Study on the Relationship between the Contents of Heavy Metals in Rice and Root Soils in Typical Townships in the Western Pearl River Delta
-
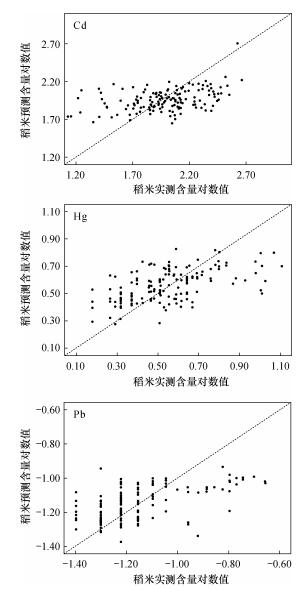
摘要: 农田土壤环境质量与稻米食用安全性关系非常密切,已有研究表明在采矿、交通、电子工业等影响下,珠三角地区积累了大量环境问题,镉汞砷等污染越来越严重。重金属在土壤-稻米系统中的迁移转化,受其总含量、土壤理化性质、有机质以及微量或大量元素的交互作用影响。为查明广东省佛山市高明区典型乡镇重金属在土壤-稻米系统中的迁移影响因素,为稻米食用安全性预测提供依据,本文在高明区明城镇、更合镇主要农田区,采集了151组稻谷及对应根系土样品,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)、原子荧光光谱法(AFS)等技术测定了土壤重金属、养分元素含量、土壤理化指标以及稻米重金属含量,分析了重金属含量特征及其迁移的影响因子,建立并验证了稻米中重金属含量定量预测模型。结果表明:①土壤重金属含量均低于第一次全国土壤污染调查获得的广东省土壤重金属含量均值,并且均低于《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618—2018)中的土壤风险管制值,土壤污染风险低;②稻米中除Cd、Pb存在轻微超标外,其余重金属含量均低于食品卫生标准限值;③土壤重金属总量、土壤理化性质(土壤pH,土壤质地,土壤有机质含量,土壤N、P、K等)是重金属在土壤-稻米系统中迁移的关键控制因素。如土壤Cd、Cu总量与其在稻米中含量呈显著正相关;除Pb外,土壤有机质土壤全氮与各稻米中各重金属含量呈显著负相关;除Cd外,土壤全磷与稻米重金属含量呈显著负相关;土壤质地(SiO2/Al2O3)与稻米各重金属含量均呈显著正相关;④根据随机抽取的130组数据,以土壤重金属总量及土壤理化指标为自变量,建立了稻米As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb含量多元回归方程,均达到显著相关,经剩余21组数据的验证,预测方程的平均误差的中位数与平均数最大为31%,最小为7.8%,总体来说预测效果较好,模型可以用来预测高明区及其相似地区的稻米重金属含量。本研究通过探讨土壤理化性质的影响,引入土壤大量营养元素作为影响因素进行探究,可为研究大量营养元素对土壤重金属迁移至稻米的影响以及科学施肥指导提供参考;同时获得的土壤-稻米系统元素迁移影响因素,可对开展重金属生物有效性研究以及水田土壤污染修复、相似地区生态风险评价提供参考;简单探讨了降低研究区重金属生物有效性的方法以及抑制重金属的迁移、降低重金属生物危害的措施,为探究重金属迁移规律特征与地方病、流行病之间的关系提供了思路。Abstract:
OBJECTIVES The environmental quality of farmland soil is closely related to the safety of edible rice. Studies have shown that under the influence of mining, transportation, and electronics industries, the Pearl River Delta has accumulated a large number of environmental problems. Pollution such as cadmium, mercury and arsenic is becoming more and more serious. The migration and transformation of heavy metals in the soil-rice system is affected by the interaction of their total content, physical and chemical properties of the soil, organic matter, and trace or major elements. OBJECTIVES To find out the factors influencing the migration of heavy metals in the soil-rice system in the typical towns of Gaoming District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province, and to provide a basis for the prediction of rice food safety. METHODS In the main farmland areas of Mingcheng Town and Genghe Town of Gaoming District, 151 groups of rice and corresponding root soil samples were collected. Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) and other techniques were used to determine heavy metals in the soil, nutrient element content, physical and chemical indicators of the soil, and heavy metal content in rice. The characteristics of heavy metal content and its influencing factors were analyzed, and the quantitative prediction model of heavy metal content in rice was established and verified. RESULTS Results showed that the heavy metal content of the soil was lower than the average heavy metal content of the soil in Guangdong Province obtained by the first national soil pollution survey, and was lower than the soil risk control value in the national standard Soil Environment Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB 15618-2018), resulting in a low soil pollution risk. Except for the slight excess of Cd and Pb in rice, the content of other heavy metals was lower than the limit of food hygiene standards. Total heavy metals and physical and chemical properties (soil pH, soil texture, soil organic matter content, soil N, P, K, etc.) were the key controlling factors for the migration of heavy metals in the soil-rice system. According to the 130 sets of randomly selected data, the total amount of soil heavy metals and soil physical and chemical indicators were used as independent variables to establish rice As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb content multiple regression equation. All reached a significant correlation. After the verification of the remaining 21 sets of data, the median and average of the average error of the prediction equation were 31% at the maximum and 7.8% at the minimum. In general, the prediction effect was good, and the model can be used to predict the heavy metal content of rice in the Gaoming District and similar regions. Conclusion A large number of soil nutrient elements were introduced as the influencing factors when exploring the influence of physical and chemical properties of the soil, and provided a reference for studying the effect of nutrient elements on the migration of heavy metals in the soil to rice, and guidance for future scientific fertilization. The influencing factors of the soil-rice system element migration obtained at the same time provide a reference for carrying out heavy metal bioavailability research, paddy soil pollution remediation, and ecological risk assessment in similar areas. This article briefly discusses methods to reduce the bioavailability of heavy metals in the study area and measures to inhibit the migration of heavy metals and reduce the biological hazards of heavy metals. It also provides ideas for exploring the relationship between the migration characteristics of heavy metals and endemic and epidemic diseases. -

-
表 1 土壤和稻米样品分析方法和分析质量控制参数
Table 1. Analysis methods of soil and rice samples and their control parameters of analysis quality
土壤样品 待测元素 分析方法 检出限 标样合格率(%) 重复样合格率(%) As 氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) 1 100 98.9 Cd 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.03 100 96.6 Cr 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)、压片制样-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 5 100 95.5 Cu 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 1 100 100 Hg 冷蒸气-原子荧光光谱法(CV-AFS) 0.5 100 98.9 Ni 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 2 100 97.7 Pb 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 2 100 98.9 Zn 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 4 100 98.9 N 氧化燃烧-气相色谱法 20 100 100 P 压片制样-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 5 100 98.9 K2O 压片制样-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 0.05 100 100 SiO2 压片制样-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 0.1 100 100 Al2O3 压片制样-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 0.05 100 100 Corg 氧化热解-电位法 0.1 100 98.9 pH 电位法 0.1 100 100 稻米样品 As 氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) 0.1 94.4 100 Cd 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.01 100 100 Cr 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.2 100 100 Cu 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 1 100 100 Hg 冷蒸气-原子荧光光谱法(CV-AFS) 0.5 100 100 Ni 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.2 97.2 100 Pb 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.5 100 100 Zn 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 2 100 100 注:pH无量纲;SiO2、Al2O3、TFe2O3、MgO、CaO、Na2O、K2O、Corg的检出限单位为%;Hg元素含量单位为ng/g,其余元素均为μg/g。 表 2 土壤样品重金属含量统计(N=151)
Table 2. Statistics of heavy metal content in soil samples (N=151)
分析项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 均值 7.18 0.126 36.4 12.5 0.143 8.18 40 49.3 中位数 4.36 0.011 31.4 11.21 0.012 7.79 34.3 44.4 标准差 8.86 0.156 19.6 6.16 0.852 4.07 16.5 44.7 最大值 68.7 1.95 99.8 45.6 0.562 29 110 565 最小值 0.761 0.003 8.8 2.87 0.003 1.09 11.5 15.1 广东省A 16.8 0.336 60.4 24.1 0.199 18.7 60.4 87.4 广东省B - 0.1 58 18 0.104 18 37.5 51 中国土壤C 11.2 0.097 53.9 20 0.04 23.4 23.6 67.7 pH≤5.5* 30 0.3 250 50 0.5 60 80 200 5.5<pH≤6.5* 30 0.4 250 50 0.5 70 100 200 pH≤5.5△ 200 1.5 800 - 2.0 - 400 - 5.5<pH≤6.5△ 150 2.0 850 - 2.5 - 500 - 注:A为第一次全国土壤污染调查广东省土壤元素含量均值[34];B为广东省表层土壤均值[35];C为全国土壤元素含量背景值[36];单位均为μg/g;“-”表示未检出;“*”为风险筛选值;“△”为风险管制值。 表 3 稻米样品重金属含量统计(N=151)
Table 3. Statistics of heavy metal content in rice samples (N=151)
分析项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 均值(μg/g) 0.146 0.118 0.166 2.78 0.004 0.341 0.078 18.2 标准差(μg/g) 0.056 0.085 0.08 0.752 0.003 0.165 0.043 2.22 最大值(μg/g) 0.69 0.457 0.64 4.9 0.019 0.99 0.32 24.7 粮食卫生标准*(μg/g) - 0.2 1.0 - 0.02 - 0.2 - 超标数量(件) - 26 0 - 0 - 4 - 富集系数 0.02 1.4 0.018 0.273 0.0004 0.028 0.006 1.19 注:标注“*”的数据来源《食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762—2017)。 表 4 稻米与根系土样品重金属含量及土壤理化性质相关系数(N=151)
Table 4. Correlation coefficient of heavy metal content and physical and chemical properties of rice and root soil samples (N=151)
分析项目 相关关系 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 土壤总含量 相关性 0.048 0.344* 0.138 0.250* -0.255* -0.178△ -0.136 -0.012 显著性 0.562 0 0.091 0.002 0.005 0.134 0.029 0.883 Corg 相关性 -0.308* -0.221* -0.384* -0.421* -0.523* -0.375* -0.099 -0.500* 显著性 0 0.006 0 0 0 0 0.228 0 pH 相关性 -0.016 0.051 -0.089 -0.134 -0.134 -0.161△ 0.170△ -0.069 显著性 0.845 0.531 0.278 0.1 0.1 0.048 0.037 0.398 SiO2/Al2O3 相关性 0.196△ 0.325* 0.240* 0.224* 0.199△ 0.242* 0.444* 0.633* 显著性 0.016 0 0.003 0.006 0.014 0.003 0 0 土壤全氮 相关性 -0.316* -0.172△ -0.454* -0.503* -0.582* -0.405* 0.063 -0.509* 显著性 0 0.035 0 0 0 0 0.443 0 土壤全磷 相关性 -0.299* -0.123 -0.312* -0.174△ -0.332* -0.304* -0.251* -0.392* 显著性 0 0.131 0 0.032 0 0 0.002 0 K2O 相关性 -0.07 -0.240* 0.039 0.063 0.135 0.021 -0.563* -0.345* 显著性 0.394 0.003 0.637 0.444 0.098 0.797 0 0 注:标注“*”的数据在p<0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;标注“△”在p<0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;除土壤总含量外,其余项目(Corg等)的相关性均为该项目与元素富集系数的相关性。 表 5 研究区水稻重金属影响因素及其预测方程
Table 5. Influencing factors and prediction equations of rice heavy metals in the study area
分析项目 常量 log[土] log[N] log[P] log[Corg] pH log[SiO2/Al2O3] log[K2O] R* log[稻As] -0.844 - - - -0.172 - - - 0.219 log[稻Cd] 0.897 0.556 - - - - - -0.363 0.421 log[稻Cr] -0.779 - - - - - - -0.166 0.221 log[稻Cu] -0.219 0.139 - 0.167 - - - - 0.354 log[稻Hg] 2.596 - -0.652 - - - - - 0.517 log[稻Ni] 0.007 - - - -0.277 -0.105 - 0.157 0.380 log[稻Pb] -6.015 - 1.608 - -1.430 - - - 0.536 log[稻As]=0.172log[Corg]-0.844 log[稻Cd]=0.556log[Cd]-0.363log[K2O]+0.897 log[稻Cr]=-0.166log[K2O]-0.779 log[稻Cu]=0.167log[P]+0.139log[土]-0.219 log[稻Hg]=-0.652log[N]+2.596 log[稻Ni]=-0.105[pH]-0.277log[Corg]+0.157log[K2O]-0.007 log[稻Pb]=1.608log[N]-1.430log[Corg]-6.015 注:“*”表示显著性水平均为p < 0.05。 表 6 预测模型误差统计值
Table 6. Statistics of prediction model errors
预测模型参数 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb 误差平均值(%) 7.8 11.0 11.0 18.5 24.0 31.6 10.2 误差中位数(%) 6.73 4.48 6.8 19.2 17.6 19.0 6.16 误差最大值(%) 22.52 43.03 32.05 53.31 58.06 77.62 34.96 误差最小值(%) 0.82 1.41 0.35 2.70 0.99 5.63 0.89 注:误差已经剔除异常值。 -
[1] 王瑶瑶, 郝毅, 张洪, 等.珠三角地区大米中的镉砷污染现状及治理措施[J].中国农学通报, 2019, 35(12):63-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgnxtb201912011
Wang Y Y, Hao Y, Zhang H, et al.Cadmium and arsenic pollution in rice in the pearl river delta and the counter measures[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(12):63-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgnxtb201912011
[2] 胡培松.土壤有毒重金属镉毒害及镉低积累型水稻筛选与改良[J].中国稻米, 2004(2):10-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdm200402003
Hu P S.Cadmium detoxification in soil and breeding of new rice with less cadmium accumulation[J].China Rice, 2004(2):10-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdm200402003
[3] 刘君, 张猛, 张士荣, 等.山东省水稻产地土壤重金属污染风险评价[J].青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 36(2):112-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lynxyxb201902006
Liu J, Zhang M, Zhang S R, et al.Pollution risk evaluation of heavy metals in paddy soils in Shandong Province[J].Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 36(2):112-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lynxyxb201902006
[4] 杭小帅, 周健民, 王火焰, 等.常熟市高风险区水稻籽粒重金属污染特征及评价[J].中国环境科学, 2009, 29(2):130-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghjkx200902004
Hang X S, Zhou J M, Wang H Y, et al.Heavy metal pollution characteristics and assessment of rice grain from a typical high risk area of Changshu City, Jiangsu Province[J].China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(2):130-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghjkx200902004
[5] Sun G X, Wiele T Ⅴ D, Alava P, et al.Arsenic in cooked rice:Effect of chemical, enzymatic and microbial processes on bioaccessibility and speciation in the human gastrointestinal tract[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 162:241-246. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.021
[6] Chen T, Liu X, Zhu M, et al.Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 151(1):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.03.004
[7] 甘国娟, 朱晓龙, 刘妍, 等.田间条件下Pb在土壤-水稻中的迁移特征[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(3):514-519. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjhx201503016
Gan G J, Zhu X L, Liu Y, et al.Transfer characteristics of Pb in soil-rice system under field conditions[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(3):514-519. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjhx201503016
[8] Usman A, Kuzyakov Y, Stahr K.Effect of clay minerals on immobilization of heavy metals and microbial activity in a sewage sludge-contaminated soil[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2005, 5(4):245-252. doi: 10.1065/jss2005.05.141
[9] Ok Y S, Lim J E, Moon D H.Stabilization of Pb and Cd contaminated soil sand soil quality improvements using waste oyster shells[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(1):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s10653-010-9329-3
[10] Moreno A M, Quintana J R, Pérez L, et al.Factors influencing lead sorption-desorption at variable added metal concentrations in Rhodoxeralfs[J].Chemosphere, 2006, 64:758-763. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.058
[11] Vega F A, Covelo E F, Andrade M L.Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils:Influence of mine soil characteristics[J].Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2006, 298(2):582-592. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/7315182_Competitive_Sorption_and_Desorption_of_Heavy_Metals_in_Mine_Soils_Influence_of_Mine_Soil_Characteristics
[12] Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A.Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced exogenous humic substances[J].Chemosphere, 2003, 52(1):265-275. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00185-1
[13] Romero F M, Villalobos M, Aguirre R, et al. Solid-phase control on lead bioaccessibility in smelter-impacted soils[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 55:566-575. doi: 10.1007/s00244-008-9152-3
[14] Ajmone-Marsan F, Biasioli M, Kralj T, et al.Metals in particle-size fractions of the soils of five European cities[J].Environmental Pollution, 2008, 152(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.05.020
[15] Luo X S, Yu S, Li X D.Distribution, availability, and sources of trace metals in different particle size fractions of urban soils in Hong Kong:Implications for assessing the risk to human health[J].Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159:1317-1326. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.01.013
[16] Madrid F, Diaz-Barrientos E, Madrid L.Availability and bio-accessibility of metals in the clay fraction of urban soils of Sevilla[J].Environmental Pollution, 2008, 156(3):605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.023
[17] Qian J, Shan X Q, Wang Z J, et al.Distribution and plant availability of heavy metals in different particle-size fractions of soil[J].The Science of the Total Environment, 1996, 187:131-141. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(96)05134-0
[18] 李杰, 朱立新, 康志强.南宁市郊周边农田土壤-农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J].中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):43-52. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyr201801006
Li J, Zhu L X, Kang Z Q.Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system of peri-urban agricultural soils of Nanning, South China[J].Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):43-52. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyr201801006
[19] 王腾云, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 等.福建沿海地区土壤-稻谷重金属含量关系与影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3):295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.013
Wang T Y, Zhou G H, Sun B B, et al.The relationship between heavy metal contents of soils and rice in coastal areas, Fujian Province, including influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3):295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.013
[20] 蒋彬, 张慧萍.水稻精米中铅镉砷含量基因型差异的研究[J].云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 22(3):37-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ynsfdxxb200203011
Jiang B, Zhang H P.Genotypic differences in concentrations of plumbum, cadmium and arsenicum in polished rice grains[J].Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2002, 22(3):37-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ynsfdxxb200203011
[21] 夏蔓蔓, 何腾兵.土壤-水稻镉生物有效性预测模型研究进展[J].天津农业科学, 2019, 25(2):12-17. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94868X/20192/7001177169.html
Xia M M, He T B.Research progresses on prediction models of cadmium bioavailability in soil-rice system[J].Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 25(2):12-17. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94868X/20192/7001177169.html
[22] Adams M L, Zhao F J, Mcgrath S P, et al. Predicting cadmium concentrations in wheat and barley grain using soil properties[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(2):532-541. doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.5320
[23] McBride M.Cadmium uptake by crops estimated from soil total Cd and pH[J].Soil Science, 2002, 167(1):62-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9b86756ceb1bdca2737c4defdfcad9e5
[24] 刘情, 陈红燕, 唐豆豆, 等.苏南典型区土壤-水稻系统中重金属迁移特征及定量模型研究[J].环境科技, 2016, 29(4):20-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jshjkj201604006
Liu Q, Chen H Y, Tang D D, et al.Migration characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metals in the typical polluted areas of Southern Jiangsu Province[J].Environment Science and Technology, 2016, 29(4):20-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jshjkj201604006
[25] 赵科理, 傅伟军, 戴巍.浙江省典型水稻产区土壤-水稻系统重金属迁移特征及定量模型[J].中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2):226-234. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stnyyj201602011
Zhao K L, Fu W J, Dai W.Characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metal transfer in soil-rice systems in typical rice production areas of Zhejiang Province[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2):226-234. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stnyyj201602011
[26] 李志博, 骆永明, 宋静, 等.基于稻米摄入风险的稻田土壤镉临界值研究:个案研究[J].土壤学报, 2008(1):76-81. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb200801010
Li Z B, Luo Y M, Song J, et al.Critical values for Cd in paddy field based on Cd risk of rice consumption:A case study[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008(1):76-81. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb200801010
[27] 陈永胜.多元线性回归建模以及MATLAB和SPSS求解[J].绥化学院学报, 2007, 27(6):166-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shszxb200706061
Chen Y S.Multiple linear regression modeling and MATLAB and SPSS solving[J].Journal of Suihua University, 2007, 27(6):166-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shszxb200706061
[28] Kempen B, Bres D J, Heuvelink G B.Updating the 1:50000 Dutch soil map using legacy soil data:A multinomial logistic regression approach[J].Geoderma, 2009, 151(3-4):311-326. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.023
[29] 王梦梦, 何梦媛, 苏德纯, 等.稻田土壤性质与稻米镉含量的定量关系[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(4):1918-1925. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkx201804054
Wang M M, He M Y, Su D C, et al.Quantitative relationship between paddy soil properties and cadmium content in rice grains[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4):1918-1925. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkx201804054
[30] 何燕, 周国华, 王学求.从微量元素与人体健康关系得到的启示[J].物探与化探, 2008, 32(1):70-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht200801016
He Y, Zhou G H, Wang X Q.The enlightenment from the relationship between trace elements and human health[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(1):70-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht200801016
[31] Zhang H K, Shao D D, Zheng L N, et al.Determination of trace mercury in water by on-line solid phase extraction and ultraviolet vapor generation-ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(2):37-41. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.02.001
[32] Oral E Ⅴ.Comparison of modified tessier and revised BCR sequential extraction procedures for the fractionation of heavy metals in malachite ore samples using ICP-OES[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(4):122-126. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.04.002
[33] Liu M T, Mao X F, Liu J X.Direct determination of ultratrace arsenic in blood samples using an in-situ dielectric barrier discharge trap coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(3):83-90. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.03.002
[34] Chen H Y, Teng Y G, Lu S J, et al.Contamination fea-tures and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512-513:143-153. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/25617996
[35] 陈俊坚, 张会化, 刘鉴明, 等.广东省区域地质背景下土壤表层重金属元素空间分布特征及其影响因子分析[J].生态环境学报, 2011, 20(4):646-651. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tryhj201104010
Chen J J, Zhang H H, Liu J M, et al.Spatial distributions and controlled factors of heavy metals in surface soils in Guangdong based on the regional geology[J].Ecology and Environmnet, 2011, 20(4):646-651. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tryhj201104010
[36] Chen J S, Wei F S, Zheng C J, et al.Background concen-trations of elements in soils of China[J].Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 1991, 57-58(1):699-712.
[37] 李婷婷, 刘子宁, 朱鑫, 等.珠三角地区土壤重金属元素异常来源浅析及其环境质量评价[J].国土资源导刊, 2016, 13(2):30-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hunandz201602006
Li T T, Liu Z N, Zhu X, et al.Origin of heavy metal element anomalies in soils of the Pearl River Delta and its environmental quality assessment[J].Land & Resources Herald, 2016, 13(2):30-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hunandz201602006
[38] 韩志轩, 王学求, 迟清华, 等.珠江三角洲冲积平原土壤重金属元素含量和来源解析[J].中国环境科学, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghjkx201809032
Han Z X, Wang X Q, Chi Q H, et al.Occurrence and source identification of heavy metals in the alluvial soils of Pearl River Delta region, South China[J].China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghjkx201809032
[39] 王开峰, 彭娜, 王凯荣, 等.长期施用有机肥对稻田土壤重金属含量及其有效性的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2008, 22(1):105-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqsystbcxb200801023
Wang K F, Peng N, Wang K R, et al.Effects of long-term manure fertilization on heavy metal content and its availability in paddy soils[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 22(1):105-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqsystbcxb200801023
[40] 周国华.土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1097-1106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht201406001
Zhou G H.Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1097-1106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht201406001
[41] 陈穗玲, 李锦文, 邓红梅.福建沿海地区农田土壤理化性质与重金属含量的关系[J].湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(13):3025-3029. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbnykx201413014
Chen S L, Li J W, Deng H M.The relationship between physical and chemical properties of soil and heavy metal content in Fujian coastal farmland[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(13):3025-3029. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbnykx201413014
[42] 刘全东, 蒋代华, 高利娟, 等.畜禽粪便有机肥源重金属在土壤-蔬菜系统中累积、迁移规律的研究进展[J].土壤通报, 2014, 45(1):252-256. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201401045
Liu Q D, Jiang D H, Gao L J, et al.Research progress on heavy metal accumulation and migration of livestock dung organic fertilizer in soil-vegetable system[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(1):252-256. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201401045
[43] 王龙龙, 郭笃发, 李桥.土壤-植物系统重金属污染研究[J].绿色科技, 2013(6):236-238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LVKJ201306094.htm
Wang L L, Guo D F, Li Q.Study on heavy metal pollution in soil-plant system[J].Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2013(6):236-238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LVKJ201306094.htm
[44] 聂呈荣, 林初夏, 杜瑞英, 等.佛山市菜园地土壤及蔬菜重金属含量特征分析[J].佛山科学技术学院学报(自然科学版), 2010(3):1-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_6168693.aspx
Nie C R, Lin C X, Du R Y, et al.Heavy metal characteristics of vegetables and their soils in Foshan city[J].Journal of Foshan University(Natural Science Edition), 2010(3):1-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_6168693.aspx
[45] 吴迪, 杨秀珍, 李存雄, 等.贵州典型铅锌矿区水稻土壤和水稻中重金属含量及健康风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(10):1992-1998. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201310013
Wu D, Yang X Z, Li C X, et al.Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soil and rice in zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou Province, China[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(10):1992-1998. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201310013
[46] 付洪波, 李取生, 骆承程.珠三角滩涂围垦农田土壤和农作物重金属污染[J].农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(6):1142-1146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh200906009
Fu H B, Li Q S, Luo C C.Heavy metals pollution in the reclaimed tidal flat soils and crops in the Pearl River Delta[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(6):1142-1146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh200906009
[47] 何江华, 柳勇, 王少毅, 等.广州市菜园土主要蔬菜重金属背景含量的研究[J].生态环境, 2003, 12(3):269-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tryhj200303004
He J H, Liu Y, Wang S Y, et al.Studies on the background levels of heavy metals in major vegetables in Guangzhou vegetable garden soils[J].Ecology and Environment, 2003, 12(3):269-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tryhj200303004
[48] 李波, 青长乐, 周正宾, 等.肥料中氮磷和有机质对土壤重金属的影响及治污中的应用[J].重庆环境科学, 2000, 22(6):37-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqhjkx200006013
Li B, Qing C L, Zhou Z B, et al.Influence of N, P and organic matter of fertilizers on heavy metals in soil and its application[J].Chongqing Environmental Science, 2000, 22(6):37-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqhjkx200006013
[49] 何电源.关于稻田施用石灰的研究[J].土壤学报, 1992, 29(1):87-93. http://www.ixueshu.com/document/946e317b94c487689768ab4375530f01318947a18e7f9386.html
He D Y.A review about studies on liming of paddy soil[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1992, 29(1):87-93. http://www.ixueshu.com/document/946e317b94c487689768ab4375530f01318947a18e7f9386.html
[50] 孙彬彬, 周国华, 刘占元, 等.黄河下游山东段沿岸土壤中重金属元素异常的成因[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(2):265-270. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200802015
Sun B B, Zhou G H, Liu Z Y, et al.Origin of heavy metal anomalies in soils along the Shandong reach of the lower Yellow River, China[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2):265-270. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200802015
[51] 刘兰英, 黄薇, 吕新, 等.田间环境下土壤-水稻系统重金属的迁移特征[J].福建农业学报, 2018, 33(1):66-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fjnyxb201801013
Liu L Y, Huang W, Lü X, et al.Migration of heavy metals from soil to rice plant[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(1):66-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fjnyxb201801013
[52] Nan Z R, Li J J, Zhang J M, et al.Cadmium and zinc interactions and their transfer in soil-crop system under actual field conditions[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 285(1-3):187-195. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00919-6
[53] Yanai J, Zhao F J, McGrath S, et al. Effect of soil characteristics on Cd uptake by the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens[J].Environmental Pollution, 2006, 139(1):67-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b3607facf9cc72793257d1e5d303f3cd
[54] Lavado R S, Rodrlguez M, Alvarez R, et al.Transfer of potentially toxic elements from biosolid-treated soil stomaize and wheat crops[J].Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2007, 118(1/4):312-318. http://europepmc.org/abstract/AGR/IND43876183
[55] Karami M, Afyuni M, Khoshgoftarmanesh A H, et al.Grain zinc, iron, and copper concentrations of wheat grown in central Iran and their relationships with soil and climate variables[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(22):10876-10882. doi: 10.1021/jf902074f
[56] Romkens P F A M, Guo H Y, Chu C L, et al.Prediction of cadmium uptake by brown rice and derivation of soil-plant transfer models to improve soil protection guidelines[J].Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8-9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.03.009
[57] Dudka S, Piotrowska M, Terelak H.Transfer of cadmium, lead, and zinc from industrially contaminated soil to crop plants:A field study[J].Environmental Pollution, 1996, 94(2):181-188. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(96)00069-3
[58] 曾翔, 张玉烛, 王凯荣, 等.不同品种水稻糙米含镉量差异[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2006, 22(1):67-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ncsthj200601015
Zeng X, Zhang Y Z, Wang K R, et al.Genotype difference of brown rices in Cd content[J].Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2006, 22(1):67-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ncsthj200601015
[59] 李正文, 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 等.不同水稻品种籽粒Cd、Cu和Se的含量差异及其人类膳食摄取风险[J].环境科学, 2003, 24(3):112-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkx200303022
Li Z W, Zhang Y L, Pan G X, et al.Grain contents of Cd, Cu and Se by 57 rice cultivars and the risk significance for Human dietary uptake[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2003, 24(3):112-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkx200303022
[60] 郭健, 姚云, 赵小旭, 等.粮食中重金属铅离子、镉离子的污染现状及对人体的危害[J].粮食科技与经济, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lskjyjj201803016
Guo J, Yao Y, Zhao X X et al.Pollution status of lead and cadmium ions in grain and its harm to human[J].Grain Technology and Economy, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lskjyjj201803016
[61] 刘建明, 亓昭英, 刘善科, 等.中微量元素与植物营养和人体健康的关系[J].化肥工业, 2016, 43(3):85-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hfgy201603025
Liu J M, Qi Z Y, Liu S K, et al. Relationship between medium and trace elements and plant nutrition and human health[J].Journal of the Chemical Fertilizer Industry, 2016, 43(3):85-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hfgy201603025
-



 下载:
下载: