbegetey deposit (Kazakhstan):Mineralogical characteristics and fluid-inclusion study[J].Mineralogical Magazine, 2006, 70(2):159-173. doi: 10.1180/0026461067020321
[4] Ottaway T L, Wicks F J, Bryndzia L T, et al.Formation of the Muzo hydrothermal emerald deposit in Colombia[J].Nature, 1994, 369:552-554. doi: 10.1038/369552a0
[5] Bragg W L, West J.The structure of beryl, Be3Al2Si6O18[J].Royal Society of London Proceedings, 1926, 111(759):691-714. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1926.0088
[6] 刘琰, 邓军, 孙岱生, 等.四川虎牙雪宝顶W-Sn-Be矿床矿物学标型特征及流体对矿物形态的影响[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(1):75-81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1997-KYDH701.007.htm
Liu Y, Deng J, Sun D S, et al.Morphology and gensis typomorphism of minerals in W-Sn-Be deposit of Huya, Sichuan[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(1):75-81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1997-KYDH701.007.htm
[7] 阮青锋, 张良钜, 张昌龙, 等.绿柱石的成因与特征的研究[J].矿产与地质, 2008, 22(3):265-269. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/40021281d4d8d15abe234e07-2.html
Ruan Q F, Zhang L J, Zhang C L, et al.Genesis and characteristics of beryl[J].Mineral Resources & Geology, 2008, 22(3):265-269. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/40021281d4d8d15abe234e07-2.html
[8] Garcí J M, Lastra A, Barriuso M T, et al.Origin of the different color of ruby and emerald[J].Physical Review B, 2005, 72(11):3104. http://www.mendeley.com/research/origin-different-color-ruby-emerald/
[9] 钟倩, 廖宗廷, 周征宇, 等.水热法合成Paraíba色绿柱石的宝石学特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(6):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bshbsxzz200201009
Zhong Q, Liao Z T, Zhou Z Y, et al.Gemmological characteristics of hydrothermal synthetic paraíba-cloour beryl[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2016, 18(6):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bshbsxzz200201009
[10] 申柯娅.天然祖母绿与合成祖母绿的成分及红外吸收光谱研究[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(2):233-237. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ce380698-cdb7-491c-8284-258a85a55ac4
Shen K Y.Study on chemical compositions and infrared absorption spectra of natural and synthetic emeralds[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(2):233-237. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ce380698-cdb7-491c-8284-258a85a55ac4
[11] 梁婷.云南祖母绿的呈色机理初探[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2001, 3(4):21-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bshbsxzz200104006
Liang T.Study on coluration mechanism of emerald from Yunnan Province[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2001, 3(4):21-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bshbsxzz200104006
[12] 梁婷.祖母绿的红外光谱特征研究[J].长安大学学报(地球科学版), 2003, 25(2):10-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RGJT201503003.htm
Liang T.The study on infrared absorption pectroscopic characteristics of emeralds[J].Journal of Chang'an University (Earth Science Edition), 2003, 25(2):10-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RGJT201503003.htm
[13] 张文兰, 王汝成, 蔡淑月.超轻元素Be元素的电子探针定量分析——以绿柱石为例[J].电子显微学报, 2006(增刊1):293-294. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_6347885
Zhang W L, Wang R C, Cai S Y.Quantitative analysis of ultralight element Be by electron microprobe-Taking beryl as an example[J].Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2006(Supplement 1):293-294. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_6347885
[14] Liu J J, Zhai D G, Dai H Z, et al.Nanoscale character-ization of Au2Te grains from the Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Northeast China[J].The Canadian Mineralogist, 2017, 55(2):181-194. doi: 10.3749/canmin.1600077
[15] Uher P, Chudík P, Bačík P, et al.Beryl composition and evolution trends:An example from granitic pegmatites of the beryl-columbite subtype, Western Carpathians, Slovakia[J].Journal of Geosciences, 2010, 55(1):69-80. http://www.oalib.com/paper/2807022
[16] Wang R C, Che X D, Zhang W L, et al.Geochemical evolution and late re-equilibration of Na-Cs-rich beryl from the Koktokay #3 pegmatite (Altai, NW China)[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 2009, 21(4):795-809. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1936
[17] Viana R R, Jordtevangelista H, Costa G M D, et al.Characterization of beryl (aquamarine variety) from pegmatites of Minas Gerais, Brazil[J].Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2002, 29(10):668-679. doi: 10.1007/s00269-002-0278-y
[18] Evensen J M.Beryllium in silicic magmas and the origin of beryl-bearing pegmatites[J].Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 2002, 50(1):445-486. http://www.mendeley.com/research/beryllium-silicic-magmas-origin-berylbearing-pegmatites/
[19] Sabot B.Fluid inclusions in Ianapera emerald, Southern Madagasca[J].International Geology Review, 2005, 47(6):647-662. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.6.647
[20] Moore T P. Emeralds of the World[M]//Mineralogical Record. 2003: 10-23, 25-33, 74-78.
[21] Groat L A, Giuliani G, Marshall D D, et al.Emerald deposits and occurrences:A review[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 34(1-2):87-112. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.09.003
[22] Groat L A, Marshall D D, Giuliani G, et al.Mineralogical and geochemical study of the Regal Ridge emerald showing, Southeastern Yukon[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 2002, 40(5):1313-1338. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.40.5.1313
[23] Cheilletz A, Féraud G, Giuliani G, et al.Time-pressure and temperature constraints on the formation of Colombian emeralds:An 40Ar/39Ar laser microprobe and fluid inclusion study[J].Economic Geology, 1994, 89:361-380. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.89.2.361
[24] 代鸿章, 王登红, 王成辉, 等.中央造山带秦巴地区发现石英脉型黑钨矿[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):559-560. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709040137
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al.New discovery of quartz vein-type of wolframite ores in the Qinling-Daba area, Central Orogenic Belt, China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):559-560. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709040137
[25] 许乃岑, 沈加林, 张静.X射线衍射-X射线荧光光谱-电子探针等分析测试技术在玄武岩矿物鉴定中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1):75-81. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.010
Xu N C, Shen J L, Zhang J.Application of X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and electron microprobe in the identification of basalt[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1):75-81. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.010
[26] 刘永先, 范洪斌.云南祖母绿特征及开发利用初探[J].矿产综合利用, 1997(6):22-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199704007.htm
Liu Y X, Fan H B.A preliminary study on the characteristics and exploitation and utilization of emeralds in Yunnan[J].Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 1997(6):22-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199704007.htm
[27] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝, 等.统矿物学(中册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1982:155-156.
Wang P, Pan Z L, Weng L B, et al.Systematic Mineralogy (Volume 2)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1982:155-156.
[28] Aurisicchio C, Fioravanti G, Grubessi O, et al.Reappra-isal of the crystal chemistry of beryl[J].American Minealogist, 1988, 73:826-837. http://rruff.info/doclib/hom/beryl.pdf
[29] 黄文清, 倪培, 水汀, 等.云南麻栗坡祖母绿的矿物学特征研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(1):103-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201501009
Huang W Q, Ni P, Shui T, et al.Mineralogical characteristics of emerald from Malipo, Yunnan Province[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(1):103-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201501009
[30] 任伟, 汪立今, 李甲平.电子探针和X射线衍射仪测定新疆祖母绿宝石[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(2):179-181. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/5a9e1771-8bd3-42f9-b2fc-d5fe67a5c11f
Ren W, Wang L J, Li J P. Detection of emerald from Xinjiang by electron probe microanalyzer and X-ray diffractometer[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(2):179-181. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/5a9e1771-8bd3-42f9-b2fc-d5fe67a5c11f
[31] JCPDS. International Center for Diffraction Data[Z]. [PDF#09-0430], 1988.
[32] Schwartz D, Giuliani G.Emerald deposits:A review[J].Australian Gemmologist, 2001, 1:17-23. http://www.documentation.ird.fr/hor/fdi:010034445
[33] Vapnik Y, Moroz I, Roth M, et al.Formation of emeralds at pegmatite-ultramafic contacts based on fluid inclusions in Kianjavato emerald, Mananjary deposits, Madagascar[J].Mineralogical Magazine, 2006, 70:141-158. doi: 10.1180/0026461067020320
[34] 汪立今, 彭雪峰, 李甲平, 等.新疆祖母绿(绿柱石)矿产出地质特征与找矿矿物学[J].矿物学报, 2011, 31(3):604-608. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Magazine?magazineId=kwxb&yearIssue=2011_3
Wang L J, Peng X F, Li J P, et al.A study on basic geological characteristics and mineralogy of ore prospecting in Xinjiang emerald (beryl) deposit[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(3):604-608. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Magazine?magazineId=kwxb&yearIssue=2011_3
[35] Dai H Z, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al.Re-Os isotopic dating of a W-Be polymetallic deposit in the Southern Qinling Region, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2018, 92(1):414-415. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2018.92.issue-1
[36] 刘茜. 陕西镇安钨矿床特征及成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1013270343.htm Liu Q. The Characterisitcs and Genesis of the Zhen'an W Deposit, Shannxi Province, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscinces (Beijing), 2013.
[37] 盛继福, 王登红.中国矿产地质志·钨矿卷[M].北京:地质出版社(待出版), 2018.
Sheng J F, Wang D H.China's Mineral Geology (Tungsten Ore Volume)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2018(in press).
-



 下载:
下载: