Characterization of Hydrous Mineral Inclusions in Ruby and Sapphire by Infrared Spectroscopy and Microscopic Confocal Laser Raman Spectroscopy
-
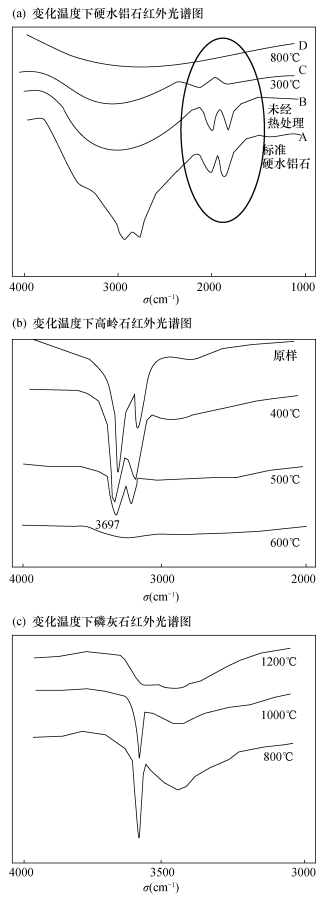
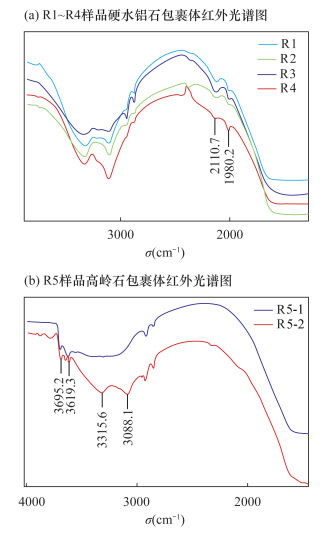
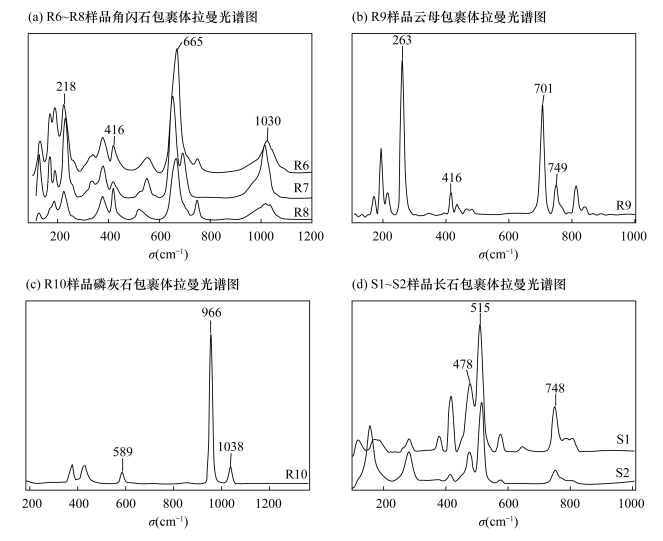
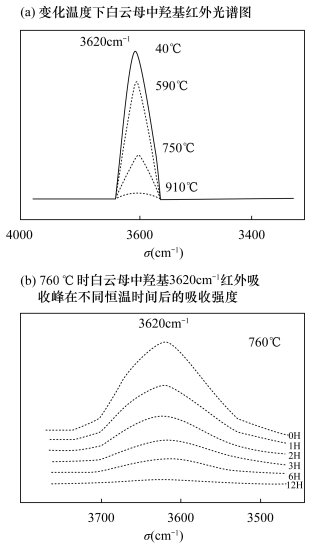
摘要: 天然红宝石和蓝宝石的包裹体中常见典型的含水矿物包裹体,这些含水矿物包裹体容易受外界环境升温而发生改变。微量含水矿物包裹体变化会对红宝石和蓝宝石的物理和化学性质产生明显影响,该性质为宝石热处理的鉴定提供了检测思路。本文采集了天然红宝石和蓝宝石样品,用显微镜放大观察包裹体特征,结合红外光谱与显微共焦激光拉曼光谱测试研究了含水矿物包裹体的特征。结果表明:天然红宝石和蓝宝石样品中含水矿物包裹体的外观轮廓清晰,晶形完整;红外光谱在2000~3700cm-1附近显示出2105~2110cm-1和1977~1985cm-1硬水铝石和3619cm-1和3696cm-1高岭石等水(H2O或-OH等)的特征吸收峰;拉曼光谱中可见角闪石、云母、磷灰石和长石等结晶度较好的典型含水矿物包裹体的特征拉曼位移。该系列特征揭示了红宝石和蓝宝石样品中含有水的特征,可作为红宝石和蓝宝石天然成因且未经过热处理的鉴定依据。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThere are water molecules and hydrous mineral inclusions in natural ruby and sapphire. The hydrous minerals disappear easily after heat treatment, which causes the physical and chemical properties of ruby and sapphire to change. Thus the hydrous mineral inclusions have important indications for identifying whether or not ruby and sapphire have been heated. OBJECTIVESTo analyze the characteristics of the hydrous mineral inclusions, and discuss the validity of the identification method for identifying whether or not ruby and sapphire have been heated through hydrous mineral inclusions. METHODSMineral inclusions were characterized by the gem microscope, infrared spectroscopy and microscopic confocal laser Raman spectroscopy. RESULTSThe hydrous mineral inclusions showed good shape and clear appearance. The infrared spectrum characteristics showed diaspore characteristic absorption peaks at 2105-2110cm-1 and 1977-1985cm-1, and kaolinite peaks at 3619cm-1 and 3696cm-1. The microscopic confocal laser Raman spectroscopy analysis showed the typical characteristic peaks of hydrous mineral inclusions such as amphibole, mica, apatite and feldspar. CONCLUSIONSThe features shown in the results reveal the water-containing characteristics of ruby and sapphire samples, which can be used to determine the natural rubies and sapphires without heat treatment. -

-
[1] 芶盛, 岳宗玉, 邸凯昌, 等.火星表面含水矿物探测进展[J].遥感学报, 2017, 21(4):531-548. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygxb201704005
Gou S, Yue Z Y, Di K C, et al.Advances in aqueous minerals detection on Martian surface[J].Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(4):531-548. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ygxb201704005
[2] 杨燕, 夏群科, 冯敏.名义上无水矿物中水的原位变温红外光谱研究[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(2):566-578. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=D141260
Yang Y, Xia Q K, Feng M.In situ FTIR investigations on noninally anlydrous minerals at varying temperatures[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(2):566-578. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=D141260
[3] 盛英明, 龚冰, 李万财, 等.名义上无水矿物中微量结构水的分析方法研究进展[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(4):443-453. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201604003
Sheng Y M, Gong B, Li W C, et al.Methodological progresses on trace amounts of structural water in noninally anlydrous minerals[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2016, 46(4):443-453. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201604003
[4] 王志海, 叶美芳, 董会, 等.流体包裹体盐度低温拉曼光谱测定方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(6):813-821. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2014.06.009
Wang Z H, Ye M F, Dong H, et al.Determining salinity of fluid inclusions by cryogenic Raman spectroscopy[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(6):813-821. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2014.06.009
[5] 何佳乐, 潘忠习, 冉敬.激光拉曼光谱法在单个流体包裹体中的应用进展[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):383-391. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.04.002
He J L, Pan Z X, Ran J.Research progress on the application of laser Raman spectroscopy in single fluid inclusions[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):383-391. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.04.002
[6] 张蓓莉, Schwarz D.世界主要彩色宝石产地研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012.
Zhang B L, Schwarz D.Geographic Origin Determination of Colored Gemstones[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2012.
[7] 陈银汉, 陈卫, 陈燕.我国红宝石, 蓝宝石及其包裹体[J].矿物学报, 1991(4):298-304. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.002
Chen Y H, Chen W, Chen Y.China's ruby and sapphire and their inclusions[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1991(4):298-304. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.002
[8] 杨坤彬, 彭金辉, 张世敏, 等.红、蓝宝石热处理现状及前景[J].贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 22(2):215-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2005.02.022
Yang K B, Peng J H, Zhang S M, et al.Advance and prospect on heat treatment of ruby and sapphire[J].Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2005, 22(2):215-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2005.02.022
[9] Wang W Y, Scarratt K, Emmtt J L, et al.The effects of heat treatment on zircon inclusions in Madagascar[J].Gems & Gemology, 2006, 42(2):134-150. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a933d62e95cbb5aaf83ad468a8caa647&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] Pardieu V, Saeseaw S, Detroyat S, et al.GIA lab reports on low-temperature heat treatment of Mozambique ruby[EB/OL].https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research-low-temperature-heat-treatment-mozambique-ruby.
[11] Tasnare S, Bbuwadol W, Tbanong L.Phase transforma-tion of epigenetic iron staining:Indication of low-temperature heat treatment in Mazambique ruby[J].The Journal of Gemmology, 2016, 35(2):156-161. doi: 10.15506/JoG.2016.35.2.156
[12] 丘志力.宝石中的包裹体——宝石鉴定的关键[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1998:45-46.
Qiu Z L.Inclusions of Gemstones-The Key Identification[M].Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988:45-46.
[13] Schwarz D.宝石学中确定宝石原产地的分析方法——以不同成因的红宝石为例[C]//2009中国珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集.北京: 国家珠宝玉石质量监督检验中心, 2009.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7710165.aspx Schwarz D.Analytical Methods Used for Origin Determination in Gemology (Case Study: Rubies Originating from Different Host Rocks)[C]//Proceedings of 2009 China Gems & Jewelry Academic Conference.Beijing: National Gemstone Testing Center, 2009.
[14] 惠鹤九, 徐永江, 潘明恩.名义上无水矿物的水含量及其地质应用[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(5):639-656. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201605004
Hui H J, Xu Y J, Pan M E.On water in noninally anlydrous minerals from mantle peridotites and magmatic rocks[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2016, 46(5):639-656. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201605004
[15] 彭文世, 刘高魁.矿物热转变的红外光谱研究[J].景德镇陶瓷, 1988(4):38-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDZT198804007.htm
Peng W S, Liu G K.The study of thermal transformation in minerals[J].Jingde Ceramics, 1988(4):38-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDZT198804007.htm
[16] 吕夏.河南省中西部石炭系铝土矿中硬水铝石的矿物学特征研究[J].地质论评, 1988, 34(4):293-301. Lü X. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.04.001
[17] 韩秀伶, 陈开惠.高岭石-多水高岭石演化系列的红外吸收光谱研究[J].地质科学, 1982(1):71-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX198201009.htm
Han X L, Chen K H.Study of infrared absorption spectra on the kaolinite-halloysite evolutionary series[J].Chinese Journal of Geology, 1982(1):71-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX198201009.htm
[18] 彭文世, 刘高魁, 柯丽琴.某些磷灰石矿物的红外吸收光谱[J].矿物学报, 1986(1):28-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB198601003.htm
Peng W S, Liu G K, Ke L Q.Infrared absorption spectra of some apatite minerals[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1986(1):28-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB198601003.htm
[19] 刘才群.用红外光谱法研究铝矾土矿物[J].中国陶瓷, 1994(1):12-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400774245
Liu C Q.A study on bauxitil clay mineral with infrared spectrometry[J].China Ceramics, 1994(1):12-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400774245
[20] 刘劲鸿.福建马坑铁矿中角闪石的谱学特征及成因意义[J].矿物岩石, 1988(1):20-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWYS198801003.htm
Liu J H.Spectroscopical characteristics and genetical significance of amphiboles in the Makeng iron ore deposit[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988(1):20-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWYS198801003.htm
[21] 顾芷娟, 张流.围压3千巴、温度700℃时角闪石羟基的变化[J].地震地质, 1982, 4(3):83-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDZ198203013.htm
Gu Z J, Zhang L.The change of hydroxyl in hornblende at confining pressure 3kb and temperature 700℃[J].Seismology and Geology, 1982, 4(3):83-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDZ198203013.htm
[22] Aines R D, Rossman G R.The high temperature behavior of trace hydrous components in silicate minerals[J].American Mineralogist, 1985, 70:1169-1179. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f61cb0d1722511fbac5bc2bf690518d4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] Tokiwai K, Nakashima S.Dehydration kinetics of mus-covite by in situ infrared microspectroscopy[J].Physics & Chemistry of Minerals, 2010, 37(2):91-101. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ff83cfd244ea51c65c656448f7cb8562&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] 曹淑慧, 张立飞, 孙樯, 等.高压下多硅白云母的拉曼光谱学研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.01.009
Cao S H, Zhang L F, Sun Q, et al.A Raman spectroscopic study of phengite under high pressure[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2006, 25(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.01.009
[25] 张蓓莉.系统宝石学(第二版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006.
Zhang B L.Systematic Gemmology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2006.
[26] 刘羽.磷灰石振动光谱的研究现状[J].武汉工程大学学报, 2002, 24(1):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2002.01.004
Liu Y.Review on the vibrational spectroscopy of apatites[J].Journal of Wuhan Institute of Chemical Technology, 2002, 24(1):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2002.01.004
[27] 屈树新, Dewijn R.羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷体外溶解实验的拉曼光谱分析[J].光散射学报, 1995(2):170-171. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500121554
Qu S X, Dewijn R.Laser Raman analysis of HA in vitro[J].Chinese Journal of Light Scattering, 1995(2):170-171. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500121554
[28] 白利平, 杜建国, 刘巍, 等.高温高压下含水矿物脱水对斜长岩纵波速度的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2003(2):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.02.004
Bai L P, Du J G, Liu W, et al.Effects of dehydration on the p-wave velocity of anorthosite at high pressure and high temperature[J].Geological Science and Technology Infomation, 2003(2):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.02.004
[29] Abraham J S D.Heat treating corundum:The Bangkok operation[J].Gems & Gemology, 1982, 18(2):79-82. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e9d3f53c8b84f98a868c3b472edbfdc2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[30] 刘学良.云南红宝石的宝石学特征及改善工艺研究[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2011.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2011350 Liu X L.Research on Gemological Characteristics and Enhancement Process of Rubies from Yunnan Province[D].Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2011.
[31] 郑越.缅甸红宝石热处理工艺及其机理研究[D].上海: 同济大学, 2014.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/D582742 Zheng Y.Mechanism Study on Rubies of Myanmar and Its Heat Treatment Techniques[D].Shanghai: Tongji University, 2014.
[32] 张恩, 彭明生.优化处理的红、蓝宝石中包裹体的变化和应用[J].矿产与地质, 2002, 16(1):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.012
Zhang E, Peng M S.The changes of inclusions in ruby and sapphire after treatment and enhancement and its applications[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2002, 16(1):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.012
-




 下载:
下载: