Research Progress on the Migration, Enrichment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in a Soil-Grape System
-
摘要:
重金属元素作为潜在有毒元素,在葡萄园土壤中的污染水平直接影响生态系统平衡及人类健康。本文通过对国内外现有研究的分析,着重探讨了葡萄园土壤-葡萄体系中重金属的含量特征,及其在体系中的迁移、富集行为和污染风险。结果显示,Cd、Cu、Zn含量会对葡萄品质存在主要影响,其余重金属须重点对照国标限量进行监测;重金属由土壤向葡萄叶片的迁移率最高,可达到向果实部分的32倍,在迁移机制作用下积累水平多表现为:叶片≈根部>茎部>果实。其中Zn在叶片和根部中的积累量最高可分别达到93mg/kg和51mg/kg,显著高于果实中的积累量0.53mg/kg。作为影响重金属迁移积累行为的关键因素,土壤酸碱度与体系中重金属的生物可利用度呈负相关,有机质含量通常与其呈正相关关系。当前进展还揭示了重金属因不同品种而产生的迁移差异性,但针对不同气候条件、土壤类型及生理特性之间的影响机制仍缺乏系统性研究。建议今后需要基于区域环境特征,全面地探究与重金属迁移能力及含量相关的影响因素,以及构建机器学习模型预测和评估在不同污染水平下该体系中重金属之间产生的相互作用及其生态风险。
Abstract:As potentially toxic elements, the pollution level of heavy metals in vineyard soils directly affects the ecosystem balance and human health. This study analyzes the current related literature, focusing on the characteristics of heavy metal content in the soil-grape system of vineyards, their migration behavior, and the associated pollution risk assessment. The findings reveal that cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) significantly influence grape quality, while other heavy metals require close monitoring against national standards. The migration rate of heavy metals from soil to grape leaves can be up to 32 times higher than to the pulp. Accumulation levels typically follow the order: leaves≈roots>stems>pulp. Specifically, Zn accumulation in leaves and roots can reach as high as 93mg/kg and 51mg/kg, respectively, far exceeding the 0.53mg/kg observed in pulp. Soil pH, as a critical factor affecting heavy metal migration and accumulation, shows a negative correlation with the bioavailability of heavy metals, while organic matter content typically exhibits a positive correlation. Current findings also highlight the varietal differences in heavy metal migration; however, systematic studies on the interaction mechanisms among climatic conditions, soil types, and physiological traits remain limited. Future research should aim to comprehensively explore the factors influencing heavy metal migration and content within the system under regional environmental characteristics. The application of machine learning models is recommended to predict and evaluate interactions among heavy metals and their ecological risks under different pollution levels.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- grape /
- heavy metal elements /
- migration /
- enrichment /
- influence factors /
- risk assessment
-

-
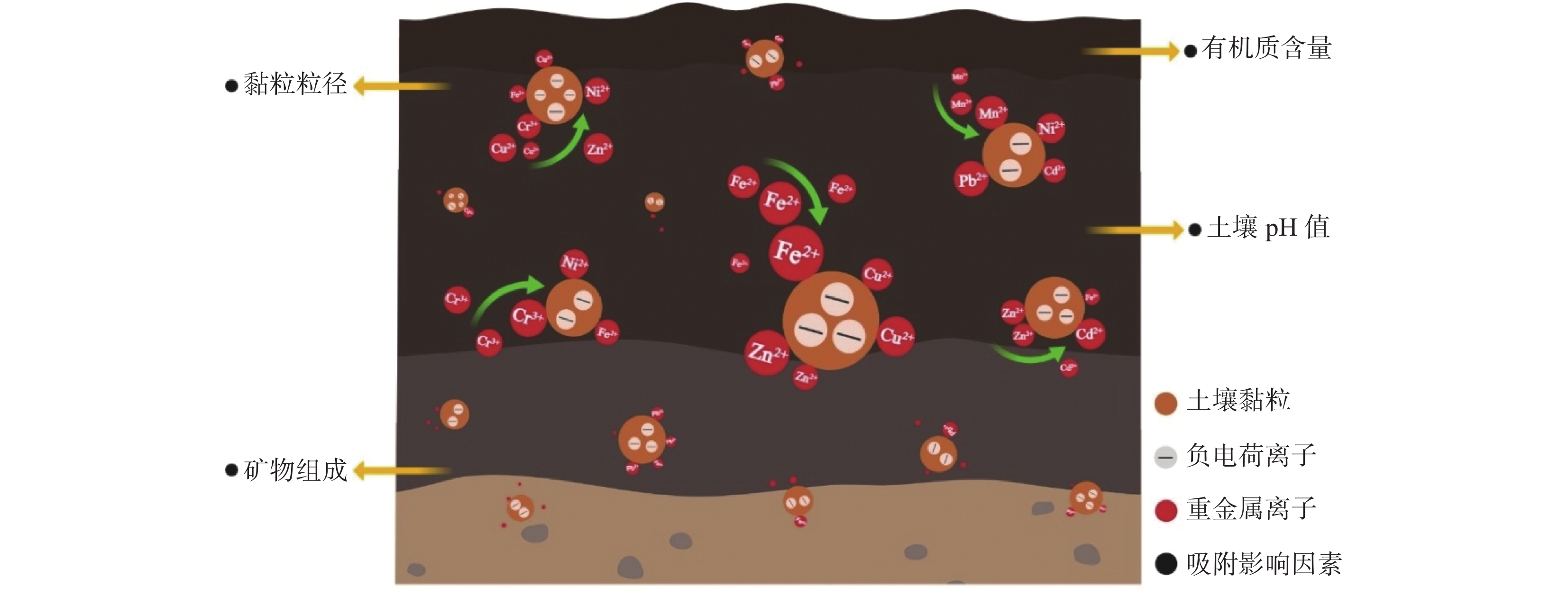
图 1 pH值与有机质对葡萄园土壤重金属生物可利用度的协同作用机制(修改自Wang等[33])
Figure 1.
图 3 不同时期重金属元素富集情况(修改自Milićević等[56])
Figure 3.
表 1 全球各地区土壤及葡萄果实中典型重金属元素含量
Table 1. Typical heavy metal element contents of soil and grape pulp in various regions of the world.
样品
类型重金属
元素重金属元素在不同国家的土壤-葡萄体系中的含量(mg/kg) 中国新疆[16] 中国宁夏[17] 中国湖南[18] 美国[19] 意大利[20] 罗马尼亚[21] 西班牙[22] 塞尔维亚[23] 葡萄
果实As − 0.0087 0.0010 0.0250 − 0.130 − 0.0022 Cd 0.0020 0.0012 0.0290 0.0013 − 0.580 − 0.0038 Pb 0 0.0340 0.100 0.0006 0.0510 0.310 0.185 0.0003 Hg − 0.00059 0.0080 − − 0.0110 0.0158 − Cr 0.100 0.0560 0.330 − 0.310 0.110 2.77 0.0039 Zn 1.26 4.70 − 4.90 1.90 1.11 3.06 1.12 Cu 0.330 1.30 − 3.00 2.30 2.85 5.51 8.80 土壤 As − 11.5 4.81 9.00 − 1.81 − 0.370 Cd 0.270 0.0821 0.0650 0.130 − 14.29 0.0761 0.227 Pb 0.100 14.5 18.9 37.0 25.9 8.49 8.68 10.8 Hg − 0.0300 0.0290 − − 0.0550 0.0299 − Cr 47.3 48.1 39.9 − 80.1 1.21 5.10 94.0 Zn 66.7 52.1 − 31.0 55.0 59.9 23.1 71.5 Cu 41.2 19.9 − 11.0 21.9 40.5 72.7 38.1 注:“−”表示暂无数据。 表 2 重金属元素在土壤-果实之间的富集系数
Table 2. Enrichment coefficients of heavy metal elements between soil and grape pulp.
重金属元素 重金属元素在不同国家的土壤-葡萄体系中的富集系数(%) 中国新疆 中国宁夏 中国湖南 美国 意大利 罗马尼亚 西班牙 塞尔维亚 As − 0.08 0.02 0.28 − 7.18 − 0.59 Cd 0.74 1.46 1.20 1.00 − 4.05 − 1.67 Pb 0.00 0.23 0.53 0.00 0.20 3.65 2.13 0.00 Hg − 1.97 0.40 − − 20.0 52.84 − Cr 0.21 0.12 0.83 − 0.39 9.10 54.31 0.00 Zn 1.89 9.02 − 15.81 3.45 1.85 13.25 1.57 Cu 0.80 6.53 − 27.27 10.50 7.04 7.58 23.10 注:“−”表示暂无数据。 表 3 不同区域的葡萄园土壤pH值范围
Table 3. Range of soil pH in vineyards of different regions.
表 4 土壤重金属污染程度分级标准(据Wang等[60]修改)
Table 4. Classification standards for heavy metals pollution level in soil (Modified from Wang, et al[60]).
单因子污染指数 $ {P}_{i} $ 综合污染指数 $ {P}_{N} $ 污染负荷指数 $ PLI $ 地质累积指数 $ {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}} $ 潜在生态风险指数 $ RI $ 范围 程度 范围 程度 范围 程度 范围 程度 范围 程度 $ {P}_{i}\le 1 $ 正常 $ {P}_{N}\le 0.7 $ 正常 $ PLI=0 $ 正常 $ {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}}\le 0 $ 正常 $ {E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i} < 40 $ 低风险 $ 1 < {P}_{i}\le 2 $ 较正常 $ 0.7 < {P}_{N}\le 1 $ 较正常 $ 0 < PLI\le 1 $ 较正常 $ 0 < {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}}\le 2 $ 轻度 $ 40\le {E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i} < 80 $ 中风险 $ 2 < {P}_{i}\le 3 $ 轻度 $ 1 < {P}_{N}\le 2 $ 轻度 $ 1 < PLI\le 2 $ 轻度 $ 2 < {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}}\le 3 $ 中度 $ 80\le {E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i} < 160 $ 较高 $ 3 < {P}_{i}\le 5 $ 中度 $ 2 < {P}_{N}\le 3 $ 中度 $ 2 < PLI\le 3 $ 中度 $ 3 < {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}}\le 5 $ 重度 $ 160\le {E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i} < 320 $ 高风险 $ {P}_{i} > 5 $ 重度 $ {P}_{N} > 3 $ 重度 $ 3 < PLI\le 4 $ 重度 $ {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}} > 5 $ 极重度 $ {E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i}\ge 320 $ 极高 注:单因素污染指数法与潜在生态风险指数法中i表示不同的重金属元素。 表 5 风险评估指数计算公式
Table 5. Calculation methods of risk assessment index.
评估类别 相关指数 计算公式 参考文献 污染评估 $ \;$
Pi (单因子污染指数)$ {P}_{i}=\dfrac{{C}_{i}}{{C}_{0}} $ [59-60] $ \;$
PN (综合污染指数)$ P_{\mathrm{N}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(P_{i\max}\right)^2+\left(P_{i\mathrm{ave}}\right)^2}{2}} $ $ $
PLI (污染负荷指数)$ PLI=\sqrt[n]{{P}_{1}\times {P}_{2}\times {P}_{3}\times \cdots \times {P}_{n}} $ [61] $ \;$
Igeo (地质累积指数)$ {I}_{{\mathrm{geo}}}={\mathrm{log}}_{2}({C}_{i}/{1.5B}_{i}) $ [62] $\; $
(潜在生态风险指数)$ RI=\displaystyle\sum _{i=1}^{n}{E}_{{\mathrm{f}}}^{i} $ [64] 迁移评估 $ \;$
TF(转运系数)$ TF={C}_{i地上部}/{C}_{i根部} $ [65] $ \;$
BCF(生物富集系数)$ BCF={C}_{葡萄}/{C}_{土壤} $ [66] $\; $
BRAI(生物利用度风险评估指数)$ BRAI=\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^nBD_i/\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^nTE_i $ [67] 健康评估 $\; $
THQ(目标危险系数)$ THQ=\dfrac{{C}_{i}\times IR\times EF\times ED}{BW\times AT\times RfD} $ [70] $ \;$
HI(危害指数)$ HI=\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^nTHQ_i $ $\; $
CR(致癌风险指数)$ CR=EDI\times SF $ [71] -
[1] 李泽敏, 王振平, 赵全胜, 等. 银川酿酒葡萄产区不同种植年限土壤重金属分布特征和评价[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024(3): 57−62. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.23176
Li Z M, Wang Z P, Zhao Q S, et al. Distribution characteristics and evaluation of soil heavy metals in different planting years in Yinchuan wine grape-producing area[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2024(3): 57−62. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.23176
[2] Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhan W, et al. Stabilization of heavy metal-contaminated soils by biochar: Challenges and recommendations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 139060. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139060
[3] Li P, Lin C, Cheng H, et al. Contamination and health risks of soil heavy metals around a lead/zinc smelter in southwestern China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 113: 391−399. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.025
[4] 路港滨, 俄胜哲, 袁金华, 等. 土壤重金属有效性影响因素及其在作物和土壤系统迁移运转规律研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(20): 67−73. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0589
Lu G B, E S Z, Yuan J H, et al. Research progress on the influencing factors of soil heavy metal availability and their migration and operation patterns in crops and soil systems[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(20): 67−73. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0589
[5] 杨博, 张波, 闫培洁, 等. 甘肃省嘉峪关市酿酒葡萄园土壤重金属空间分布特征及风险评价[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2021, 47(6): 777−786. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2021.02.081
Yang B, Zhang B, Yan P J, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in wine-making vineyard in Jiayuguan City, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 2021, 47(6): 777−786. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2021.02.081
[6] 宋长征. 锌元素对梅鹿辄葡萄果实与葡萄酒质量及幼苗生长的影响[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2018.
Song C Z. The effect of zinc element on the quality of Merlot grape fruit and wine, as well as the growth of seedlings[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2018.
[7] 王志刚, 林海, 庞乾林. 农田重金属污染对作物的影响及其调控[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(3): 39−43.
Wang Z G, Lin H, Pang Q L. The impact and regulation of heavy metal pollution in farmland on crops[J]. China Rice, 2018, 24(3): 39−43.
[8] Yang L, Ren Q, Zheng K, et al. Migration of heavy metals in the soil-grape system and potential health risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150646. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150646
[9] Blotevogel S, Oliva P, Denaix L, et al. Stable Cu isotope ratios show changes in Cu uptake and transport mechanisms in vitis vinifera due to high Cu exposure[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 12: 755944. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.755944
[10] 刘旭, 金倩, 谭军. 水分胁迫和氮肥水平对葡萄吸收重金属铅的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(9): 2031−2034.
Liu X, Jin Q, Tan J. The effects of water stress and nitrogen fertilizer levels on the absorption of heavy metal lead by grapes[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(9): 2031−2034.
[11] 余涛, 蒋天宇, 刘旭, 等. 土壤重金属污染现状及检测分析技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(2): 460−476. doi: 10.12029/gc20210208
Yu T, Jiang T Y, Liu X, et al. Current status of soil heavy metal pollution and research progress in detection and analysis technologies[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 460−476. doi: 10.12029/gc20210208
[12] Sun X, Liu L, Zhao Y, et al. Effect of copper stress on growth characteristics and fermentation properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the pathway of copper adsorption during wine fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 192: 43−52. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.107
[13] Wang Y, Zheng K, Zhan W, et al. Highly effective stabilization of Cd and Cu in two different soils and improvement of soil properties by multiple-modified biochar[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 207: 111294. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111294
[14] Petousi I, Daskalakis G, Fountoulakis M S, et al. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on the establishment of young grapevines[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658: 485−492. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.065
[15] Jimenez-Ballesta R, Bravo S, Amoros J A, et al. Soil and leaf mineral element contents in Mediterranean vineyards: Bioaccumulation and potential soil pollution[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2022, 233(1): 20. doi: 10.1007/s11270-021-05485-6
[16] 李泽涵, 李函伦, 彭昕, 等. 新疆葡萄酒产区土壤、葡萄叶、葡萄果实和葡萄酒中矿物质元素含量及其相关性分析[J]. 中国酿造, 2022, 41(10): 30−35.
Li Z H, Li H L, Peng X, et al. Mineral element content and correlation analysis in soil, grape leaves, grape fruits, and wine in Xinjiang wine producing areas[J]. China Brewing, 2022, 41(10): 30−35.
[17] 陈翔, 开建荣, 牛艳, 等. 产地土壤重金属对贺兰山东麓酿酒葡萄的影响及风险评估[J]. 中国酿造, 2020, 39(7): 178−181. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.07.034
Chen X, Kai J R, Niu Y, et al. Effects of heavy metals in soil on wine grape in the Helan Mountain’s Eastern Region and risk assessment[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(7): 178−181. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.07.034
[18] 郭亮. 长株潭地区葡萄园重金属含量评价及镉对葡萄生理特性的影响[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2016.
Guo L. Evaluation of heavy metal content in vineyards in Changzhutan area and the effect of cadmium on the physiological characteristics of grapes[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2016.
[19] Richardson J B, Chase J K. Transfer of macronutrients, micronutrients, and toxic elements from soil to grapes to white wines in uncontaminated vineyards [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(24): 13271. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413271
[20] Protano G, Rossi S. Relationship between soil geochemistry and grape composition in Tuscany (Italy)[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2014, 177(4): 500−508. doi: 10.1002/jpln.201300055
[21] Bora F D, Bunea C I, Rusu T, et al. Vertical distribution and analysis of micro-, macroelements and heavy metals in the system soil-grapevine-wine in vineyard from North-West Romania[J]. Chemistry Central Journal, 2015, 9: 19. doi: 10.1186/s13065-015-0095-2
[22] Vázquez F A V, Cid B P, Segade S R. Assessment of metal bioavailability in the vineyard soil-grapevine system using different extraction methods[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 208: 199−208. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.005
[23] Milićević T, Aničić U M, Relić D, et al. Environmental pollution influence to soil-plant-air system in organic vineyard: Bioavailability, environmental, and health risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(3): 3361−3374. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10649-8
[24] Shaheen N, Irfan N M, Khan I N, et al. Presence of heavy metals in fruits and vegetables: Health risk implications in Bangladesh[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152: 431−438. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.060
[25] 张鑫荣, 杨洪强, 隋静, 等. 葡萄根系钙处理对叶片镉伤害的保护作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2008, 35(10): 1405−1410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2008.10.001
Zhang X R, Yang H Q, Sui J, et al. Calcium protects grape leaves against cadmium stress by root treatment[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2008, 35(10): 1405−1410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2008.10.001
[26] 黄雨珊, 范舒悦, 勾叙衡, 等. 金属元素在葡萄酒中的作用[J]. 中国食品学报, 2023, 23(11): 446−456. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2023.11.042
Huang Y S, Fan S Y, Gou X H, et al. The role of metal elements in wine[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2023, 23(11): 446−456. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2023.11.042
[27] Yuliya V, Reelika R, Nina K, et al. Comparison of soil-to-root transfer and translocation coefficients of trace elements in vines of Chardonnay and Muscat white grown in the same vineyard[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2015, 192: 89−96. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.05.019
[28] Gulan L, Stajic J M, Milenkovic B, et al. Plant uptake and soil retention of radionuclides and metals in vineyard environments[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(36): 49651−49662. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14239-0
[29] Castillo P, Serra I, Townley B, et al. Biogeochemistry of plant essential mineral nutrients across rock, soil, water and fruits in vineyards of Central Chile[J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 104905. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104905
[30] Zhong X, Chen Z, Li Y, et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123289. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123289
[31] Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, et al. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1): 84−91. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019
[32] 曹勤英, 黄志宏. 污染土壤重金属形态分析及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(6): 222−232. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2017.06.030
Cao Q Y, Huang Z H. Research progress on heavy metal forms analysis and influencing factors in polluted soil[J]. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(6): 222−232. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2017.06.030
[33] 王逸群, 许端平, 薛杨, 等. Pb和Cd赋存形态与土壤理化性质相关性研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(5): 451−455. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.118
Wang Y Q, Xu D P, Xue Y, et al. Study on the correlation between the occurrence forms of Pb and Cd and soil physicochemical properties[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(5): 451−455. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.118
[34] 徐伟. 湖南省不同地区葡萄园土壤理化特性和重金属污染风险研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2021.
Xu W. Study on the physical and chemical characteristics of vineyard soil and the risk of heavy metal pollution in different regions of Hunan Province[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.
[35] 谢玉明, 聂松青, 聂俊, 等. 广东东莞地区阳光玫瑰葡萄园土壤养分状况分析[J]. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(3): 197−204. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2021.03.023
Xie Y M, Nie S Q, Nie J, et al. Analysis of soil nutrient status in sunshine rose vineyards in Dongguan, Guangdong Province[J]. Nonwood Forest Research, 2021, 39(3): 197−204. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2021.03.023
[36] 范晓晖, 刘文婷, 谢星, 等. 寿宁县高山设施葡萄园土壤养分状况及施肥管理建议[J]. 海峡科学, 2023(5): 64−67.
Fan X H, Liu W T, Xie X, et al. Soil nutrient status and fertilization management suggestions for high-altitude facility vineyards in Shouning County[J]. Staits Science, 2023(5): 64−67.
[37] 王茜, 朱晓宝, 姜英, 等. 秦皇岛产区葡萄园土壤养分状况调查与分析[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2022(5): 80−87. doi: 10.13414/j.cnki.zwpp.2022.05.012
Wang Q, Zhu X B, Jiang Y, et al. Investigation and analysis of soil nutrient status in vineyards in Qinhuangdao production area[J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2022(5): 80−87. doi: 10.13414/j.cnki.zwpp.2022.05.012
[38] 包红静, 邢月华, 刘艳, 等. 辽南葡萄主产区土壤养分特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(5): 1149−1155. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2021021801
Bao H J, Xing Y H, Liu Y, et al. Study on soil nutrient characteristics in the main grape production area of Southern Liaoning Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(5): 1149−1155. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2021021801
[39] van Poucke R, Ainsworth J, Maeseele M, et al. Chemical stabilization of Cd-contaminated soil using biochar[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 88: 122−130. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.09.001
[40] Tu C, Wei J, Guan F, et al. Biochar and bacteria inoculated biochar enhanced Cd and Cu immobilization and enzymatic activity in a polluted soil[J]. Environment International, 2020, 137: 105576. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105576
[41] Hao X, Gao F, Wu H, et al. From soil to grape and wine: Geographical variations in elemental profiles in different chinese regions[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(12): 3108. doi: 10.3390/foods10123108
[42] 张云峰, 李艳, 严斌, 等. 葡萄园土壤中4种金属元素的测定及其对葡萄和葡萄酒的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2010, 31(24): 374−379.
Zhang Y F, Li Y, Yan B, et al. Determination of four metal elements in vineyard soil and their effects on grapes and wines[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2010, 31(24): 374−379.
[43] 侯彪. 不同粒径团聚体中重金属的分配规律及影响因素[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2019.
Hou B. Distribution patterns and influencing factors of heavy metals in aggregates of different particle sizes[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019.
[44] Pham N T H, Babcsányi I, Balling P, et al. Accumulation patterns and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in the topsoil of two sloping vineyards (Tokaj-Hegyalja, Hungary)[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2022, 22(10): 2671−2689. doi: 10.1007/s11368-022-03252-6
[45] Han X, Lu H, Wang Y, et al. Region, vintage, and grape maturity co-shaped the ionomic signatures of the Cabernet Sauvignon wines[J]. Food Research International, 2023, 163: 112165. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112165
[46] Yuliya V, Liliya R, Dmytro D, et al. Trace metals in wine and vineyard environment in Southern Ukraine[J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 146: 339−344. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.091
[47] Khaska S, Le Gal La Salle C, Sassine L, et al. Innovative isotopic method to evaluate bioaccumulation of As and MTEs in Vitis vinifera[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 1126−1136. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.222
[48] 庞荣丽, 王书言, 王瑞萍, 等. 重金属在土壤-葡萄体系中的富集和迁移规律[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(4): 515−521. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0410
Pang R L, Wang S Y, Wang R P, et al. The enrichment and migration patterns of heavy metals in the soil grape system[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019, 35(4): 515−521. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0410
[49] 刘强, 呼丽萍, 鱼潮水. 土壤-樱桃系统重金属累积和樱桃食用健康风险评价[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(2): 161−169. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20180224
Liu Q, Hu L P, Yu C S. Heavy metal accumulation in the soil cherry system and health risk assessment of cherry consumption[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2018(2): 161−169. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20180224
[50] 李非里, 刘丛强, 杨元根, 等. 贵阳市郊菜园土-辣椒体系中重金属的迁移特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2007(4): 52−56.
Li F L, Liu C Q, Yang Y G, et al. Migration characteristics of heavy metals in the vegetable garden soil chili system in the suburbs of Guiyang City[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2007(4): 52−56.
[51] 江水英, 吴声东, 肖化云, 等. 贵溪冶炼厂周边菜园地土壤—辣椒系统中重金属的迁移特征[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2010, 32(3): 628−632. doi: 10.13836/j.jjau.2010116
Jiang S Y, Wu S D, Xiao H Y, et al. Migration characteristics of heavy metals in the soil pepper system of vegetable gardens around Guixi Smelter[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2010, 32(3): 628−632. doi: 10.13836/j.jjau.2010116
[52] Bora F D, Bunea C I, Chira R, et al. Assessment of the quality of polluted areas in Northwest Romania based on the content of elements in different organs of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. )[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(3): 750. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030750
[53] Mirzaei M, Verrelst J, Bakhtiari A R, et al. Potential use of grapevine cv Askari for heavy metal phytoremediation purposes at greenhouse scale[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(10): 12447−12458. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11129-9
[54] Mirzaei M, Marofi S, Solgi E, et al. Ecological and health risks of soil and grape heavy metals in long-term fertilized vineyards (Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province of Iran)[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(1): 27−43. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00242-5
[55] 杨玉, 尹春峰, 汤佳乐, 等. 长沙和株洲地区葡萄园土壤重金属含量分析及污染评价[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2017(8): 41−44. doi: 10.16498/j.cnki.hnnykx.2017.008.011
Yang Y, Yin C F, Tang J L, et al. Analysis and pollution evaluation of heavy metal content in vineyard soil in Changsha and Zhuzhou regions[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2017(8): 41−44. doi: 10.16498/j.cnki.hnnykx.2017.008.011
[56] Milićević T, Urošević M A, Relić D, et al. Bioavailability of potentially toxic elements in soil–grapevine (leaf, skin, pulp and seed) system and environmental and health risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 626: 528−545. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.094
[57] 邵小杰. 葡萄根系和叶片对氯化镉处理的生理学与细胞学响应[D]. 济南:山东农业大学, 2009.
Shao X J. Physiological and cytological responses of grape roots and leaves to cadmium chloride treatment[D]. Jinan: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009.
[58] Chopin E I B, Marin B, Mkoungafoko R, et al. Factors affecting distribution and mobility of trace elements (Cu, Pb, Zn) in a perennial grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. ) in the Champagne region of France[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 156(3): 1092−1098. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.04.015
[59] 王棣, 李杰飞, 杨浩, 等. 洛阳市栾川县矿区周边土壤重金属污染特征、来源与生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2024, 43(10): 3363−3376.
Wang D, Li J F, Yang H, et al. Characteristics, sources and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in the surrounding areas of Luanchuan County, Luoyang City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2024, 43(10): 3363−3376.
[60] 王海洋, 韩玲, 谢丹妮, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2104−2114. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106218
Wang H Y, Han L, Xie D N, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in farmland soil around mining areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2104−2114. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106218
[61] Li C, Quan Q, Gan Y, et al. Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 749: 141555. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141555
[62] 麦尔哈巴·图尔贡. 吐鲁番盆地葡萄园土壤重金属污染及潜在风险评价[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆师范大学, 2021.
Turrhun M. Heavy metal pollution and potential risk assessment of vineyard soil in Turpan Basin[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2021.
[63] 张文强, 滕跃, 柳浩然, 等. 聊城市典型农业区土壤重金属分布特征、生态风险及来源解析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2024, 38(4): 171−180. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2024.088
Zhang W Q, Teng Y, Liu H R, et al. Distribution characteristics, ecological risks, and source analysis of soil heavy metals in typical agricultural areas of Liaocheng City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2024, 38(4): 171−180. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2024.088
[64] 胡兆鑫, 吴泽燕, 罗为群, 等. 典型岩溶县土壤重金属含量、来源及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(9): 5506−5516. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202310071
Hu Z X, Wu Z Y, Luo W Q, et al. Soil heavy metal content, sources, and ecological risk assessment in typical karst counties[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(9): 5506−5516. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202310071
[65] Zinicovscaia I, Sturza R, Gurmeza I, et al. Metal bioaccumulation in the soil–leaf–fruit system determined by neutron activation analysis[J]. Journal of Food Measurement & Characterization, 2019, 13(1): 592−601. doi: 10.1007/s11694-018-9972-4
[66] Jimenez-Ballesta R, Bravo S, Amoros J A, et al. Preliminary assessment of the occurrence of six rare earth elements in calcareous vineyard soils[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2021, 232(2): 76. doi: 10.1007/s11270-021-05034-1
[67] Milićević T, Relić D, Urošević M A, et al. Integrated approach to environmental pollution investigation—Spatial and temporal patterns of potentially toxic elements and magnetic particles in vineyard through the entire grapevine season[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 163: 245−254. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.078
[68] Wang Q, Liu J, Cheng S. Heavy metals in apple orchard soils and fruits and their health risks in Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(1): 4178. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4178-7
[69] 麦尔哈巴·图尔贡, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 王维维. 吐鲁番盆地葡萄园土壤重金属污染及其潜在健康风险[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2020, 37(6): 558−565. doi: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2020.19816
Turrhun M, Eziz M, Wang W W. Heavy metal pollution and potential health risks of vineyard soil in Turpan Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 2020, 37(6): 558−565. doi: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2020.19816
[70] Kukusamude C, Sricharoen P, Limchoowong N, et al. Heavy metals and probabilistic risk assessment via rice consumption in Thailand[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 334: 127402. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127402
[71] 单爱琴, 张威, 周洪英. 徐州市不同功能区重金属污染与健康风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(9): 125−129. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201609027
Shan A Q, Zhang W, Zhou H Y. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment in different functional areas of Xuzhou City[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(9): 125−129. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201609027
[72] Rezaei M, Ghasemidehkordi B, Peykarestan B, et al. Potentially toxic element concentration in fruits collected from Markazi Province (Iran): A probabilistic health risk assessment[J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 839−853. doi: 10.3967/bes2019.105
[73] Alagić S C, Tošić S B, Dimitrijević M D, et al. The content of the potentially toxic elements, iron and manganese, in the grapevine cv Tamjanika growing near the biggest copper mining/metallurgical complex on the Balkan Peninsula: Phytoremediation, biomonitoring, and some toxicological aspects[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(34): 34139−34154. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3362-7
-




 下载:
下载: