Vertical Distribution of Phosphorus Species at the Sediment-Water Interface of the Tuojiang River and Its Spatial and Temporal Characteristics
-
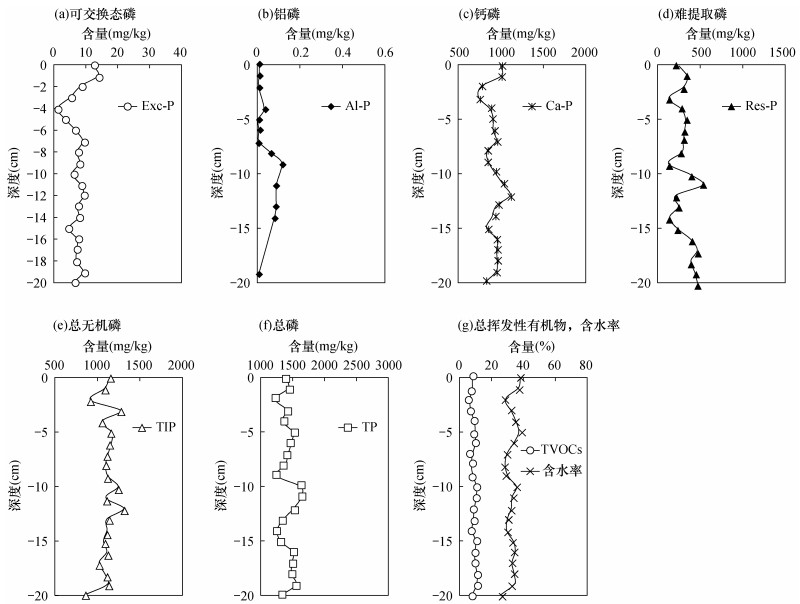
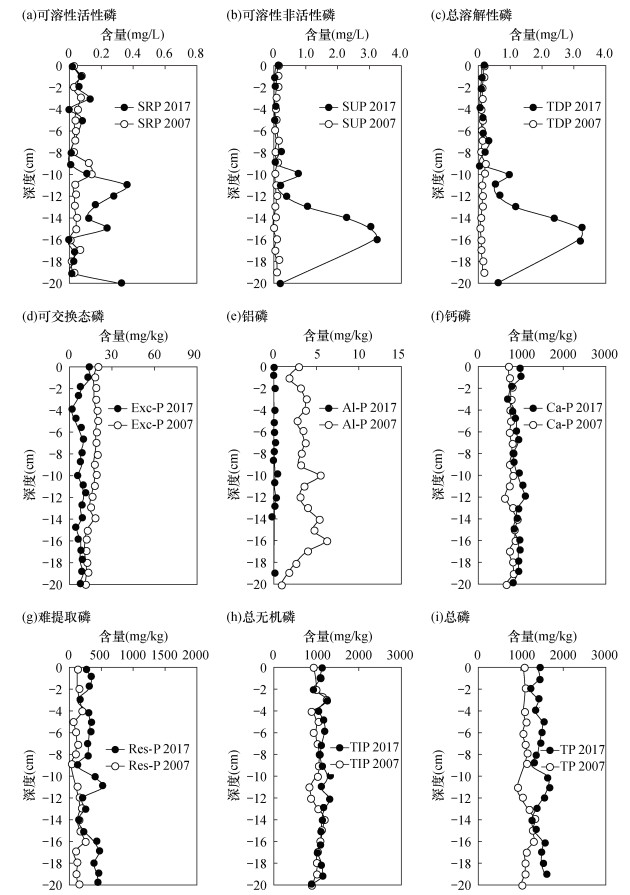
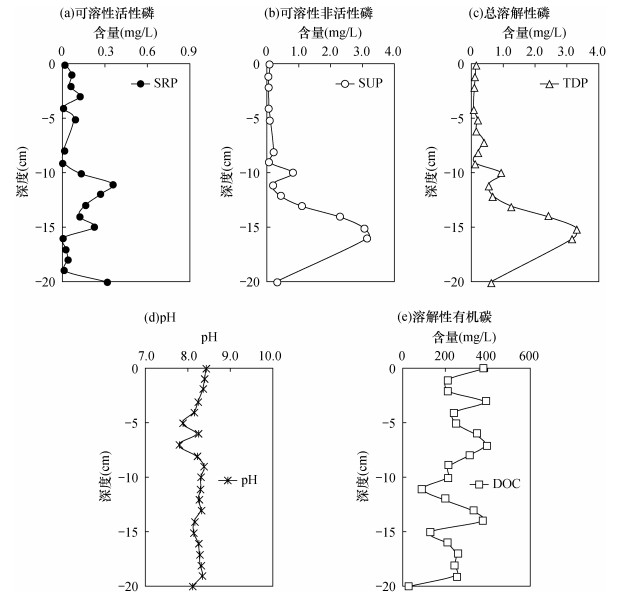
摘要: 水体中富营养化水平与磷元素的赋存形态密切相关。目前围绕引起富营养化关键因子之一的磷形态的垂向分布特征、各磷形态间的迁移转化行为及其影响因素取得了比较明确的研究进展。为进一步揭示不同磷形态在沉积物-水体系中迁移转化行为随时空的变化特征,本文采用磷钼蓝分光光度法对沱江流域简阳段间隙水中可溶性活性磷(SRP)、可溶性非活性磷(SUP)及总溶解性磷(TDP)进行测定;采用SMT法和改进的沉积物无机磷形态连续提取法对沉积物中总无机磷(TIP)、总磷(TP)、难提取磷(Res-P)、可交换态磷(Exc-P)、铁结合态磷(Fe-P)、铝结合态磷(Al-P)、钙结合态磷(Ca-P)进行提取,磷钼蓝分光光度法进行测定,以揭示沉积物-水体系中磷的赋存形态垂向分布行为特征,并将实验数据与十年前该地区磷的赋存形态结果进行对比,探讨磷赋存形态的变化趋势及影响因素。结果表明:间隙水中SRP、SUP和TDP的含量分别为0.004~0.36mg/L、0.080~3.19mg/L和0.056~3.28mg/L;沉积物中TP、TIP、Res-P、Exc-P、Al-P、Ca-P含量分别为1235.40~1646.94mg/kg、860.00~1318.59mg/kg、130.31~537.13mg/kg、1.35~14.10mg/kg、0.007~0.12mg/kg、743.13~1109.91mg/kg,Fe-P未检出。对比十年前后沉积物-水体系中磷赋存形态的变化可知,由于受到外源磷输入的影响,间隙水中SRP、SUP以及TDP含量虽然在-10cm以上变化不明显,但在-10cm以下明显增大,且导致沉积物中TP、TIP含量增加;偏碱性的沉积环境导致Al-P的释放,其含量明显减小;Exc-P含量的减小与其转化为稳定的Ca-P或Res-P形态有关。研究认为:随着时空的变化,沱江简阳段沉积物呈现外源磷输入和内源磷释放的综合污染。总体而言,由于输入的磷形态大部分以稳定的Ca-P和Res-P形态存在于沉积物中,使得表层间隙水中生物可直接利用的磷含量总体变化不大,该地区富营养化程度不会加重。维持沉积环境的弱碱性,有利于Al-P、Exc-P等向Ca-P的有效转换,抑制河流富营养化。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDThe eutrophication level in water is related to the phosphorus species in porewater and sediment closely. At present, as the one of the eutrophic elements, the vertical distribution characteristics of phosphorus species, the transfer and transformation behavior among phosphorus species and its influencing factors have made clear research progress. OBJECTIVESIn order to further reveal the temporal and spatial characteristics of the transfer and transformation of different forms of phosphorus in porewaters and sediments, and assess the ecological restoration in the area by analyzing the soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), soluble unreactive phosphorus (SUP) and total dissolved phosphorus (TDP) in porewaters, and by analyzing total inorganic phosphorus (TIP), total phosphorus (TP), residual phosphorus (Res-P), exchangeable phosphorus (Exc-P), Fe-bound phosphorus(Fe-P), Al-bound phosphorus (Al-P) and Ca-bound phosphorus (Ca-P) in sediments in Jianyang section of Tuojiang River. And the results were compared with the records of phosphorus species in the same place ten years ago to discuss the change trend and influencing factors of phosphorus occurrence. METHODSSRP, SUP and TDP in porewaters were determined by phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometry. TIP, TP, Res-P, Exc-P, Fe-P, Al-P and Ca-P in sediments were extracted by SMT method and the improved sequential extraction method. The concentration of the phosphorus species were determined by phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometry. RESULTSThe content of SRP, SUP and TDP in porewaters ranged from 0.004 to 0.36mg/L, 0.080 to 3.19mg/L and 0.056 to 3.28mg/L, respectively. The content of TP, TIP, Res-P, Exc-P, Al-P and Ca-P in sediment ranged from 1235.40 to 1646.94mg/kg, 860.00 to 1318.59mg/kg, 130.31 to 537.13mg/kg, 1.35 to 14.10mg/kg, 0.007 to 0.12mg/kg and 743.13 to 1109.91mg/kg, respectively. However, Fe-P in the sediment samples were not detected. Compared with the results of phosphorus species in sediment-water system ten years ago, it was found that although the content of SRP, SUP and TDP in porewaters were not significantly changed above -10cm, but they increased below -10cm due to the influence of exogenous phosphorus input, which also led to the increase of TP and TIP in sediments. The weak alkaline environment resulted in the release of Al-P, and the decrease of Exc-P was related to its transformation into stable forms of Ca-P or Res-P. CONCLUSIONSThe sediment in Jianyang section of Tuojiang River presents the comprehensive pollution of exogenous input and endogenous release. Generally speaking, because most of the input phosphorus exist in the forms of stable Ca-P and Res-P in sediments finally, the part of phosphorus which can be directly used by organisms in the sediment-water interface has little changed. So the eutrophication degree in this area has not increased with the change of time and space. To maintain the weak alkalinity of the sedimentary environment is conducive to the effective conversion of Al-P and Exc-P to Ca-P, and to inhibit the river eutrophication. -

-
表 1 简阳段沉积物-水体系不同赋存形态磷相关性分析
Table 1. Correlation coefficient (r) among phosphorus species in sediment-water system of Jianyang section, Tuojiang River
指标 SRP SUP TDP pH DOC Exc-P Al-P Ca-P Res-P TIP TP TVOCs SRP 1 SUP 0.063 1 TDP 0.169 0.994▲ 1 pH -0.207 -0.181 -0.070 1 DOC -0.563* 0.017 -0.134 -0.130 1 Exc-P -0.041 -0.176 -0.177 0.449* 0.124 1 Al-P 0.556* 0.260 0.363 0.206 -0.375 -0.047 1 Ca-P 0.163 -0.066 -0.041 0.152 -0.064 0.505* 0.434 1 Res-P 0.184 -0.142 -0.100 0.019 -0.536* 0.049 -0.211 0.304 1 TIP -0.011 0.069 0.028 0.002 0.445* 0.041 0.662▲ 0.378 -0.413 1 TP 0.169 -0.064 -0.060 0.020 -0.129 0.083 0.267 0.624▲ 0.605▲ 0.475* 1 TVOCs 0.088 0.310 0.296 -0.010 -0.291 -0.230 0.247 0.494* 0.479* 0.260 0.690▲ 1 含水率 -0.311 0.013 -0.011 0.176 0.105 0.067 -0.159 0.444* 0.118 0.450* 0.508* 0.531* 注:“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;“▲”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 2 简阳段沉积物和间隙水中十年前后各形态磷、TVOCs以及含水率等变化值间的相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficient (r) among the difference of phosphorus species and TVOCs, moisture content before and after ten years both in sediments and porewaters in Jianyang section, Tuojiang River
指标 ΔSRP ΔSUP ΔTDP ΔExc-P ΔAl-P ΔCa-P ΔRes-P ΔTIP ΔTP ΔTVS ΔSRP 1 ΔSUP 0.192 1 ΔTDP 0.288 0.995▲ 1 ΔExc-P 0.084 0.337 0.374 1 ΔAl-P -0.096 -0.781▲ -0.744▲ 0.459 1 ΔCa-P 0.301 -0.456 -0.407 0.317 0.334 1 ΔRes-P 0.078 -0.365 -0.353 0.290 0.477 0.240 1 ΔTIP 0.390 -0.404 -0.377 -0.219 0.043 0.699▲ 0.056 1 ΔTP 0.357 -0.545 -0.510 0.084 0.541 0.766▲ 0.691▲ 0.760▲ 1 ΔTVOCs 0.099 0.068 0.103 0.151 0.093 0.178 0.380 0.449 0.510* 1 Δ含水率 0.202 -0.495 -0.472 -0.203 0.422 0.559▲ 0.347 0.635▲ 0.761▲ 0.233 注:“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;“▲”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 -
[1] Feng W Y, Wu F C, He Z Q, et al.Simulated bioav-ailability of phosphorus from aquatic macrophytes and phytoplankton by aqueous suspension and incubation with alkaline phosphatase[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616-617:1431-1439. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.172
[2] Li Y, Wang H Z, Liang X M, et al.Total phytoplankton abundance is determined by phosphorus input:Evidence from an 18-month fertilization experiment in four subtropical ponds[J].Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquuatic Sciences, 2017, 74(9):1454-1461. doi: 10.1139/cjfas-2016-0057
[3] Zhang W Q, Jin X, Liu D, et al.Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment for a typical arid river-Fuyang River in Northern China[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 55:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.004
[4] Meinikmann K, Hupfer M, Lewandowski J.Phosphorus in groundwater discharge-A potential source for lake eutrophication[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 524:214-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.02.031
[5] 袁建, 王亚平, 许春雪.湖泊沉积物中磷形态标准物质研制[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(6):857-862. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/a784bf12-0c30-4de9-aae0-25d7ec262f34
Yuan J, Wang Y P, Xu C X.Preparation of phosphorus speciation reference materials from lake sediments[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(6):857-862. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/a784bf12-0c30-4de9-aae0-25d7ec262f34
[6] 吴怡, 邓天龙, 徐青, 等.水环境中磷的赋存形态及其分析方法研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(5):557-564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.05.017 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100517
Wu Y, Deng T L, Xu Q, et al.Research progress on speciation analysis of phosphorus in aquatic environment[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(5):557-564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.05.017 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100517
[7] 秦丽欢, 曾庆慧, 李叙勇, 等.密云水库沉积物磷形态分布特征[J].生态学杂志, 2017, 36(3):774-781. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201703027
Qin L H, Zeng Q H, Li X Y, et al.The distribution characteristics of P forms in Miyun Reservoir sediments[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(3):774-781. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201703027
[8] Zhao S N, Shi X H, Li C Y, et al.Diffusion flux of phosphorus nutrients at the sediment-water interface of the Ulansuhai Lake in Northern China[J].Water Science and Technology, 2017, 75(6):1455-1465. doi: 10.2166/wst.2017.017
[9] Wang C Y, Zhang Y, Li H L, et al.Sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in sediment[J].Limnology, 2013, 14(2):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s10201-012-0397-1
[10] 贾滨洋, 张伟, 张峰瑜.严重污染事故后河流的生态恢复——以沱江为例[J].环境科学导刊, 2008, 27(5):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2008.05.010
Jia B Y, Zhang W, Zhang F Y.Ecological restoration of river after serious pollution accident by Tuo River as case study[J].Environmental Science Survey, 2008, 27(5):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2008.05.010
[11] 杜明, 柳强, 罗彬, 等.岷江、沱江流域水环境质量现状评价及分析[J].四川环境, 2016, 35(5):20-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2016.05.004
Du M, Liu Q, Luo B, et al.Evaluation and analysis of present water environment quality of Minjiang & Tuojiang River basins[J].Sichuan Environment, 2016, 35(5):20-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2016.05.004
[12] 张蓉.沱江流域沉积物-水界面氮的赋存形态及环境地球化学研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2008.
Zhang R.Environmental Geochemistry of Nitrogen Species at the Sediment-Water Interface in Water of Tuojiang River[D].Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008.
[13] Xu Q, Yu X P, Guo Y F, et al.Seasonal variations of phosphorus species in the Tuohe River, China.PartⅠ.Sediments[J].Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2018, 36(6):1950-1961. doi: 10.1007/s00343-018-7315-2
[14] 李佳宣, 施泽明, 郑林, 等.沱江流域水系沉积物重金属的潜在生态风险评价[J].地球与环境, 2010, 38(4):481-487. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7260530
Li J X, Shi Z M, Zheng L, et al.Evaluation on potential ecological risk of heavy metals pollution in sediments from Tuojiang drainage[J].Earth and Environment, 2010, 38(4):481-487. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7260530
[15] 陶敏, 谢碧文, 齐泽民, 等.沱江浮游植物群落特征及水质评价[J].海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(4):854-861. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201604020
Tao M, Xie B W, Qi Z M, et al.Phytoplankton community structure and water quality assessment in Tuojiang River[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(4):854-861. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201604020
[16] 陶敏, 王永明, 谢碧文, 等.沱江浮游生物群落时空分布及相关环境因子分析[J].水生生物学报, 2016, 40(2):301-312. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ssswxb201602011
Tao M, Wang Y M, Xie B W, et al.Spatio-temporal distribution of plankton and driving environmental factors in the Tuojiang River[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2016, 40(2):301-312. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ssswxb201602011
[17] Zirino A, Elwany H, Facca C, et al.Nitrogen to pho-sphorus ratio in the Venice (Italy) Lagoon (2001-2010) and its relation to macroalgae[J].Marine Chemistry, 2016, 180:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2016.01.002
[18] 杨华, 江辉煌, 万晔, 等.灌河口北部海域氮磷营养盐分布及富营养化评价[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2015(1):155-161. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhztb201501022
Yang H, Jiang H H, Wan Y, et al.Study on the characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication assessment of the north waters near Guanhe Estuary[J].Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015(1):155-161. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyhztb201501022
[19] 刘霞, 徐青, 史淼森, 等.沱江流域沉积物中氮赋存状态及其垂向分布特征[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):320-326. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801250012
Liu X, Xu Q, Shi M S, et al.Nitrogen species and vertical distribution characteristics in the sediment of the Tuo River[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):320-326. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801250012
[20] 徐青.沱江流域沉积物-水界面磷的赋存形态及环境地球化学研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2008.
Xu Q.Environmental Geochemistry of Phosphorus Species at the Sediment-Water Interface of Tuojiang River[D].Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008.
[21] Neal C, Neal M, Wickham H.Phosphate measurement in natural waters:Two examples of analytical problems associated with silica interference using phosphomolybdic acid methodologies[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2000, 251-252:211-222. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=895789153bd9a993eb9ded1b297cf7ba&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] Aydin I, Temel Z, Gunduz B, et al.Comparative deter-mination of phosphorus fractions in coastal surface sediment (NE Mediterranean Sea) by ICP-OES and UV/Vis spectrometry[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(5):193-197.
[23] 闫兴成, 王明玥, 许晓光, 等.富营养化湖泊沉积物有机质矿化过程中碳、氮、磷的迁移特征[J].湖泊科学, 2018, 30(2):306-313. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hpkx201802003
Yan X C, Wang M Y, Xu X G, et al.Migration of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus during organic matter mineralization in eutrophic lake sediments[J].Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(2):306-313. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hpkx201802003
[24] Wang Y M, Li K F, Liang R F, et al.Distribution and release characteristics of phosphorus in a reservoir in Southwest China[J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16:1-12. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3bc2f3ce17589738156a354604df91d9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] 潘延安, 雷沛, 张洪, 等.重庆园博园龙景湖新建初期内源氮磷分布特征及扩散通量估算[J].环境科学, 2014, 35(5):1727-1734. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201405013
Pan Y A, Lei P, Zhang H, et al.Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediments and estimation nutrients fluxes in Longjinghu Lake, Chongqing City, during the impoundment period[J].Environmental Science, 2014, 35(5):1727-1734. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201405013
[26] 龚梦丹, 金增锋, 王燕, 等.长江中下游典型浅水湖泊沉积物-水界面磷和铁的耦合关系[J].湖泊科学, 2017, 29(5):1103-1111. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97421X/201705/673097240.html
Gong M D, Jin Z F, Wang Y, et al.Coupling between iron and phosphorus in sediments of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River using diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT)[J].Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(5):1103-1111. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97421X/201705/673097240.html
[27] Cao X Y, Song C L, Zhou Y Y.Limitations of using extracellular alkaline phosphatase activities as a general indicator for describing P deficiency of phytoplankton in Chinese shallow lakes[J].Journal of Applied Phycology, 2010, 22(1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s10811-009-9422-0
[28] 周纯, 宋春雷, 曹秀云, 等.太湖不同解有机磷菌株胞外碱性磷酸酶活性对蓝藻碎屑的响应[J].水生生物学报, 2012, 36(1):119-125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ssswxb201201017
Zhou C, Song C L, Cao X Y, et al.Responses of extracellular alkaline phosphatase activity in different organic phosphorus mineralizing bacteria strains isolated from Lake Taihu to the cyanobacterium detritus[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2012, 36(1):119-125. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ssswxb201201017
[29] 宋炜, 袁丽娜, 肖琳, 等.太湖沉积物中解磷细菌分布及其与碱性磷酸酶活性的关系[J].环境科学, 2007, 28(10):2355-2360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.10.035
Song W, Yuan L N, Xiao L, et al.Alpase activity and the distribution of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the relationship between them in sediments of Lake Taihu[J].Environmental Science, 2007, 28(10):2355-2360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.10.035
[30] Subhajit D, Tapan K J, Tarun K D.Vertical profile of phosphatase activity in the Sundarban Mangrove Forest, north east coast of bay of Bengal, India[J].Geomicrobiology Journal, 2014, 31:716-725. doi: 10.1080/01490451.2013.866705
[31] Alperin M J, Albert D B, Martens C S.Seasonal varia-tions in production and consumption rates of dissolved organic carbon in an organic-rich coastal sediment[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(22):4909-4930. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90221-6
[32] 倪建宇, Maggiulli M.赤道东北太平洋沉积物间隙水中溶解有机碳的分布特征[J].海洋学报, 2007, 29(1):155-160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.01.022
Ni J Y, Maggiulli M.Dissolved organic carbon in sediments from the equatorial Northeastern Pacific[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(1):155-160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.01.022
[33] 陈晶, 张毅敏, 杨飞, 等.基于核磁共振技术的滆湖沉积物有机磷垂直分布特征[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(9):850-856. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj201809011
Chen J, Zhang Y M, Yang F, et al.Characteristics of vertical distribution of organic phosphorus by 31P-NMR technique from different sources of core sediments in Gehu Lake[J].Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2018, 34(9):850-856. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj201809011
[34] 陈海龙, 袁旭音, 王欢, 等.苕溪干流悬浮物和沉积物的磷形态分布及成因分析[J].环境科学, 2015, 36(2):464-470. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201502013
Chen H L, Yuan X Y, Wang H, et al.Distributions of phosphorus fraction in suspended sediments and surface sediments of Tiaoxi mainstreams and cause analysis[J].Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2):464-470. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201502013
[35] Zhang W, Jin X, Meng X, et al.Phosphorus trans-formations at the sediment-water interface in shallow freshwater ecosystems caused by decomposition of plant debris[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 201:328-334. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.006
[36] Guo S K, Xiao S B.Distribution characteristics of pho-sphorus in sediments of Dianchi[J].Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering A, 2018(7):225-227.
[37] Wu Y, Wen Y, Zhou J, et al.Phosphorus release from lake sediments:Effects of pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen[J].KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2014, 18(1):323-329. doi: 10.1007/s12205-014-0192-0
[38] 常琛朝, 程东会, 钱康.渭河咸阳段非饱和层状沉积物中水分分布特征[J].中国水土保持科学, 2017, 15(4):104-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgstbckx201704013
Chang C C, Cheng D H, Qian K.Water content distribution of unsaturated layered sediments of Weihe River in Xianyang section[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 15(4):104-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgstbckx201704013
-



 下载:
下载: