Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Barite-associated Rare Earth Ores by Alkaline Precipitation Separation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry
-
摘要: 采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定伴生重晶石轻稀土矿中的稀土元素时,Ba以及轻稀土元素La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm等对中重稀土造成严重的质谱重叠干扰,因此在保证矿石完全消解的同时,若能选择合适的前处理方法实现目标元素与基体的有效分离,将有利于减少质谱干扰。本文采用过氧化钠-碳酸钠熔融分解伴生重晶石的稀土矿样品,熔融物用三乙醇胺溶液提取,将沉淀过滤去除硅、铁、锰、铝等大量基体元素,而稀土元素与钡、锶、钙等留存于沉淀中,沉淀经盐酸溶解后再用氨水进行二次沉淀,将稀土元素与伴生的高含量钡、锶、钙等元素分离,分离率超过96%,从而极大地降低了由钡的氧化物和氢氧化物对153Eu等元素质量数的质谱干扰。轻稀土元素对中重稀土元素的干扰则通过测定高浓度的单元素标准溶液在m/z 138~175处的表观浓度来计算干扰校正系数,对干扰量进行扣除校正。该方法通过稀土矿石标准物质GBW07187、GBW07188验证,测定值与认定值的相对误差 < 10%;应用于伴生重晶石稀土矿石实际样品分析,相对标准偏差(RSD,n=12)为0.5%~4.6%,证明了本方法可用于分析高钡矿石中的稀土元素。
-
关键词:
- 重晶石 /
- 稀土元素 /
- 过氧化钠-碳酸钠熔融 /
- 沉淀分离 /
- 钡 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUNDWhen inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is used to determine the rare earth elements (REE) in the barite-associated light rare earth ores, Ba and light rare earth elements La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, cause severe mass spectral overlap interference to the medium and heavy rare earths. Therefore, under the condition that complete digestion of oress, if the appropriate pretreatment method can be selected to achieve effective separation of the target elements from the matrix, it will be beneficial to reduce mass spectrum interferences. OBJECTIVESTo reduce the mass spectrum interferences by establishing a simple and effective pretreatment method for separation of rare earth elements from barium and other coexisting elements in barite-associated rare earth ores. METHODSThe barite-associated rare earth ores samples were fused with sodium peroxide and sodium carbonate. After dissolution of the fusion cake, the target REE and the undesired barium were precipitated in triethanolamine solution, but some matrix elements like Si, Fe, Mg, and Al in samples, and most fusion agents, were separated by filtration. The target REE were secondly precipitated in ammonium hydroxide after dissolution of the precipitates by acid, so that Ba, Sr and Ca could be separated from REE. The separation exceeds 96%, so the mass spectrum interferences caused by barium polyatomic ions were effectively reduced. In addition, the interference correction coefficients by measuring the interference concentration at m/z 138-175 of the high concentration lighter rare earths standard single element solution were adopted to account for the oxide and hydroxide overlap problem for the determination of middle and heavier rare earth elements. RESULTSThe validity of the method was evaluated by analyses of rare earth ores certified reference materials and the results were in good agreement with certified values (|RE| < 10%). For the actual sample analysis of the barite-associated rare earth ores, the relative standard deviations (n=12) were from 0.5% to 4.6%, which proved that the method can be used to analyze rare earth elements in high-Ba ores. CONCLUSIONSThe results demonstrate that this method is both practical and effective for rare earth elements analysis in barite-associated rare earth ores. -

-
表 1 各稀土元素的标准系列浓度
Table 1. Concentrations of REE in calibration standard solutions
稀土元素 标准系列1浓度
(ng/mL)标准系列2浓度
(ng/mL)标准系列3浓度
(ng/mL)标准系列4浓度
(ng/mL)La 200 2000 20000 - Ce 200 2000 20000 - Pr 50 100 1000 2000 Nd 100 1000 2000 5000 Sm 10 50 200 500 Eu 1.0 10 50 100 Gd 1.0 10 50 100 Tb 1.0 5.0 10 50 Dy 5.0 10 50 100 Ho 1.0 5.0 10 100 Er 1.0 5.0 10 50 Tm 0.5 1.0 5.0 50 Yb 1.0 5.0 10 20 Lu 0.1 0.5 1.0 5.0 Y 50 100 200 - 表 2 不同溶样方法处理样品MNP-2的稀土元素测定结果
Table 2. Analytical results of REE in MNP-2 with different sample digestion methods
稀土元素 样品MNP-2测定值(μg/g) 四酸敞开酸溶法 五酸敞开酸溶法 氢氟酸-硝酸封闭压力酸溶法 过氧化钠-碳酸钠碱熔法 La 7014 7471 8153 10720 Ce 9668 11760 11287 15020 Pr 822 905 965 1278 Nd 2331 2626 2900 3567 Sm 196 243 233 300 Y 93.8 114 88.6 146 表 3 残留的共存元素含量(μg/g,结果均按0.25g称样量换算至样品含量)
Table 3. Residual content of coexisting elements (μg/g, results were converted to sample content by 0.25g weighing amount)
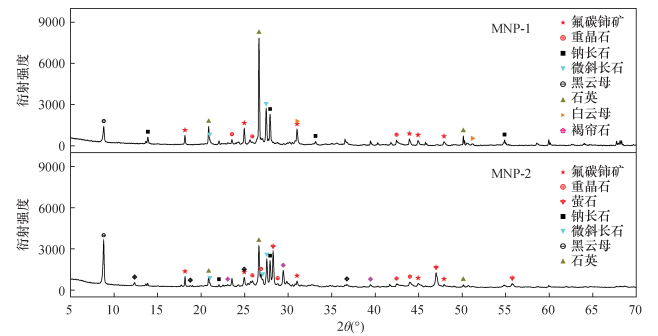
共存元素 MNP-1 MNP-2 碱熔-水提取-沉淀过滤
(方法1)碱熔-水提取-沉淀酸溶后氨水二次沉淀
(方法2)碱熔-三乙醇胺提取-沉淀过滤
(方法3)碱熔-三乙醇胺提取-沉淀酸溶后氨水二次沉淀
(方法4)碱熔-水提取-沉淀过滤
(方法1)碱熔-水提取-沉淀酸溶后氨水二次沉淀
(方法2)碱熔-三乙醇胺提取-沉淀过滤
(方法3)碱熔-三乙醇胺提取-沉淀酸溶后氨水二次沉淀
(方法4)Ba 18025 296 17510 232 29310 1136 28555 1112 Al 34770 8282 3106 2793 52526 14204 5027 4486 Ca 14303 428 8026 292 111652 2980 112635 3070 Fe 90997 83757 922 859 31034 27652 442 452 K 464 ND 156 ND 427 ND 191 ND Na 185222 487 79675 433 247129 708 114542 721 Mg 6875 265 6963 124 6890 274 6317 267 Ti 4572 4551 3523 3868 1808 1817 1499 1470 Mn 1205 924 50 51 1452 1351 128 119 Sr 175 ND 183 ND 38330 566 37460 578 Cu 46.8 2.9 4.0 3.9 65.1 2.6 1.7 1.2 表 4 稀土元素测量质量数及干扰校正系数
Table 4. Measured m/z and the interference correction coefficient for rare earth elements
稀土元素 选择质量数 干扰元素 干扰系数(k) La 139 - - Ce 140 - - Pr 141 - - Nd 146 - - Sm 147 - - Eu 153 Ba 0.0003837 Gd 160 Ce 0.0000332 Pr 0.0000330 Nd 0.0262500 Sm 0.0011850 Dy 0.0939759 Tb 159 Ce 0.0001934 Pr 0.0000568 Nd 0.0027455 Dy 163 Nd 0.0005330 Sm 0.0036453 Ho 165 Nd 0.0000450 Sm 0.0009010 Er 167 Nd 0.0001986 Sm 0.0001243 Eu 0.0023075 Tm 169 Sm 0.0001023 Eu 0.0005733 Yb 172 Ce 0.0000098 Gd 0.0125540 Lu 175 Ce 0.0000363 Gd 0.0003113 Tb 0.0151550 表 5 标准物质分析结果
Table 5. Analytical results of REE in reference material samples
稀土元素 GBW07187 GBW07188 认定值
(μg/g)测定值
(μg/g)加钡后测定值
(μg/g)认定值
(μg/g)测定值
(μg/g)加钡后测定值
(μg/g)La 2132 2100 2067 1961 1817 1784 Ce 171 165 160 431 391 392 Pr 546 556 548 737 680 681 Nd 2058 1903 1947 3429 3213 3246 Sm 569 526 526 1725 1831 1821 Eu 8.26 8.32 8.23 18.9 20.5 20 Gd 790 796 791 2169 2156 2148 Tb 162 150 154 468 454 450 Dy 1046 969 972 3224 2979 2947 Ho 201 196 199 559 536 536 Er 595 604 601 1749 1769 1756 Tm 72.6 74.3 76.1 271 251 252 Yb 448 427 428 1844 1737 1706 Lu 56.7 59.9 59.2 264 243 249 Y 6300 6464 6491 17009 17130 17400 表 6 实际样品分析结果
Table 6. Analytical results of rare earth elements in practical samples
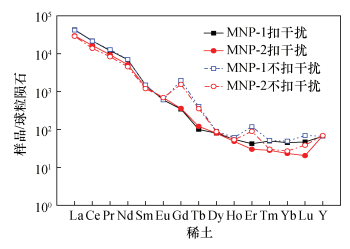
稀土元素 MNP-1 MNP-2 测定平均值(μg/g) RSD(%) 测定平均值(μg/g) RSD(%) La 15805 1.0 10780 0.5 Ce 21023 1.4 15108 1.7 Pr 1664 2.2 1272 1.6 Nd 4934 1.4 3545 1.6 Sm 348 1.7 299 1.4 Eu 52.7 1.5 60.4 1.3 Gd 106 4.6 111 1.3 Tb 5.83 4.3 7.04 3.2 Dy 30.6 0.8 30.6 1.7 Ho 4.72 0.8 4.14 2.3 Er 11.8 1.4 8.45 1.3 Tm 1.78 0.5 1.01 1.0 Yb 11.2 1.7 5.82 3.3 Lu 1.77 3.9 0.77 3.7 Y 140 0.6 145 1.5 -
[1] 王春梅, 刘玉柱, 赵龙胜, 等.我国稀土材料与绿色制备技术现状与发展趋势[J].中国材料进展, 2018, 37(11):841-847. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgcljz201811001
Wang C M, Liu Y Z, Zhao L S, et al.Current situation and development tendency on rare earth materials and its green preparation technologies in China[J].Materials China, 2018, 37(11):841-847. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgcljz201811001
[2] 季根源, 张洪平, 李秋玲, 等.中国稀土矿产资源现状及其可持续发展对策[J].中国矿业, 2018, 27(8):9-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgky201808002
Ji G Y, Zhang H P, Li Q L, et al.Current status of rare earth resources in China and strategies for its sustainable development[J].China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(8):9-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgky201808002
[3] 王宝磊, 吴玉锋, 章启军, 等.草酸盐重量法测定荧光粉废料中稀土氧化物的总量[J].稀土, 2016, 37(5):92-96. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8834691
Wang B L, Wu Y F, Zhang Q J, et al.Determination of total rare earth oxides content in waste phosphors with oxalate gravimetric method[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(5):92-96. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8834691
[4] 张燕辉, 杜若冰, 王振兴, 等.氯乙酸缓冲体系在稀土测定中的应用研究[J].中国稀土学报, 2013, 31(5):636-640. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxtxb201305015
Zhang Y H, Du R B, Wang Z X, et al.Research on buffer solution of chloroacetic acid in rare earth detection[J].Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2013, 31(5):636-640. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxtxb201305015
[5] 孙志峰, 张志刚, 张翼明, 等.镝铁合金中稀土总量的测定——EDTA容量法[J].稀土, 2010, 31(1):77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.01.017
Sun Z F, Zhang Z G, Zhang Y M, et al.Determination of total rare earth content in Dy-Fe alloy with EDTA volume method[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2010, 31(1):77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.01.017
[6] Khorge C R, Patwardhan A A.Separation and determina-tion of REEs and Y in columbite-tantalite mineral by ICP-OES:A rapid approach[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(2):75-80.
[7] Balarama Krishna M V, Venkateswarlu G, Karunasagar D.Development of simple and robust microwave-assisted decomposition method for the determination of rare earth elements in coal fly ash by ICP-OES[J].Analytical Methods, 2017, 9:2031-2040. doi: 10.1039/C7AY00286F
[8] 艾军, 陶德刚, 李素芝.ICP-AES直接测定地质样品中微量稀土元素[J].武汉化工学院学报, 2001, 23(1):18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2001.01.006
Ai J, Tao D G, Li S Z.Direct determination of rare earth elements in geochemical samples by ICP-AES[J].Journal of Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2001, 23(1):18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2001.01.006
[9] 胡璇, 刘万超, 石磊.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定赤泥浸出液中稀土元素[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(12):46-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjfx201512010
Hu X, Liu W C, Shi L.Determination of rare earth elements in leaching solution of red mud by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(12):46-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjfx201512010
[10] 吴石头, 王亚平, 孙德忠, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定稀土矿石中15种稀土元素——四种前处理方法的比较[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/2c32f0ea-719c-486f-aa0d-027493aec6da
Wu S T, Wang Y P, Sun D Z, et al.Determination of 15 rare earth elements in rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry:A comparison of four different pretreatment methods[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/2c32f0ea-719c-486f-aa0d-027493aec6da
[11] 尹明, 符廷发, 袁玄晖.感耦等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中痕量稀土元素的研究[J].岩矿测试, 1989, 8(2):81-86. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19890234
Yin M, Fu T F, Yuan X H.A study of determination of trace REE in geological samples by ICP-MS[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1989, 8(2):81-86. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19890234
[12] Vaughan M A, Horlick G.Correction procedures for rare earth element analyses in inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Applied Spectroscopy, 1990, 44(4):587-593. doi: 10.1366/0003702904087488
[13] Aggarwal J K, Shabani M B, Palmer M R, et al.Deter-mination of the rare earth elements in aqueous samples at sub-ppt levels by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and flow injection ICPMS[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1996, 68(24):4418-4423. doi: 10.1021/ac9602074
[14] 胡圣虹, 林守麟, 刘勇胜, 等.等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中痕量稀土元素的基体效应及多原子离子干扰的校正研究[J].高等学校化学学报, 2000, 21(3):368-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0251-0790.2000.03.009
Hu S H, Lin S L, Liu Y S, et al.Studies on the calibration of matrix effects and polyatomic ion for rare earth elements in geological samples by ICP-MS[J].Chemical Jouranl of Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(3):368-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0251-0790.2000.03.009
[15] 王冠, 李华玲, 任静, 等.高分辨电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中稀土元素的氧化物干扰研究[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(4):561-567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.04.007 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/38069f63-06ff-42f3-987f-79bf9cdbb629
Wang G, Li H L, Ren J, et al.Characterization of oxide interference for the determination of rare earth elements in geological samples by high resolution ICP-MS[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(4):561-567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.04.007 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/38069f63-06ff-42f3-987f-79bf9cdbb629
[16] Naga B K, Deb S B, Saxena M K, et al.Quantification of trace level rare earth elements in Al matrices by ICP-MS[J].Radiochmica Acta, 2019, 107(3):215-220. doi: 10.1515/ract-2018-3019
[17] 吴磊, 刘义博, 王家松, 等.高压密闭消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定锰矿石中的稀土元素前处理方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6):637-643. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712060189
Wu L, Liu Y B, Wang J S, et al.Sample treatment methods for determination of rare earth elements in manganese ore by high-pressure closed digestion-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6):637-643. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712060189
[18] Yan X Y, Dai S F, Graham I T, et al.Determination of Eu concentrations in coal, fly ash and sedimentary rocks using a cation exchange resin and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 191:152-156. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.03.009
[19] Wang Y Q, Huang X X, Sun Y L, et al.A new method for the separation of LREEs in geological materials using a single TODGA resin column and its application to the determination of Nd isotope compositions by MC-ICPMS[J].Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(23):3531-3540. doi: 10.1039/C7AY00966F
[20] Satyanarayanan M, Balaram V, Sawant S S, et al.Rapid determination of REEs, PGEs, and other trace elements in geological and environmental materials by high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(1):1-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=399d63251e1afd27679392d6e00fdd4d
[21] 袁静, 沈加林, 刘建坤, 等.高能偏振能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(2):582-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201802041
Yuan J, Shen J L, Liu J K, et al.Determination of rare earth elements in geological samples by high-energy polarized energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(2):582-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201802041
[22] 周伟, 曾梦, 王健, 等.熔融制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定稀土矿石中的主量元素和稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):298-305. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706280113
Zhou W, Zeng M, Wang J, et al.Determination of major and rare earth elements in rare earth ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with fusion sample preparation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):298-305. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706280113
[23] 田春霞, 刘文华, 刘璟.稀土元素分析[J].分析试验室, 2018, 37(2):222-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz200904021
Tian C X, Liu W H, Liu J.Rare earth elements analysis[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2018, 37(2):222-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz200904021
[24] 胡圣虹, 李清澜, 林守麟, 等.感耦等离子体质谱法直接测定碳酸盐岩中超痕量稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2000, 19(4):249-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.04.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20000474
Hu S H, Li Q L, Lin S L, et al.Determination of ultra-trace rare earth elements in carbonate by ICP-MS[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2000, 19(4):249-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.04.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20000474
[25] Raut N M, Huang L, Lin K, et al.Uncertainty propaga-tion through correction methodology for the determination of rare earth elements by quadrupole based inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2005, 530(1):91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2004.08.067
[26] 曹心德, 尹明, 王晓蓉.AG50W-x8树脂分离去除钡的多原子离子对电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定稀土元素的质谱干扰[J].分析化学, 2001, 29(8):890-893. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2001.08.005
Cao X D, Yin M, Wang X R.Elimination of the spectral interference from barium polyatomic ions on rare earth elements in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry by AG50W-x8 cation exchange chromatographic separation[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 29(8):890-893. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2001.08.005
[27] 李艳玲, 熊采华, 黄慧萍, 等.基体分离-电感耦合等离子体质谱测定重晶石中超痕量稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2005, 24(2):87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.02.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20050225
Li Y L, Xiong C H, Huang H P, et al.Determination of ultra-trace rare earth elements in barite by ICP-MS after matrix separation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(2):87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.02.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20050225
[28] 尹明, 李冰.感耦等离子体质谱法在高纯稀土氧化物分析中基体谱线干扰的研究[J].岩矿测试, 1994, 13(2):81-91. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19940238
Yin M, Li B.Matrix-induced polyatomic ion interferences in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric analysis of high purity rare earth oxides[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1994, 13(2):81-91. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19940238
[29] 刘贵磊, 许俊玉, 温宏利, 等.动态反应池-电感耦合等离子体质谱法精确测定配分差异显著的重稀土元素[J].桂林理工大学学报, 2016, 36(1):176-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.024
Liu G L, Xu J Y, Wen H L, et al.Determination of heavy rare earth elements of special rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a dynamic reaction cell[J].Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2016, 36(1):176-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.024
[30] 陈从德, 蒲广平.牦牛坪稀土矿床地质特征及其成因初探[J].地质与勘探, 1991(5):18-23.
Chen C D, Pu G P.Geological features and genesis of the Maoniuping rare earth element deposit, Sichuan[J].Geology and Exploration, 1991(5):18-23.
[31] 《岩石矿物分析》编委会.岩石矿物分析(第四版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2011.
The Editorial Committee of Rock and Mineral Analysis.Rock and Mineral Analysis (The Fourth Edition)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2011.
[32] Taylor S R, Mcclenan S M.The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M].Oxford:Blackwell, 1985:312.
[33] Yu Z S, Robinson P, McGoldrick P.An evaluation of me-thods for the chemical decomposition of geological materials for trace element determination using ICP-MS[J].Geostandards & Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 25(2-3):199-217. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=70e22e5516f40de6bf750145f18bb901&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-



 下载:
下载: