PETRO-GEOCHEMISTRY AND GENESIS OF THE PUMICES AT DONGDAO OF XISHA ISLANDS
-
摘要:
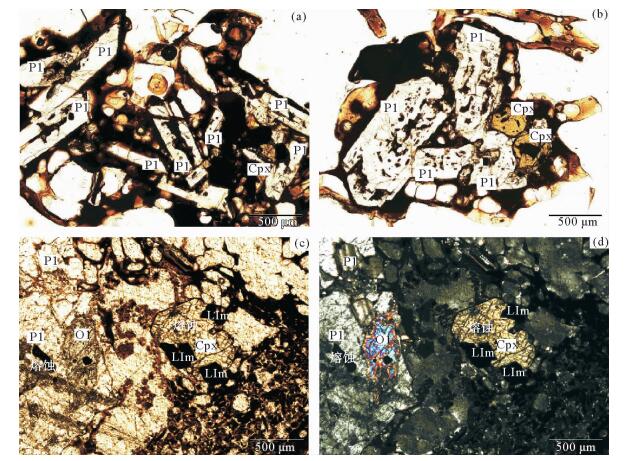
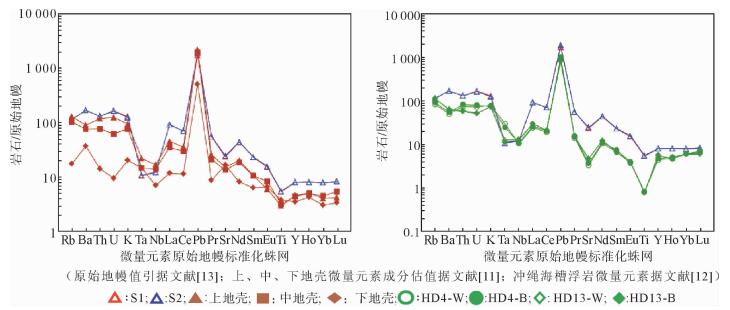
对采自西沙群岛东岛的2件浮岩样品进行了岩石学和地球化学初步研究,结果表明, 研究区样品全岩化学组成落入粗面岩区域,稀土配分曲线明显呈右倾,具Eu负异常,富集不相容元素,微量元素标准化曲线特征与中下地壳相似。斜长石及辉石斑晶矿物具有中心熔蚀结构,橄榄石呈熔蚀状。认为研究区浮岩是由西沙地块中地壳减压熔融产生粗面质岩浆后经历短暂的岩浆房冷凝时期,由于板块继续拉张形成东岛西侧的狭窄海槽,而引起岩浆通道突发性张裂,导致压力的突然释放,岩浆沿拉张裂谷急速上升,在浅水中猛烈喷出而形成。
Abstract:In this paper, two pumices samples collected from the Dongdao Island are studied for petrography and mineral geochemistry. With chemical composition, the samples are defined as trachyte, and their rare earth distribution curves are both dipping rightward, with negative Eu anomalies, enriched incompatible elements, and a trace element normalized curve similar to the lower crust. The porphyritic minerals of plagioclase and pyroxene show a central melting structure, and olivine is molten. It is believed that the pumices are formed by an explosion of a short-term condensed magma chamber after the melting and pressure reduction of the crust at the Xisha block, due to the continuous spreading of the plate and the formation of the narrow trough on the west side of the Dongdao Island. The process caused the sudden release of pressure, and rapid eruption of magma along the stretching rift into the shallow water.
-
Key words:
- pumice /
- petro-geochemistry /
- magmatic activity /
- Dongdao
-

-
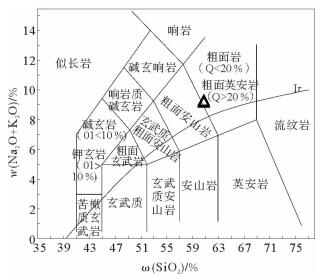
图 3 研究区浮岩TAS分类(据文献[9])
Figure 3.
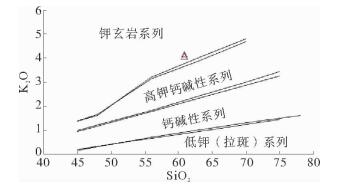
图 4 研究区浮岩K2O—SiO2图解(据文献[10])
Figure 4.
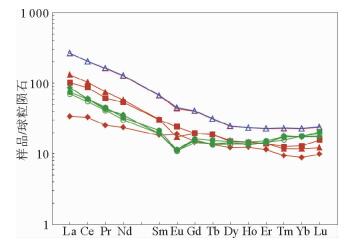
图 6 研究区浮岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式(图例同图 5)
Figure 6.
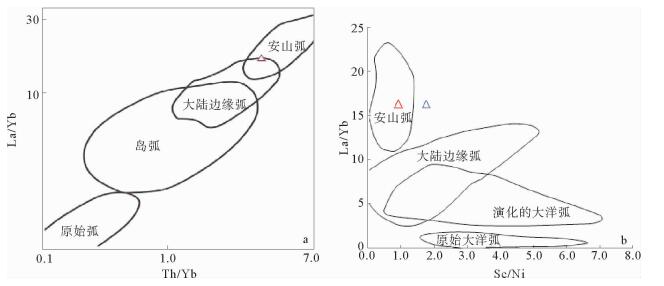
图 7 研究区样品La/Yb—Th/Yb、Sc/Ni—La/Yb划分图解(据文献[20])
Figure 7.
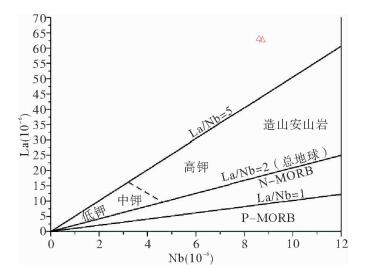
图 8 研究区样品La—Nb构造环境判别图(据文献[21])
Figure 8.
表 1 研究区浮岩主量元素(w)和微量元素(×10-6)分析测试结果及相关参数
Table 1. Contents of major oxides (w) and trace elements(×10-6) of Dongdao pumice and related parameters
样品号 S1 S2 样品号 S1 S2 样品号 S1 S2 SiO2 60.85 60.87 Y 36.2 36.2 La 62.7 63.1 TiO2 0.96 0.99 Nb 8.74 8.59 Ce 123.8 123.7 Al2O3 14.79 15.63 Ta 0.44 0.43 Pr 15.27 15.4 TFe2O3 2.86 2.94 Ba 1 170 1 170 Nd 58.8 59.7 MnO 0.39 0.38 Cu 17.5 14.6 Sm 10.2 10.3 MgO 1.66 1.64 Sr 493 515 Eu 2.54 2.62 CaO 4.1 3.94 V 83.8 91.8 Gd 8.24 8.31 Na2O 5.14 5.13 Zn 138.2 130.5 Tb 1.16 1.17 K2O 4.15 4.08 Li 22.3 21 Dy 6.19 6.29 P2O5 1.57 1.4 Be 2.22 2.08 Ho 1.32 1.32 LOI 3.41 2.87 Sc 9 9.4 Er 3.75 3.78 Total 99.88 99.89 Cr 17.9 10.8 Tm 0.58 0.59 DI 80.02 78.83 Co 8.7 9.3 Yb 3.86 3.88 SI 12.15 12.02 Ni 9.79 5.32 Lu 0.6 0.61 AR 2.94 2.78 Ga 20.5 20.3 бEu 0.82 0.84 σ43 4.61 4.56 Rb 72 72.4 бCe 0.95 0.94 Q 9.46 9.16 Mo 3.47 3.48 LREE 273.31 274.82 A 62.89 58.97 Cd 1.17 0.34 HREE 25.7 25.95 P 12.88 18.51 W 0.52 0.47 ∑REE 299.01 300.77 液相密度 2.45 2.45 Pb 13.5 14.9 LREE/HREE 10.63 10.59 干黏度 5.64 5.61 Th 11.1 11.1 (La/Yb)N 11.65 11.67 湿黏度 4.72 4.74 U 3.48 3.4 液相线温 974 980 K 32 294.5 30 837.8 -
[1] 丘学林, 曾钢平, 胥颐, 等.南海西沙石岛地震台下的地壳结构研究[J].地球物理学报, 2006, 49(6):1720-1729. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.06.019
[2] 万玲, 曾维军, 吴能友, 等.南海北部陆缘西沙海槽—台湾恒春半岛地学断面[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(3):564-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.006
[3] 黄海波, 丘学林, 徐辉龙, 等.南海西沙地块岛屿与地震观测和海陆联测初步结果[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12):3161-3170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.016
[4] Liu X D, Zhao S P, Sun L G, et al.Geochemical evidence for the variation of historical seabird population on Dongdao Island of the South China sea[J].Journal of Paleolimnology, 2006, 36(3):259-279. doi: 10.1007/s10933-006-9006-9
[5] 游长江, 侯佩旭, 邓灿芳, 等.西沙群岛旅游资源调查与评价[J].资源科学, 2015, 37(8):1609-1620. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZRZY201508014.htm
[6] 阮爱国, 李家彪, 郝天姚, 等.石岛地震台远震记录反演研究[J].海洋学报, 2006, 28(2):85-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2006.02.010
[7] 郭晓然, 赵明辉, 黄海波, 等.西沙地块地壳结构及其构造属性[J].地球物理学报, 2016, 59(4):1414-1425. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201604022
[8] 业治铮, 何起祥, 张明书, 等.西沙群岛岛屿类型划分及其特征的研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1985, 5(1):3-15.
[9] Le Maitre R W.A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms:Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks[M].Oxford:Blackwell, 1989.
[10] 路远发.GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(5):459-464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004
[11] Rudnick R L,Gao S.Composition of Continental Crust[M]// Rudnick R L. The Crust: Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005,3: 1-64.
[12] 廖仁强, 黄朋, 胡宁静, 等.冲绳海槽黑色与白色浮岩特征及其对岩浆演化的指示[J].海洋科学, 2016, 40(5):121-130. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx201605019
[13] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts; Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[M]//Sauders A D, Norry M J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basins.London:Geol.Soc.Spec.Publ., 1989:313-345.
[14] Mingram B, Trumbull R B, Littman S, et al.A petrogenetic study of anorogenic felsic magmatism in the Cretaceous Paresis ring complex, Namibia:evidence for mixing of crust and mantle-derived components[J].Lithos, 2000, 54(1/2):1-22. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00033-5
[15] 项媛馨,巫建华.广东北部早白垩世粗面岩的成因:Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约[J]高校地质学报,2011,17(3):436-446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2011.03.008
[16] 吴昌志, 顾连兴, 任作伟, 等.辽河盆地沙三期火山-侵入岩地球化学与岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(3):545-556. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200403018
[17] 章邦桐, 陈培荣, 杨东生, 等.赣南中生代橄榄玄粗岩系列厘定的地质证据[J].地质学报, 2001(2):213-220+291. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.02.010
[18] 高山.大陆地壳组成研究的进展[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2005:44-78.
[19] 赵振华.微量元素地球化学原理[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016.
[20] Gondie K C.Geochemisty and tectonic setting of early Proterozoic suprocrustal rocks in the southwestern United States[J].Jour.Geol., 1986, 94(6):845-864. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0024493789900200
[21] Bailey J C.Geochemical criteria for a refined tectonic discrimination of orogenic andesites[J].Chemical Geology, 1981, 32(1):139-154. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(81)90135-2
[22] 翟世奎.冲绳海槽浮岩的分布及其斑晶矿物学特征[J].海洋与湖沼, 1986, 17(6):504-512.
-



 下载:
下载: